Wesley Scivetti
Unpacking Let Alone: Human-Scale Models Generalize to a Rare Construction in Form but not Meaning
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Humans have a remarkable ability to acquire and understand grammatical phenomena that are seen rarely, if ever, during childhood. Recent evidence suggests that language models with human-scale pretraining data may possess a similar ability by generalizing from frequent to rare constructions. However, it remains an open question how widespread this generalization ability is, and to what extent this knowledge extends to meanings of rare constructions, as opposed to just their forms. We fill this gap by testing human-scale transformer language models on their knowledge of both the form and meaning of the (rare and quirky) English LET-ALONE construction. To evaluate our LMs we construct a bespoke synthetic benchmark that targets syntactic and semantic properties of the construction. We find that human-scale LMs are sensitive to form, even when related constructions are filtered from the dataset. However, human-scale LMs do not make correct generalizations about LET-ALONE's meaning. These results point to an asymmetry in the current architectures' sample efficiency between language form and meaning, something which is not present in human language learners.
Construction Identification and Disambiguation Using BERT: A Case Study of NPN
Mar 24, 2025
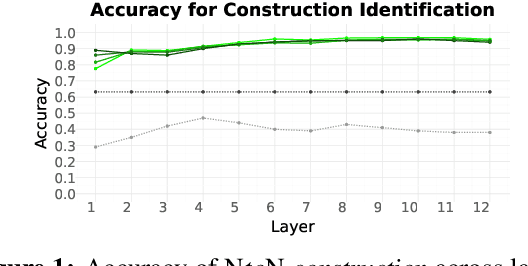
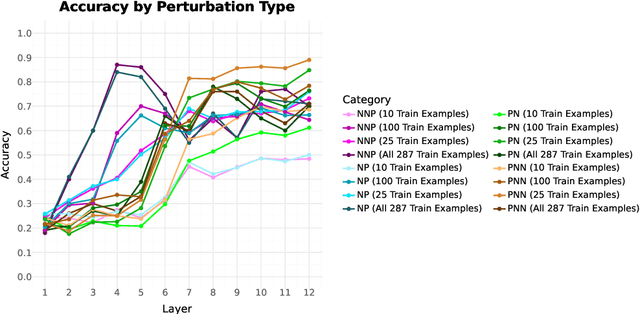
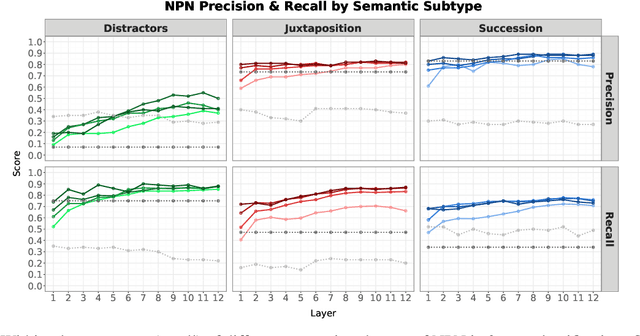
Abstract:Construction Grammar hypothesizes that knowledge of a language consists chiefly of knowledge of form-meaning pairs (''constructions'') that include vocabulary, general grammar rules, and even idiosyncratic patterns. Recent work has shown that transformer language models represent at least some constructional patterns, including ones where the construction is rare overall. In this work, we probe BERT's representation of the form and meaning of a minor construction of English, the NPN (noun-preposition-noun) construction -- exhibited in such expressions as face to face and day to day -- which is known to be polysemous. We construct a benchmark dataset of semantically annotated corpus instances (including distractors that superficially resemble the construction). With this dataset, we train and evaluate probing classifiers. They achieve decent discrimination of the construction from distractors, as well as sense disambiguation among true instances of the construction, revealing that BERT embeddings carry indications of the construction's semantics. Moreover, artificially permuting the word order of true construction instances causes them to be rejected, indicating sensitivity to matters of form. We conclude that BERT does latently encode at least some knowledge of the NPN construction going beyond a surface syntactic pattern and lexical cues.
Assessing Language Comprehension in Large Language Models Using Construction Grammar
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models, despite their significant capabilities, are known to fail in surprising and unpredictable ways. Evaluating their true `understanding' of language is particularly challenging due to the extensive web-scale data they are trained on. Therefore, we construct an evaluation to systematically assess natural language understanding (NLU) in LLMs by leveraging Construction Grammar (CxG), which provides insights into the meaning captured by linguistic elements known as constructions (Cxns). CxG is well-suited for this purpose because provides a theoretical basis to construct targeted evaluation sets. These datasets are carefully constructed to include examples which are unlikely to appear in pre-training data, yet intuitive and easy for humans to understand, enabling a more targeted and reliable assessment. Our experiments focus on downstream natural language inference and reasoning tasks by comparing LLMs' understanding of the underlying meanings communicated through 8 unique Cxns with that of humans. The results show that while LLMs demonstrate some knowledge of constructional information, even the latest models including GPT-o1 struggle with abstract meanings conveyed by these Cxns, as demonstrated in cases where test sentences are dissimilar to their pre-training data. We argue that such cases provide a more accurate test of true language understanding, highlighting key limitations in LLMs' semantic capabilities. We make our novel dataset and associated experimental data including prompts and model responses publicly available.
GDTB: Genre Diverse Data for English Shallow Discourse Parsing across Modalities, Text Types, and Domains
Nov 01, 2024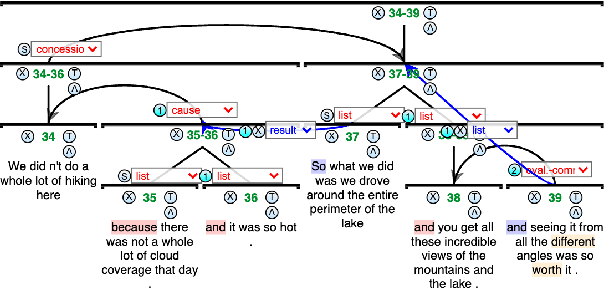
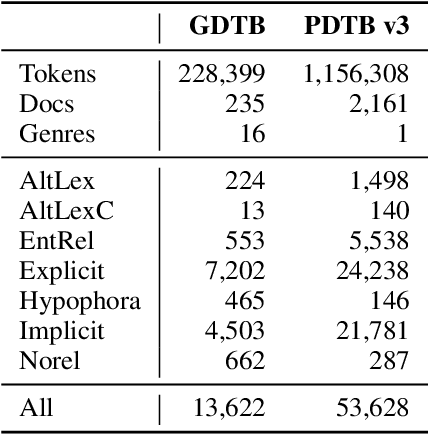
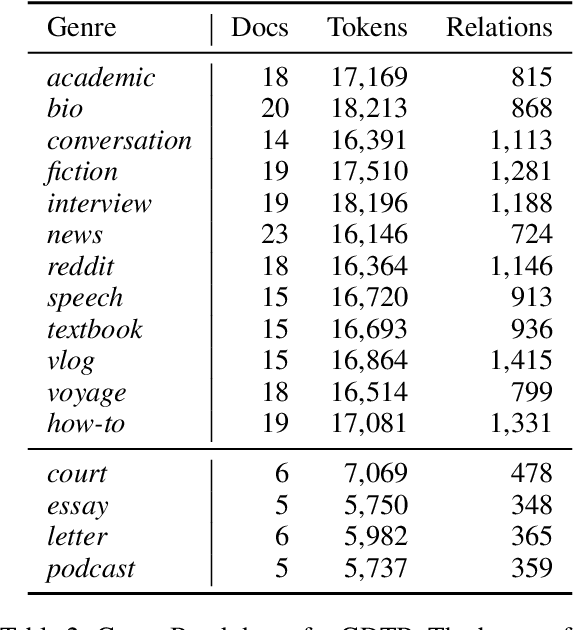
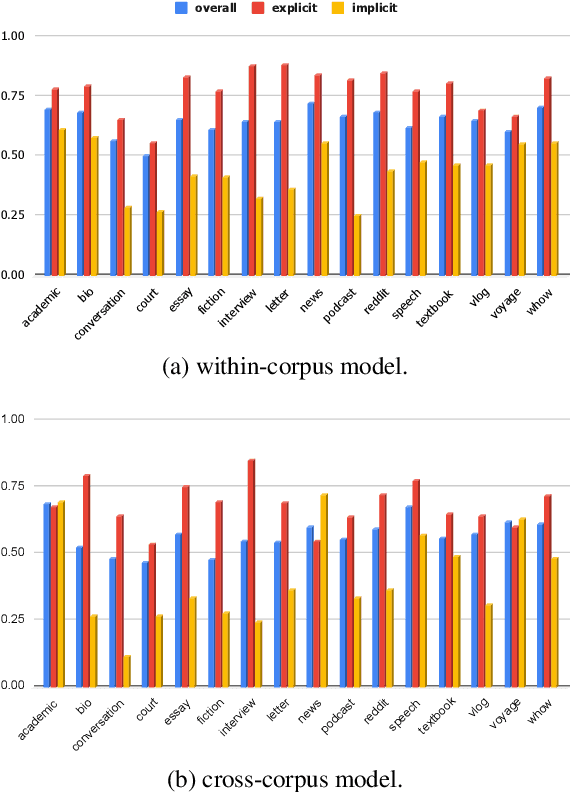
Abstract:Work on shallow discourse parsing in English has focused on the Wall Street Journal corpus, the only large-scale dataset for the language in the PDTB framework. However, the data is not openly available, is restricted to the news domain, and is by now 35 years old. In this paper, we present and evaluate a new open-access, multi-genre benchmark for PDTB-style shallow discourse parsing, based on the existing UD English GUM corpus, for which discourse relation annotations in other frameworks already exist. In a series of experiments on cross-domain relation classification, we show that while our dataset is compatible with PDTB, substantial out-of-domain degradation is observed, which can be alleviated by joint training on both datasets.
UCxn: Typologically Informed Annotation of Constructions Atop Universal Dependencies
Mar 26, 2024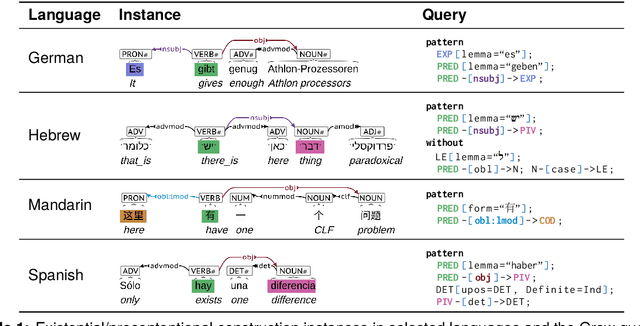
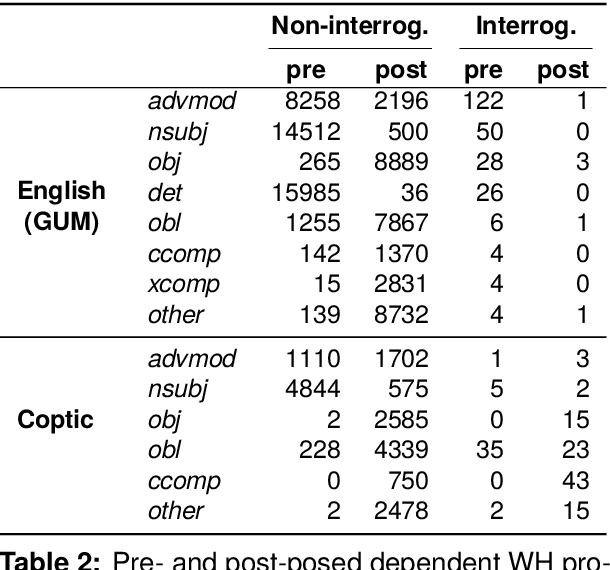
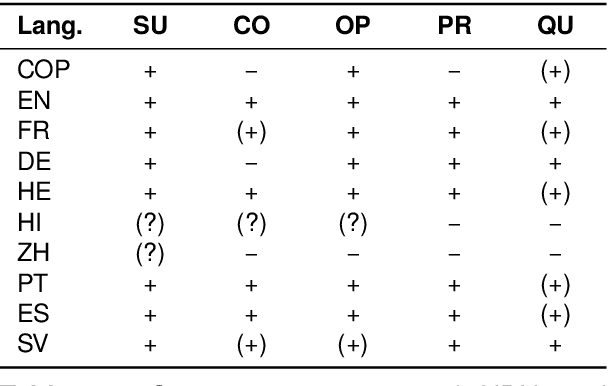
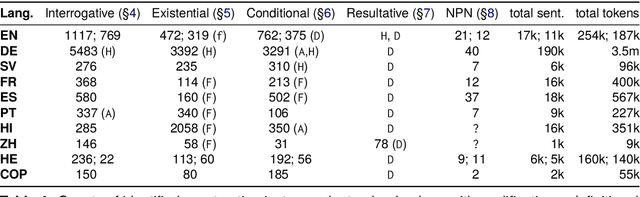
Abstract:The Universal Dependencies (UD) project has created an invaluable collection of treebanks with contributions in over 140 languages. However, the UD annotations do not tell the full story. Grammatical constructions that convey meaning through a particular combination of several morphosyntactic elements -- for example, interrogative sentences with special markers and/or word orders -- are not labeled holistically. We argue for (i) augmenting UD annotations with a 'UCxn' annotation layer for such meaning-bearing grammatical constructions, and (ii) approaching this in a typologically informed way so that morphosyntactic strategies can be compared across languages. As a case study, we consider five construction families in ten languages, identifying instances of each construction in UD treebanks through the use of morphosyntactic patterns. In addition to findings regarding these particular constructions, our study yields important insights on methodology for describing and identifying constructions in language-general and language-particular ways, and lays the foundation for future constructional enrichment of UD treebanks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge