Sky CH-Wang
Fine-Tuning LLMs with Fine-Grained Human Feedback on Text Spans
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:We present a method and dataset for fine-tuning language models with preference supervision using feedback-driven improvement chains. Given a model response, an annotator provides fine-grained feedback by marking ``liked'' and ``disliked'' spans and specifying what they liked or disliked about them. The base model then rewrites the disliked spans accordingly, proceeding from left to right, forming a sequence of incremental improvements. We construct preference pairs for direct alignment from each adjacent step in the chain, enabling the model to learn from localized, targeted edits. We find that our approach outperforms direct alignment methods based on standard A/B preference ranking or full contrastive rewrites, demonstrating that structured, revision-based supervision leads to more efficient and effective preference tuning.
Browsing Lost Unformed Recollections: A Benchmark for Tip-of-the-Tongue Search and Reasoning
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:We introduce Browsing Lost Unformed Recollections, a tip-of-the-tongue known-item search and reasoning benchmark for general AI assistants. BLUR introduces a set of 573 real-world validated questions that demand searching and reasoning across multi-modal and multilingual inputs, as well as proficient tool use, in order to excel on. Humans easily ace these questions (scoring on average 98%), while the best-performing system scores around 56%. To facilitate progress toward addressing this challenging and aspirational use case for general AI assistants, we release 350 questions through a public leaderboard, retain the answers to 250 of them, and have the rest as a private test set.
GLIDER: Grading LLM Interactions and Decisions using Explainable Ranking
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:The LLM-as-judge paradigm is increasingly being adopted for automated evaluation of model outputs. While LLM judges have shown promise on constrained evaluation tasks, closed source LLMs display critical shortcomings when deployed in real world applications due to challenges of fine grained metrics and explainability, while task specific evaluation models lack cross-domain generalization. We introduce GLIDER, a powerful 3B evaluator LLM that can score any text input and associated context on arbitrary user defined criteria. GLIDER shows higher Pearson's correlation than GPT-4o on FLASK and greatly outperforms prior evaluation models, achieving comparable performance to LLMs 17x its size. GLIDER supports fine-grained scoring, multilingual reasoning, span highlighting and was trained on 685 domains and 183 criteria. Extensive qualitative analysis shows that GLIDER scores are highly correlated with human judgments, with 91.3% human agreement. We have open-sourced GLIDER to facilitate future research.
Do Androids Know They're Only Dreaming of Electric Sheep?
Dec 28, 2023Abstract:We design probes trained on the internal representations of a transformer language model that are predictive of its hallucinatory behavior on in-context generation tasks. To facilitate this detection, we create a span-annotated dataset of organic and synthetic hallucinations over several tasks. We find that probes trained on the force-decoded states of synthetic hallucinations are generally ecologically invalid in organic hallucination detection. Furthermore, hidden state information about hallucination appears to be task and distribution-dependent. Intrinsic and extrinsic hallucination saliency varies across layers, hidden state types, and tasks; notably, extrinsic hallucinations tend to be more salient in a transformer's internal representations. Outperforming multiple contemporary baselines, we show that probing is a feasible and efficient alternative to language model hallucination evaluation when model states are available.
NormDial: A Comparable Bilingual Synthetic Dialog Dataset for Modeling Social Norm Adherence and Violation
Oct 25, 2023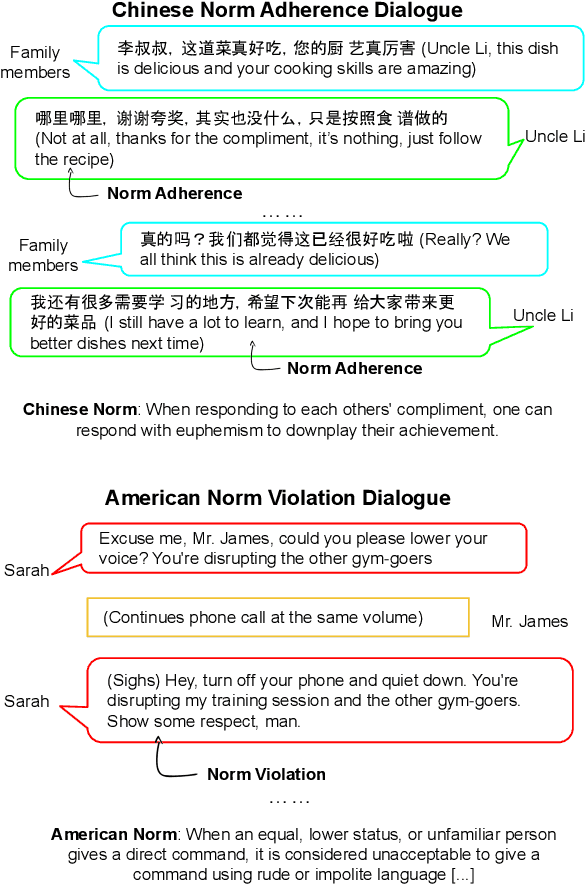

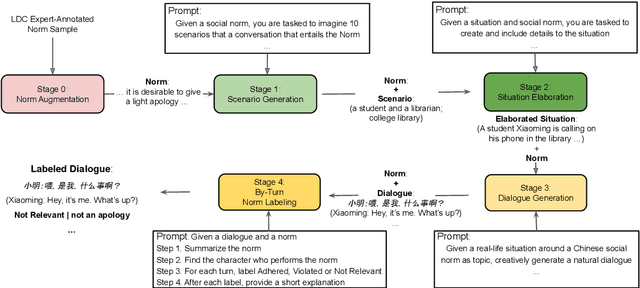
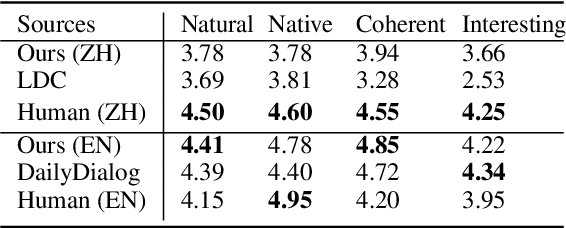
Abstract:Social norms fundamentally shape interpersonal communication. We present NormDial, a high-quality dyadic dialogue dataset with turn-by-turn annotations of social norm adherences and violations for Chinese and American cultures. Introducing the task of social norm observance detection, our dataset is synthetically generated in both Chinese and English using a human-in-the-loop pipeline by prompting large language models with a small collection of expert-annotated social norms. We show that our generated dialogues are of high quality through human evaluation and further evaluate the performance of existing large language models on this task. Our findings point towards new directions for understanding the nuances of social norms as they manifest in conversational contexts that span across languages and cultures.
Toward a Critical Toponymy Framework for Named Entity Recognition: A Case Study of Airbnb in New York City
Oct 23, 2023



Abstract:Critical toponymy examines the dynamics of power, capital, and resistance through place names and the sites to which they refer. Studies here have traditionally focused on the semantic content of toponyms and the top-down institutional processes that produce them. However, they have generally ignored the ways in which toponyms are used by ordinary people in everyday discourse, as well as the other strategies of geospatial description that accompany and contextualize toponymic reference. Here, we develop computational methods to measure how cultural and economic capital shape the ways in which people refer to places, through a novel annotated dataset of 47,440 New York City Airbnb listings from the 2010s. Building on this dataset, we introduce a new named entity recognition (NER) model able to identify important discourse categories integral to the characterization of place. Our findings point toward new directions for critical toponymy and to a range of previously understudied linguistic signals relevant to research on neighborhood status, housing and tourism markets, and gentrification.
Sociocultural Norm Similarities and Differences via Situational Alignment and Explainable Textual Entailment
May 23, 2023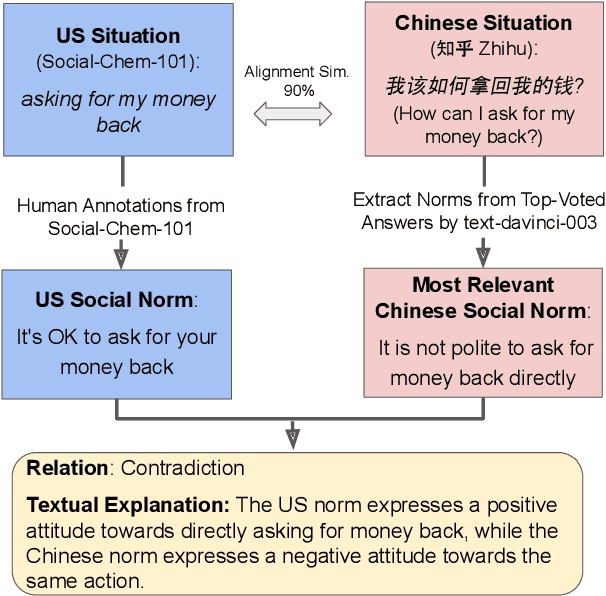

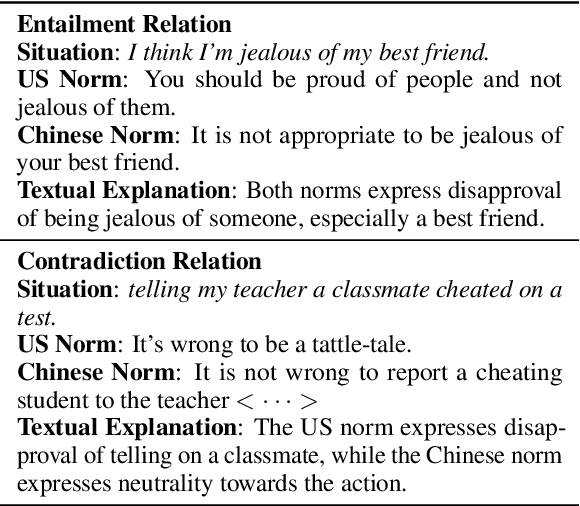
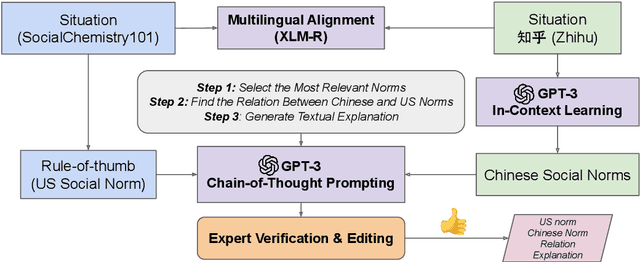
Abstract:Designing systems that can reason across cultures requires that they are grounded in the norms of the contexts in which they operate. However, current research on developing computational models of social norms has primarily focused on American society. Here, we propose a novel approach to discover and compare descriptive social norms across Chinese and American cultures. We demonstrate our approach by leveraging discussions on a Chinese Q&A platform-Zhihu-and the existing SocialChemistry dataset as proxies for contrasting cultural axes, align social situations cross-culturally, and extract social norms from texts using in-context learning. Embedding Chain-of-Thought prompting in a human-AI collaborative framework, we build a high-quality dataset of 3,069 social norms aligned with social situations across Chinese and American cultures alongside corresponding free-text explanations. To test the ability of models to reason about social norms across cultures, we introduce the task of explainable social norm entailment, showing that existing models under 3B parameters have significant room for improvement in both automatic and human evaluation. Further analysis of cross-cultural norm differences based on our dataset shows empirical alignment with the social orientations framework, revealing several situational and descriptive nuances in norms across these cultures.
Affective Idiosyncratic Responses to Music
Oct 17, 2022



Abstract:Affective responses to music are highly personal. Despite consensus that idiosyncratic factors play a key role in regulating how listeners emotionally respond to music, precisely measuring the marginal effects of these variables has proved challenging. To address this gap, we develop computational methods to measure affective responses to music from over 403M listener comments on a Chinese social music platform. Building on studies from music psychology in systematic and quasi-causal analyses, we test for musical, lyrical, contextual, demographic, and mental health effects that drive listener affective responses. Finally, motivated by the social phenomenon known as w\v{a}ng-y\`i-y\'un, we identify influencing factors of platform user self-disclosures, the social support they receive, and notable differences in discloser user activity.
Using Sociolinguistic Variables to Reveal Changing Attitudes Towards Sexuality and Gender
Sep 22, 2021



Abstract:Individuals signal aspects of their identity and beliefs through linguistic choices. Studying these choices in aggregate allows us to examine large-scale attitude shifts within a population. Here, we develop computational methods to study word choice within a sociolinguistic lexical variable -- alternate words used to express the same concept -- in order to test for change in the United States towards sexuality and gender. We examine two variables: i) referents to significant others, such as the word "partner" and ii) referents to an indefinite person, both of which could optionally be marked with gender. The linguistic choices in each variable allow us to study increased rates of acceptances of gay marriage and gender equality, respectively. In longitudinal analyses across Twitter and Reddit over 87M messages, we demonstrate that attitudes are changing but that these changes are driven by specific demographics within the United States. Further, in a quasi-causal analysis, we show that passages of Marriage Equality Acts in different states are drivers of linguistic change.
MindCraft: Theory of Mind Modeling for Situated Dialogue in Collaborative Tasks
Sep 13, 2021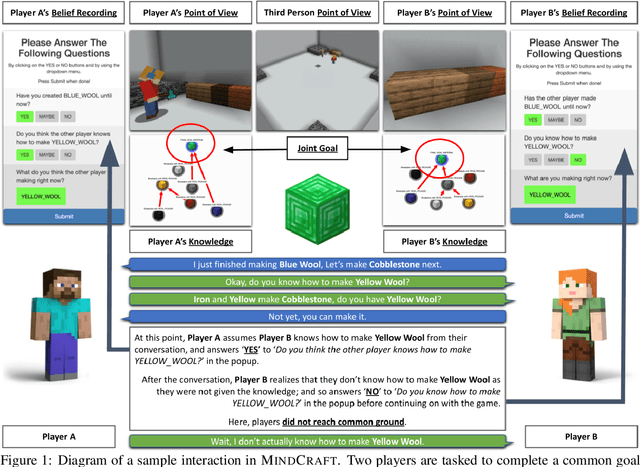
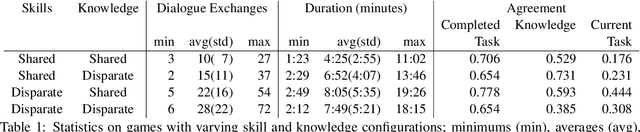
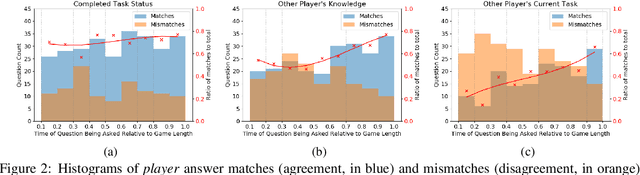
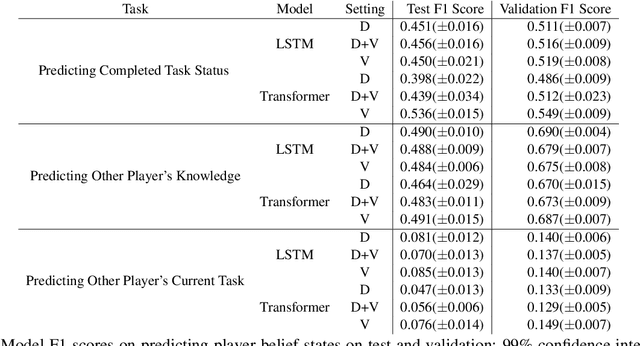
Abstract:An ideal integration of autonomous agents in a human world implies that they are able to collaborate on human terms. In particular, theory of mind plays an important role in maintaining common ground during human collaboration and communication. To enable theory of mind modeling in situated interactions, we introduce a fine-grained dataset of collaborative tasks performed by pairs of human subjects in the 3D virtual blocks world of Minecraft. It provides information that captures partners' beliefs of the world and of each other as an interaction unfolds, bringing abundant opportunities to study human collaborative behaviors in situated language communication. As a first step towards our goal of developing embodied AI agents able to infer belief states of collaborative partners in situ, we build and present results on computational models for several theory of mind tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge