Jakob Prange
OMoS-QA: A Dataset for Cross-Lingual Extractive Question Answering in a German Migration Context
Jul 22, 2024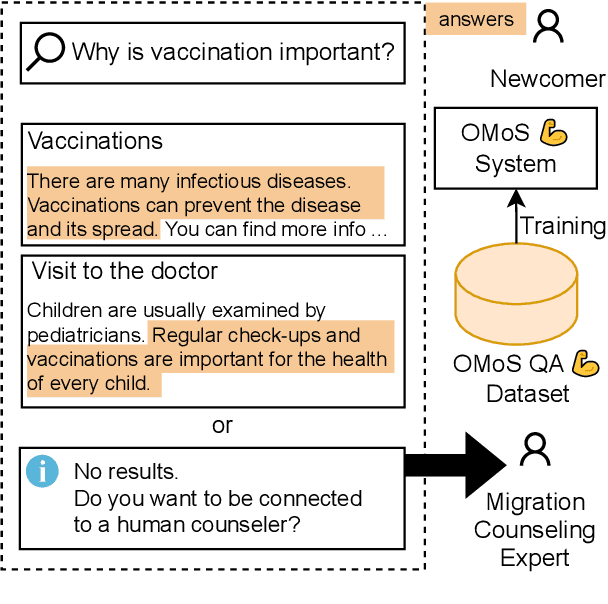
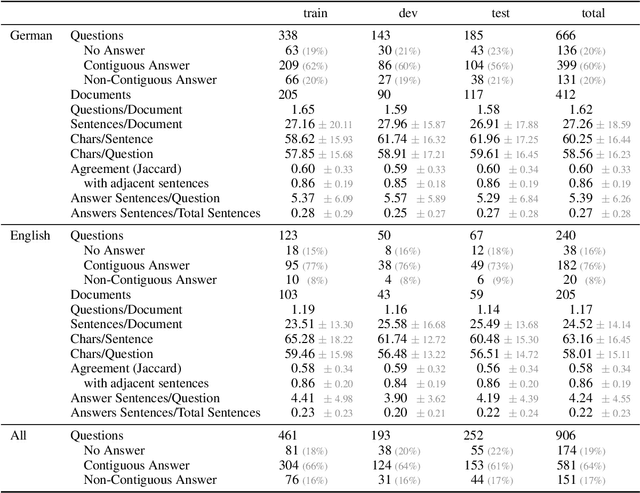
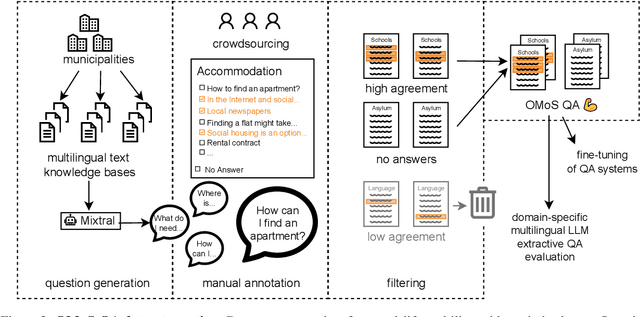
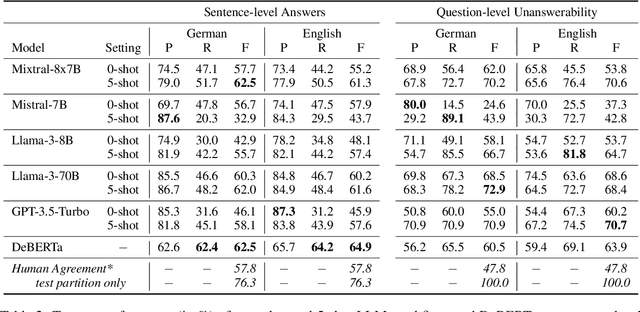
Abstract:When immigrating to a new country, it is easy to feel overwhelmed by the need to obtain information on financial support, housing, schooling, language courses, and other issues. If relocation is rushed or even forced, the necessity for high-quality answers to such questions is all the more urgent. Official immigration counselors are usually overbooked, and online systems could guide newcomers to the requested information or a suitable counseling service. To this end, we present OMoS-QA, a dataset of German and English questions paired with relevant trustworthy documents and manually annotated answers, specifically tailored to this scenario. Questions are automatically generated with an open-source large language model (LLM) and answer sentences are selected by crowd workers with high agreement. With our data, we conduct a comparison of 5 pretrained LLMs on the task of extractive question answering (QA) in German and English. Across all models and both languages, we find high precision and low-to-mid recall in selecting answer sentences, which is a favorable trade-off to avoid misleading users. This performance even holds up when the question language does not match the document language. When it comes to identifying unanswerable questions given a context, there are larger differences between the two languages.
Empirical Sufficiency Lower Bounds for Language Modeling with Locally-Bootstrapped Semantic Structures
May 30, 2023



Abstract:In this work we build upon negative results from an attempt at language modeling with predicted semantic structure, in order to establish empirical lower bounds on what could have made the attempt successful. More specifically, we design a concise binary vector representation of semantic structure at the lexical level and evaluate in-depth how good an incremental tagger needs to be in order to achieve better-than-baseline performance with an end-to-end semantic-bootstrapping language model. We envision such a system as consisting of a (pretrained) sequential-neural component and a hierarchical-symbolic component working together to generate text with low surprisal and high linguistic interpretability. We find that (a) dimensionality of the semantic vector representation can be dramatically reduced without losing its main advantages and (b) lower bounds on prediction quality cannot be established via a single score alone, but need to take the distributions of signal and noise into account.
Reanalyzing L2 Preposition Learning with Bayesian Mixed Effects and a Large Language Model
Feb 16, 2023



Abstract:We use both Bayesian and neural models to dissect a data set of Chinese learners' pre- and post-interventional responses to two tests measuring their understanding of English prepositions. The results mostly replicate previous findings from frequentist analyses and newly reveal crucial interactions between student ability, task type, and stimulus sentence. Given the sparsity of the data as well as high diversity among learners, the Bayesian method proves most useful; but we also see potential in using language model probabilities as predictors of grammaticality and learnability.
Oracle Linguistic Graphs Complement a Pretrained Transformer Language Model: A Cross-formalism Comparison
Dec 15, 2021



Abstract:We examine the extent to which, in principle, linguistic graph representations can complement and improve neural language modeling. With an ensemble setup consisting of a pretrained Transformer and ground-truth graphs from one of 7 different formalisms, we find that, overall, semantic constituency structures are most useful to language modeling performance -- outpacing syntactic constituency structures as well as syntactic and semantic dependency structures. Further, effects vary greatly depending on part-of-speech class. In sum, our findings point to promising tendencies in neuro-symbolic language modeling and invite future research quantifying the design choices made by different formalisms.
UCCA's Foundational Layer: Annotation Guidelines v2.1
Dec 31, 2020Abstract:This is the annotation manual for Universal Conceptual Cognitive Annotation (UCCA; Abend and Rappoport, 2013), specifically the Foundational Layer. UCCA is a graph-based semantic annotation scheme based on typological linguistic principles. It has been applied to several languages; for ease of exposition these guidelines give examples mainly in English. New annotators may wish to start with the tutorial on the UCCA framework (Abend et al., 2020). Further resources are available at the project homepage: https://universalconceptualcognitiveannotation.github.io
Supertagging the Long Tail with Tree-Structured Decoding of Complex Categories
Dec 11, 2020



Abstract:Although current CCG supertaggers achieve high accuracy on the standard WSJ test set, few systems make use of the categories' internal structure that will drive the syntactic derivation during parsing. The tagset is traditionally truncated, discarding the many rare and complex category types in the long tail. However, supertags are themselves trees. Rather than give up on rare tags, we investigate constructive models that account for their internal structure, including novel methods for tree-structured prediction. Our best tagger is capable of recovering a sizeable fraction of the long-tail supertags and even generates CCG categories that have never been seen in training, while approximating the prior state of the art in overall tag accuracy with fewer parameters. We further investigate how well different approaches generalize to out-of-domain evaluation sets.
Comparison by Conversion: Reverse-Engineering UCCA from Syntax and Lexical Semantics
Nov 02, 2020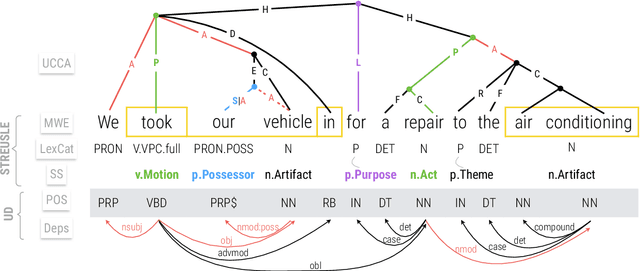


Abstract:Building robust natural language understanding systems will require a clear characterization of whether and how various linguistic meaning representations complement each other. To perform a systematic comparative analysis, we evaluate the mapping between meaning representations from different frameworks using two complementary methods: (i) a rule-based converter, and (ii) a supervised delexicalized parser that parses to one framework using only information from the other as features. We apply these methods to convert the STREUSLE corpus (with syntactic and lexical semantic annotations) to UCCA (a graph-structured full-sentence meaning representation). Both methods yield surprisingly accurate target representations, close to fully supervised UCCA parser quality---indicating that UCCA annotations are partially redundant with STREUSLE annotations. Despite this substantial convergence between frameworks, we find several important areas of divergence.
Made for Each Other: Broad-coverage Semantic Structures Meet Preposition Supersenses
Sep 19, 2019



Abstract:Universal Conceptual Cognitive Annotation (UCCA; Abend and Rappoport, 2013) is a typologically-informed, broad-coverage semantic annotation scheme that describes coarse-grained predicate-argument structure but currently lacks semantic roles. We argue that lexicon-free annotation of the semantic roles marked by prepositions, as formulated by Schneider et al. (2018b), is complementary and suitable for integration within UCCA. We show empirically for English that the schemes, though annotated independently, are compatible and can be combined in a single semantic graph. A comparison of several approaches to parsing the integrated representation lays the groundwork for future research on this task.
Semantically Constrained Multilayer Annotation: The Case of Coreference
Jun 11, 2019



Abstract:We propose a coreference annotation scheme as a layer on top of the Universal Conceptual Cognitive Annotation foundational layer, treating units in predicate-argument structure as a basis for entity and event mentions. We argue that this allows coreference annotators to sidestep some of the challenges faced in other schemes, which do not enforce consistency with predicate-argument structure and vary widely in what kinds of mentions they annotate and how. The proposed approach is examined with a pilot annotation study and compared with annotations from other schemes.
Adposition and Case Supersenses v2: Guidelines for English
Jul 02, 2018Abstract:This document offers a detailed linguistic description of SNACS (Semantic Network of Adposition and Case Supersenses; Schneider et al., 2018), an inventory of 50 semantic labels ("supersenses") that characterize the use of adpositions and case markers at a somewhat coarse level of granularity, as demonstrated in the STREUSLE 4.1 corpus (https://github.com/nert-gu/streusle/). Though the SNACS inventory aspires to be universal, this document is specific to English; documentation for other languages will be published separately. Version 2 is a revision of the supersense inventory proposed for English by Schneider et al. (2015, 2016) (henceforth "v1"), which in turn was based on previous schemes. The present inventory was developed after extensive review of the v1 corpus annotations for English, plus previously unanalyzed genitive case possessives (Blodgett and Schneider, 2018), as well as consideration of adposition and case phenomena in Hebrew, Hindi, Korean, and German. Hwang et al. (2017) present the theoretical underpinnings of the v2 scheme. Schneider et al. (2018) summarize the scheme, its application to English corpus data, and an automatic disambiguation task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge