Philip Resnik
University of Maryland
Medical Triage as Pairwise Ranking: A Benchmark for Urgency in Patient Portal Messages
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Medical triage is the task of allocating medical resources and prioritizing patients based on medical need. This paper introduces the first large-scale public dataset for studying medical triage in the context of asynchronous outpatient portal messages. Our novel task formulation views patient message triage as a pairwise inference problem, where we train LLMs to choose `"which message is more medically urgent" in a head-to-head tournament-style re-sort of a physician's inbox. Our novel benchmark PMR-Bench contains 1569 unique messages and 2,000+ high-quality test pairs for pairwise medical urgency assessment alongside a scalable training data generation pipeline. PMR-Bench includes samples that contain both unstructured patient-written messages alongside real electronic health record (EHR) data, emulating a real-world medical triage scenario. We develop a novel automated data annotation strategy to provide LLMs with in-domain guidance on this task. The resulting data is used to train two model classes, UrgentReward and UrgentSFT, leveraging Bradley-Terry and next token prediction objective, respectively to perform pairwise urgency classification. We find that UrgentSFT achieves top performance on PMR-Bench, with UrgentReward showing distinct advantages in low-resource settings. For example, UrgentSFT-8B and UrgentReward-8B provide a 15- and 16-point boost, respectively, on inbox sorting metrics over off-the-shelf 8B models. Paper resources can be found at https://tinyurl.com/Patient-Message-Triage
Are Language Models Models?
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Futrell and Mahowald claim LMs "serve as model systems", but an assessment at each of Marr's three levels suggests the claim is clearly not true at the implementation level, poorly motivated at the algorithmic-representational level, and problematic at the computational theory level. LMs are good candidates as tools; calling them cognitive models overstates the case and unnecessarily feeds LLM hype.
ProxAnn: Use-Oriented Evaluations of Topic Models and Document Clustering
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:Topic model and document-clustering evaluations either use automated metrics that align poorly with human preferences or require expert labels that are intractable to scale. We design a scalable human evaluation protocol and a corresponding automated approximation that reflect practitioners' real-world usage of models. Annotators -- or an LLM-based proxy -- review text items assigned to a topic or cluster, infer a category for the group, then apply that category to other documents. Using this protocol, we collect extensive crowdworker annotations of outputs from a diverse set of topic models on two datasets. We then use these annotations to validate automated proxies, finding that the best LLM proxies are statistically indistinguishable from a human annotator and can therefore serve as a reasonable substitute in automated evaluations. Package, web interface, and data are at https://github.com/ahoho/proxann
Multimodal Biomarkers for Schizophrenia: Towards Individual Symptom Severity Estimation
May 21, 2025Abstract:Studies on schizophrenia assessments using deep learning typically treat it as a classification task to detect the presence or absence of the disorder, oversimplifying the condition and reducing its clinical applicability. This traditional approach overlooks the complexity of schizophrenia, limiting its practical value in healthcare settings. This study shifts the focus to individual symptom severity estimation using a multimodal approach that integrates speech, video, and text inputs. We develop unimodal models for each modality and a multimodal framework to improve accuracy and robustness. By capturing a more detailed symptom profile, this approach can help in enhancing diagnostic precision and support personalized treatment, offering a scalable and objective tool for mental health assessment.
Conversational User-AI Intervention: A Study on Prompt Rewriting for Improved LLM Response Generation
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:Human-LLM conversations are increasingly becoming more pervasive in peoples' professional and personal lives, yet many users still struggle to elicit helpful responses from LLM Chatbots. One of the reasons for this issue is users' lack of understanding in crafting effective prompts that accurately convey their information needs. Meanwhile, the existence of real-world conversational datasets on the one hand, and the text understanding faculties of LLMs on the other, present a unique opportunity to study this problem, and its potential solutions at scale. Thus, in this paper we present the first LLM-centric study of real human-AI chatbot conversations, focused on investigating aspects in which user queries fall short of expressing information needs, and the potential of using LLMs to rewrite suboptimal user prompts. Our findings demonstrate that rephrasing ineffective prompts can elicit better responses from a conversational system, while preserving the user's original intent. Notably, the performance of rewrites improves in longer conversations, where contextual inferences about user needs can be made more accurately. Additionally, we observe that LLMs often need to -- and inherently do -- make \emph{plausible} assumptions about a user's intentions and goals when interpreting prompts. Our findings largely hold true across conversational domains, user intents, and LLMs of varying sizes and families, indicating the promise of using prompt rewriting as a solution for better human-AI interactions.
Understanding Common Ground Misalignment in Goal-Oriented Dialog: A Case-Study with Ubuntu Chat Logs
Mar 16, 2025



Abstract:While it is commonly accepted that maintaining common ground plays a role in conversational success, little prior research exists connecting conversational grounding to success in task-oriented conversations. We study failures of grounding in the Ubuntu IRC dataset, where participants use text-only communication to resolve technical issues. We find that disruptions in conversational flow often stem from a misalignment in common ground, driven by a divergence in beliefs and assumptions held by participants. These disruptions, which we call conversational friction, significantly correlate with task success. We find that although LLMs can identify overt cases of conversational friction, they struggle with subtler and more context-dependent instances requiring pragmatic or domain-specific reasoning.
Large Language Models are Biased Because They Are Large Language Models
Jun 19, 2024Abstract:This paper's primary goal is to provoke thoughtful discussion about the relationship between bias and fundamental properties of large language models. We do this by seeking to convince the reader that harmful biases are an inevitable consequence arising from the design of any large language model as LLMs are currently formulated. To the extent that this is true, it suggests that the problem of harmful bias cannot be properly addressed without a serious reconsideration of AI driven by LLMs, going back to the foundational assumptions underlying their design.
A Multimodal Framework for the Assessment of the Schizophrenia Spectrum
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a novel multimodal framework to distinguish between different symptom classes of subjects in the schizophrenia spectrum and healthy controls using audio, video, and text modalities. We implemented Convolution Neural Network and Long Short Term Memory based unimodal models and experimented on various multimodal fusion approaches to come up with the proposed framework. We utilized a minimal Gated multimodal unit (mGMU) to obtain a bi-modal intermediate fusion of the features extracted from the input modalities before finally fusing the outputs of the bimodal fusions to perform subject-wise classifications. The use of mGMU units in the multimodal framework improved the performance in both weighted f1-score and weighted AUC-ROC scores.
The Prompt Report: A Systematic Survey of Prompting Techniques
Jun 06, 2024Abstract:Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) systems are being increasingly deployed across all parts of industry and research settings. Developers and end users interact with these systems through the use of prompting or prompt engineering. While prompting is a widespread and highly researched concept, there exists conflicting terminology and a poor ontological understanding of what constitutes a prompt due to the area's nascency. This paper establishes a structured understanding of prompts, by assembling a taxonomy of prompting techniques and analyzing their use. We present a comprehensive vocabulary of 33 vocabulary terms, a taxonomy of 58 text-only prompting techniques, and 40 techniques for other modalities. We further present a meta-analysis of the entire literature on natural language prefix-prompting.
Words, Subwords, and Morphemes: What Really Matters in the Surprisal-Reading Time Relationship?
Oct 26, 2023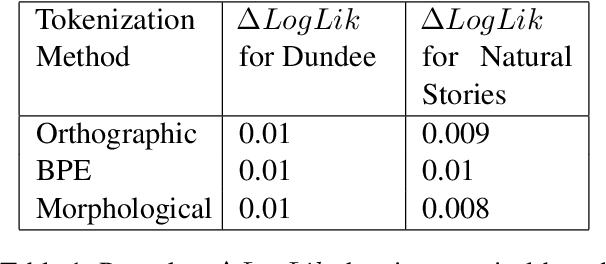
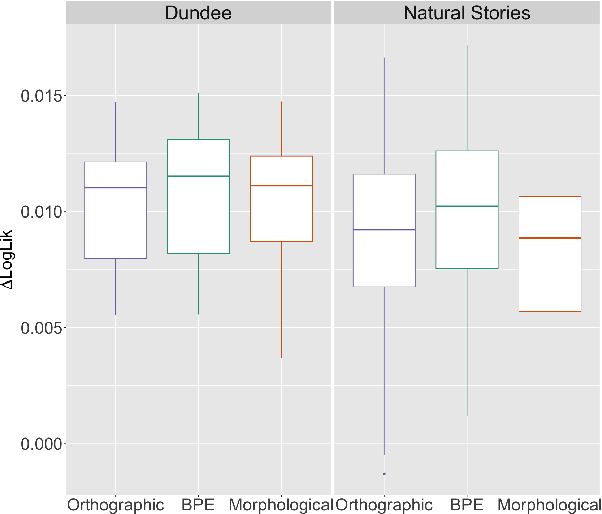
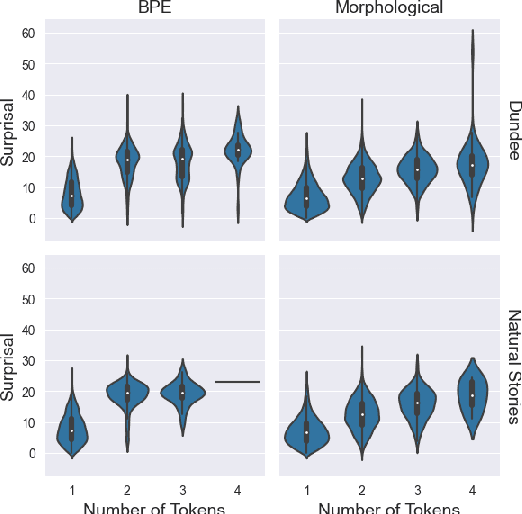
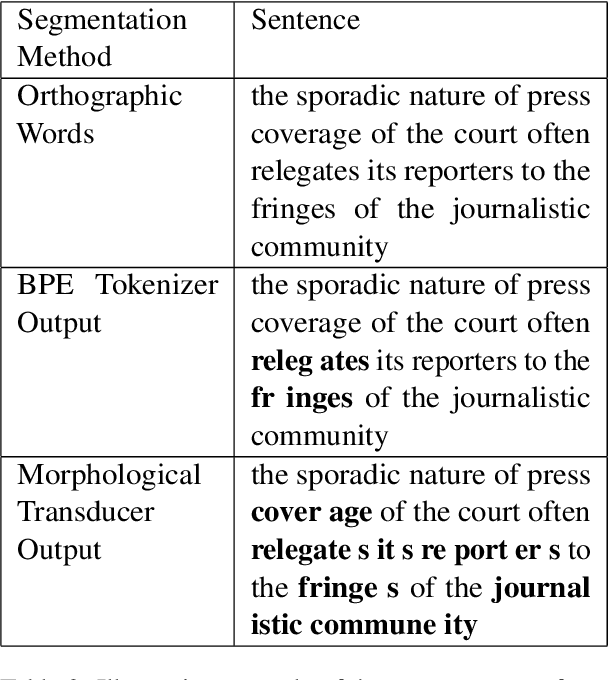
Abstract:An important assumption that comes with using LLMs on psycholinguistic data has gone unverified. LLM-based predictions are based on subword tokenization, not decomposition of words into morphemes. Does that matter? We carefully test this by comparing surprisal estimates using orthographic, morphological, and BPE tokenization against reading time data. Our results replicate previous findings and provide evidence that in the aggregate, predictions using BPE tokenization do not suffer relative to morphological and orthographic segmentation. However, a finer-grained analysis points to potential issues with relying on BPE-based tokenization, as well as providing promising results involving morphologically-aware surprisal estimates and suggesting a new method for evaluating morphological prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge