Smaranda Muresan
LLMs as Science Journalists: Supporting Early-stage Researchers in Communicating Their Science to the Public
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:The scientific community needs tools that help early-stage researchers effectively communicate their findings and innovations to the public. Although existing general-purpose Large Language Models (LLMs) can assist in this endeavor, they are not optimally aligned for it. To address this, we propose a framework for training LLMs to emulate the role of a science journalist that can be used by early-stage researchers to learn how to properly communicate their papers to the general public. We evaluate the usefulness of our trained LLM Journalists in leading conversations with both simulated and human researchers. %compared to the general-purpose ones. Our experiments indicate that LLMs trained using our framework ask more relevant questions that address the societal impact of research, prompting researchers to clarify and elaborate on their findings. In the user study, the majority of participants who interacted with our trained LLM Journalist appreciated it more than interacting with general-purpose LLMs.
Death of the Novel(ty): Beyond n-Gram Novelty as a Metric for Textual Creativity
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:N-gram novelty is widely used to evaluate language models' ability to generate text outside of their training data. More recently, it has also been adopted as a metric for measuring textual creativity. However, theoretical work on creativity suggests that this approach may be inadequate, as it does not account for creativity's dual nature: novelty (how original the text is) and appropriateness (how sensical and pragmatic it is). We investigate the relationship between this notion of creativity and n-gram novelty through 7542 expert writer annotations (n=26) of novelty, pragmaticality, and sensicality via close reading of human and AI-generated text. We find that while n-gram novelty is positively associated with expert writer-judged creativity, ~91% of top-quartile expressions by n-gram novelty are not judged as creative, cautioning against relying on n-gram novelty alone. Furthermore, unlike human-written text, higher n-gram novelty in open-source LLMs correlates with lower pragmaticality. In an exploratory study with frontier close-source models, we additionally confirm that they are less likely to produce creative expressions than humans. Using our dataset, we test whether zero-shot, few-shot, and finetuned models are able to identify creative expressions (a positive aspect of writing) and non-pragmatic ones (a negative aspect). Overall, frontier LLMs exhibit performance much higher than random but leave room for improvement, especially struggling to identify non-pragmatic expressions. We further find that LLM-as-a-Judge novelty scores from the best-performing model were predictive of expert writer preferences.
Forecasting Communication Derailments Through Conversation Generation
Apr 11, 2025
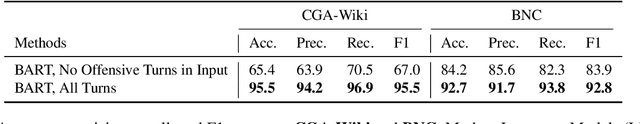
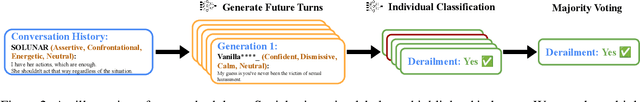
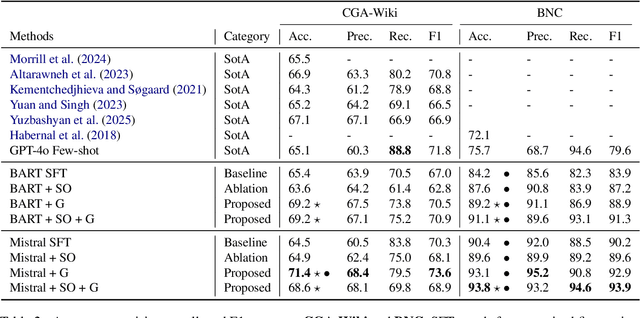
Abstract:Forecasting communication derailment can be useful in real-world settings such as online content moderation, conflict resolution, and business negotiations. However, despite language models' success at identifying offensive speech present in conversations, they struggle to forecast future communication derailments. In contrast to prior work that predicts conversation outcomes solely based on the past conversation history, our approach samples multiple future conversation trajectories conditioned on existing conversation history using a fine-tuned LLM. It predicts the communication outcome based on the consensus of these trajectories. We also experimented with leveraging socio-linguistic attributes, which reflect turn-level conversation dynamics, as guidance when generating future conversations. Our method of future conversation trajectories surpasses state-of-the-art results on English communication derailment prediction benchmarks and demonstrates significant accuracy gains in ablation studies.
Browsing Lost Unformed Recollections: A Benchmark for Tip-of-the-Tongue Search and Reasoning
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:We introduce Browsing Lost Unformed Recollections, a tip-of-the-tongue known-item search and reasoning benchmark for general AI assistants. BLUR introduces a set of 573 real-world validated questions that demand searching and reasoning across multi-modal and multilingual inputs, as well as proficient tool use, in order to excel on. Humans easily ace these questions (scoring on average 98%), while the best-performing system scores around 56%. To facilitate progress toward addressing this challenging and aspirational use case for general AI assistants, we release 350 questions through a public leaderboard, retain the answers to 250 of them, and have the rest as a private test set.
Latent Space Interpretation for Stylistic Analysis and Explainable Authorship Attribution
Sep 11, 2024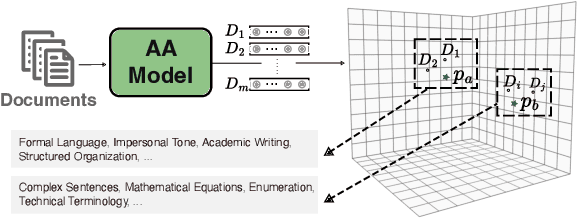
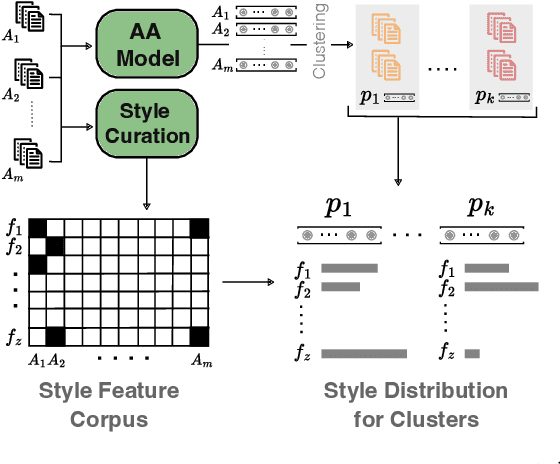

Abstract:Recent state-of-the-art authorship attribution methods learn authorship representations of texts in a latent, non-interpretable space, hindering their usability in real-world applications. Our work proposes a novel approach to interpreting these learned embeddings by identifying representative points in the latent space and utilizing LLMs to generate informative natural language descriptions of the writing style of each point. We evaluate the alignment of our interpretable space with the latent one and find that it achieves the best prediction agreement compared to other baselines. Additionally, we conduct a human evaluation to assess the quality of these style descriptions, validating their utility as explanations for the latent space. Finally, we investigate whether human performance on the challenging AA task improves when aided by our system's explanations, finding an average improvement of around +20% in accuracy.
"Is ChatGPT a Better Explainer than My Professor?": Evaluating the Explanation Capabilities of LLMs in Conversation Compared to a Human Baseline
Jun 26, 2024Abstract:Explanations form the foundation of knowledge sharing and build upon communication principles, social dynamics, and learning theories. We focus specifically on conversational approaches for explanations because the context is highly adaptive and interactive. Our research leverages previous work on explanatory acts, a framework for understanding the different strategies that explainers and explainees employ in a conversation to both explain, understand, and engage with the other party. We use the 5-Levels dataset was constructed from the WIRED YouTube series by Wachsmuth et al., and later annotated by Booshehri et al. with explanatory acts. These annotations provide a framework for understanding how explainers and explainees structure their response when crafting a response. With the rise of generative AI in the past year, we hope to better understand the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and how they can augment expert explainer's capabilities in conversational settings. To achieve this goal, the 5-Levels dataset (We use Booshehri et al.'s 2023 annotated dataset with explanatory acts.) allows us to audit the ability of LLMs in engaging in explanation dialogues. To evaluate the effectiveness of LLMs in generating explainer responses, we compared 3 different strategies, we asked human annotators to evaluate 3 different strategies: human explainer response, GPT4 standard response, GPT4 response with Explanation Moves.
Connecting the Dots: Evaluating Abstract Reasoning Capabilities of LLMs Using the New York Times Connections Word Game
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:The New York Times Connections game has emerged as a popular and challenging pursuit for word puzzle enthusiasts. We collect 200 Connections games to evaluate the performance of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) against expert and novice human players. Our results show that even the best-performing LLM, GPT-4o, which has otherwise shown impressive reasoning abilities on a wide variety of benchmarks, can only fully solve 8% of the games. Compared to GPT-4o, novice and expert players perform better, with expert human players significantly outperforming GPT-4o. To deepen our understanding we create a taxonomy of the knowledge types required to successfully categorize words in the Connections game, revealing that LLMs struggle with associative, encyclopedic, and linguistic knowledge. Our findings establish the New York Times Connections game as a challenging benchmark for evaluating abstract reasoning capabilities in humans and AI systems.
V-FLUTE: Visual Figurative Language Understanding with Textual Explanations
May 02, 2024Abstract:Large Vision-Language models (VLMs) have demonstrated strong reasoning capabilities in tasks requiring a fine-grained understanding of literal images and text, such as visual question-answering or visual entailment. However, there has been little exploration of these models' capabilities when presented with images and captions containing figurative phenomena such as metaphors or humor, the meaning of which is often implicit. To close this gap, we propose a new task and a high-quality dataset: Visual Figurative Language Understanding with Textual Explanations (V-FLUTE). We frame the visual figurative language understanding problem as an explainable visual entailment task, where the model has to predict whether the image (premise) entails a claim (hypothesis) and justify the predicted label with a textual explanation. Using a human-AI collaboration framework, we build a high-quality dataset, V-FLUTE, that contains 6,027 <image, claim, label, explanation> instances spanning five diverse multimodal figurative phenomena: metaphors, similes, idioms, sarcasm, and humor. The figurative phenomena can be present either in the image, the caption, or both. We further conduct both automatic and human evaluations to assess current VLMs' capabilities in understanding figurative phenomena.
Navigating the Landscape of Hint Generation Research: From the Past to the Future
Apr 06, 2024Abstract:Digital education has gained popularity in the last decade, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. With the improving capabilities of large language models to reason and communicate with users, envisioning intelligent tutoring systems (ITSs) that can facilitate self-learning is not very far-fetched. One integral component to fulfill this vision is the ability to give accurate and effective feedback via hints to scaffold the learning process. In this survey article, we present a comprehensive review of prior research on hint generation, aiming to bridge the gap between research in education and cognitive science, and research in AI and Natural Language Processing. Informed by our findings, we propose a formal definition of the hint generation task, and discuss the roadmap of building an effective hint generation system aligned with the formal definition, including open challenges, future directions and ethical considerations.
Large Language Models are Few-Shot Training Example Generators: A Case Study in Fallacy Recognition
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:Recognizing fallacies is crucial for ensuring the quality and validity of arguments across various domains. However, computational fallacy recognition faces challenges due to the diverse genres, domains, and types of fallacies found in datasets. This leads to a highly multiclass, and even multi-label, setup with substantial class imbalance. In this study, we aim to enhance existing models for fallacy recognition by incorporating additional context and by leveraging large language models to generate synthetic data, thus increasing the representation of the infrequent classes. We experiment with GPT3.5 to generate synthetic examples and we examine the impact of prompt settings for this. Moreover, we explore zero-shot and few-shot scenarios to evaluate the effectiveness of using the generated examples for training smaller models within a unified fallacy recognition framework. Furthermore, we analyze the overlap between the synthetic data and existing fallacy datasets. Finally, we investigate the usefulness of providing supplementary context for detecting fallacy types that need such context, e.g., diversion fallacies. Our evaluation results demonstrate consistent improvements across fallacy types, datasets, and generators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge