Rachel Rudinger
BenchMarker: An Education-Inspired Toolkit for Highlighting Flaws in Multiple-Choice Benchmarks
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Multiple-choice question answering (MCQA) is standard in NLP, but benchmarks lack rigorous quality control. We present BenchMarker, an education-inspired toolkit using LLM judges to flag three common MCQ flaws: 1) contamination - items appearing exactly online; 2) shortcuts - cues in the choices that enable guessing; and 3) writing errors - structural/grammatical issues based on a 19-rule education rubric. We validate BenchMarker with human annotations, then run the tool to audit 12 benchmarks, revealing: 2) contaminated MCQs tend to inflate accuracy, while writing errors tend to lower it and change rankings beyond random; and 3) prior benchmark repairs address their targeted issues (i.e., lowering accuracy with LLM-written distractors), but inadvertently add new flaws (i.e. implausible distractors, many correct answers). Overall, flaws in MCQs degrade NLP evaluation, but education research offers a path forward. We release BenchMarker to bridge the fields and improve MCQA benchmark design.
Take Out Your Calculators: Estimating the Real Difficulty of Question Items with LLM Student Simulations
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Standardized math assessments require expensive human pilot studies to establish the difficulty of test items. We investigate the predictive value of open-source large language models (LLMs) for evaluating the difficulty of multiple-choice math questions for real-world students. We show that, while LLMs are poor direct judges of problem difficulty, simulation-based approaches with LLMs yield promising results under the right conditions. Under the proposed approach, we simulate a "classroom" of 4th, 8th, or 12th grade students by prompting the LLM to role-play students of varying proficiency levels. We use the outcomes of these simulations to fit Item Response Theory (IRT) models, comparing learned difficulty parameters for items to their real-world difficulties, as determined by item-level statistics furnished by the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP). We observe correlations as high as 0.75, 0.76, and 0.82 for grades 4, 8, and 12, respectively. In our simulations, we experiment with different "classroom sizes," showing tradeoffs between computation size and accuracy. We find that role-plays with named students improves predictions (compared to student ids), and stratifying names across gender and race further improves predictions. Our results show that LLMs with relatively weaker mathematical abilities (Gemma) actually yield better real-world difficulty predictions than mathematically stronger models (Llama and Qwen), further underscoring the suitability of open-source models for the task.
Test-Time Reasoners Are Strategic Multiple-Choice Test-Takers
Oct 09, 2025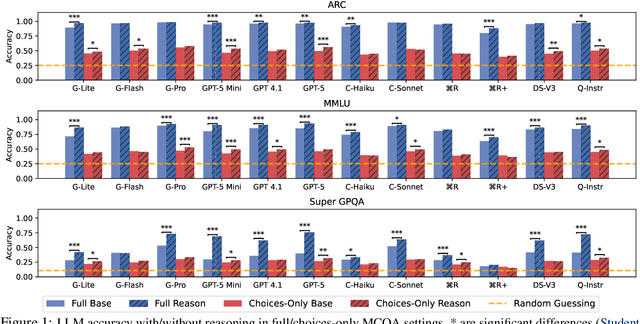
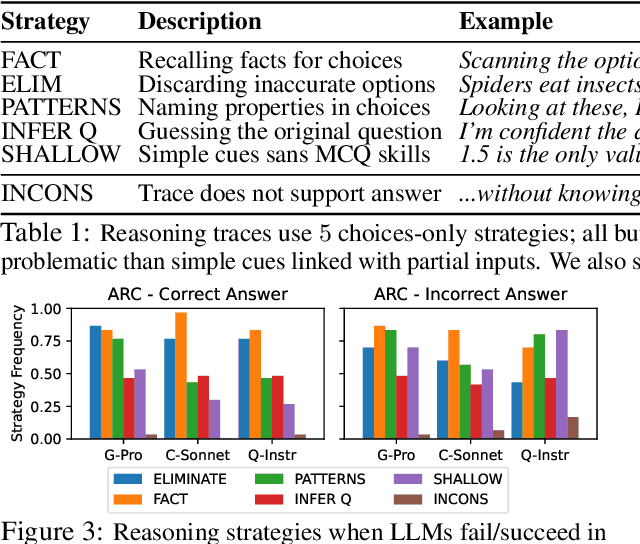
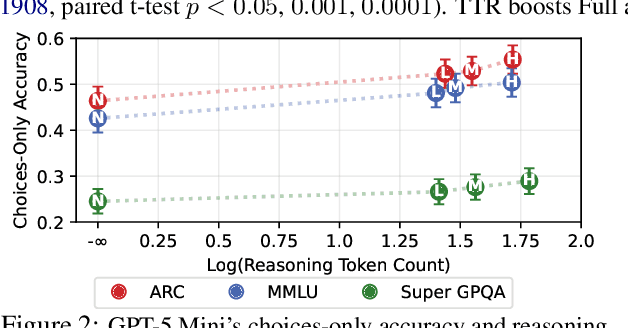
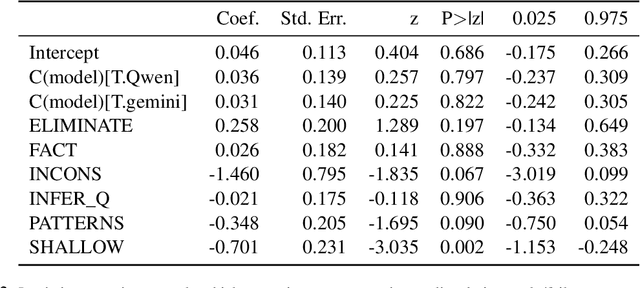
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) now give reasoning before answering, excelling in tasks like multiple-choice question answering (MCQA). Yet, a concern is that LLMs do not solve MCQs as intended, as work finds LLMs sans reasoning succeed in MCQA without using the question, i.e., choices-only. Such partial-input success is often deemed problematic, but reasoning traces could reveal if these strategies are truly shallow in choices-only settings. To study these strategies, reasoning LLMs solve MCQs in full and choices-only inputs; test-time reasoning often boosts accuracy on full and in choices-only half the time. While possibly due to shallow shortcuts, choices-only success is barely affected by the length of reasoning traces, and after finding traces pass faithfulness tests, we show they use less problematic strategies like inferring missing questions. In all, we challenge claims that partial-input success is always a flaw, so we discuss how reasoning traces could separate problematic data from less problematic reasoning.
Multiple LLM Agents Debate for Equitable Cultural Alignment
May 30, 2025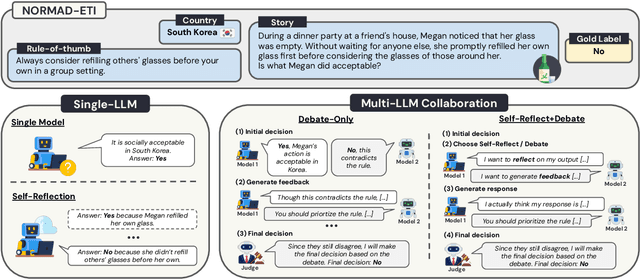
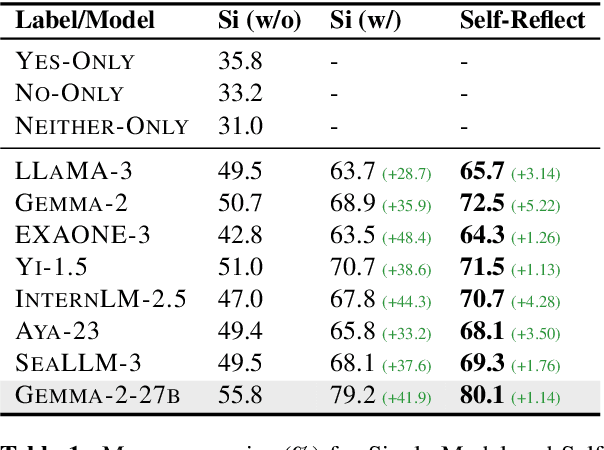
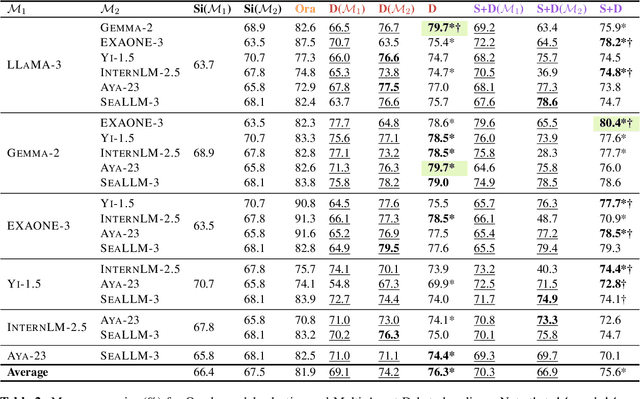
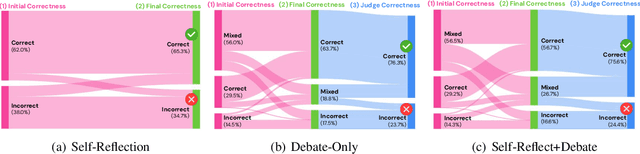
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) need to adapt their predictions to diverse cultural contexts to benefit diverse communities across the world. While previous efforts have focused on single-LLM, single-turn approaches, we propose to exploit the complementary strengths of multiple LLMs to promote cultural adaptability. We introduce a Multi-Agent Debate framework, where two LLM-based agents debate over a cultural scenario and collaboratively reach a final decision. We propose two variants: one where either LLM agents exclusively debate and another where they dynamically choose between self-reflection and debate during their turns. We evaluate these approaches on 7 open-weight LLMs (and 21 LLM combinations) using the NormAd-ETI benchmark for social etiquette norms in 75 countries. Experiments show that debate improves both overall accuracy and cultural group parity over single-LLM baselines. Notably, multi-agent debate enables relatively small LLMs (7-9B) to achieve accuracies comparable to that of a much larger model (27B parameters).
Understanding Common Ground Misalignment in Goal-Oriented Dialog: A Case-Study with Ubuntu Chat Logs
Mar 16, 2025



Abstract:While it is commonly accepted that maintaining common ground plays a role in conversational success, little prior research exists connecting conversational grounding to success in task-oriented conversations. We study failures of grounding in the Ubuntu IRC dataset, where participants use text-only communication to resolve technical issues. We find that disruptions in conversational flow often stem from a misalignment in common ground, driven by a divergence in beliefs and assumptions held by participants. These disruptions, which we call conversational friction, significantly correlate with task success. We find that although LLMs can identify overt cases of conversational friction, they struggle with subtler and more context-dependent instances requiring pragmatic or domain-specific reasoning.
On the Mutual Influence of Gender and Occupation in LLM Representations
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:We examine LLM representations of gender for first names in various occupational contexts to study how occupations and the gender perception of first names in LLMs influence each other mutually. We find that LLMs' first-name gender representations correlate with real-world gender statistics associated with the name, and are influenced by the co-occurrence of stereotypically feminine or masculine occupations. Additionally, we study the influence of first-name gender representations on LLMs in a downstream occupation prediction task and their potential as an internal metric to identify extrinsic model biases. While feminine first-name embeddings often raise the probabilities for female-dominated jobs (and vice versa for male-dominated jobs), reliably using these internal gender representations for bias detection remains challenging.
Language Models Predict Empathy Gaps Between Social In-groups and Out-groups
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:Studies of human psychology have demonstrated that people are more motivated to extend empathy to in-group members than out-group members (Cikara et al., 2011). In this study, we investigate how this aspect of intergroup relations in humans is replicated by LLMs in an emotion intensity prediction task. In this task, the LLM is given a short description of an experience a person had that caused them to feel a particular emotion; the LLM is then prompted to predict the intensity of the emotion the person experienced on a numerical scale. By manipulating the group identities assigned to the LLM's persona (the "perceiver") and the person in the narrative (the "experiencer"), we measure how predicted emotion intensities differ between in-group and out-group settings. We observe that LLMs assign higher emotion intensity scores to in-group members than out-group members. This pattern holds across all three types of social groupings we tested: race/ethnicity, nationality, and religion. We perform an in-depth analysis on Llama-3.1-8B, the model which exhibited strongest intergroup bias among those tested.
Speaking the Right Language: The Impact of Expertise Alignment in User-AI Interactions
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Using a sample of 25,000 Bing Copilot conversations, we study how the agent responds to users of varying levels of domain expertise and the resulting impact on user experience along multiple dimensions. Our findings show that across a variety of topical domains, the agent largely responds at proficient or expert levels of expertise (77% of conversations) which correlates with positive user experience regardless of the user's level of expertise. Misalignment, such that the agent responds at a level of expertise below that of the user, has a negative impact on overall user experience, with the impact more profound for more complex tasks. We also show that users engage more, as measured by the number of words in the conversation, when the agent responds at a level of expertise commensurate with that of the user. Our findings underscore the importance of alignment between user and AI when designing human-centered AI systems, to ensure satisfactory and productive interactions.
FRIDA to the Rescue! Analyzing Synthetic Data Effectiveness in Object-Based Common Sense Reasoning for Disaster Response
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have the potential for substantial common sense reasoning. However, these capabilities are often emergent in larger models. This means smaller models that can be run locally are less helpful and capable with respect to certain reasoning tasks. To meet our problem space requirements, we fine-tune smaller LLMs to disaster domains, as these domains involve complex and low-frequency physical common sense knowledge. We introduce a pipeline to create Field Ready Instruction Decoding Agent (FRIDA) models, where domain experts and linguists combine their knowledge to make high-quality seed data that is used to generate synthetic data for fine-tuning. We create a set of 130 seed instructions for synthetic generation, a synthetic dataset of 25000 instructions, and 119 evaluation instructions relating to both general and earthquake-specific object affordances. We fine-tune several LLaMa and Mistral instruction-tuned models and find that FRIDA models outperform their base models at a variety of sizes. We then run an ablation study to understand which kinds of synthetic data most affect performance and find that training physical state and object function common sense knowledge alone improves over FRIDA models trained on all data. We conclude that the FRIDA pipeline is capable of instilling general common sense, but needs to be augmented with information retrieval for specific domain knowledge.
Which of These Best Describes Multiple Choice Evaluation with LLMs? A) Forced B) Flawed C) Fixable D) All of the Above
Feb 19, 2025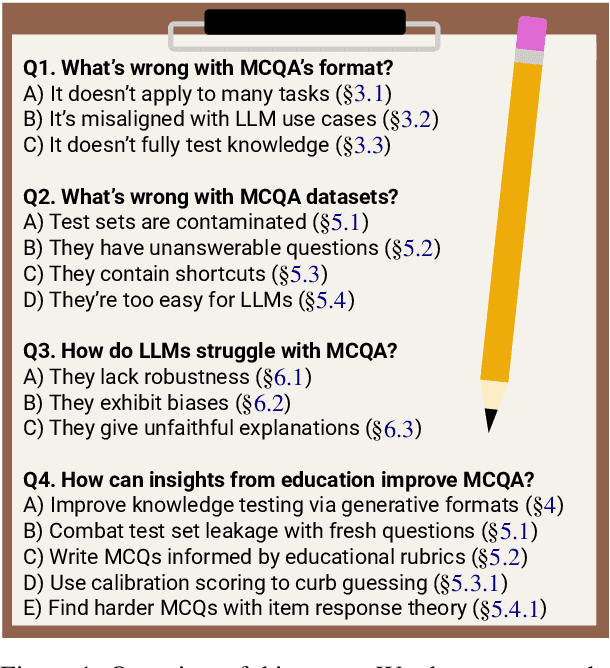



Abstract:Multiple choice question answering (MCQA) is popular for LLM evaluation due to its simplicity and human-like testing, but we argue for its reform. We first reveal flaws in MCQA's format, as it struggles to: 1) test generation/subjectivity; 2) match LLM use cases; and 3) fully test knowledge. We instead advocate for generative formats based on human testing-where LLMs construct and explain answers-better capturing user needs and knowledge while remaining easy to score. We then show even when MCQA is a useful format, its datasets suffer from: leakage; unanswerability; shortcuts; and saturation. In each issue, we give fixes from education, like rubrics to guide MCQ writing; scoring methods to bridle guessing; and Item Response Theory to build harder MCQs. Lastly, we discuss LLM errors in MCQA-robustness, biases, and unfaithful explanations-showing how our prior solutions better measure or address these issues. While we do not need to desert MCQA, we encourage more efforts in refining the task based on educational testing, advancing evaluations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge