Binny Mathew
A Community-Centric Perspective for Characterizing and Detecting Anti-Asian Violence-Provoking Speech
Jul 21, 2024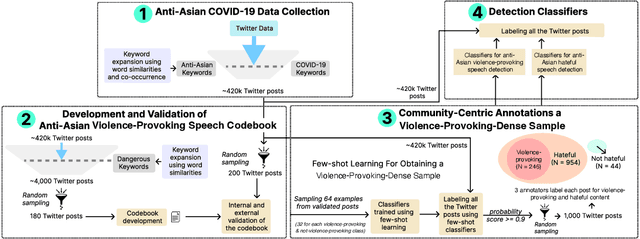

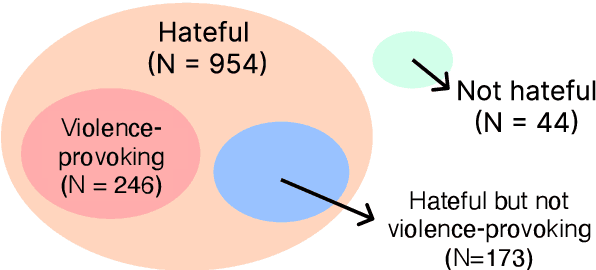

Abstract:Violence-provoking speech -- speech that implicitly or explicitly promotes violence against the members of the targeted community, contributed to a massive surge in anti-Asian crimes during the pandemic. While previous works have characterized and built tools for detecting other forms of harmful speech, like fear speech and hate speech, our work takes a community-centric approach to studying anti-Asian violence-provoking speech. Using data from ~420k Twitter posts spanning a 3-year duration (January 1, 2020 to February 1, 2023), we develop a codebook to characterize anti-Asian violence-provoking speech and collect a community-crowdsourced dataset to facilitate its large-scale detection using state-of-the-art classifiers. We contrast the capabilities of natural language processing classifiers, ranging from BERT-based to LLM-based classifiers, in detecting violence-provoking speech with their capabilities to detect anti-Asian hateful speech. In contrast to prior work that has demonstrated the effectiveness of such classifiers in detecting hateful speech ($F_1 = 0.89$), our work shows that accurate and reliable detection of violence-provoking speech is a challenging task ($F_1 = 0.69$). We discuss the implications of our findings, particularly the need for proactive interventions to support Asian communities during public health crises. The resources related to the study are available at https://claws-lab.github.io/violence-provoking-speech/.
InfFeed: Influence Functions as a Feedback to Improve the Performance of Subjective Tasks
Mar 09, 2024Abstract:Recently, influence functions present an apparatus for achieving explainability for deep neural models by quantifying the perturbation of individual train instances that might impact a test prediction. Our objectives in this paper are twofold. First we incorporate influence functions as a feedback into the model to improve its performance. Second, in a dataset extension exercise, using influence functions to automatically identify data points that have been initially `silver' annotated by some existing method and need to be cross-checked (and corrected) by annotators to improve the model performance. To meet these objectives, in this paper, we introduce InfFeed, which uses influence functions to compute the influential instances for a target instance. Toward the first objective, we adjust the label of the target instance based on its influencer(s) label. In doing this, InfFeed outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines (including LLMs) by a maximum macro F1-score margin of almost 4% for hate speech classification, 3.5% for stance classification, and 3% for irony and 2% for sarcasm detection. Toward the second objective we show that manually re-annotating only those silver annotated data points in the extension set that have a negative influence can immensely improve the model performance bringing it very close to the scenario where all the data points in the extension set have gold labels. This allows for huge reduction of the number of data points that need to be manually annotated since out of the silver annotated extension dataset, the influence function scheme picks up ~1/1000 points that need manual correction.
HateMM: A Multi-Modal Dataset for Hate Video Classification
May 06, 2023



Abstract:Hate speech has become one of the most significant issues in modern society, having implications in both the online and the offline world. Due to this, hate speech research has recently gained a lot of traction. However, most of the work has primarily focused on text media with relatively little work on images and even lesser on videos. Thus, early stage automated video moderation techniques are needed to handle the videos that are being uploaded to keep the platform safe and healthy. With a view to detect and remove hateful content from the video sharing platforms, our work focuses on hate video detection using multi-modalities. To this end, we curate ~43 hours of videos from BitChute and manually annotate them as hate or non-hate, along with the frame spans which could explain the labelling decision. To collect the relevant videos we harnessed search keywords from hate lexicons. We observe various cues in images and audio of hateful videos. Further, we build deep learning multi-modal models to classify the hate videos and observe that using all the modalities of the videos improves the overall hate speech detection performance (accuracy=0.798, macro F1-score=0.790) by ~5.7% compared to the best uni-modal model in terms of macro F1 score. In summary, our work takes the first step toward understanding and modeling hateful videos on video hosting platforms such as BitChute.
On the rise of fear speech in online social media
Mar 18, 2023



Abstract:Recently, social media platforms are heavily moderated to prevent the spread of online hate speech, which is usually fertile in toxic words and is directed toward an individual or a community. Owing to such heavy moderation, newer and more subtle techniques are being deployed. One of the most striking among these is fear speech. Fear speech, as the name suggests, attempts to incite fear about a target community. Although subtle, it might be highly effective, often pushing communities toward a physical conflict. Therefore, understanding their prevalence in social media is of paramount importance. This article presents a large-scale study to understand the prevalence of 400K fear speech and over 700K hate speech posts collected from Gab.com. Remarkably, users posting a large number of fear speech accrue more followers and occupy more central positions in social networks than users posting a large number of hate speech. They can also reach out to benign users more effectively than hate speech users through replies, reposts, and mentions. This connects to the fact that, unlike hate speech, fear speech has almost zero toxic content, making it look plausible. Moreover, while fear speech topics mostly portray a community as a perpetrator using a (fake) chain of argumentation, hate speech topics hurl direct multitarget insults, thus pointing to why general users could be more gullible to fear speech. Our findings transcend even to other platforms (Twitter and Facebook) and thus necessitate using sophisticated moderation policies and mass awareness to combat fear speech.
HateProof: Are Hateful Meme Detection Systems really Robust?
Feb 11, 2023Abstract:Exploiting social media to spread hate has tremendously increased over the years. Lately, multi-modal hateful content such as memes has drawn relatively more traction than uni-modal content. Moreover, the availability of implicit content payloads makes them fairly challenging to be detected by existing hateful meme detection systems. In this paper, we present a use case study to analyze such systems' vulnerabilities against external adversarial attacks. We find that even very simple perturbations in uni-modal and multi-modal settings performed by humans with little knowledge about the model can make the existing detection models highly vulnerable. Empirically, we find a noticeable performance drop of as high as 10% in the macro-F1 score for certain attacks. As a remedy, we attempt to boost the model's robustness using contrastive learning as well as an adversarial training-based method - VILLA. Using an ensemble of the above two approaches, in two of our high resolution datasets, we are able to (re)gain back the performance to a large extent for certain attacks. We believe that ours is a first step toward addressing this crucial problem in an adversarial setting and would inspire more such investigations in the future.
RAFT: Rationale adaptor for few-shot abusive language detection
Nov 30, 2022

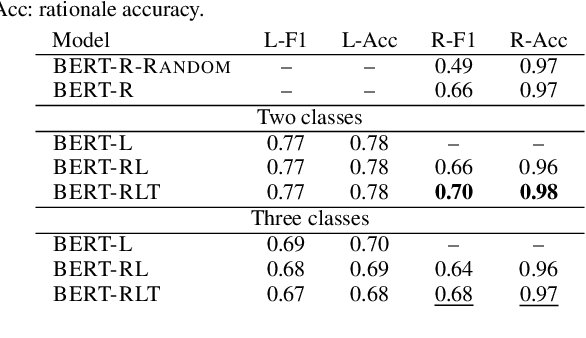

Abstract:Abusive language is a concerning problem in online social media. Past research on detecting abusive language covers different platforms, languages, demographies, etc. However, models trained using these datasets do not perform well in cross-domain evaluation settings. To overcome this, a common strategy is to use a few samples from the target domain to train models to get better performance in that domain (cross-domain few-shot training). However, this might cause the models to overfit the artefacts of those samples. A compelling solution could be to guide the models toward rationales, i.e., spans of text that justify the text's label. This method has been found to improve model performance in the in-domain setting across various NLP tasks. In this paper, we propose RAFT (Rationale Adaptor for Few-shoT classification) for abusive language detection. We first build a multitask learning setup to jointly learn rationales, targets, and labels, and find a significant improvement of 6% macro F1 on the rationale detection task over training solely rationale classifiers. We introduce two rationale-integrated BERT-based architectures (the RAFT models) and evaluate our systems over five different abusive language datasets, finding that in the few-shot classification setting, RAFT-based models outperform baseline models by about 7% in macro F1 scores and perform competitively to models finetuned on other source domains. Furthermore, RAFT-based models outperform LIME/SHAP-based approaches in terms of plausibility and are close in performance in terms of faithfulness.
CounterGeDi: A controllable approach to generate polite, detoxified and emotional counterspeech
May 09, 2022
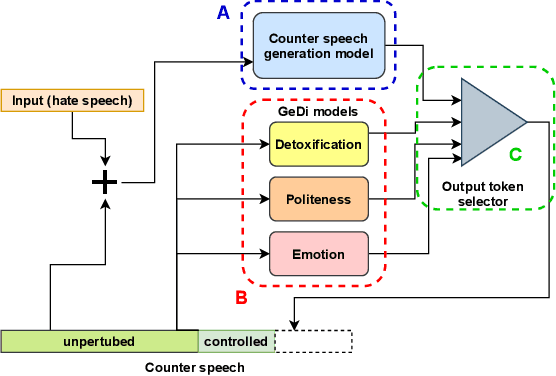

Abstract:Recently, many studies have tried to create generation models to assist counter speakers by providing counterspeech suggestions for combating the explosive proliferation of online hate. However, since these suggestions are from a vanilla generation model, they might not include the appropriate properties required to counter a particular hate speech instance. In this paper, we propose CounterGeDi - an ensemble of generative discriminators (GeDi) to guide the generation of a DialoGPT model toward more polite, detoxified, and emotionally laden counterspeech. We generate counterspeech using three datasets and observe significant improvement across different attribute scores. The politeness and detoxification scores increased by around 15% and 6% respectively, while the emotion in the counterspeech increased by at least 10% across all the datasets. We also experiment with triple-attribute control and observe significant improvement over single attribute results when combining complementing attributes, e.g., politeness, joyfulness and detoxification. In all these experiments, the relevancy of the generated text does not deteriorate due to the application of these controls
HateCheckHIn: Evaluating Hindi Hate Speech Detection Models
Apr 30, 2022



Abstract:Due to the sheer volume of online hate, the AI and NLP communities have started building models to detect such hateful content. Recently, multilingual hate is a major emerging challenge for automated detection where code-mixing or more than one language have been used for conversation in social media. Typically, hate speech detection models are evaluated by measuring their performance on the held-out test data using metrics such as accuracy and F1-score. While these metrics are useful, it becomes difficult to identify using them where the model is failing, and how to resolve it. To enable more targeted diagnostic insights of such multilingual hate speech models, we introduce a set of functionalities for the purpose of evaluation. We have been inspired to design this kind of functionalities based on real-world conversation on social media. Considering Hindi as a base language, we craft test cases for each functionality. We name our evaluation dataset HateCheckHIn. To illustrate the utility of these functionalities , we test state-of-the-art transformer based m-BERT model and the Perspective API.
You too Brutus! Trapping Hateful Users in Social Media: Challenges, Solutions & Insights
Aug 01, 2021



Abstract:Hate speech is regarded as one of the crucial issues plaguing the online social media. The current literature on hate speech detection leverages primarily the textual content to find hateful posts and subsequently identify hateful users. However, this methodology disregards the social connections between users. In this paper, we run a detailed exploration of the problem space and investigate an array of models ranging from purely textual to graph based to finally semi-supervised techniques using Graph Neural Networks (GNN) that utilize both textual and graph-based features. We run exhaustive experiments on two datasets -- Gab, which is loosely moderated and Twitter, which is strictly moderated. Overall the AGNN model achieves 0.791 macro F1-score on the Gab dataset and 0.780 macro F1-score on the Twitter dataset using only 5% of the labeled instances, considerably outperforming all the other models including the fully supervised ones. We perform detailed error analysis on the best performing text and graph based models and observe that hateful users have unique network neighborhood signatures and the AGNN model benefits by paying attention to these signatures. This property, as we observe, also allows the model to generalize well across platforms in a zero-shot setting. Lastly, we utilize the best performing GNN model to analyze the evolution of hateful users and their targets over time in Gab.
"Short is the Road that Leads from Fear to Hate": Fear Speech in Indian WhatsApp Groups
Feb 07, 2021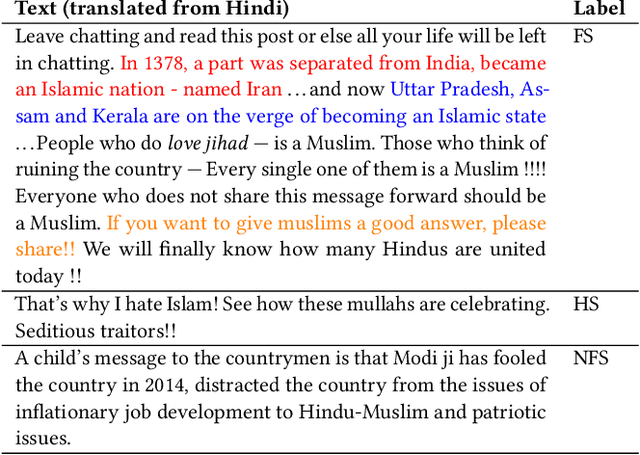
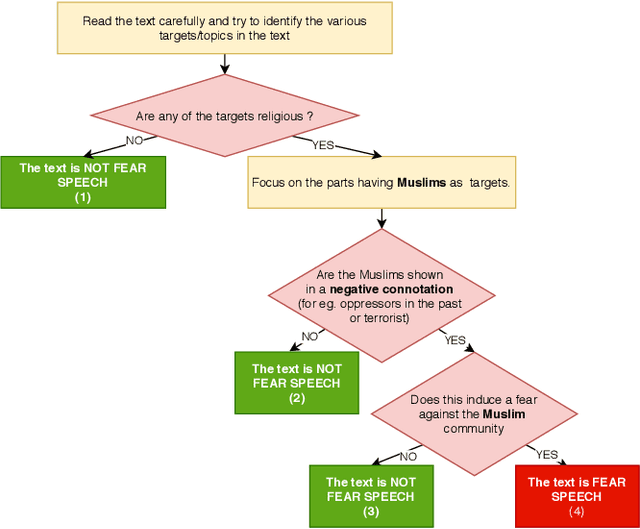
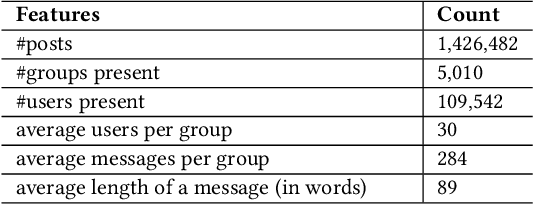
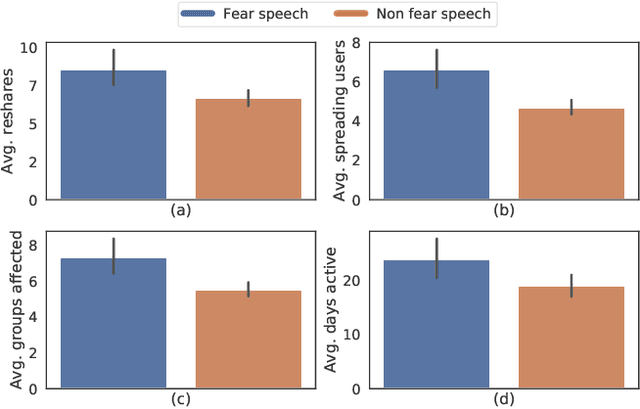
Abstract:WhatsApp is the most popular messaging app in the world. Due to its popularity, WhatsApp has become a powerful and cheap tool for political campaigning being widely used during the 2019 Indian general election, where it was used to connect to the voters on a large scale. Along with the campaigning, there have been reports that WhatsApp has also become a breeding ground for harmful speech against various protected groups and religious minorities. Many such messages attempt to instil fear among the population about a specific (minority) community. According to research on inter-group conflict, such `fear speech' messages could have a lasting impact and might lead to real offline violence. In this paper, we perform the first large scale study on fear speech across thousands of public WhatsApp groups discussing politics in India. We curate a new dataset and try to characterize fear speech from this dataset. We observe that users writing fear speech messages use various events and symbols to create the illusion of fear among the reader about a target community. We build models to classify fear speech and observe that current state-of-the-art NLP models do not perform well at this task. Fear speech messages tend to spread faster and could potentially go undetected by classifiers built to detect traditional toxic speech due to their low toxic nature. Finally, using a novel methodology to target users with Facebook ads, we conduct a survey among the users of these WhatsApp groups to understand the types of users who consume and share fear speech. We believe that this work opens up new research questions that are very different from tackling hate speech which the research community has been traditionally involved in.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge