Jeffrey Flanigan
Prompt, Translate, Fine-Tune, Re-Initialize, or Instruction-Tune? Adapting LLMs for In-Context Learning in Low-Resource Languages
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:LLMs are typically trained in high-resource languages, and tasks in lower-resourced languages tend to underperform the higher-resource language counterparts for in-context learning. Despite the large body of work on prompting settings, it is still unclear how LLMs should be adapted cross-lingually specifically for in-context learning in the low-resource target languages. We perform a comprehensive study spanning five diverse target languages, three base LLMs, and seven downstream tasks spanning over 4,100 GPU training hours (9,900+ TFLOPs) across various adaptation techniques: few-shot prompting, translate-test, fine-tuning, embedding re-initialization, and instruction fine-tuning. Our results show that the few-shot prompting and translate-test settings tend to heavily outperform the gradient-based adaptation methods. To better understand this discrepancy, we design a novel metric, Valid Output Recall (VOR), and analyze model outputs to empirically attribute the degradation of these trained models to catastrophic forgetting. To the extent of our knowledge, this is the largest study done on in-context learning for low-resource languages with respect to train compute and number of adaptation techniques considered. We make all our datasets and trained models available for public use.
RAC: Efficient LLM Factuality Correction with Retrieval Augmentation
Oct 21, 2024
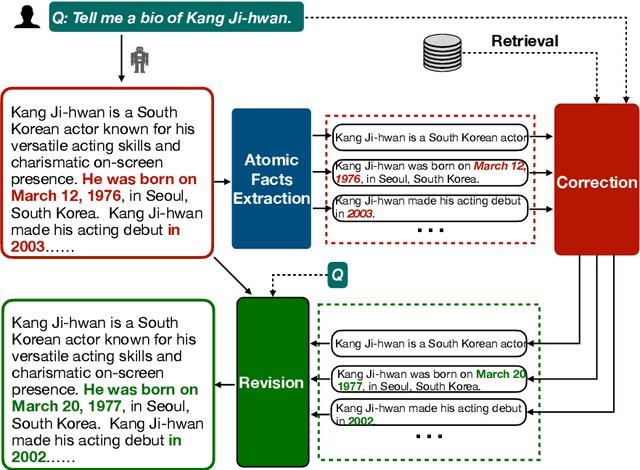
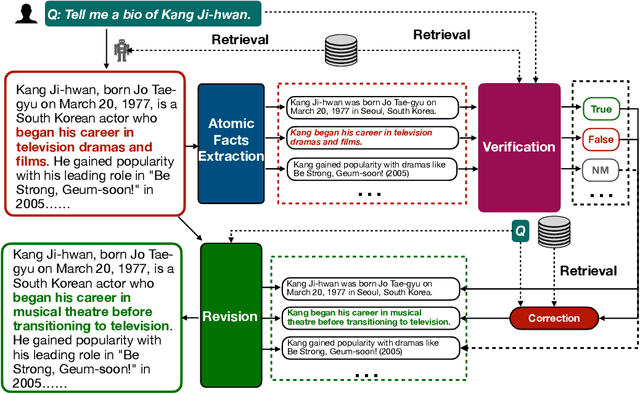

Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit impressive results across a wide range of natural language processing (NLP) tasks, yet they can often produce factually incorrect outputs. This paper introduces a simple but effective low-latency post-correction method, \textbf{Retrieval Augmented Correction (RAC)}, aimed at enhancing the factual performance of LLMs without requiring additional fine-tuning. Our method is general and can be used with any instruction-tuned LLM, and has greatly reduced latency compared to prior approaches. RAC decomposes the LLM's output into atomic facts and applies a fine-grained verification and correction process with retrieved content to verify and correct the LLM-generated output. Our extensive experiments show that RAC yields up to 30\% improvements over state-of-the-art baselines across two popular factuality evaluation datasets, validating its efficacy and robustness in both with and without the integration of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) across different LLMs.\footnote{Our code is at \url{https://github.com/jlab-nlp/Retrieval-Augmented-Correction}}
Large Language Model Unlearning via Embedding-Corrupted Prompts
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have advanced to encompass extensive knowledge across diverse domains. Yet controlling what a large language model should not know is important for ensuring alignment and thus safe use. However, accurately and efficiently unlearning knowledge from an LLM remains challenging due to the potential collateral damage caused by the fuzzy boundary between retention and forgetting, and the large computational requirements for optimization across state-of-the-art models with hundreds of billions of parameters. In this work, we present Embedding-COrrupted (ECO) Prompts, a lightweight unlearning framework for large language models to address both the challenges of knowledge entanglement and unlearning efficiency. Instead of relying on the LLM itself to unlearn, we enforce an unlearned state during inference by employing a prompt classifier to identify and safeguard prompts to forget. We learn corruptions added to prompt embeddings via zeroth order optimization toward the unlearning objective offline and corrupt prompts flagged by the classifier during inference. We find that these embedding-corrupted prompts not only lead to desirable outputs that satisfy the unlearning objective but also closely approximate the output from a model that has never been trained on the data intended for forgetting. Through extensive experiments on unlearning, we demonstrate the superiority of our method in achieving promising unlearning at nearly zero side effects in general domains and domains closely related to the unlearned ones. Additionally, we highlight the scalability of our method to 100 LLMs, ranging from 0.5B to 236B parameters, incurring no additional cost as the number of parameters increases.
The Power of the Noisy Channel: Unsupervised End-to-End Task-Oriented Dialogue with LLMs
Apr 23, 2024



Abstract:Training task-oriented dialogue systems typically requires turn-level annotations for interacting with their APIs: e.g. a dialogue state and the system actions taken at each step. These annotations can be costly to produce, error-prone, and require both domain and annotation expertise. With advances in LLMs, we hypothesize unlabelled data and a schema definition are sufficient for building a working task-oriented dialogue system, completely unsupervised. Using only (1) a well-defined API schema (2) a set of unlabelled dialogues between a user and agent, we develop a novel approach for inferring turn-level annotations as latent variables using a noisy channel model. We iteratively improve these pseudo-labels with expectation-maximization (EM), and use the inferred labels to train an end-to-end dialogue agent. Evaluating our approach on the MultiWOZ benchmark, our method more than doubles the dialogue success rate of a strong GPT-3.5 baseline.
Future Language Modeling from Temporal Document History
Apr 16, 2024Abstract:Predicting the future is of great interest across many aspects of human activity. Businesses are interested in future trends, traders are interested in future stock prices, and companies are highly interested in future technological breakthroughs. While there are many automated systems for predicting future numerical data, such as weather, stock prices, and demand for products, there is relatively little work in automatically predicting textual data. Humans are interested in textual data predictions because it is a natural format for our consumption, and experts routinely make predictions in a textual format (Christensen et al., 2004; Tetlock & Gardner, 2015; Frick, 2015). However, there has been relatively little formalization of this general problem in the machine learning or natural language processing communities. To address this gap, we introduce the task of future language modeling: probabilistic modeling of texts in the future based on a temporal history of texts. To our knowledge, our work is the first work to formalize the task of predicting the future in this way. We show that it is indeed possible to build future language models that improve upon strong non-temporal language model baselines, opening the door to working on this important, and widely applicable problem.
Task Contamination: Language Models May Not Be Few-Shot Anymore
Dec 26, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) offer impressive performance in various zero-shot and few-shot tasks. However, their success in zero-shot and few-shot settings may be affected by task contamination, a potential limitation that has not been thoroughly examined. This paper investigates how zero-shot and few-shot performance of LLMs has changed chronologically over time. Utilizing GPT-3 series models and several other recent open-sourced LLMs, and controlling for dataset difficulty, we find that on datasets released before the LLM training data creation date, LLMs perform surprisingly better than on datasets released after. This strongly indicates that, for many LLMs, there exists task contamination on zero-shot and few-shot evaluation for datasets released prior to the LLMs' training data creation date. Additionally, we utilize training data inspection, task example extraction, and a membership inference attack, which reveal further evidence of task contamination. Importantly, we find that for classification tasks with no possibility of task contamination, LLMs rarely demonstrate statistically significant improvements over simple majority baselines, in both zero and few-shot settings.
Understanding the Role of Optimization in Double Descent
Dec 06, 2023
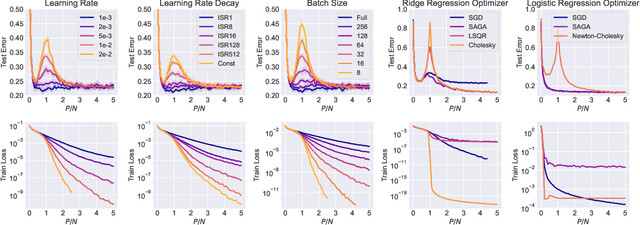

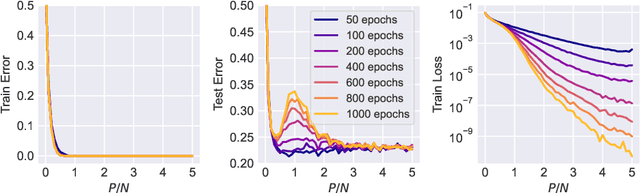
Abstract:The phenomenon of model-wise double descent, where the test error peaks and then reduces as the model size increases, is an interesting topic that has attracted the attention of researchers due to the striking observed gap between theory and practice \citep{Belkin2018ReconcilingMM}. Additionally, while double descent has been observed in various tasks and architectures, the peak of double descent can sometimes be noticeably absent or diminished, even without explicit regularization, such as weight decay and early stopping. In this paper, we investigate this intriguing phenomenon from the optimization perspective and propose a simple optimization-based explanation for why double descent sometimes occurs weakly or not at all. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to demonstrate that many disparate factors contributing to model-wise double descent (initialization, normalization, batch size, learning rate, optimization algorithm) are unified from the viewpoint of optimization: model-wise double descent is observed if and only if the optimizer can find a sufficiently low-loss minimum. These factors directly affect the condition number of the optimization problem or the optimizer and thus affect the final minimum found by the optimizer, reducing or increasing the height of the double descent peak. We conduct a series of controlled experiments on random feature models and two-layer neural networks under various optimization settings, demonstrating this optimization-based unified view. Our results suggest the following implication: Double descent is unlikely to be a problem for real-world machine learning setups. Additionally, our results help explain the gap between weak double descent peaks in practice and strong peaks observable in carefully designed setups.
A New Approach Towards Autoformalization
Oct 19, 2023Abstract:Verifying mathematical proofs is difficult, but can be automated with the assistance of a computer. Autoformalization is the task of automatically translating natural language mathematics into a formal language that can be verified by a program. This is a challenging task, and especially for higher-level mathematics found in research papers. Research paper mathematics requires large amounts of background and context. In this paper, we propose an avenue towards tackling autoformalization for research-level mathematics, by breaking the task into easier and more approachable subtasks: unlinked formalization (formalization with unlinked definitions and theorems), entity linking (linking to the proper theorems and definitions), and finally adjusting types so it passes the type checker. In addition, we present arXiv2Formal, a benchmark dataset for unlinked formalization consisting of 50 theorems formalized for the Lean theorem prover sampled from papers on arXiv.org. We welcome any contributions from the community to future versions of this dataset.
Does the "most sinfully decadent cake ever" taste good? Answering Yes/No Questions from Figurative Contexts
Sep 24, 2023Abstract:Figurative language is commonplace in natural language, and while making communication memorable and creative, can be difficult to understand. In this work, we investigate the robustness of Question Answering (QA) models on figurative text. Yes/no questions, in particular, are a useful probe of figurative language understanding capabilities of large language models. We propose FigurativeQA, a set of 1000 yes/no questions with figurative and non-figurative contexts, extracted from the domains of restaurant and product reviews. We show that state-of-the-art BERT-based QA models exhibit an average performance drop of up to 15\% points when answering questions from figurative contexts, as compared to non-figurative ones. While models like GPT-3 and ChatGPT are better at handling figurative texts, we show that further performance gains can be achieved by automatically simplifying the figurative contexts into their non-figurative (literal) counterparts. We find that the best overall model is ChatGPT with chain-of-thought prompting to generate non-figurative contexts. Our work provides a promising direction for building more robust QA models with figurative language understanding capabilities.
Diverse Retrieval-Augmented In-Context Learning for Dialogue State Tracking
Jul 04, 2023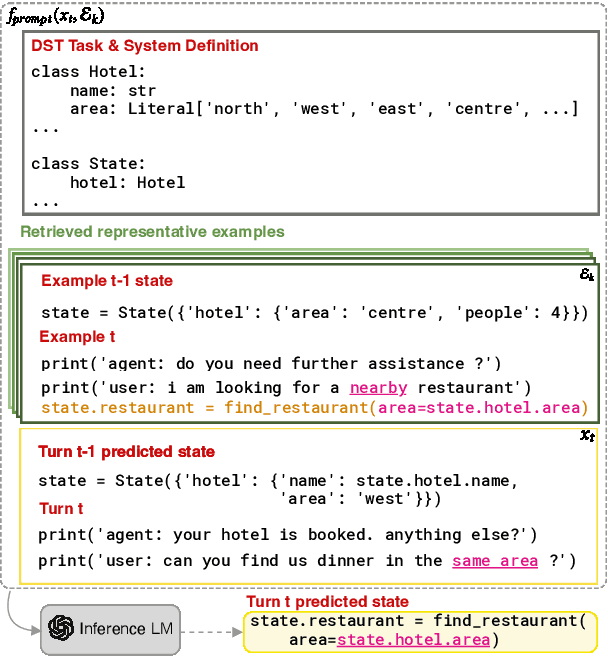

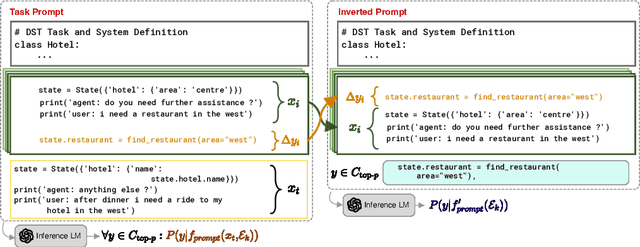
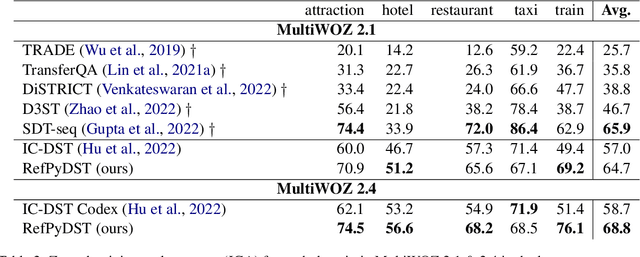
Abstract:There has been significant interest in zero and few-shot learning for dialogue state tracking (DST) due to the high cost of collecting and annotating task-oriented dialogues. Recent work has demonstrated that in-context learning requires very little data and zero parameter updates, and even outperforms trained methods in the few-shot setting (Hu et al. 2022). We propose RefPyDST, which advances the state of the art with three advancements to in-context learning for DST. First, we formulate DST as a Python programming task, explicitly modeling language coreference as variable reference in Python. Second, since in-context learning depends highly on the context examples, we propose a method to retrieve a diverse set of relevant examples to improve performance. Finally, we introduce a novel re-weighting method during decoding that takes into account probabilities of competing surface forms, and produces a more accurate dialogue state prediction. We evaluate our approach using MultiWOZ and achieve state-of-the-art multi-domain joint-goal accuracy in zero and few-shot settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge