Kanishk Singh
TinyStyler: Efficient Few-Shot Text Style Transfer with Authorship Embeddings
Jun 21, 2024
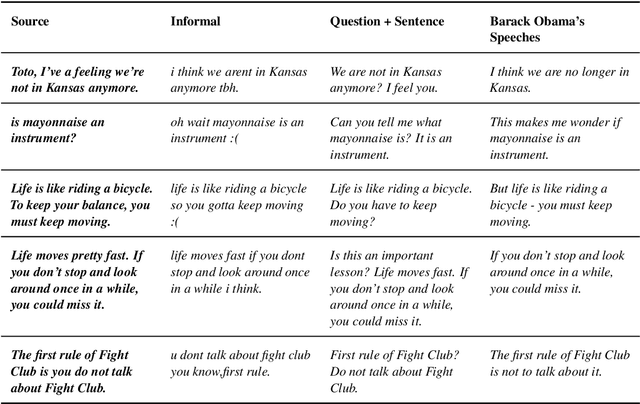
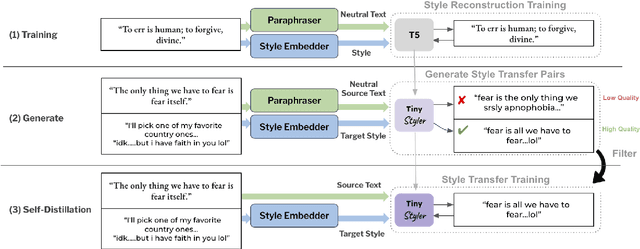
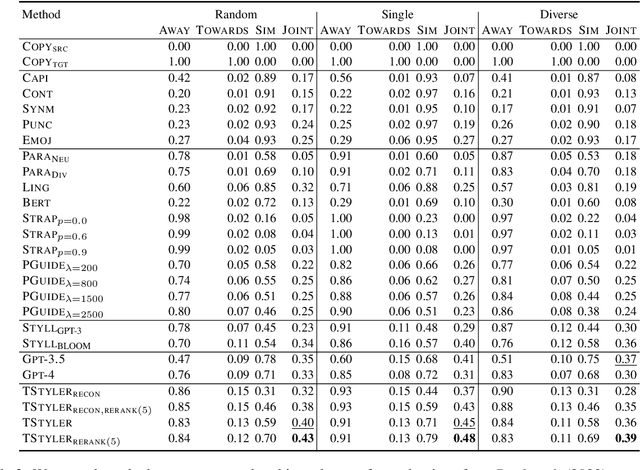
Abstract:The goal of text style transfer is to transform the style of texts while preserving their original meaning, often with only a few examples of the target style. Existing style transfer methods generally rely on the few-shot capabilities of large language models or on complex controllable text generation approaches that are inefficient and underperform on fluency metrics. We introduce TinyStyler, a lightweight but effective approach, which leverages a small language model (800M params) and pre-trained authorship embeddings to perform efficient, few-shot text style transfer. We evaluate on the challenging task of authorship style transfer and find TinyStyler outperforms strong approaches such as GPT-4. We also evaluate TinyStyler's ability to perform text attribute style transfer (formal $\leftrightarrow$ informal) with automatic and human evaluations and find that the approach outperforms recent controllable text generation methods. Our model has been made publicly available at https://huggingface.co/tinystyler/tinystyler .
Learning to Follow Object-Centric Image Editing Instructions Faithfully
Oct 29, 2023Abstract:Natural language instructions are a powerful interface for editing the outputs of text-to-image diffusion models. However, several challenges need to be addressed: 1) underspecification (the need to model the implicit meaning of instructions) 2) grounding (the need to localize where the edit has to be performed), 3) faithfulness (the need to preserve the elements of the image not affected by the edit instruction). Current approaches focusing on image editing with natural language instructions rely on automatically generated paired data, which, as shown in our investigation, is noisy and sometimes nonsensical, exacerbating the above issues. Building on recent advances in segmentation, Chain-of-Thought prompting, and visual question answering, we significantly improve the quality of the paired data. In addition, we enhance the supervision signal by highlighting parts of the image that need to be changed by the instruction. The model fine-tuned on the improved data is capable of performing fine-grained object-centric edits better than state-of-the-art baselines, mitigating the problems outlined above, as shown by automatic and human evaluations. Moreover, our model is capable of generalizing to domains unseen during training, such as visual metaphors.
CounterGeDi: A controllable approach to generate polite, detoxified and emotional counterspeech
May 09, 2022
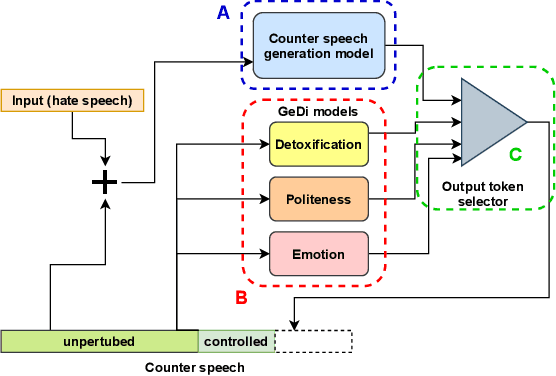
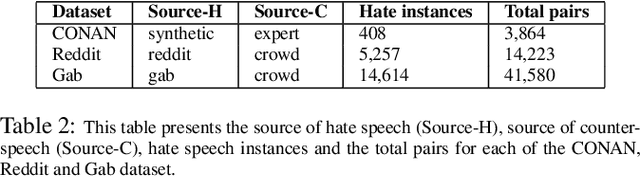

Abstract:Recently, many studies have tried to create generation models to assist counter speakers by providing counterspeech suggestions for combating the explosive proliferation of online hate. However, since these suggestions are from a vanilla generation model, they might not include the appropriate properties required to counter a particular hate speech instance. In this paper, we propose CounterGeDi - an ensemble of generative discriminators (GeDi) to guide the generation of a DialoGPT model toward more polite, detoxified, and emotionally laden counterspeech. We generate counterspeech using three datasets and observe significant improvement across different attribute scores. The politeness and detoxification scores increased by around 15% and 6% respectively, while the emotion in the counterspeech increased by at least 10% across all the datasets. We also experiment with triple-attribute control and observe significant improvement over single attribute results when combining complementing attributes, e.g., politeness, joyfulness and detoxification. In all these experiments, the relevancy of the generated text does not deteriorate due to the application of these controls
Team Phoenix at WASSA 2021: Emotion Analysis on News Stories with Pre-Trained Language Models
Mar 10, 2021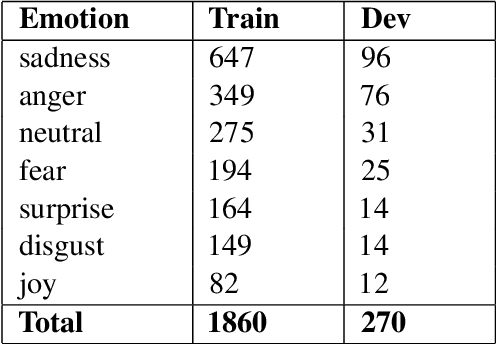
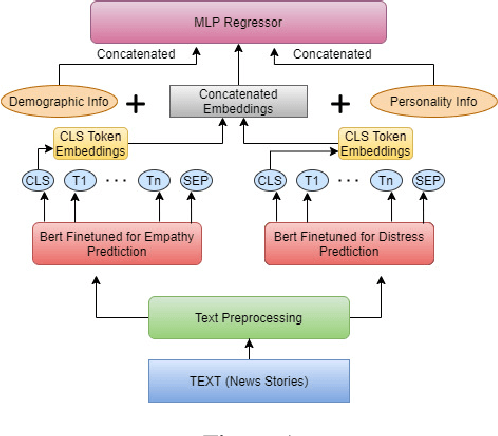
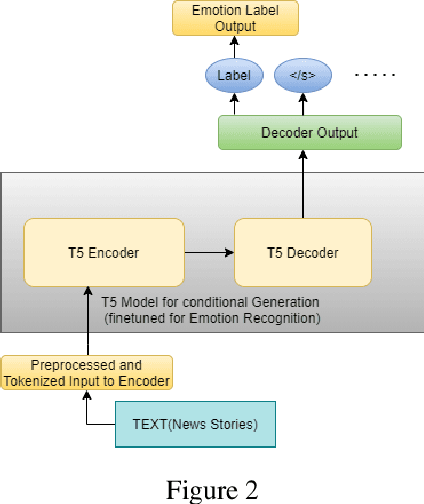
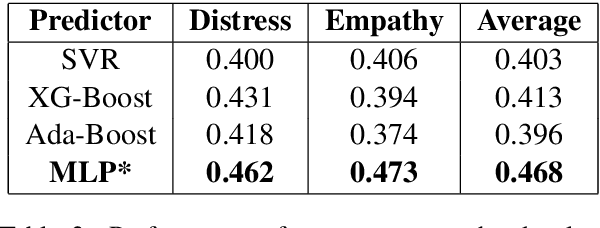
Abstract:Emotion is fundamental to humanity. The ability to perceive, understand and respond to social interactions in a human-like manner is one of the most desired capabilities in artificial agents, particularly in social-media bots. Over the past few years, computational understanding and detection of emotional aspects in language have been vital in advancing human-computer interaction. The WASSA Shared Task 2021 released a dataset of news-stories across two tracks, Track-1 for Empathy and Distress Prediction and Track-2 for Multi-Dimension Emotion prediction at the essay-level. We describe our system entry for the WASSA 2021 Shared Task (for both Track-1 and Track-2), where we leveraged the information from Pre-trained language models for Track-specific Tasks. Our proposed models achieved an Average Pearson Score of 0.417 and a Macro-F1 Score of 0.502 in Track 1 and Track 2, respectively. In the Shared Task leaderboard, we secured 4th rank in Track 1 and 2nd rank in Track 2.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge