Austin Blodgett
FRIDA to the Rescue! Analyzing Synthetic Data Effectiveness in Object-Based Common Sense Reasoning for Disaster Response
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have the potential for substantial common sense reasoning. However, these capabilities are often emergent in larger models. This means smaller models that can be run locally are less helpful and capable with respect to certain reasoning tasks. To meet our problem space requirements, we fine-tune smaller LLMs to disaster domains, as these domains involve complex and low-frequency physical common sense knowledge. We introduce a pipeline to create Field Ready Instruction Decoding Agent (FRIDA) models, where domain experts and linguists combine their knowledge to make high-quality seed data that is used to generate synthetic data for fine-tuning. We create a set of 130 seed instructions for synthetic generation, a synthetic dataset of 25000 instructions, and 119 evaluation instructions relating to both general and earthquake-specific object affordances. We fine-tune several LLaMa and Mistral instruction-tuned models and find that FRIDA models outperform their base models at a variety of sizes. We then run an ablation study to understand which kinds of synthetic data most affect performance and find that training physical state and object function common sense knowledge alone improves over FRIDA models trained on all data. We conclude that the FRIDA pipeline is capable of instilling general common sense, but needs to be augmented with information retrieval for specific domain knowledge.
Assessing Language Comprehension in Large Language Models Using Construction Grammar
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models, despite their significant capabilities, are known to fail in surprising and unpredictable ways. Evaluating their true `understanding' of language is particularly challenging due to the extensive web-scale data they are trained on. Therefore, we construct an evaluation to systematically assess natural language understanding (NLU) in LLMs by leveraging Construction Grammar (CxG), which provides insights into the meaning captured by linguistic elements known as constructions (Cxns). CxG is well-suited for this purpose because provides a theoretical basis to construct targeted evaluation sets. These datasets are carefully constructed to include examples which are unlikely to appear in pre-training data, yet intuitive and easy for humans to understand, enabling a more targeted and reliable assessment. Our experiments focus on downstream natural language inference and reasoning tasks by comparing LLMs' understanding of the underlying meanings communicated through 8 unique Cxns with that of humans. The results show that while LLMs demonstrate some knowledge of constructional information, even the latest models including GPT-o1 struggle with abstract meanings conveyed by these Cxns, as demonstrated in cases where test sentences are dissimilar to their pre-training data. We argue that such cases provide a more accurate test of true language understanding, highlighting key limitations in LLMs' semantic capabilities. We make our novel dataset and associated experimental data including prompts and model responses publicly available.
DocAMR: Multi-Sentence AMR Representation and Evaluation
Dec 15, 2021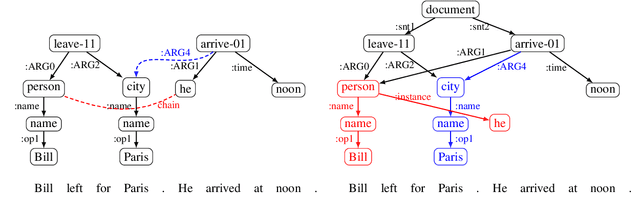
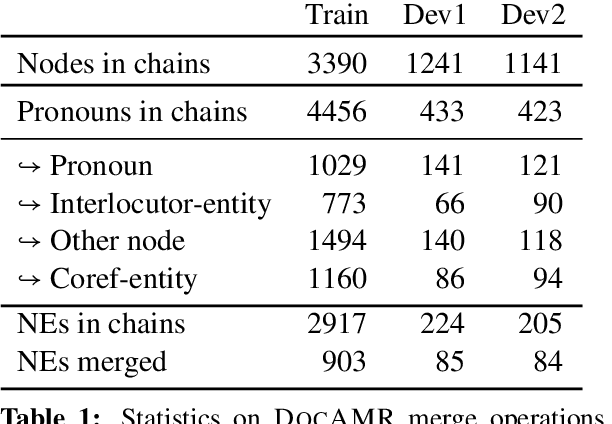
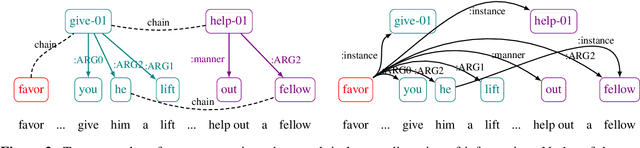
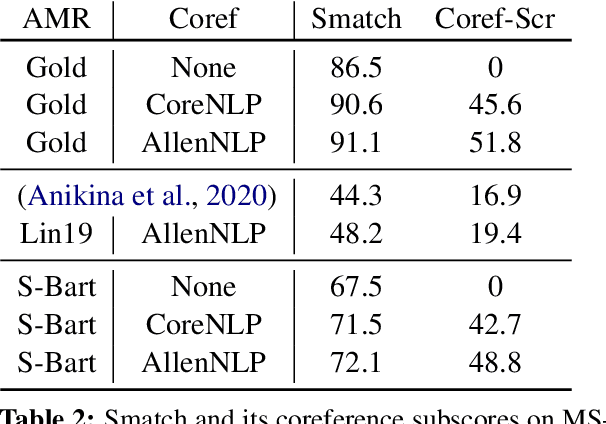
Abstract:Despite extensive research on parsing of English sentences into Abstraction Meaning Representation (AMR) graphs, which are compared to gold graphs via the Smatch metric, full-document parsing into a unified graph representation lacks well-defined representation and evaluation. Taking advantage of a super-sentential level of coreference annotation from previous work, we introduce a simple algorithm for deriving a unified graph representation, avoiding the pitfalls of information loss from over-merging and lack of coherence from under-merging. Next, we describe improvements to the Smatch metric to make it tractable for comparing document-level graphs, and use it to re-evaluate the best published document-level AMR parser. We also present a pipeline approach combining the top performing AMR parser and coreference resolution systems, providing a strong baseline for future research.
Probabilistic, Structure-Aware Algorithms for Improved Variety, Accuracy, and Coverage of AMR Alignments
Jun 10, 2021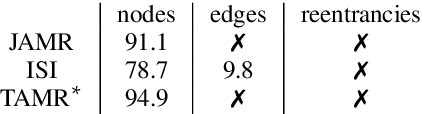
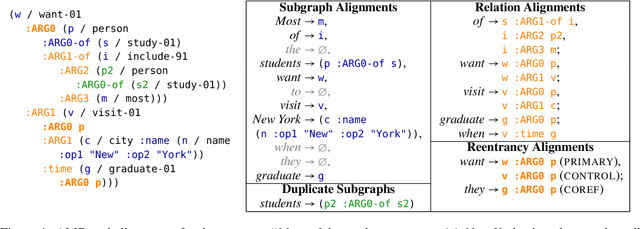
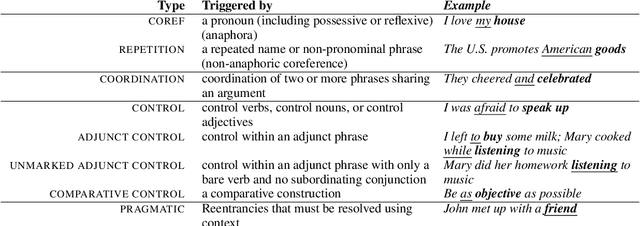
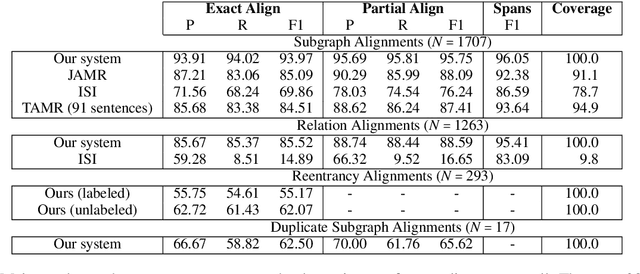
Abstract:We present algorithms for aligning components of Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR) graphs to spans in English sentences. We leverage unsupervised learning in combination with heuristics, taking the best of both worlds from previous AMR aligners. Our unsupervised models, however, are more sensitive to graph substructures, without requiring a separate syntactic parse. Our approach covers a wider variety of AMR substructures than previously considered, achieves higher coverage of nodes and edges, and does so with higher accuracy. We will release our LEAMR datasets and aligner for use in research on AMR parsing, generation, and evaluation.
Transition-based Parsing with Stack-Transformers
Oct 20, 2020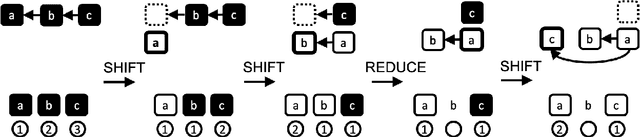
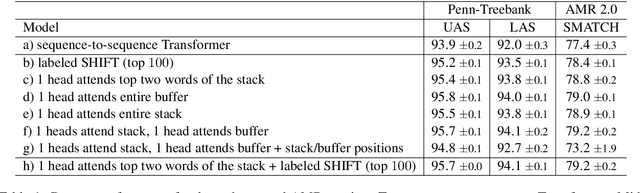
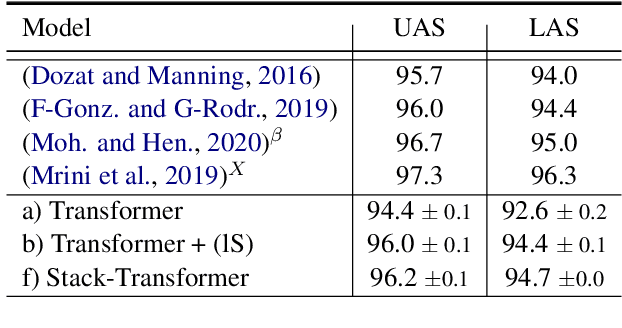
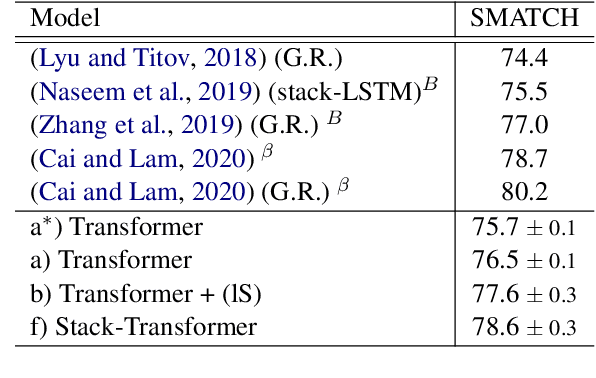
Abstract:Modeling the parser state is key to good performance in transition-based parsing. Recurrent Neural Networks considerably improved the performance of transition-based systems by modelling the global state, e.g. stack-LSTM parsers, or local state modeling of contextualized features, e.g. Bi-LSTM parsers. Given the success of Transformer architectures in recent parsing systems, this work explores modifications of the sequence-to-sequence Transformer architecture to model either global or local parser states in transition-based parsing. We show that modifications of the cross attention mechanism of the Transformer considerably strengthen performance both on dependency and Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR) parsing tasks, particularly for smaller models or limited training data.
A Corpus of Adpositional Supersenses for Mandarin Chinese
Mar 18, 2020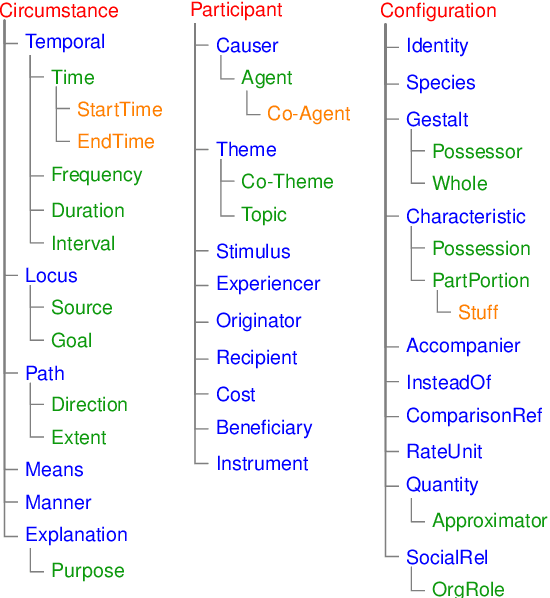
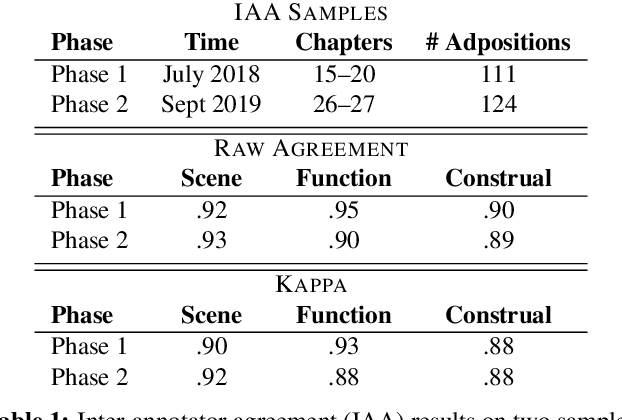
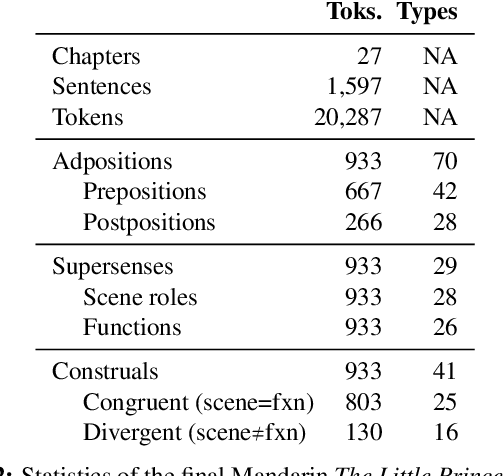
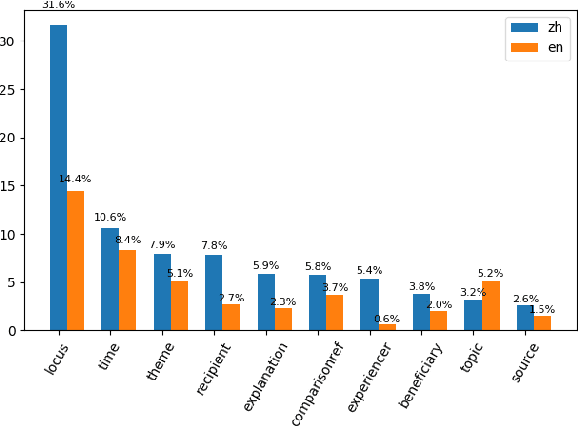
Abstract:Adpositions are frequent markers of semantic relations, but they are highly ambiguous and vary significantly from language to language. Moreover, there is a dearth of annotated corpora for investigating the cross-linguistic variation of adposition semantics, or for building multilingual disambiguation systems. This paper presents a corpus in which all adpositions have been semantically annotated in Mandarin Chinese; to the best of our knowledge, this is the first Chinese corpus to be broadly annotated with adposition semantics. Our approach adapts a framework that defined a general set of supersenses according to ostensibly language-independent semantic criteria, though its development focused primarily on English prepositions (Schneider et al., 2018). We find that the supersense categories are well-suited to Chinese adpositions despite syntactic differences from English. On a Mandarin translation of The Little Prince, we achieve high inter-annotator agreement and analyze semantic correspondences of adposition tokens in bitext.
An Improved Approach for Semantic Graph Composition with CCG
Apr 10, 2019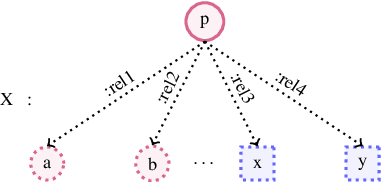
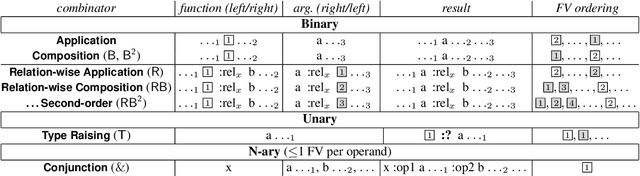
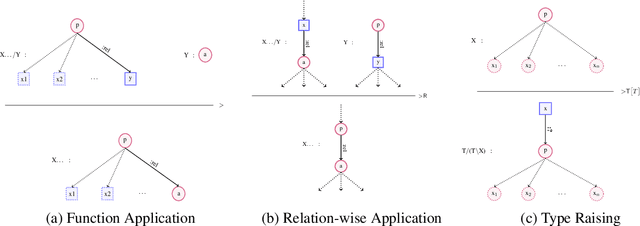
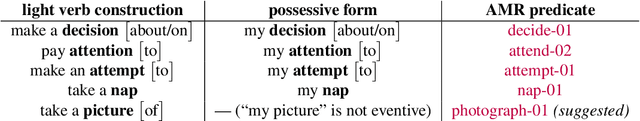
Abstract:This paper builds on previous work using Combinatory Categorial Grammar (CCG) to derive a transparent syntax-semantics interface for Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR) parsing. We define new semantics for the CCG combinators that is better suited to deriving AMR graphs. In particular, we define relation-wise alternatives for the application and composition combinators: these require that the two constituents being combined overlap in one AMR relation. We also provide a new semantics for type raising, which is necessary for certain constructions. Using these mechanisms, we suggest an analysis of eventive nouns, which present a challenge for deriving AMR graphs. Our theoretical analysis will facilitate future work on robust and transparent AMR parsing using CCG.
Adpositional Supersenses for Mandarin Chinese
Dec 06, 2018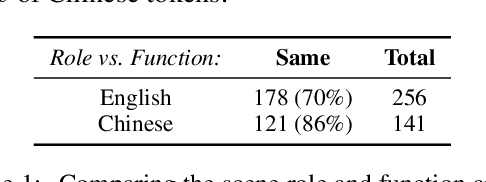
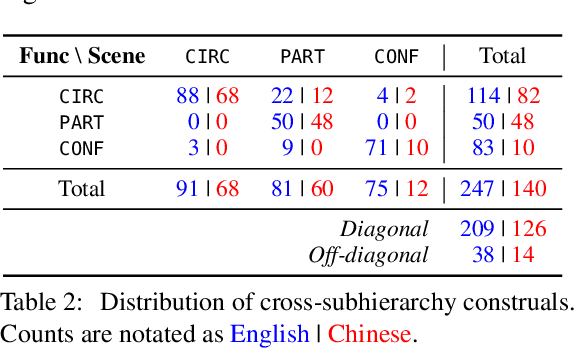
Abstract:This study adapts Semantic Network of Adposition and Case Supersenses (SNACS) annotation to Mandarin Chinese and demonstrates that the same supersense categories are appropriate for Chinese adposition semantics. We annotated 15 chapters of The Little Prince, with high interannotator agreement. The parallel corpus gives insight into differences in construal between the two languages' adpositions, namely a number of construals that are frequent in Chinese but rare or unattested in the English corpus. The annotated corpus can further support automatic disambiguation of adpositions in Chinese, and the common inventory of supersenses between the two languages can potentially serve cross-linguistic tasks such as machine translation.
* 4 pages
Adposition and Case Supersenses v2: Guidelines for English
Jul 02, 2018Abstract:This document offers a detailed linguistic description of SNACS (Semantic Network of Adposition and Case Supersenses; Schneider et al., 2018), an inventory of 50 semantic labels ("supersenses") that characterize the use of adpositions and case markers at a somewhat coarse level of granularity, as demonstrated in the STREUSLE 4.1 corpus (https://github.com/nert-gu/streusle/). Though the SNACS inventory aspires to be universal, this document is specific to English; documentation for other languages will be published separately. Version 2 is a revision of the supersense inventory proposed for English by Schneider et al. (2015, 2016) (henceforth "v1"), which in turn was based on previous schemes. The present inventory was developed after extensive review of the v1 corpus annotations for English, plus previously unanalyzed genitive case possessives (Blodgett and Schneider, 2018), as well as consideration of adposition and case phenomena in Hebrew, Hindi, Korean, and German. Hwang et al. (2017) present the theoretical underpinnings of the v2 scheme. Schneider et al. (2018) summarize the scheme, its application to English corpus data, and an automatic disambiguation task.
Comprehensive Supersense Disambiguation of English Prepositions and Possessives
May 13, 2018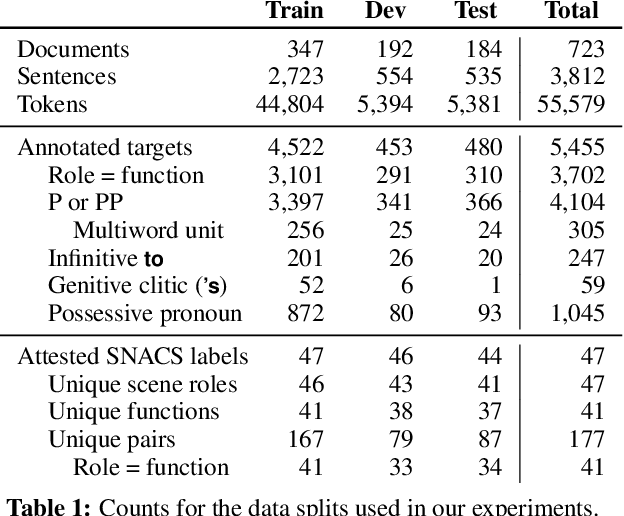
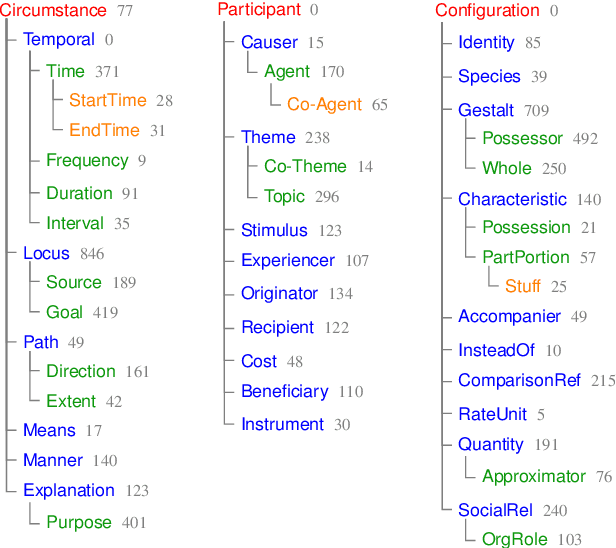
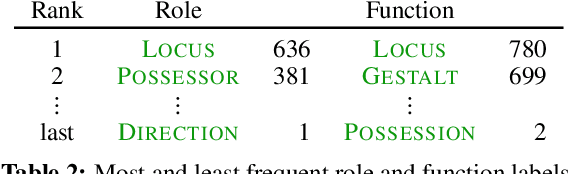
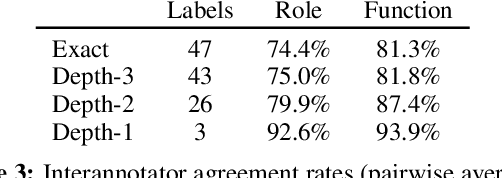
Abstract:Semantic relations are often signaled with prepositional or possessive marking--but extreme polysemy bedevils their analysis and automatic interpretation. We introduce a new annotation scheme, corpus, and task for the disambiguation of prepositions and possessives in English. Unlike previous approaches, our annotations are comprehensive with respect to types and tokens of these markers; use broadly applicable supersense classes rather than fine-grained dictionary definitions; unite prepositions and possessives under the same class inventory; and distinguish between a marker's lexical contribution and the role it marks in the context of a predicate or scene. Strong interannotator agreement rates, as well as encouraging disambiguation results with established supervised methods, speak to the viability of the scheme and task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge