Taylor Cassidy
MetaPAD: Meta Pattern Discovery from Massive Text Corpora
Mar 14, 2017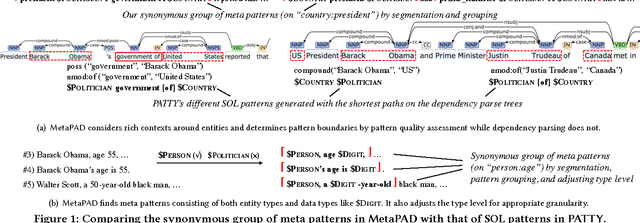
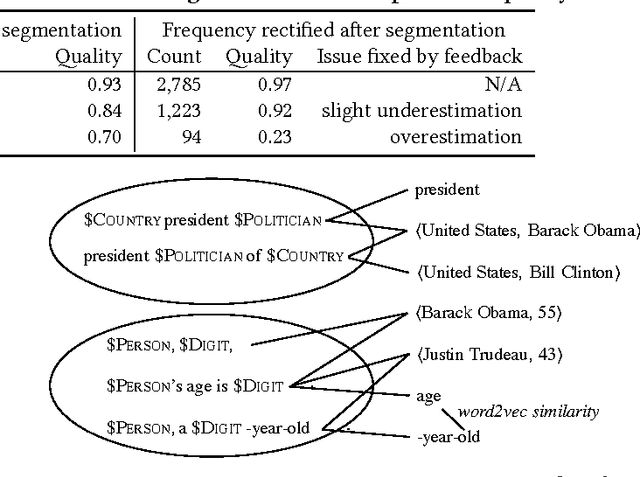

Abstract:Mining textual patterns in news, tweets, papers, and many other kinds of text corpora has been an active theme in text mining and NLP research. Previous studies adopt a dependency parsing-based pattern discovery approach. However, the parsing results lose rich context around entities in the patterns, and the process is costly for a corpus of large scale. In this study, we propose a novel typed textual pattern structure, called meta pattern, which is extended to a frequent, informative, and precise subsequence pattern in certain context. We propose an efficient framework, called MetaPAD, which discovers meta patterns from massive corpora with three techniques: (1) it develops a context-aware segmentation method to carefully determine the boundaries of patterns with a learnt pattern quality assessment function, which avoids costly dependency parsing and generates high-quality patterns; (2) it identifies and groups synonymous meta patterns from multiple facets---their types, contexts, and extractions; and (3) it examines type distributions of entities in the instances extracted by each group of patterns, and looks for appropriate type levels to make discovered patterns precise. Experiments demonstrate that our proposed framework discovers high-quality typed textual patterns efficiently from different genres of massive corpora and facilitates information extraction.
Applying the Wizard-of-Oz Technique to Multimodal Human-Robot Dialogue
Mar 10, 2017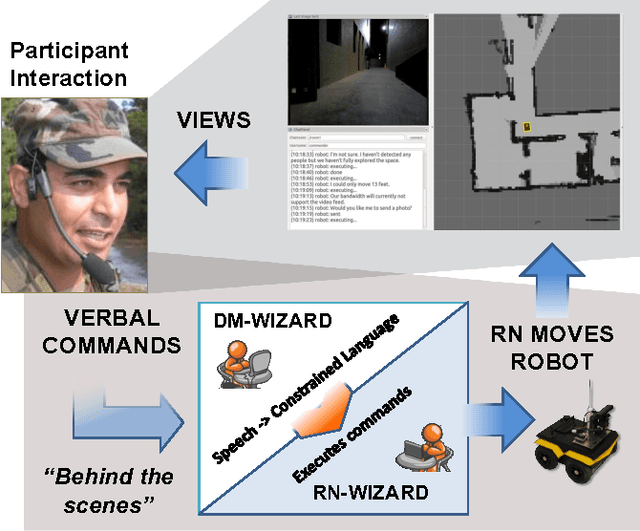
Abstract:Our overall program objective is to provide more natural ways for soldiers to interact and communicate with robots, much like how soldiers communicate with other soldiers today. We describe how the Wizard-of-Oz (WOz) method can be applied to multimodal human-robot dialogue in a collaborative exploration task. While the WOz method can help design robot behaviors, traditional approaches place the burden of decisions on a single wizard. In this work, we consider two wizards to stand in for robot navigation and dialogue management software components. The scenario used to elicit data is one in which a human-robot team is tasked with exploring an unknown environment: a human gives verbal instructions from a remote location and the robot follows them, clarifying possible misunderstandings as needed via dialogue. We found the division of labor between wizards to be workable, which holds promise for future software development.
Using a Distributional Semantic Vector Space with a Knowledge Base for Reasoning in Uncertain Conditions
Jun 13, 2016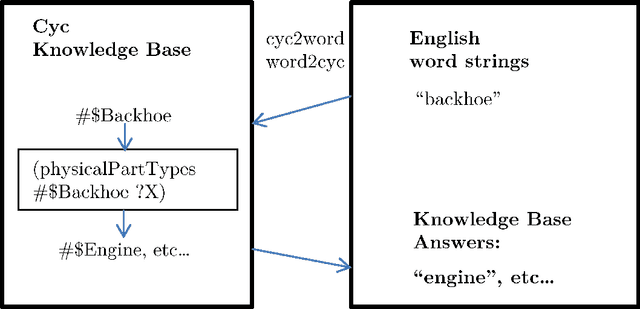

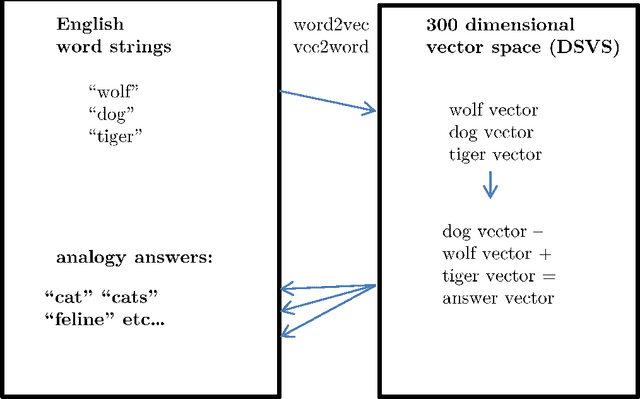
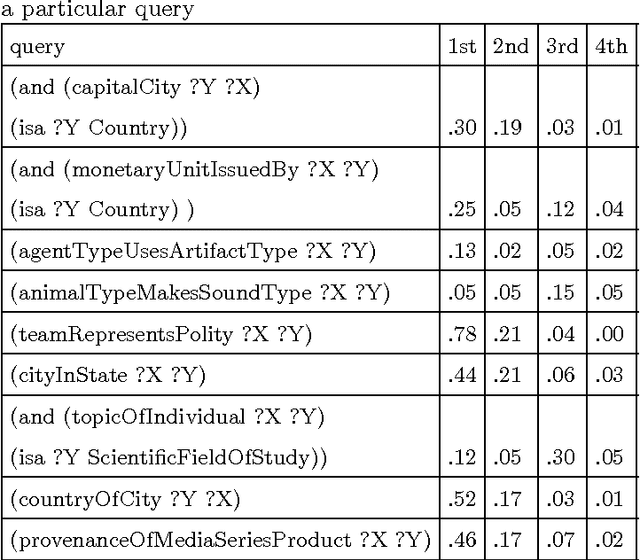
Abstract:The inherent inflexibility and incompleteness of commonsense knowledge bases (KB) has limited their usefulness. We describe a system called Displacer for performing KB queries extended with the analogical capabilities of the word2vec distributional semantic vector space (DSVS). This allows the system to answer queries with information which was not contained in the original KB in any form. By performing analogous queries on semantically related terms and mapping their answers back into the context of the original query using displacement vectors, we are able to give approximate answers to many questions which, if posed to the KB alone, would return no results. We also show how the hand-curated knowledge in a KB can be used to increase the accuracy of a DSVS in solving analogy problems. In these ways, a KB and a DSVS can make up for each other's weaknesses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge