Connor Baumler
On the Mutual Influence of Gender and Occupation in LLM Representations
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:We examine LLM representations of gender for first names in various occupational contexts to study how occupations and the gender perception of first names in LLMs influence each other mutually. We find that LLMs' first-name gender representations correlate with real-world gender statistics associated with the name, and are influenced by the co-occurrence of stereotypically feminine or masculine occupations. Additionally, we study the influence of first-name gender representations on LLMs in a downstream occupation prediction task and their potential as an internal metric to identify extrinsic model biases. While feminine first-name embeddings often raise the probabilities for female-dominated jobs (and vice versa for male-dominated jobs), reliably using these internal gender representations for bias detection remains challenging.
Anti-stereotypical Predictive Text Suggestions Do Not Reliably Yield Anti-stereotypical Writing
Sep 30, 2024


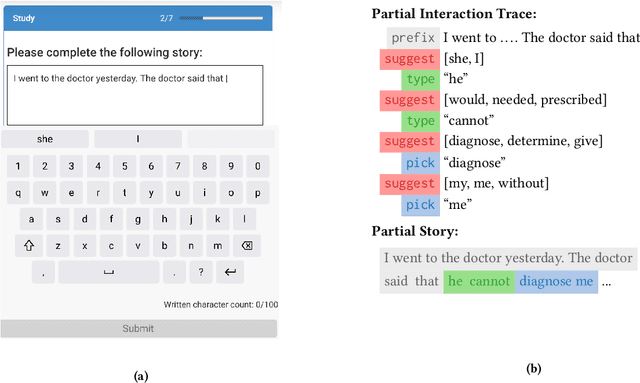
Abstract:AI-based systems such as language models can replicate and amplify social biases reflected in their training data. Among other questionable behavior, this can lead to LM-generated text--and text suggestions--that contain normatively inappropriate stereotypical associations. In this paper, we consider the question of how "debiasing" a language model impacts stories that people write using that language model in a predictive text scenario. We find that (n=414), in certain scenarios, language model suggestions that align with common social stereotypes are more likely to be accepted by human authors. Conversely, although anti-stereotypical language model suggestions sometimes lead to an increased rate of anti-stereotypical stories, this influence is far from sufficient to lead to "fully debiased" stories.
The Impact of Explanations on Fairness in Human-AI Decision-Making: Protected vs Proxy Features
Oct 12, 2023



Abstract:AI systems have been known to amplify biases in real world data. Explanations may help human-AI teams address these biases for fairer decision-making. Typically, explanations focus on salient input features. If a model is biased against some protected group, explanations may include features that demonstrate this bias, but when biases are realized through proxy features, the relationship between this proxy feature and the protected one may be less clear to a human. In this work, we study the effect of the presence of protected and proxy features on participants' perception of model fairness and their ability to improve demographic parity over an AI alone. Further, we examine how different treatments -- explanations, model bias disclosure and proxy correlation disclosure -- affect fairness perception and parity. We find that explanations help people detect direct biases but not indirect biases. Additionally, regardless of bias type, explanations tend to increase agreement with model biases. Disclosures can help mitigate this effect for indirect biases, improving both unfairness recognition and the decision-making fairness. We hope that our findings can help guide further research into advancing explanations in support of fair human-AI decision-making.
What Else Do I Need to Know? The Effect of Background Information on Users' Reliance on AI Systems
May 23, 2023Abstract:AI systems have shown impressive performance at answering questions by retrieving relevant context. However, with the increasingly large models, it is impossible and often undesirable to constrain models' knowledge or reasoning to only the retrieved context. This leads to a mismatch between the information that these models access to derive the answer and the information available to the user consuming the AI predictions to assess the AI predicted answer. In this work, we study how users interact with AI systems in absence of sufficient information to assess AI predictions. Further, we ask the question of whether adding the requisite background alleviates the concerns around over-reliance in AI predictions. Our study reveals that users rely on AI predictions even in the absence of sufficient information needed to assess its correctness. Providing the relevant background, however, helps users catch AI errors better, reducing over-reliance on incorrect AI predictions. On the flip side, background information also increases users' confidence in their correct as well as incorrect judgments. Contrary to common expectation, aiding a user's perusal of the context and the background through highlights is not helpful in alleviating the issue of over-confidence stemming from availability of more information. Our work aims to highlight the gap between how NLP developers perceive informational need in human-AI interaction and the actual human interaction with the information available to them.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge