Miguel Ballesteros
Budget-Aware Anytime Reasoning with LLM-Synthesized Preference Data
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:We study the reasoning behavior of large language models (LLMs) under limited computation budgets. In such settings, producing useful partial solutions quickly is often more practical than exhaustive reasoning, which incurs high inference costs. Many real-world tasks, such as trip planning, require models to deliver the best possible output within a fixed reasoning budget. We introduce an anytime reasoning framework and the Anytime Index, a metric that quantifies how effectively solution quality improves as reasoning tokens increase. To further enhance efficiency, we propose an inference-time self-improvement method using LLM-synthesized preference data, where models learn from their own reasoning comparisons to produce better intermediate solutions. Experiments on NaturalPlan (Trip), AIME, and GPQA datasets show consistent gains across Grok-3, GPT-oss, GPT-4.1/4o, and LLaMA models, improving both reasoning quality and efficiency under budget constraints.
Tree-based Dialogue Reinforced Policy Optimization for Red-Teaming Attacks
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Despite recent rapid progress in AI safety, current large language models remain vulnerable to adversarial attacks in multi-turn interaction settings, where attackers strategically adapt their prompts across conversation turns and pose a more critical yet realistic challenge. Existing approaches that discover safety vulnerabilities either rely on manual red-teaming with human experts or employ automated methods using pre-defined templates and human-curated attack data, with most focusing on single-turn attacks. However, these methods did not explore the vast space of possible multi-turn attacks, failing to consider novel attack trajectories that emerge from complex dialogue dynamics and strategic conversation planning. This gap is particularly critical given recent findings that LLMs exhibit significantly higher vulnerability to multi-turn attacks compared to single-turn attacks. We propose DialTree-RPO, an on-policy reinforcement learning framework integrated with tree search that autonomously discovers diverse multi-turn attack strategies by treating the dialogue as a sequential decision-making problem, enabling systematic exploration without manually curated data. Through extensive experiments, our approach not only achieves more than 25.9% higher ASR across 10 target models compared to previous state-of-the-art approaches, but also effectively uncovers new attack strategies by learning optimal dialogue policies that maximize attack success across multiple turns.
MetaSynth: Meta-Prompting-Driven Agentic Scaffolds for Diverse Synthetic Data Generation
Apr 17, 2025



Abstract:Recent smaller language models such Phi-3.5 and Phi-4 rely on synthetic data generated using larger Language models. Questions remain about leveraging synthetic data for other use cases, such as adapting LLMs to specific domains. A key limitation of synthetic data is low diversity, which negatively impacts its downstream applicability for improving other models. To address this, we propose MetaSynth, a method for generating synthetic data that enhances diversity through meta-prompting, where a language model orchestrates multiple "expert" LLM agents to collaboratively generate data. Using only 25 million tokens of synthetic data generated with MetaSynth, we successfully adapt a well-trained LLM (Mistral-7B-v0.3) to two specialized domains-Finance and Biomedicine-without compromising the capabilities of the resulting model in general tasks. In addition, we evaluate the diversity of our synthetic data using seven automated metrics, and find that it approaches the diversity of LLM pre-training corpora. Continually pre-training Mistral-7B-v0.3 with MetaSynth notably outperforms the base LLM, showing improvements of up to 4.08% in Finance and 13.75% in Biomedicine. The same model shows degraded performance when trained on data generated using a template prompt, even when the template includes prior generations and varying In-Context exemplars of real data. Our findings suggest that a few million tokens of diverse synthetic data without mixing any real data, is sufficient for effective domain adaptation when using MetaSynth.
Unraveling and Mitigating Safety Alignment Degradation of Vision-Language Models
Oct 11, 2024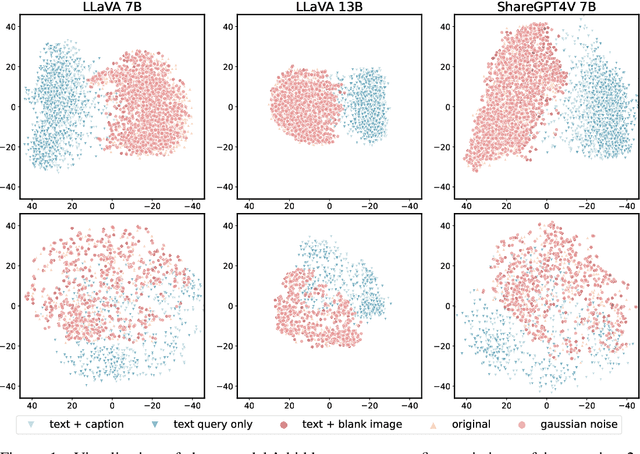
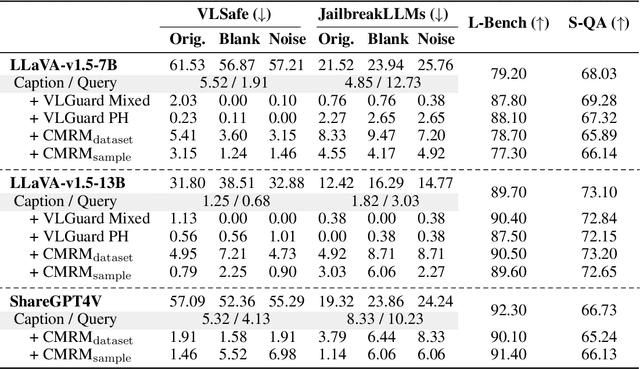
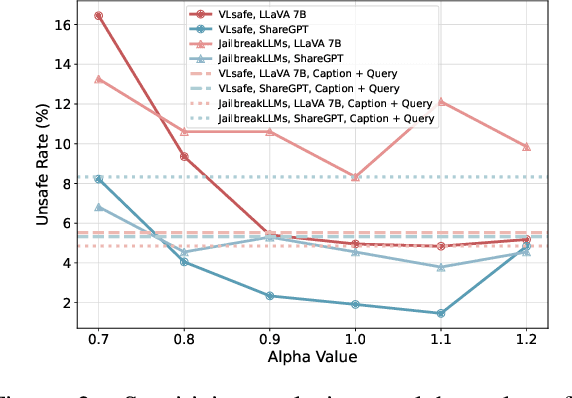
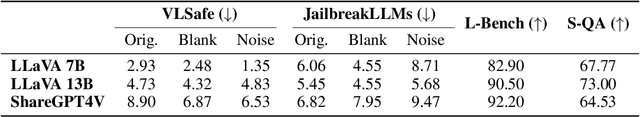
Abstract:The safety alignment ability of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) is prone to be degraded by the integration of the vision module compared to its LLM backbone. We investigate this phenomenon, dubbed as ''safety alignment degradation'' in this paper, and show that the challenge arises from the representation gap that emerges when introducing vision modality to VLMs. In particular, we show that the representations of multi-modal inputs shift away from that of text-only inputs which represent the distribution that the LLM backbone is optimized for. At the same time, the safety alignment capabilities, initially developed within the textual embedding space, do not successfully transfer to this new multi-modal representation space. To reduce safety alignment degradation, we introduce Cross-Modality Representation Manipulation (CMRM), an inference time representation intervention method for recovering the safety alignment ability that is inherent in the LLM backbone of VLMs, while simultaneously preserving the functional capabilities of VLMs. The empirical results show that our framework significantly recovers the alignment ability that is inherited from the LLM backbone with minimal impact on the fluency and linguistic capabilities of pre-trained VLMs even without additional training. Specifically, the unsafe rate of LLaVA-7B on multi-modal input can be reduced from 61.53% to as low as 3.15% with only inference-time intervention. WARNING: This paper contains examples of toxic or harmful language.
Detecting Training Data of Large Language Models via Expectation Maximization
Oct 10, 2024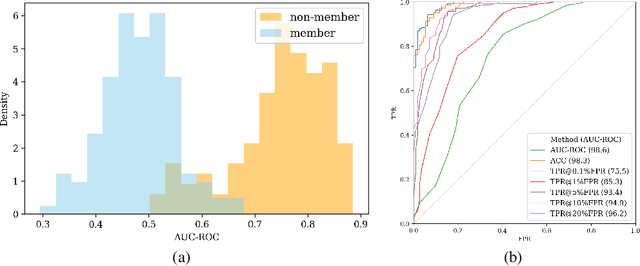
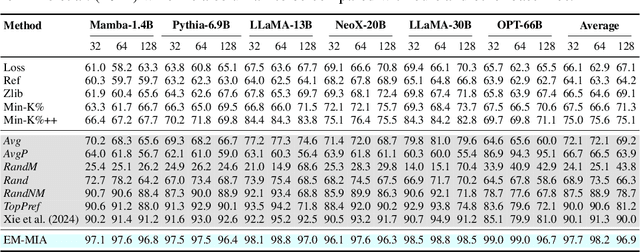

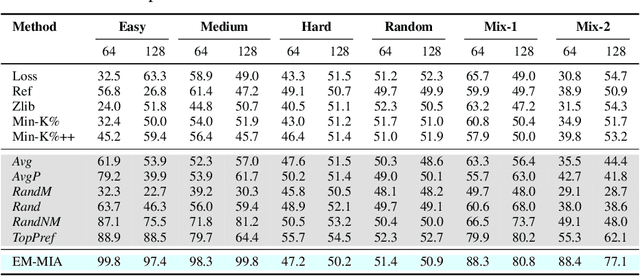
Abstract:The widespread deployment of large language models (LLMs) has led to impressive advancements, yet information about their training data, a critical factor in their performance, remains undisclosed. Membership inference attacks (MIAs) aim to determine whether a specific instance was part of a target model's training data. MIAs can offer insights into LLM outputs and help detect and address concerns such as data contamination and compliance with privacy and copyright standards. However, applying MIAs to LLMs presents unique challenges due to the massive scale of pre-training data and the ambiguous nature of membership. Additionally, creating appropriate benchmarks to evaluate MIA methods is not straightforward, as training and test data distributions are often unknown. In this paper, we introduce EM-MIA, a novel MIA method for LLMs that iteratively refines membership scores and prefix scores via an expectation-maximization algorithm, leveraging the duality that the estimates of these scores can be improved by each other. Membership scores and prefix scores assess how each instance is likely to be a member and discriminative as a prefix, respectively. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results on the WikiMIA dataset. To further evaluate EM-MIA, we present OLMoMIA, a benchmark built from OLMo resources, which allows us to control the difficulty of MIA tasks with varying degrees of overlap between training and test data distributions. We believe that EM-MIA serves as a robust MIA method for LLMs and that OLMoMIA provides a valuable resource for comprehensively evaluating MIA approaches, thereby driving future research in this critical area.
Active Evaluation Acquisition for Efficient LLM Benchmarking
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) become increasingly versatile, numerous large scale benchmarks have been developed to thoroughly assess their capabilities. These benchmarks typically consist of diverse datasets and prompts to evaluate different aspects of LLM performance. However, comprehensive evaluations on hundreds or thousands of prompts incur tremendous costs in terms of computation, money, and time. In this work, we investigate strategies to improve evaluation efficiency by selecting a subset of examples from each benchmark using a learned policy. Our approach models the dependencies across test examples, allowing accurate prediction of the evaluation outcomes for the remaining examples based on the outcomes of the selected ones. Consequently, we only need to acquire the actual evaluation outcomes for the selected subset. We rigorously explore various subset selection policies and introduce a novel RL-based policy that leverages the captured dependencies. Empirical results demonstrate that our approach significantly reduces the number of evaluation prompts required while maintaining accurate performance estimates compared to previous methods.
General Purpose Verification for Chain of Thought Prompting
Apr 30, 2024



Abstract:Many of the recent capabilities demonstrated by Large Language Models (LLMs) arise primarily from their ability to exploit contextual information. In this paper, we explore ways to improve reasoning capabilities of LLMs through (1) exploration of different chains of thought and (2) validation of the individual steps of the reasoning process. We propose three general principles that a model should adhere to while reasoning: (i) Relevance, (ii) Mathematical Accuracy, and (iii) Logical Consistency. We apply these constraints to the reasoning steps generated by the LLM to improve the accuracy of the final generation. The constraints are applied in the form of verifiers: the model itself is asked to verify if the generated steps satisfy each constraint. To further steer the generations towards high-quality solutions, we use the perplexity of the reasoning steps as an additional verifier. We evaluate our method on 4 distinct types of reasoning tasks, spanning a total of 9 different datasets. Experiments show that our method is always better than vanilla generation, and, in 6 out of the 9 datasets, it is better than best-of N sampling which samples N reasoning chains and picks the lowest perplexity generation.
NewsQs: Multi-Source Question Generation for the Inquiring Mind
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:We present NewsQs (news-cues), a dataset that provides question-answer pairs for multiple news documents. To create NewsQs, we augment a traditional multi-document summarization dataset with questions automatically generated by a T5-Large model fine-tuned on FAQ-style news articles from the News On the Web corpus. We show that fine-tuning a model with control codes produces questions that are judged acceptable more often than the same model without them as measured through human evaluation. We use a QNLI model with high correlation with human annotations to filter our data. We release our final dataset of high-quality questions, answers, and document clusters as a resource for future work in query-based multi-document summarization.
Characterizing and Measuring Linguistic Dataset Drift
May 26, 2023


Abstract:NLP models often degrade in performance when real world data distributions differ markedly from training data. However, existing dataset drift metrics in NLP have generally not considered specific dimensions of linguistic drift that affect model performance, and they have not been validated in their ability to predict model performance at the individual example level, where such metrics are often used in practice. In this paper, we propose three dimensions of linguistic dataset drift: vocabulary, structural, and semantic drift. These dimensions correspond to content word frequency divergences, syntactic divergences, and meaning changes not captured by word frequencies (e.g. lexical semantic change). We propose interpretable metrics for all three drift dimensions, and we modify past performance prediction methods to predict model performance at both the example and dataset level for English sentiment classification and natural language inference. We find that our drift metrics are more effective than previous metrics at predicting out-of-domain model accuracies (mean 16.8% root mean square error decrease), particularly when compared to popular fine-tuned embedding distances (mean 47.7% error decrease). Fine-tuned embedding distances are much more effective at ranking individual examples by expected performance, but decomposing into vocabulary, structural, and semantic drift produces the best example rankings of all considered model-agnostic drift metrics (mean 6.7% ROC AUC increase).
Taxonomy Expansion for Named Entity Recognition
May 22, 2023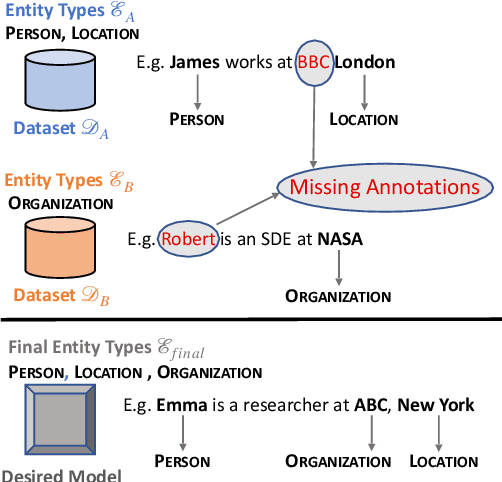
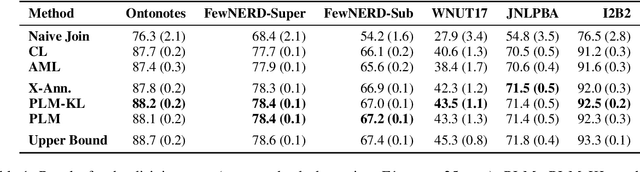
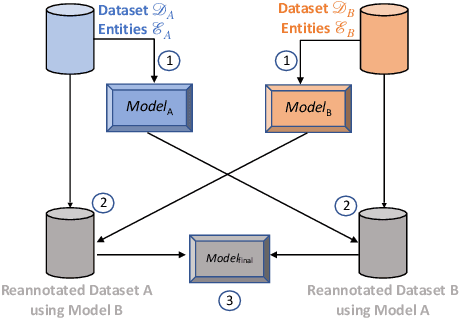
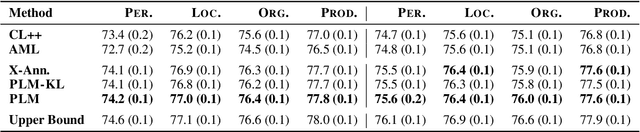
Abstract:Training a Named Entity Recognition (NER) model often involves fixing a taxonomy of entity types. However, requirements evolve and we might need the NER model to recognize additional entity types. A simple approach is to re-annotate entire dataset with both existing and additional entity types and then train the model on the re-annotated dataset. However, this is an extremely laborious task. To remedy this, we propose a novel approach called Partial Label Model (PLM) that uses only partially annotated datasets. We experiment with 6 diverse datasets and show that PLM consistently performs better than most other approaches (0.5 - 2.5 F1), including in novel settings for taxonomy expansion not considered in prior work. The gap between PLM and all other approaches is especially large in settings where there is limited data available for the additional entity types (as much as 11 F1), thus suggesting a more cost effective approaches to taxonomy expansion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge