MindCraft: Theory of Mind Modeling for Situated Dialogue in Collaborative Tasks
Paper and Code
Sep 13, 2021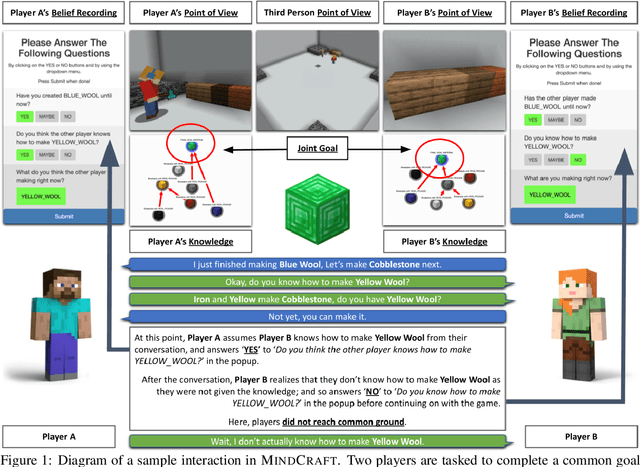
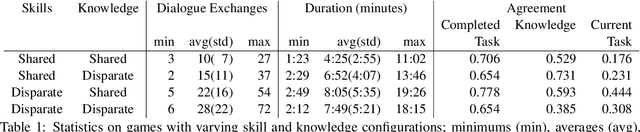
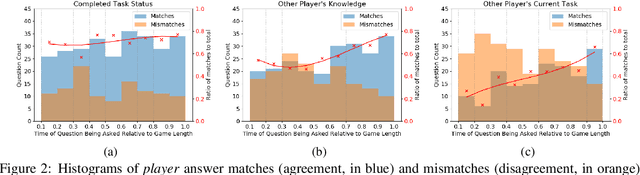
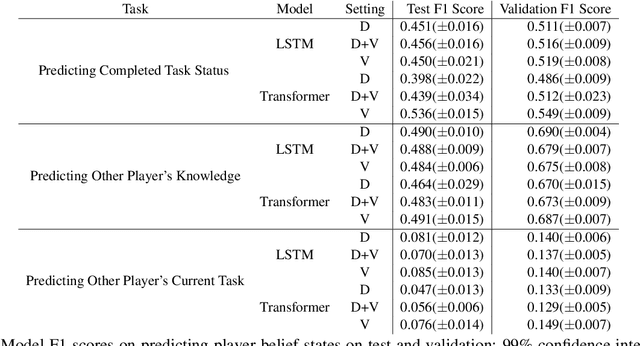
An ideal integration of autonomous agents in a human world implies that they are able to collaborate on human terms. In particular, theory of mind plays an important role in maintaining common ground during human collaboration and communication. To enable theory of mind modeling in situated interactions, we introduce a fine-grained dataset of collaborative tasks performed by pairs of human subjects in the 3D virtual blocks world of Minecraft. It provides information that captures partners' beliefs of the world and of each other as an interaction unfolds, bringing abundant opportunities to study human collaborative behaviors in situated language communication. As a first step towards our goal of developing embodied AI agents able to infer belief states of collaborative partners in situ, we build and present results on computational models for several theory of mind tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge