Nirupama Chandrasekaran
Conversational User-AI Intervention: A Study on Prompt Rewriting for Improved LLM Response Generation
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:Human-LLM conversations are increasingly becoming more pervasive in peoples' professional and personal lives, yet many users still struggle to elicit helpful responses from LLM Chatbots. One of the reasons for this issue is users' lack of understanding in crafting effective prompts that accurately convey their information needs. Meanwhile, the existence of real-world conversational datasets on the one hand, and the text understanding faculties of LLMs on the other, present a unique opportunity to study this problem, and its potential solutions at scale. Thus, in this paper we present the first LLM-centric study of real human-AI chatbot conversations, focused on investigating aspects in which user queries fall short of expressing information needs, and the potential of using LLMs to rewrite suboptimal user prompts. Our findings demonstrate that rephrasing ineffective prompts can elicit better responses from a conversational system, while preserving the user's original intent. Notably, the performance of rewrites improves in longer conversations, where contextual inferences about user needs can be made more accurately. Additionally, we observe that LLMs often need to -- and inherently do -- make \emph{plausible} assumptions about a user's intentions and goals when interpreting prompts. Our findings largely hold true across conversational domains, user intents, and LLMs of varying sizes and families, indicating the promise of using prompt rewriting as a solution for better human-AI interactions.
Speaking the Right Language: The Impact of Expertise Alignment in User-AI Interactions
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Using a sample of 25,000 Bing Copilot conversations, we study how the agent responds to users of varying levels of domain expertise and the resulting impact on user experience along multiple dimensions. Our findings show that across a variety of topical domains, the agent largely responds at proficient or expert levels of expertise (77% of conversations) which correlates with positive user experience regardless of the user's level of expertise. Misalignment, such that the agent responds at a level of expertise below that of the user, has a negative impact on overall user experience, with the impact more profound for more complex tasks. We also show that users engage more, as measured by the number of words in the conversation, when the agent responds at a level of expertise commensurate with that of the user. Our findings underscore the importance of alignment between user and AI when designing human-centered AI systems, to ensure satisfactory and productive interactions.
Knowledge-Augmented Large Language Models for Personalized Contextual Query Suggestion
Nov 10, 2023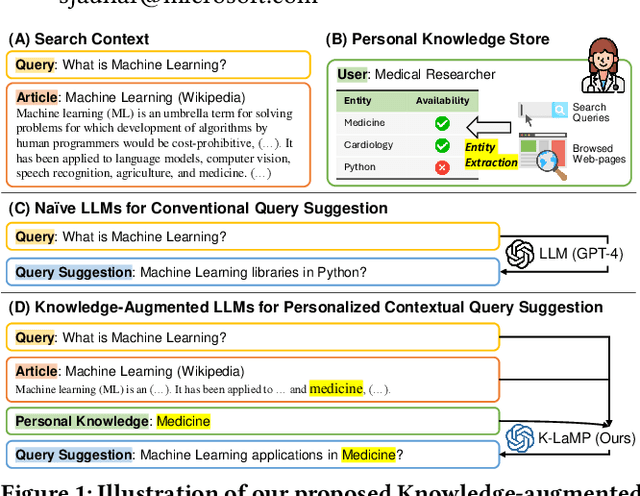


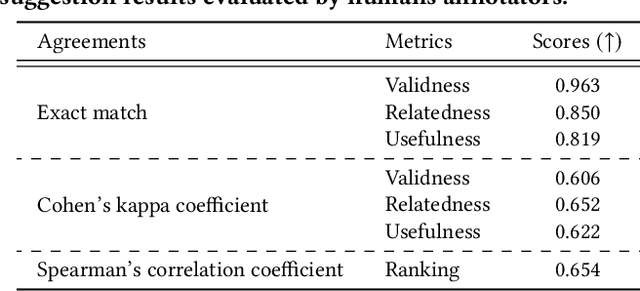
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at tackling various natural language tasks. However, due to the significant costs involved in re-training or fine-tuning them, they remain largely static and difficult to personalize. Nevertheless, a variety of applications could benefit from generations that are tailored to users' preferences, goals, and knowledge. Among them is web search, where knowing what a user is trying to accomplish, what they care about, and what they know can lead to improved search experiences. In this work, we propose a novel and general approach that augments an LLM with relevant context from users' interaction histories with a search engine in order to personalize its outputs. Specifically, we construct an entity-centric knowledge store for each user based on their search and browsing activities on the web, which is then leveraged to provide contextually relevant LLM prompt augmentations. This knowledge store is light-weight, since it only produces user-specific aggregate projections of interests and knowledge onto public knowledge graphs, and leverages existing search log infrastructure, thereby mitigating the privacy, compliance, and scalability concerns associated with building deep user profiles for personalization. We then validate our approach on the task of contextual query suggestion, which requires understanding not only the user's current search context but also what they historically know and care about. Through a number of experiments based on human evaluation, we show that our approach is significantly better than several other LLM-powered baselines, generating query suggestions that are contextually more relevant, personalized, and useful.
Modeling Tag Prediction based on Question Tagging Behavior Analysis of CommunityQA Platform Users
Jul 04, 2023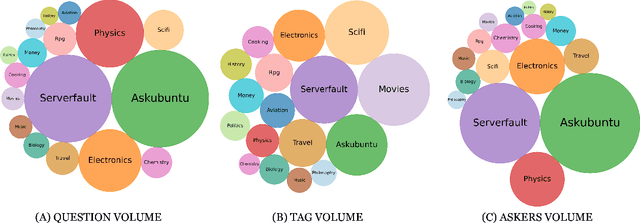
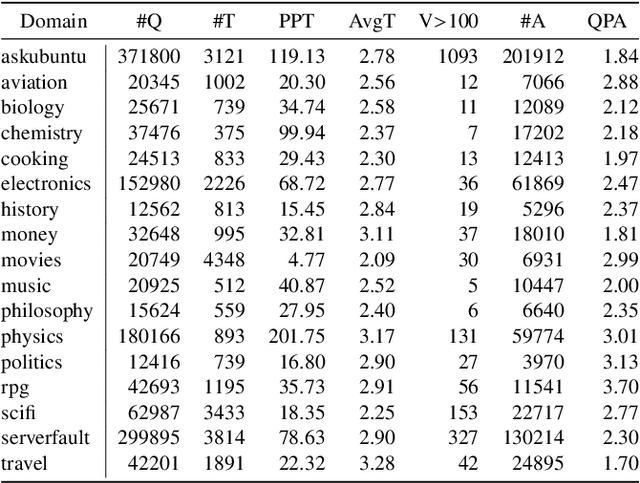
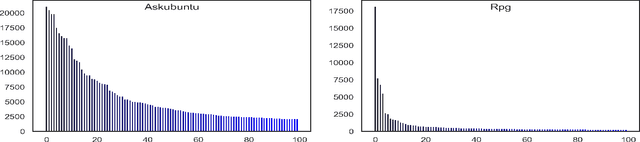
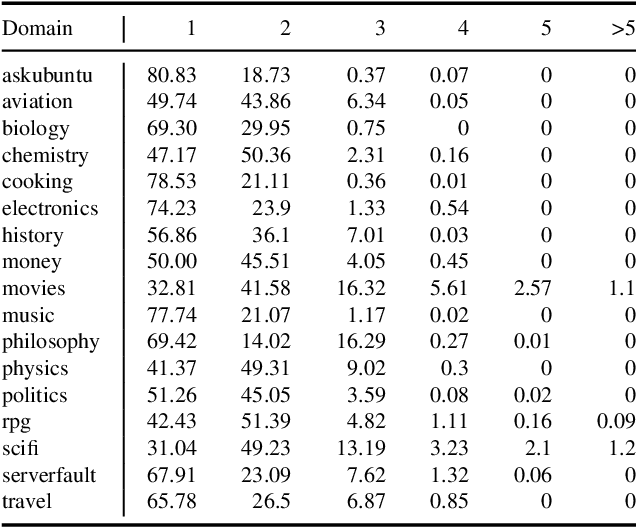
Abstract:In community question-answering platforms, tags play essential roles in effective information organization and retrieval, better question routing, faster response to questions, and assessment of topic popularity. Hence, automatic assistance for predicting and suggesting tags for posts is of high utility to users of such platforms. To develop better tag prediction across diverse communities and domains, we performed a thorough analysis of users' tagging behavior in 17 StackExchange communities. We found various common inherent properties of this behavior in those diverse domains. We used the findings to develop a flexible neural tag prediction architecture, which predicts both popular tags and more granular tags for each question. Our extensive experiments and obtained performance show the effectiveness of our model
MS-LaTTE: A Dataset of Where and When To-do Tasks are Completed
Nov 12, 2021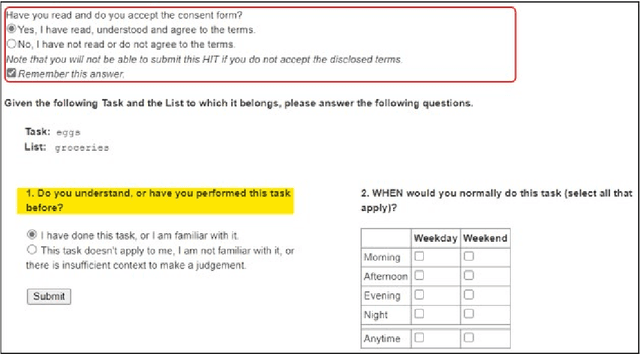
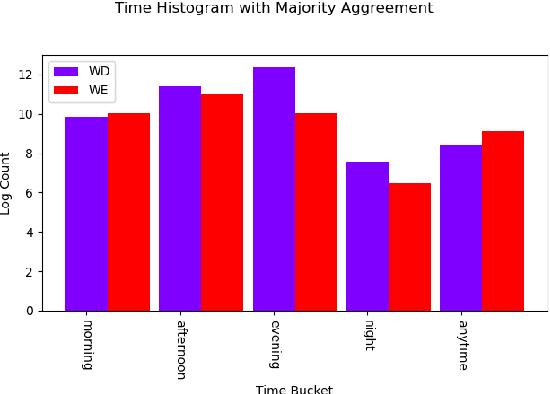
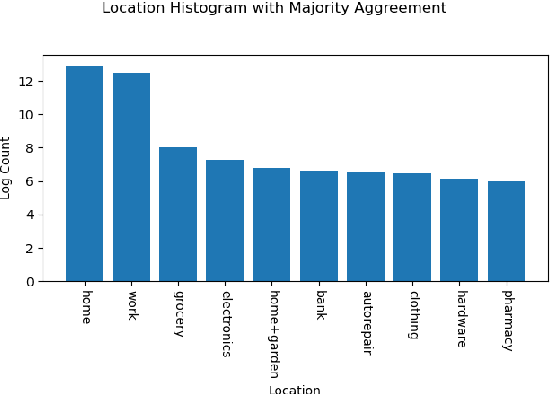
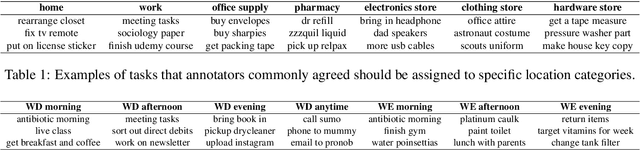
Abstract:Tasks are a fundamental unit of work in the daily lives of people, who are increasingly using digital means to keep track of, organize, triage and act on them. These digital tools -- such as task management applications -- provide a unique opportunity to study and understand tasks and their connection to the real world, and through intelligent assistance, help people be more productive. By logging signals such as text, timestamp information, and social connectivity graphs, an increasingly rich and detailed picture of how tasks are created and organized, what makes them important, and who acts on them, can be progressively developed. Yet the context around actual task completion remains fuzzy, due to the basic disconnect between actions taken in the real world and telemetry recorded in the digital world. Thus, in this paper we compile and release a novel, real-life, large-scale dataset called MS-LaTTE that captures two core aspects of the context surrounding task completion: location and time. We describe our annotation framework and conduct a number of analyses on the data that were collected, demonstrating that it captures intuitive contextual properties for common tasks. Finally, we test the dataset on the two problems of predicting spatial and temporal task co-occurrence, concluding that predictors for co-location and co-time are both learnable, with a BERT fine-tuned model outperforming several other baselines. The MS-LaTTE dataset provides an opportunity to tackle many new modeling challenges in contextual task understanding and we hope that its release will spur future research in task intelligence more broadly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge