Clare Voss
Navigating to Success in Multi-Modal Human-Robot Collaboration: Analysis and Corpus Release
Oct 26, 2023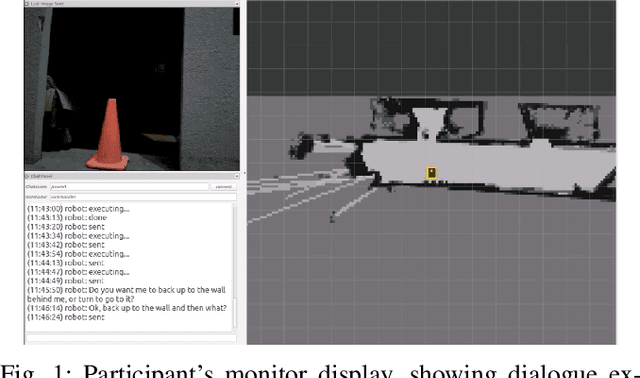
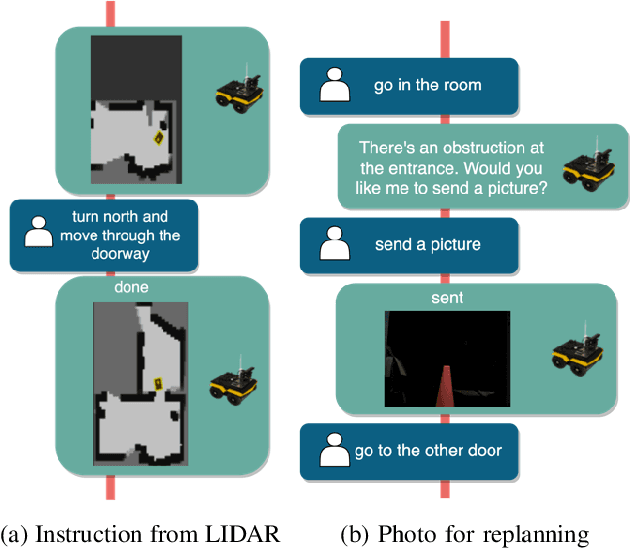
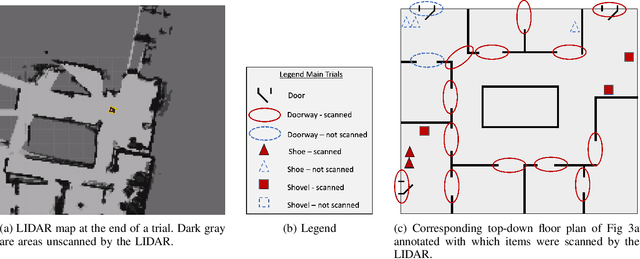
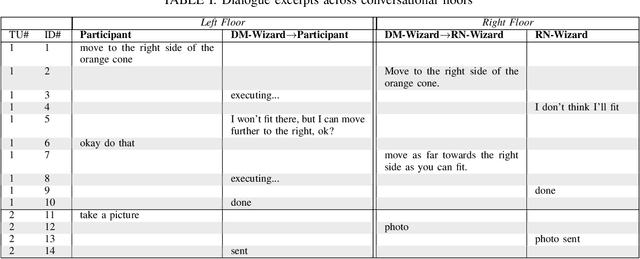
Abstract:Human-guided robotic exploration is a useful approach to gathering information at remote locations, especially those that might be too risky, inhospitable, or inaccessible for humans. Maintaining common ground between the remotely-located partners is a challenge, one that can be facilitated by multi-modal communication. In this paper, we explore how participants utilized multiple modalities to investigate a remote location with the help of a robotic partner. Participants issued spoken natural language instructions and received from the robot: text-based feedback, continuous 2D LIDAR mapping, and upon-request static photographs. We noticed that different strategies were adopted in terms of use of the modalities, and hypothesize that these differences may be correlated with success at several exploration sub-tasks. We found that requesting photos may have improved the identification and counting of some key entities (doorways in particular) and that this strategy did not hinder the amount of overall area exploration. Future work with larger samples may reveal the effects of more nuanced photo and dialogue strategies, which can inform the training of robotic agents. Additionally, we announce the release of our unique multi-modal corpus of human-robot communication in an exploration context: SCOUT, the Situated Corpus on Understanding Transactions.
* 7 pages, 3 figures
Future is not One-dimensional: Graph Modeling based Complex Event Schema Induction for Event Prediction
Apr 15, 2021



Abstract:Event schemas encode knowledge of stereotypical structures of events and their connections. As events unfold, schemas are crucial to act as a scaffolding. Previous work on event schema induction either focuses on atomic events or linear temporal event sequences, ignoring the interplay between events via arguments and argument relations. We introduce the concept of Temporal Complex Event Schema: a graph-based schema representation that encompasses events, arguments, temporal connections and argument relations. Additionally, we propose a Temporal Event Graph Model that models the emergence of event instances following the temporal complex event schema. To build and evaluate such schemas, we release a new schema learning corpus containing 6,399 documents accompanied with event graphs, and manually constructed gold schemas. Intrinsic evaluation by schema matching and instance graph perplexity, prove the superior quality of our probabilistic graph schema library compared to linear representations. Extrinsic evaluation on schema-guided event prediction further demonstrates the predictive power of our event graph model, significantly surpassing human schemas and baselines by more than 17.8% on HITS@1.
COVID-19 Literature Knowledge Graph Construction and Drug Repurposing Report Generation
Jul 06, 2020
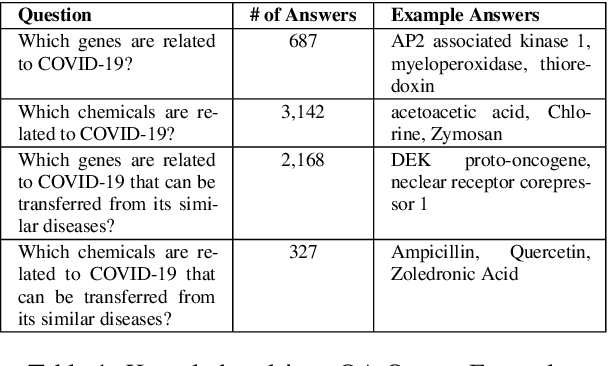
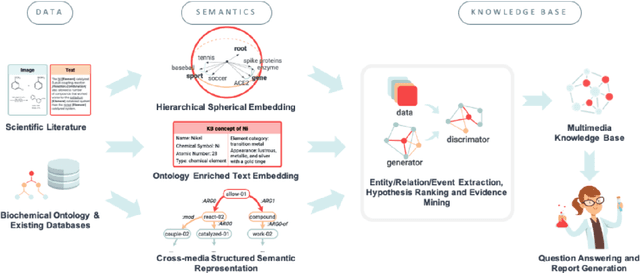
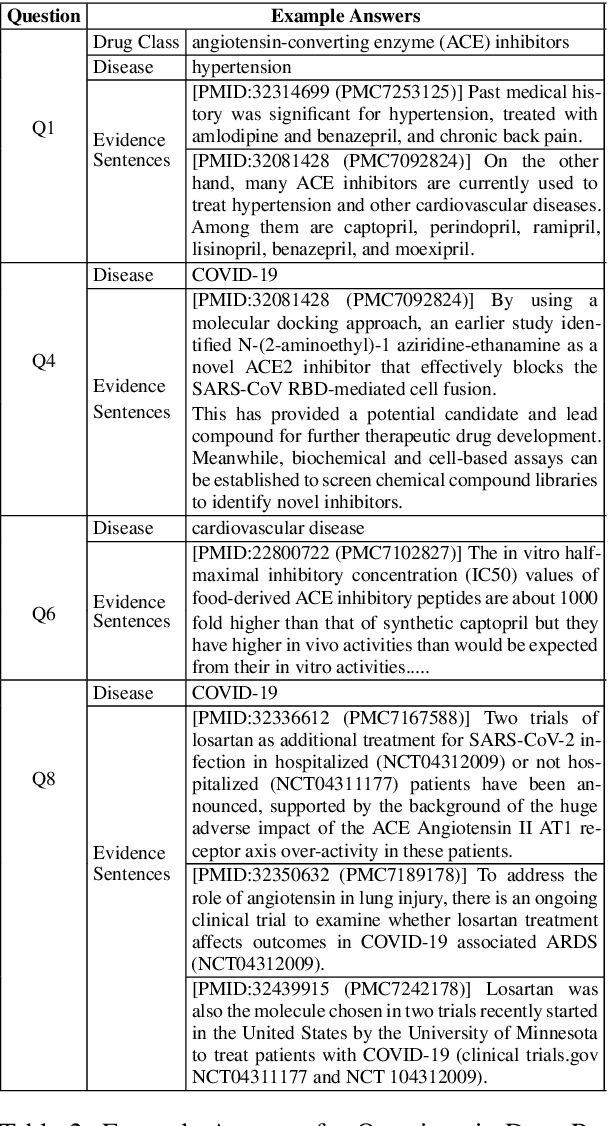
Abstract:To combat COVID-19, clinicians and scientists all need to digest the vast amount of relevant biomedical knowledge in literature to understand the disease mechanism and the related biological functions. We have developed a novel and comprehensive knowledge discovery framework, COVID-KG, which leverages novel semantic representation and external ontologies to represent text and images in the input literature data, and then performs various extraction components to extract fine-grained multimedia knowledge elements (entities, relations and events). We then exploit the constructed multimedia KGs for question answering and report generation, using drug repurposing as a case study. Our framework also provides detailed contextual sentences, subfigures and knowledge subgraphs as evidence. All of the data, KGs, resources, and shared services are publicly available.
A Research Platform for Multi-Robot Dialogue with Humans
Oct 12, 2019


Abstract:This paper presents a research platform that supports spoken dialogue interaction with multiple robots. The demonstration showcases our crafted MultiBot testing scenario in which users can verbally issue search, navigate, and follow instructions to two robotic teammates: a simulated ground robot and an aerial robot. This flexible language and robotic platform takes advantage of existing tools for speech recognition and dialogue management that are compatible with new domains, and implements an inter-agent communication protocol (tactical behavior specification), where verbal instructions are encoded for tasks assigned to the appropriate robot.
Balancing Efficiency and Coverage in Human-Robot Dialogue Collection
Oct 07, 2018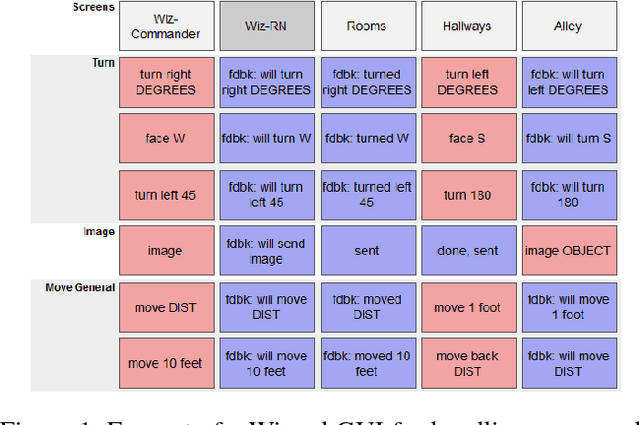
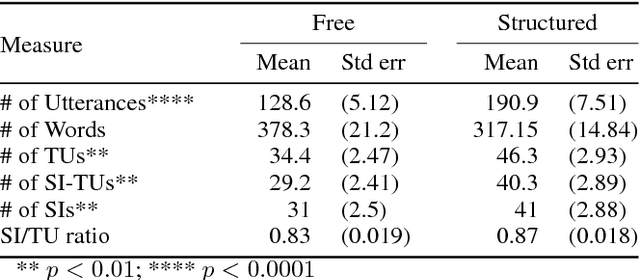
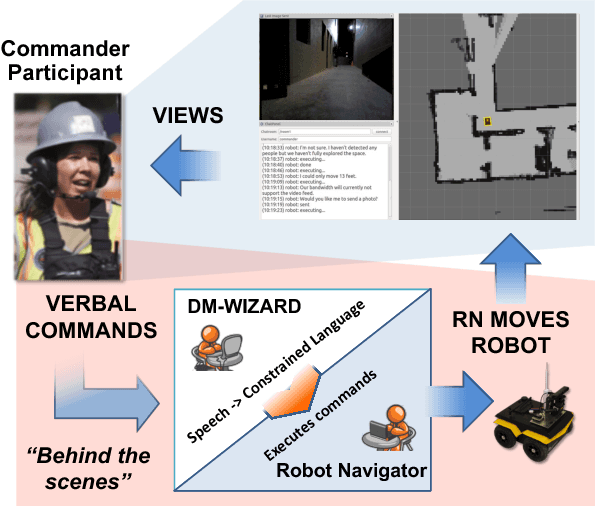
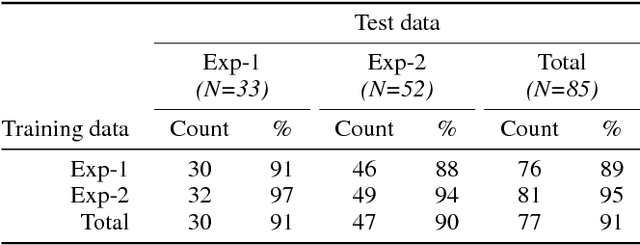
Abstract:We describe a multi-phased Wizard-of-Oz approach to collecting human-robot dialogue in a collaborative search and navigation task. The data is being used to train an initial automated robot dialogue system to support collaborative exploration tasks. In the first phase, a wizard freely typed robot utterances to human participants. For the second phase, this data was used to design a GUI that includes buttons for the most common communications, and templates for communications with varying parameters. Comparison of the data gathered in these phases show that the GUI enabled a faster pace of dialogue while still maintaining high coverage of suitable responses, enabling more efficient targeted data collection, and improvements in natural language understanding using GUI-collected data. As a promising first step towards interactive learning, this work shows that our approach enables the collection of useful training data for navigation-based HRI tasks.
Object and Text-guided Semantics for CNN-based Activity Recognition
May 04, 2018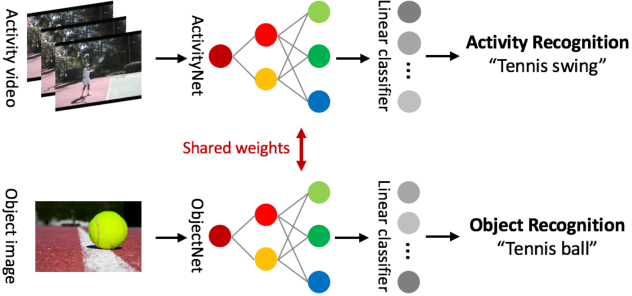
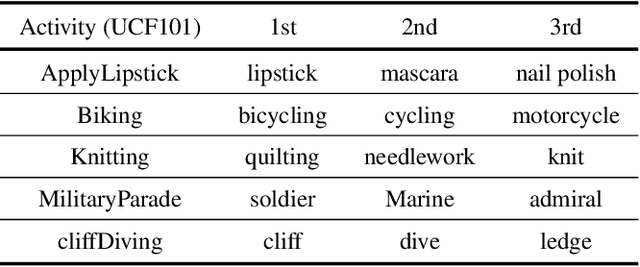
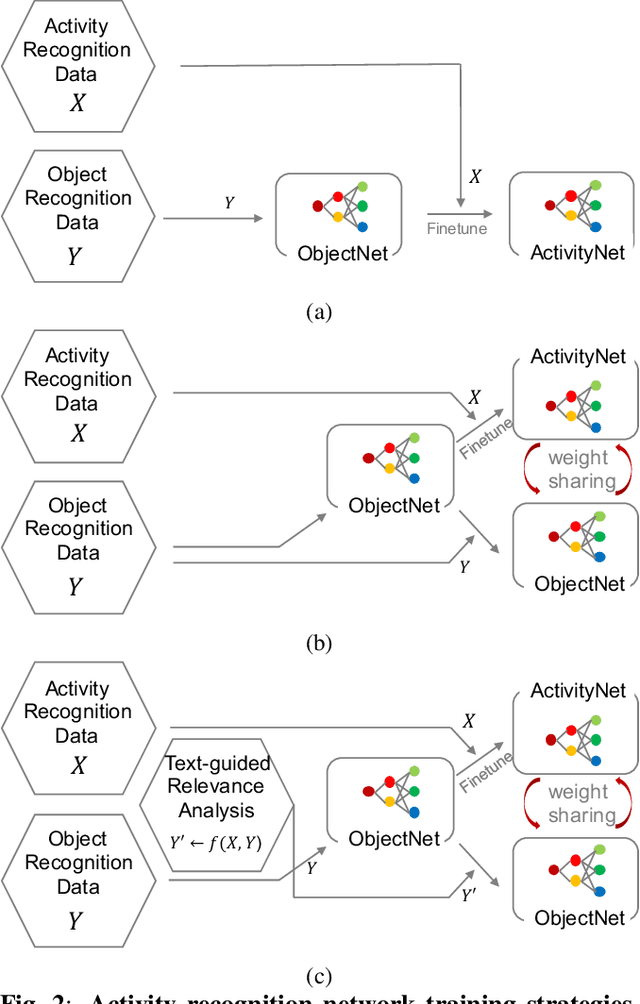
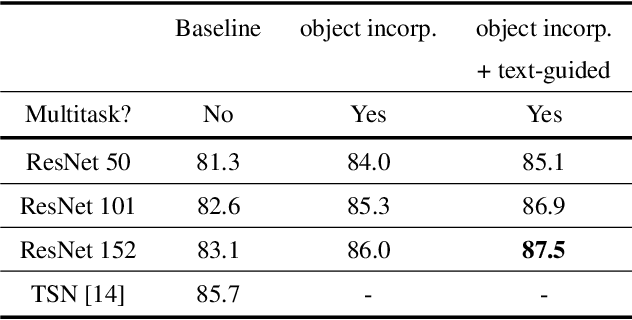
Abstract:Many previous methods have demonstrated the importance of considering semantically relevant objects for carrying out video-based human activity recognition, yet none of the methods have harvested the power of large text corpora to relate the objects and the activities to be transferred into learning a unified deep convolutional neural network. We present a novel activity recognition CNN which co-learns the object recognition task in an end-to-end multitask learning scheme to improve upon the baseline activity recognition performance. We further improve upon the multitask learning approach by exploiting a text-guided semantic space to select the most relevant objects with respect to the target activities. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to investigate this approach.
Applying the Wizard-of-Oz Technique to Multimodal Human-Robot Dialogue
Mar 10, 2017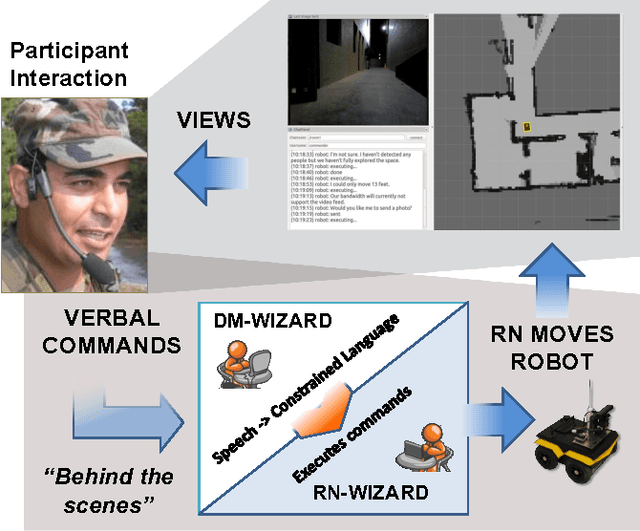
Abstract:Our overall program objective is to provide more natural ways for soldiers to interact and communicate with robots, much like how soldiers communicate with other soldiers today. We describe how the Wizard-of-Oz (WOz) method can be applied to multimodal human-robot dialogue in a collaborative exploration task. While the WOz method can help design robot behaviors, traditional approaches place the burden of decisions on a single wizard. In this work, we consider two wizards to stand in for robot navigation and dialogue management software components. The scenario used to elicit data is one in which a human-robot team is tasked with exploring an unknown environment: a human gives verbal instructions from a remote location and the robot follows them, clarifying possible misunderstandings as needed via dialogue. We found the division of labor between wizards to be workable, which holds promise for future software development.
Using a Distributional Semantic Vector Space with a Knowledge Base for Reasoning in Uncertain Conditions
Jun 13, 2016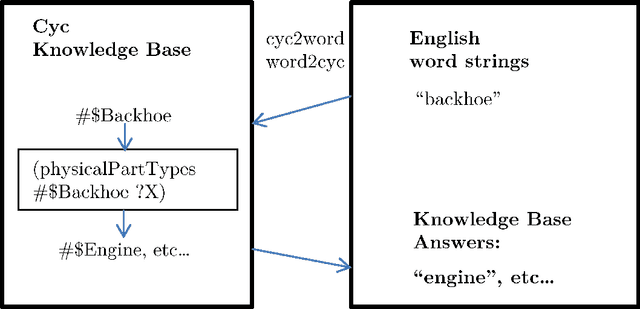

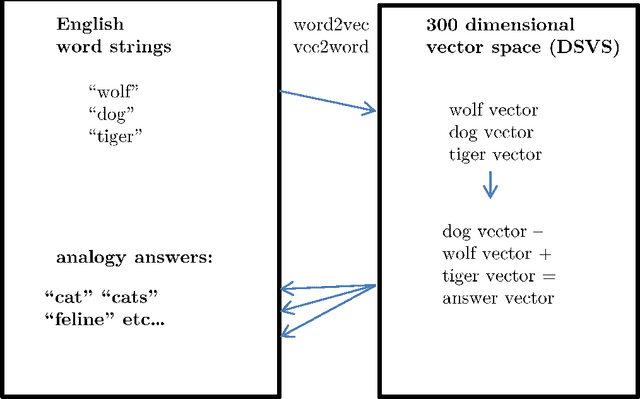
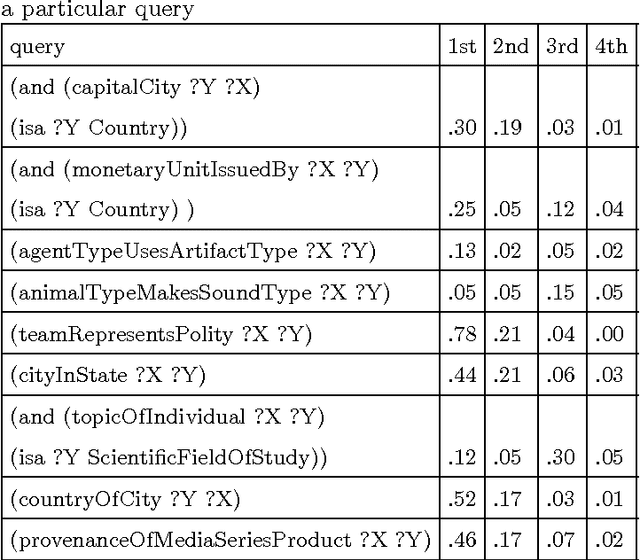
Abstract:The inherent inflexibility and incompleteness of commonsense knowledge bases (KB) has limited their usefulness. We describe a system called Displacer for performing KB queries extended with the analogical capabilities of the word2vec distributional semantic vector space (DSVS). This allows the system to answer queries with information which was not contained in the original KB in any form. By performing analogous queries on semantically related terms and mapping their answers back into the context of the original query using displacement vectors, we are able to give approximate answers to many questions which, if posed to the KB alone, would return no results. We also show how the hand-curated knowledge in a KB can be used to increase the accuracy of a DSVS in solving analogy problems. In these ways, a KB and a DSVS can make up for each other's weaknesses.
Scalable Topical Phrase Mining from Text Corpora
Nov 19, 2014

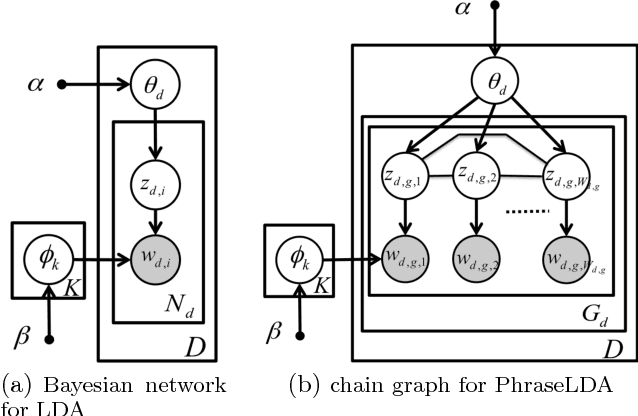

Abstract:While most topic modeling algorithms model text corpora with unigrams, human interpretation often relies on inherent grouping of terms into phrases. As such, we consider the problem of discovering topical phrases of mixed lengths. Existing work either performs post processing to the inference results of unigram-based topic models, or utilizes complex n-gram-discovery topic models. These methods generally produce low-quality topical phrases or suffer from poor scalability on even moderately-sized datasets. We propose a different approach that is both computationally efficient and effective. Our solution combines a novel phrase mining framework to segment a document into single and multi-word phrases, and a new topic model that operates on the induced document partition. Our approach discovers high quality topical phrases with negligible extra cost to the bag-of-words topic model in a variety of datasets including research publication titles, abstracts, reviews, and news articles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge