Claire Bonial
Neither Stochastic Parroting nor AGI: LLMs Solve Tasks through Context-Directed Extrapolation from Training Data Priors
May 29, 2025Abstract:In this position paper we raise critical awareness of a realistic view of LLM capabilities that eschews extreme alternative views that LLMs are either "stochastic parrots" or in possession of "emergent" advanced reasoning capabilities, which, due to their unpredictable emergence, constitute an existential threat. Our middle-ground view is that LLMs extrapolate from priors from their training data, and that a mechanism akin to in-context learning enables the targeting of the appropriate information from which to extrapolate. We call this "context-directed extrapolation." Under this view, substantiated though existing literature, while reasoning capabilities go well beyond stochastic parroting, such capabilities are predictable, controllable, not indicative of advanced reasoning akin to high-level cognitive capabilities in humans, and not infinitely scalable with additional training. As a result, fears of uncontrollable emergence of agency are allayed, while research advances are appropriately refocused on the processes of context-directed extrapolation and how this interacts with training data to produce valuable capabilities in LLMs. Future work can therefore explore alternative augmenting techniques that do not rely on inherent advanced reasoning in LLMs.
Understanding Common Ground Misalignment in Goal-Oriented Dialog: A Case-Study with Ubuntu Chat Logs
Mar 16, 2025



Abstract:While it is commonly accepted that maintaining common ground plays a role in conversational success, little prior research exists connecting conversational grounding to success in task-oriented conversations. We study failures of grounding in the Ubuntu IRC dataset, where participants use text-only communication to resolve technical issues. We find that disruptions in conversational flow often stem from a misalignment in common ground, driven by a divergence in beliefs and assumptions held by participants. These disruptions, which we call conversational friction, significantly correlate with task success. We find that although LLMs can identify overt cases of conversational friction, they struggle with subtler and more context-dependent instances requiring pragmatic or domain-specific reasoning.
FRIDA to the Rescue! Analyzing Synthetic Data Effectiveness in Object-Based Common Sense Reasoning for Disaster Response
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have the potential for substantial common sense reasoning. However, these capabilities are often emergent in larger models. This means smaller models that can be run locally are less helpful and capable with respect to certain reasoning tasks. To meet our problem space requirements, we fine-tune smaller LLMs to disaster domains, as these domains involve complex and low-frequency physical common sense knowledge. We introduce a pipeline to create Field Ready Instruction Decoding Agent (FRIDA) models, where domain experts and linguists combine their knowledge to make high-quality seed data that is used to generate synthetic data for fine-tuning. We create a set of 130 seed instructions for synthetic generation, a synthetic dataset of 25000 instructions, and 119 evaluation instructions relating to both general and earthquake-specific object affordances. We fine-tune several LLaMa and Mistral instruction-tuned models and find that FRIDA models outperform their base models at a variety of sizes. We then run an ablation study to understand which kinds of synthetic data most affect performance and find that training physical state and object function common sense knowledge alone improves over FRIDA models trained on all data. We conclude that the FRIDA pipeline is capable of instilling general common sense, but needs to be augmented with information retrieval for specific domain knowledge.
Assessing Language Comprehension in Large Language Models Using Construction Grammar
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models, despite their significant capabilities, are known to fail in surprising and unpredictable ways. Evaluating their true `understanding' of language is particularly challenging due to the extensive web-scale data they are trained on. Therefore, we construct an evaluation to systematically assess natural language understanding (NLU) in LLMs by leveraging Construction Grammar (CxG), which provides insights into the meaning captured by linguistic elements known as constructions (Cxns). CxG is well-suited for this purpose because provides a theoretical basis to construct targeted evaluation sets. These datasets are carefully constructed to include examples which are unlikely to appear in pre-training data, yet intuitive and easy for humans to understand, enabling a more targeted and reliable assessment. Our experiments focus on downstream natural language inference and reasoning tasks by comparing LLMs' understanding of the underlying meanings communicated through 8 unique Cxns with that of humans. The results show that while LLMs demonstrate some knowledge of constructional information, even the latest models including GPT-o1 struggle with abstract meanings conveyed by these Cxns, as demonstrated in cases where test sentences are dissimilar to their pre-training data. We argue that such cases provide a more accurate test of true language understanding, highlighting key limitations in LLMs' semantic capabilities. We make our novel dataset and associated experimental data including prompts and model responses publicly available.
Human-Robot Dialogue Annotation for Multi-Modal Common Ground
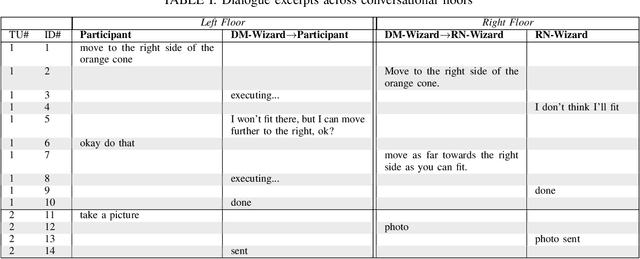
Nov 19, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we describe the development of symbolic representations annotated on human-robot dialogue data to make dimensions of meaning accessible to autonomous systems participating in collaborative, natural language dialogue, and to enable common ground with human partners. A particular challenge for establishing common ground arises in remote dialogue (occurring in disaster relief or search-and-rescue tasks), where a human and robot are engaged in a joint navigation and exploration task of an unfamiliar environment, but where the robot cannot immediately share high quality visual information due to limited communication constraints. Engaging in a dialogue provides an effective way to communicate, while on-demand or lower-quality visual information can be supplemented for establishing common ground. Within this paradigm, we capture propositional semantics and the illocutionary force of a single utterance within the dialogue through our Dialogue-AMR annotation, an augmentation of Abstract Meaning Representation. We then capture patterns in how different utterances within and across speaker floors relate to one another in our development of a multi-floor Dialogue Structure annotation schema. Finally, we begin to annotate and analyze the ways in which the visual modalities provide contextual information to the dialogue for overcoming disparities in the collaborators' understanding of the environment. We conclude by discussing the use-cases, architectures, and systems we have implemented from our annotations that enable physical robots to autonomously engage with humans in bi-directional dialogue and navigation.
* 52 pages, 14 figures
SCOUT: A Situated and Multi-Modal Human-Robot Dialogue Corpus
Nov 19, 2024



Abstract:We introduce the Situated Corpus Of Understanding Transactions (SCOUT), a multi-modal collection of human-robot dialogue in the task domain of collaborative exploration. The corpus was constructed from multiple Wizard-of-Oz experiments where human participants gave verbal instructions to a remotely-located robot to move and gather information about its surroundings. SCOUT contains 89,056 utterances and 310,095 words from 278 dialogues averaging 320 utterances per dialogue. The dialogues are aligned with the multi-modal data streams available during the experiments: 5,785 images and 30 maps. The corpus has been annotated with Abstract Meaning Representation and Dialogue-AMR to identify the speaker's intent and meaning within an utterance, and with Transactional Units and Relations to track relationships between utterances to reveal patterns of the Dialogue Structure. We describe how the corpus and its annotations have been used to develop autonomous human-robot systems and enable research in open questions of how humans speak to robots. We release this corpus to accelerate progress in autonomous, situated, human-robot dialogue, especially in the context of navigation tasks where details about the environment need to be discovered.
* 14 pages, 7 figures
Navigating to Success in Multi-Modal Human-Robot Collaboration: Analysis and Corpus Release
Oct 26, 2023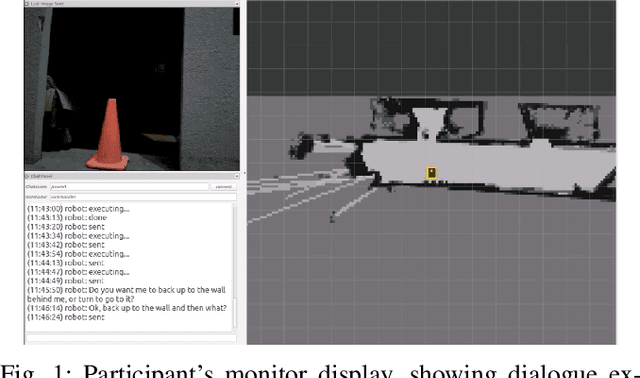
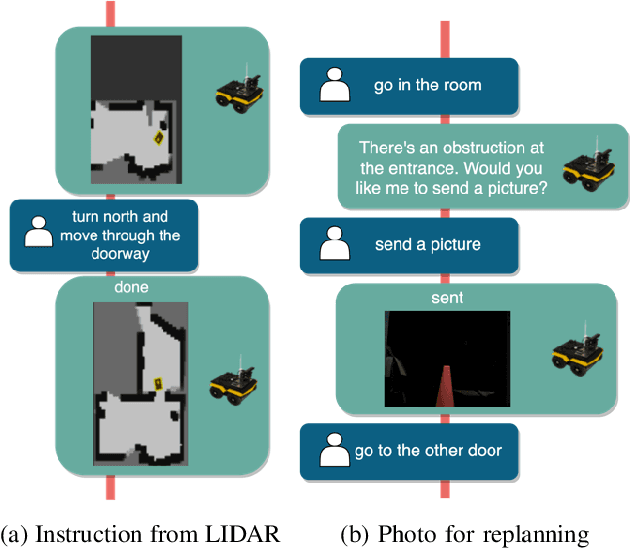
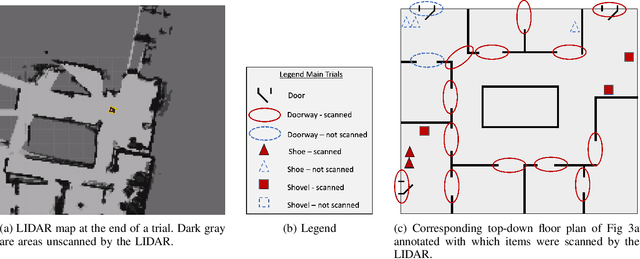
Abstract:Human-guided robotic exploration is a useful approach to gathering information at remote locations, especially those that might be too risky, inhospitable, or inaccessible for humans. Maintaining common ground between the remotely-located partners is a challenge, one that can be facilitated by multi-modal communication. In this paper, we explore how participants utilized multiple modalities to investigate a remote location with the help of a robotic partner. Participants issued spoken natural language instructions and received from the robot: text-based feedback, continuous 2D LIDAR mapping, and upon-request static photographs. We noticed that different strategies were adopted in terms of use of the modalities, and hypothesize that these differences may be correlated with success at several exploration sub-tasks. We found that requesting photos may have improved the identification and counting of some key entities (doorways in particular) and that this strategy did not hinder the amount of overall area exploration. Future work with larger samples may reveal the effects of more nuanced photo and dialogue strategies, which can inform the training of robotic agents. Additionally, we announce the release of our unique multi-modal corpus of human-robot communication in an exploration context: SCOUT, the Situated Corpus on Understanding Transactions.
* 7 pages, 3 figures
What Else Do I Need to Know? The Effect of Background Information on Users' Reliance on AI Systems
May 23, 2023Abstract:AI systems have shown impressive performance at answering questions by retrieving relevant context. However, with the increasingly large models, it is impossible and often undesirable to constrain models' knowledge or reasoning to only the retrieved context. This leads to a mismatch between the information that these models access to derive the answer and the information available to the user consuming the AI predictions to assess the AI predicted answer. In this work, we study how users interact with AI systems in absence of sufficient information to assess AI predictions. Further, we ask the question of whether adding the requisite background alleviates the concerns around over-reliance in AI predictions. Our study reveals that users rely on AI predictions even in the absence of sufficient information needed to assess its correctness. Providing the relevant background, however, helps users catch AI errors better, reducing over-reliance on incorrect AI predictions. On the flip side, background information also increases users' confidence in their correct as well as incorrect judgments. Contrary to common expectation, aiding a user's perusal of the context and the background through highlights is not helpful in alleviating the issue of over-confidence stemming from availability of more information. Our work aims to highlight the gap between how NLP developers perceive informational need in human-AI interaction and the actual human interaction with the information available to them.
Visual Understanding and Narration: A Deeper Understanding and Explanation of Visual Scenes
May 31, 2019
Abstract:We describe the task of Visual Understanding and Narration, in which a robot (or agent) generates text for the images that it collects when navigating its environment, by answering open-ended questions, such as 'what happens, or might have happened, here?'
Balancing Efficiency and Coverage in Human-Robot Dialogue Collection
Oct 07, 2018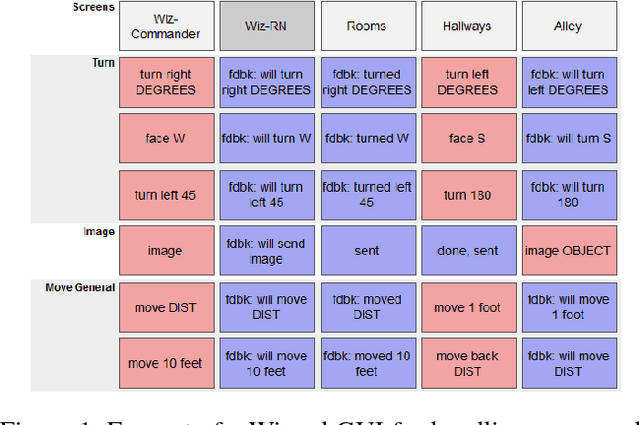
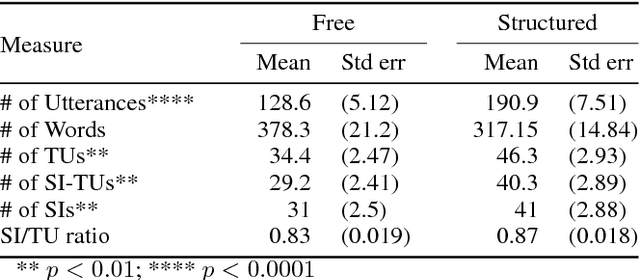
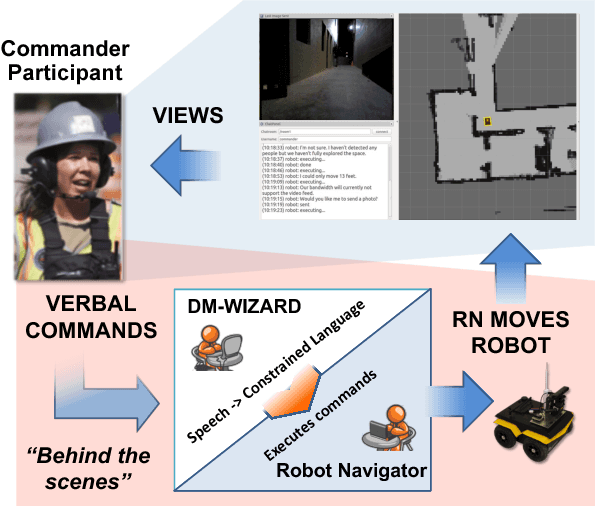
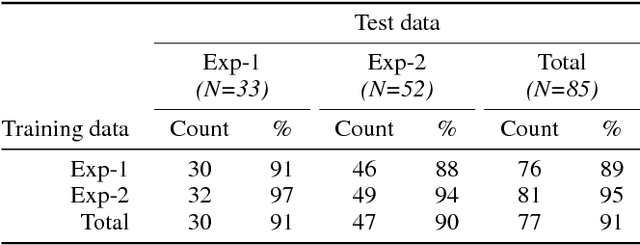
Abstract:We describe a multi-phased Wizard-of-Oz approach to collecting human-robot dialogue in a collaborative search and navigation task. The data is being used to train an initial automated robot dialogue system to support collaborative exploration tasks. In the first phase, a wizard freely typed robot utterances to human participants. For the second phase, this data was used to design a GUI that includes buttons for the most common communications, and templates for communications with varying parameters. Comparison of the data gathered in these phases show that the GUI enabled a faster pace of dialogue while still maintaining high coverage of suitable responses, enabling more efficient targeted data collection, and improvements in natural language understanding using GUI-collected data. As a promising first step towards interactive learning, this work shows that our approach enables the collection of useful training data for navigation-based HRI tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge