Ari Rappoport
UCCA's Foundational Layer: Annotation Guidelines v2.1
Dec 31, 2020Abstract:This is the annotation manual for Universal Conceptual Cognitive Annotation (UCCA; Abend and Rappoport, 2013), specifically the Foundational Layer. UCCA is a graph-based semantic annotation scheme based on typological linguistic principles. It has been applied to several languages; for ease of exposition these guidelines give examples mainly in English. New annotators may wish to start with the tutorial on the UCCA framework (Abend et al., 2020). Further resources are available at the project homepage: https://universalconceptualcognitiveannotation.github.io
Content Differences in Syntactic and Semantic Representations
Mar 29, 2019



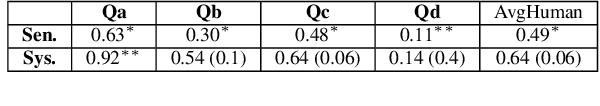
Abstract:Syntactic analysis plays an important role in semantic parsing, but the nature of this role remains a topic of ongoing debate. The debate has been constrained by the scarcity of empirical comparative studies between syntactic and semantic schemes, which hinders the development of parsing methods informed by the details of target schemes and constructions. We target this gap, and take Universal Dependencies (UD) and UCCA as a test case. After abstracting away from differences of convention or formalism, we find that most content divergences can be ascribed to: (1) UCCA's distinction between a Scene and a non-Scene; (2) UCCA's distinction between primary relations, secondary ones and participants; (3) different treatment of multi-word expressions, and (4) different treatment of inter-clause linkage. We further discuss the long tail of cases where the two schemes take markedly different approaches. Finally, we show that the proposed comparison methodology can be used for fine-grained evaluation of UCCA parsing, highlighting both challenges and potential sources for improvement. The substantial differences between the schemes suggest that semantic parsers are likely to benefit downstream text understanding applications beyond their syntactic counterparts.
SemEval 2019 Task 1: Cross-lingual Semantic Parsing with UCCA
Mar 06, 2019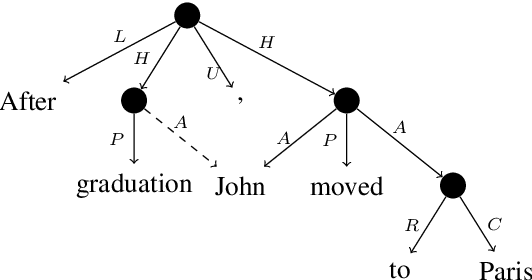

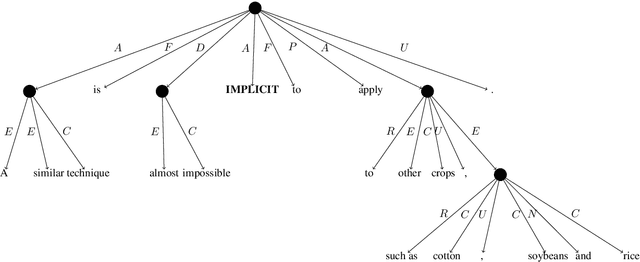
Abstract:We present the SemEval 2019 shared task on UCCA parsing in English, German and French, and discuss the participating systems and results. UCCA is a cross-linguistically applicable framework for semantic representation, which builds on extensive typological work and supports rapid annotation. UCCA poses a challenge for existing parsing techniques, as it exhibits reentrancy (resulting in DAG structures), discontinuous structures and non-terminal nodes corresponding to complex semantic units. The shared task has yielded improvements over the state-of-the-art baseline in all languages and settings. Full results can be found in the task's website \url{https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/19160}.
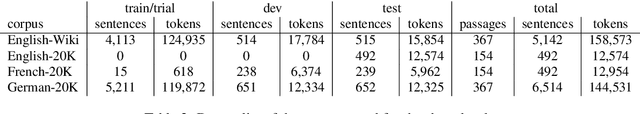
BLEU is Not Suitable for the Evaluation of Text Simplification
Oct 14, 2018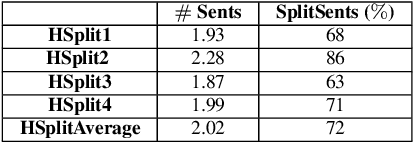
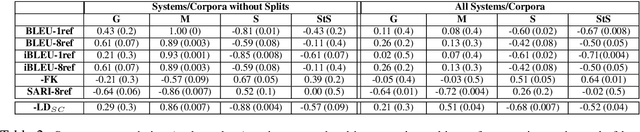
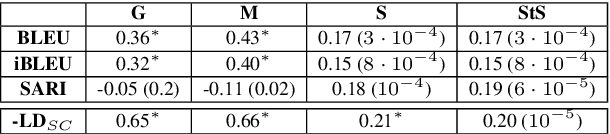
Abstract:BLEU is widely considered to be an informative metric for text-to-text generation, including Text Simplification (TS). TS includes both lexical and structural aspects. In this paper we show that BLEU is not suitable for the evaluation of sentence splitting, the major structural simplification operation. We manually compiled a sentence splitting gold standard corpus containing multiple structural paraphrases, and performed a correlation analysis with human judgments. We find low or no correlation between BLEU and the grammaticality and meaning preservation parameters where sentence splitting is involved. Moreover, BLEU often negatively correlates with simplicity, essentially penalizing simpler sentences.
Simple and Effective Text Simplification Using Semantic and Neural Methods
Oct 11, 2018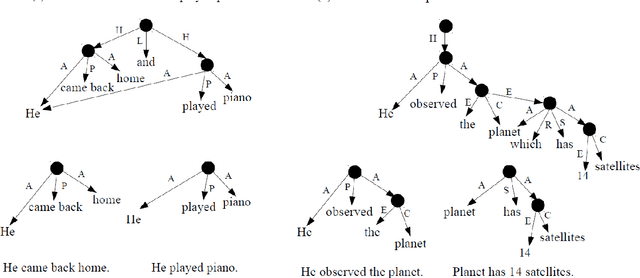
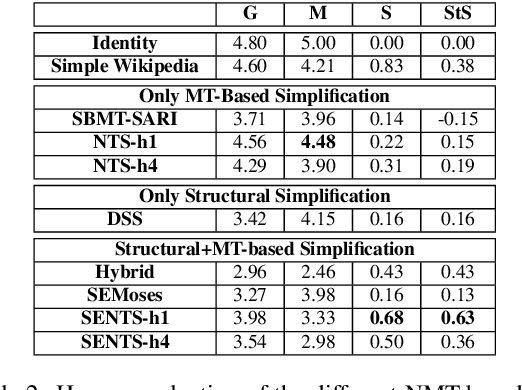
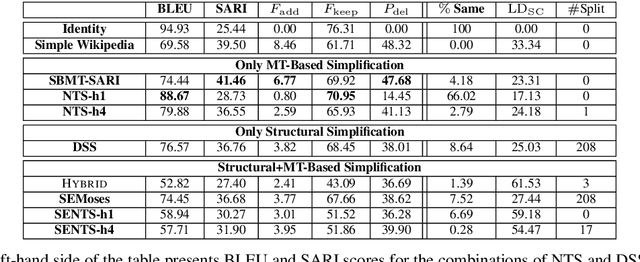
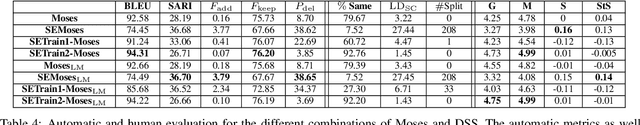
Abstract:Sentence splitting is a major simplification operator. Here we present a simple and efficient splitting algorithm based on an automatic semantic parser. After splitting, the text is amenable for further fine-tuned simplification operations. In particular, we show that neural Machine Translation can be effectively used in this situation. Previous application of Machine Translation for simplification suffers from a considerable disadvantage in that they are over-conservative, often failing to modify the source in any way. Splitting based on semantic parsing, as proposed here, alleviates this issue. Extensive automatic and human evaluation shows that the proposed method compares favorably to the state-of-the-art in combined lexical and structural simplification.
Semantic Structural Evaluation for Text Simplification
Oct 11, 2018
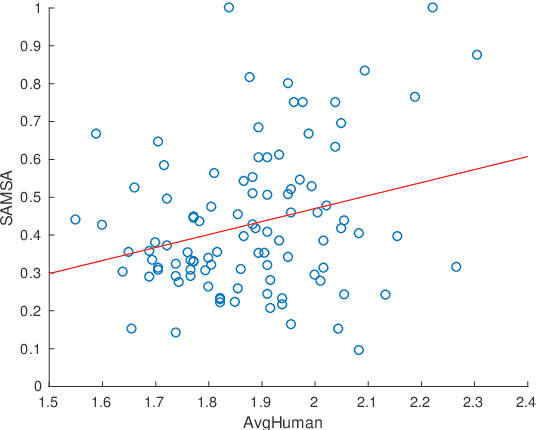
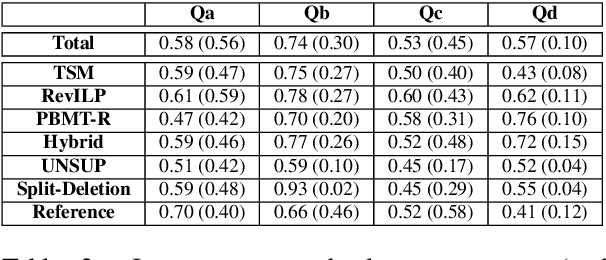
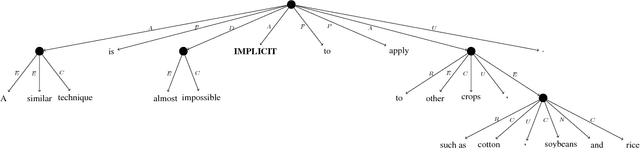
Abstract:Current measures for evaluating text simplification systems focus on evaluating lexical text aspects, neglecting its structural aspects. In this paper we propose the first measure to address structural aspects of text simplification, called SAMSA. It leverages recent advances in semantic parsing to assess simplification quality by decomposing the input based on its semantic structure and comparing it to the output. SAMSA provides a reference-less automatic evaluation procedure, avoiding the problems that reference-based methods face due to the vast space of valid simplifications for a given sentence. Our human evaluation experiments show both SAMSA's substantial correlation with human judgments, as well as the deficiency of existing reference-based measures in evaluating structural simplification.
Universal Dependency Parsing with a General Transition-Based DAG Parser
Aug 28, 2018



Abstract:This paper presents our experiments with applying TUPA to the CoNLL 2018 UD shared task. TUPA is a general neural transition-based DAG parser, which we use to present the first experiments on recovering enhanced dependencies as part of the general parsing task. TUPA was designed for parsing UCCA, a cross-linguistic semantic annotation scheme, exhibiting reentrancy, discontinuity and non-terminal nodes. By converting UD trees and graphs to a UCCA-like DAG format, we train TUPA almost without modification on the UD parsing task. The generic nature of our approach lends itself naturally to multitask learning. Our code is available at https://github.com/CoNLL-UD-2018/HUJI
SemEval 2019 Shared Task: Cross-lingual Semantic Parsing with UCCA - Call for Participation
Aug 19, 2018
Abstract:We announce a shared task on UCCA parsing in English, German and French, and call for participants to submit their systems. UCCA is a cross-linguistically applicable framework for semantic representation, which builds on extensive typological work and supports rapid annotation. UCCA poses a challenge for existing parsing techniques, as it exhibits reentrancy (resulting in DAG structures), discontinuous structures and non-terminal nodes corresponding to complex semantic units. Given the success of recent semantic parsing shared tasks (on SDP and AMR), we expect the task to have a significant contribution to the advancement of UCCA parsing in particular, and semantic parsing in general. Furthermore, existing applications for semantic evaluation that are based on UCCA will greatly benefit from better automatic methods for UCCA parsing. The competition website is https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/19160
Computing Word Classes Using Spectral Clustering
Aug 16, 2018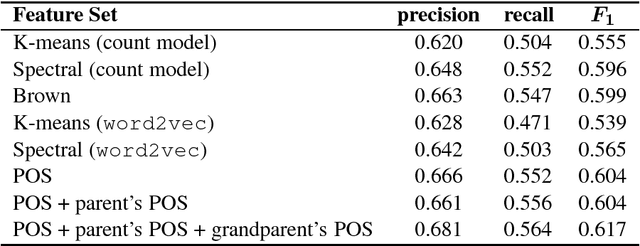

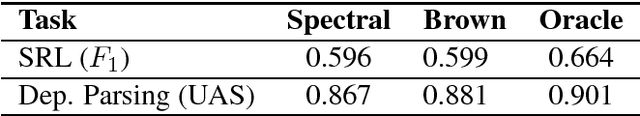
Abstract:Clustering a lexicon of words is a well-studied problem in natural language processing (NLP). Word clusters are used to deal with sparse data in statistical language processing, as well as features for solving various NLP tasks (text categorization, question answering, named entity recognition and others). Spectral clustering is a widely used technique in the field of image processing and speech recognition. However, it has scarcely been explored in the context of NLP; specifically, the method used in this (Meila and Shi, 2001) has never been used to cluster a general word lexicon. We apply spectral clustering to a lexicon of words, evaluating the resulting clusters by using them as features for solving two classical NLP tasks: semantic role labeling and dependency parsing. We compare performance with Brown clustering, a widely-used technique for word clustering, as well as with other clustering methods. We show that spectral clusters produce similar results to Brown clusters, and outperform other clustering methods. In addition, we quantify the overlap between spectral and Brown clusters, showing that each model captures some information which is uncaptured by the other.
Multitask Parsing Across Semantic Representations
May 01, 2018



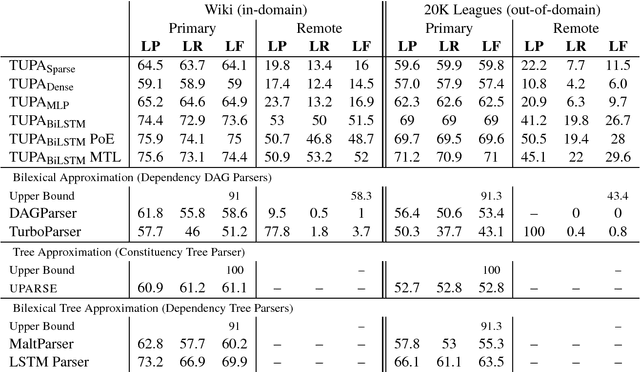
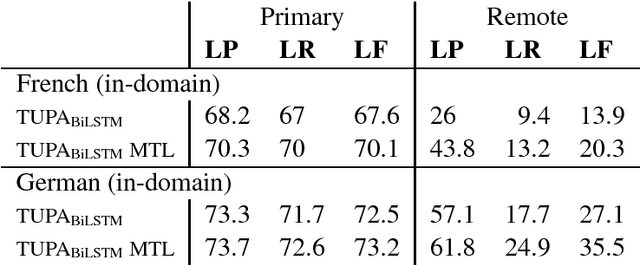
Abstract:The ability to consolidate information of different types is at the core of intelligence, and has tremendous practical value in allowing learning for one task to benefit from generalizations learned for others. In this paper we tackle the challenging task of improving semantic parsing performance, taking UCCA parsing as a test case, and AMR, SDP and Universal Dependencies (UD) parsing as auxiliary tasks. We experiment on three languages, using a uniform transition-based system and learning architecture for all parsing tasks. Despite notable conceptual, formal and domain differences, we show that multitask learning significantly improves UCCA parsing in both in-domain and out-of-domain settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge