Michael Gamon
Modeling Tag Prediction based on Question Tagging Behavior Analysis of CommunityQA Platform Users
Jul 04, 2023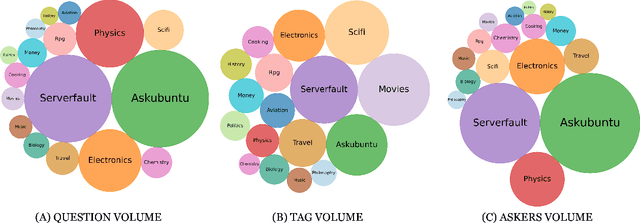
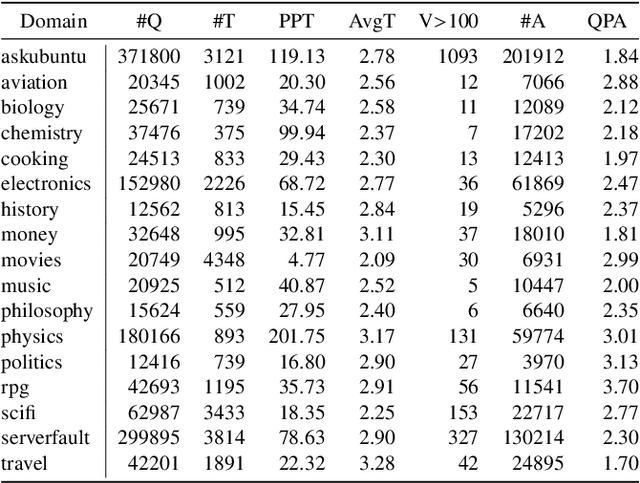
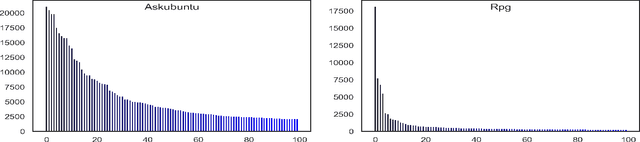
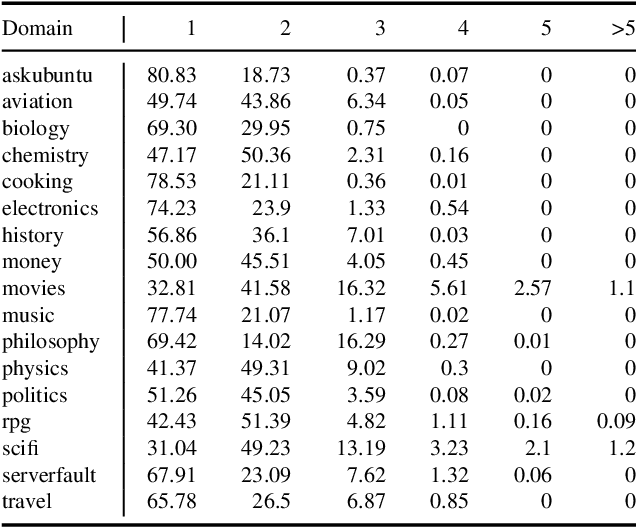
Abstract:In community question-answering platforms, tags play essential roles in effective information organization and retrieval, better question routing, faster response to questions, and assessment of topic popularity. Hence, automatic assistance for predicting and suggesting tags for posts is of high utility to users of such platforms. To develop better tag prediction across diverse communities and domains, we performed a thorough analysis of users' tagging behavior in 17 StackExchange communities. We found various common inherent properties of this behavior in those diverse domains. We used the findings to develop a flexible neural tag prediction architecture, which predicts both popular tags and more granular tags for each question. Our extensive experiments and obtained performance show the effectiveness of our model
Supporting Complex Information-Seeking Tasks with Implicit Constraints
May 02, 2022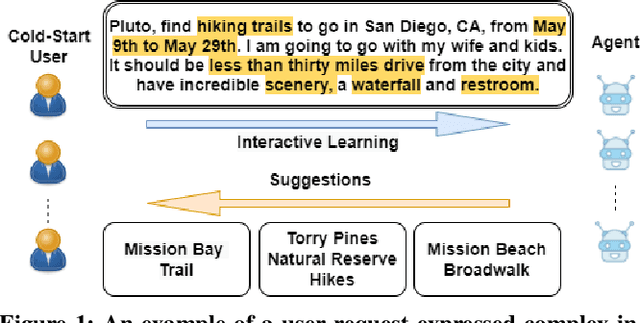
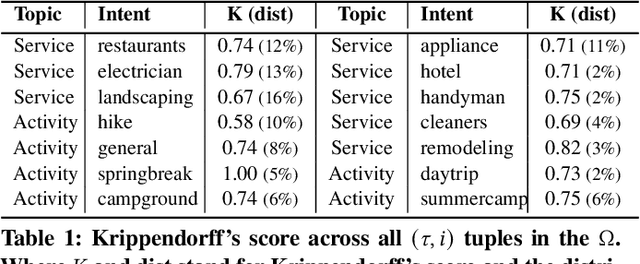
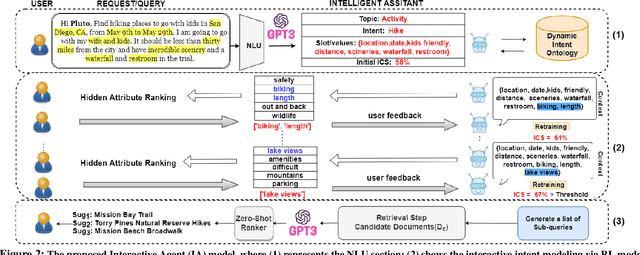
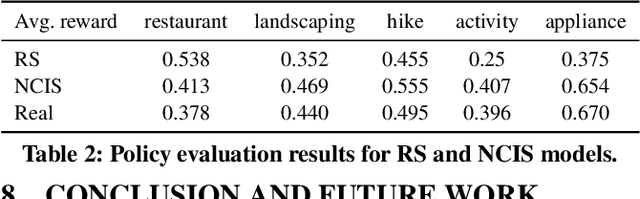
Abstract:Current interactive systems with natural language interface lack an ability to understand a complex information-seeking request which expresses several implicit constraints at once, and there is no prior information about user preferences, e.g., "find hiking trails around San Francisco which are accessible with toddlers and have beautiful scenery in summer", where output is a list of possible suggestions for users to start their exploration. In such scenarios, the user requests can be issued at once in the form of a complex and long query, unlike conversational and exploratory search models that require short utterances or queries where they often require to be fed into the system step by step. This advancement provides the final user more flexibility and precision in expressing their intent through the search process. Such systems are inherently helpful for day-today user tasks requiring planning that are usually time-consuming, sometimes tricky, and cognitively taxing. We have designed and deployed a platform to collect the data from approaching such complex interactive systems. In this paper, we propose an Interactive Agent (IA) that allows intricately refined user requests by making it complete, which should lead to better retrieval. To demonstrate the performance of the proposed modeling paradigm, we have adopted various pre-retrieval metrics that capture the extent to which guided interactions with our system yield better retrieval results. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrated that our method significantly outperforms several robust baselines
MS-LaTTE: A Dataset of Where and When To-do Tasks are Completed
Nov 12, 2021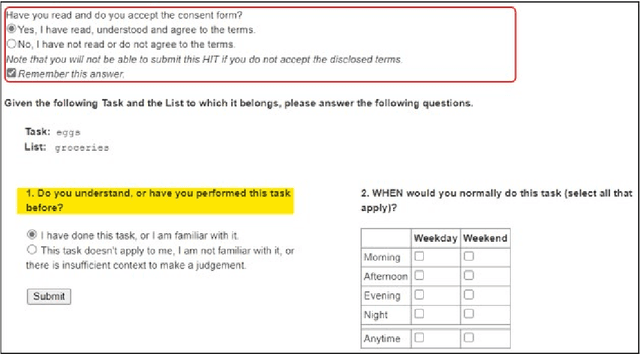
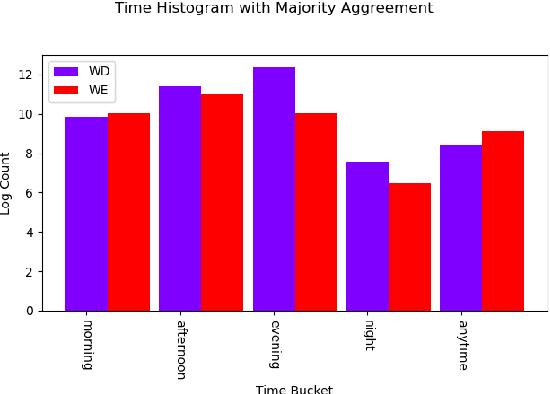
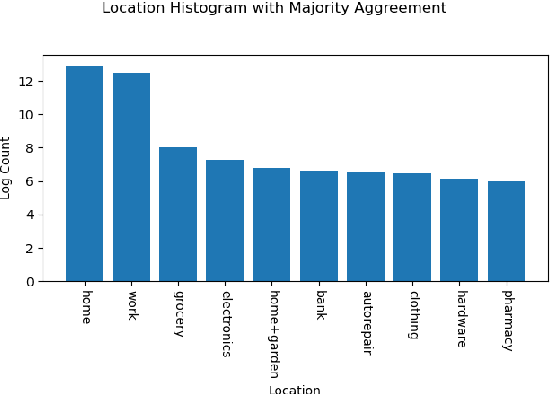
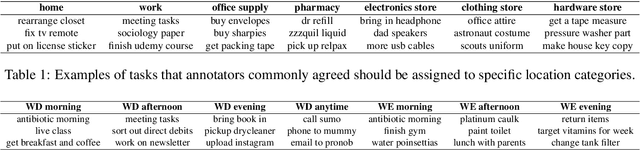
Abstract:Tasks are a fundamental unit of work in the daily lives of people, who are increasingly using digital means to keep track of, organize, triage and act on them. These digital tools -- such as task management applications -- provide a unique opportunity to study and understand tasks and their connection to the real world, and through intelligent assistance, help people be more productive. By logging signals such as text, timestamp information, and social connectivity graphs, an increasingly rich and detailed picture of how tasks are created and organized, what makes them important, and who acts on them, can be progressively developed. Yet the context around actual task completion remains fuzzy, due to the basic disconnect between actions taken in the real world and telemetry recorded in the digital world. Thus, in this paper we compile and release a novel, real-life, large-scale dataset called MS-LaTTE that captures two core aspects of the context surrounding task completion: location and time. We describe our annotation framework and conduct a number of analyses on the data that were collected, demonstrating that it captures intuitive contextual properties for common tasks. Finally, we test the dataset on the two problems of predicting spatial and temporal task co-occurrence, concluding that predictors for co-location and co-time are both learnable, with a BERT fine-tuned model outperforming several other baselines. The MS-LaTTE dataset provides an opportunity to tackle many new modeling challenges in contextual task understanding and we hope that its release will spur future research in task intelligence more broadly.
Characterizing Stage-Aware Writing Assistance in Collaborative Document Authoring
Aug 18, 2020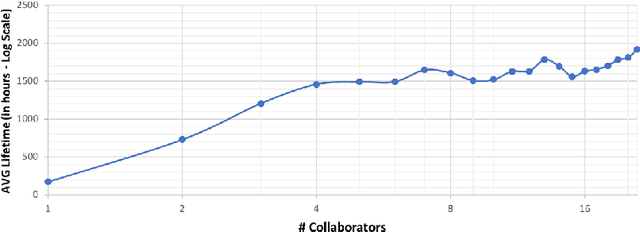
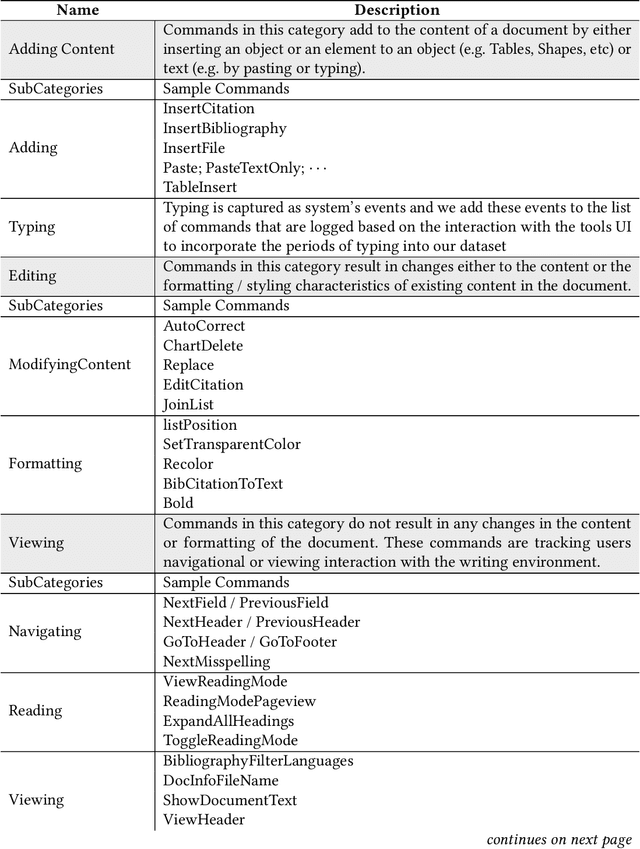
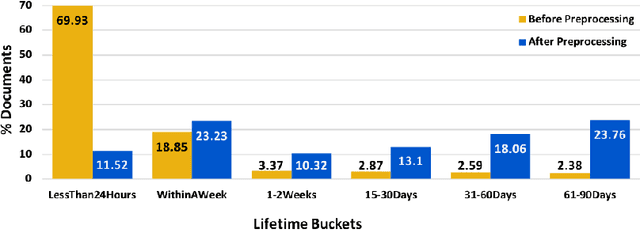
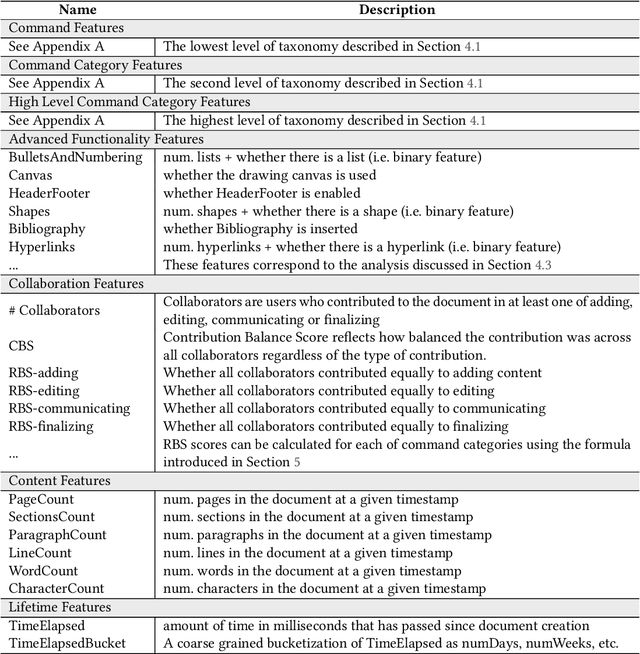
Abstract:Writing is a complex non-linear process that begins with a mental model of intent, and progresses through an outline of ideas, to words on paper (and their subsequent refinement). Despite past research in understanding writing, Web-scale consumer and enterprise collaborative digital writing environments are yet to greatly benefit from intelligent systems that understand the stages of document evolution, providing opportune assistance based on authors' situated actions and context. In this paper, we present three studies that explore temporal stages of document authoring. We first survey information workers at a large technology company about their writing habits and preferences, concluding that writers do in fact conceptually progress through several distinct phases while authoring documents. We also explore, qualitatively, how writing stages are linked to document lifespan. We supplement these qualitative findings with an analysis of the longitudinal user interaction logs of a popular digital writing platform over several million documents. Finally, as a first step towards facilitating an intelligent digital writing assistant, we conduct a preliminary investigation into the utility of user interaction log data for predicting the temporal stage of a document. Our results support the benefit of tools tailored to writing stages, identify primary tasks associated with these stages, and show that it is possible to predict stages from anonymous interaction logs. Together, these results argue for the benefit and feasibility of more tailored digital writing assistance.
* Accepted for publication at CSCW 2020
SemEval-2020 Task 7: Assessing Humor in Edited News Headlines
Aug 01, 2020

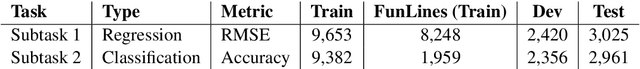
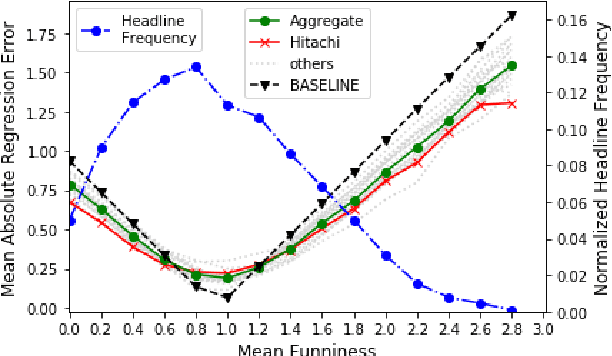
Abstract:This paper describes the SemEval-2020 shared task "Assessing Humor in Edited News Headlines." The task's dataset contains news headlines in which short edits were applied to make them funny, and the funniness of these edited headlines was rated using crowdsourcing. This task includes two subtasks, the first of which is to estimate the funniness of headlines on a humor scale in the interval 0-3. The second subtask is to predict, for a pair of edited versions of the same original headline, which is the funnier version. To date, this task is the most popular shared computational humor task, attracting 48 teams for the first subtask and 31 teams for the second.
"President Vows to Cut <Taxes> Hair": Dataset and Analysis of Creative Text Editing for Humorous Headlines
Jun 01, 2019
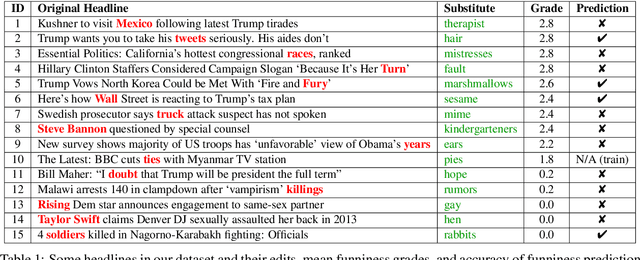
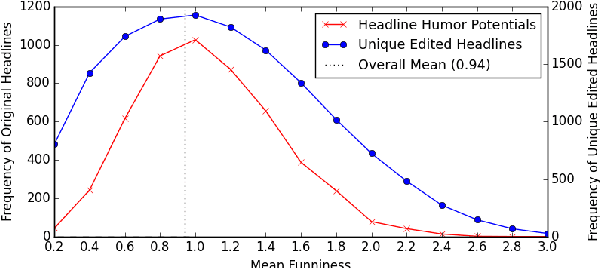
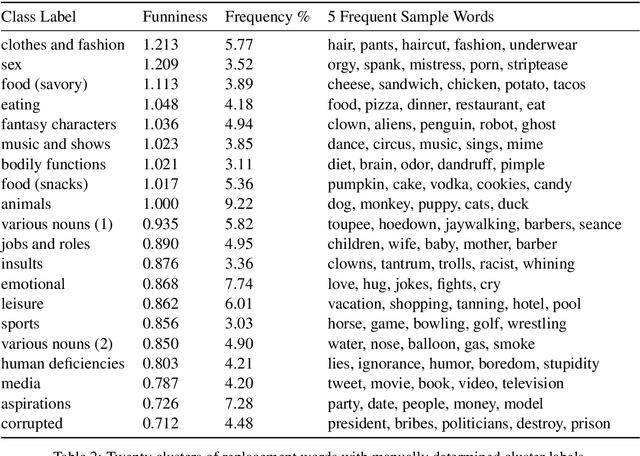
Abstract:We introduce, release, and analyze a new dataset, called Humicroedit, for research in computational humor. Our publicly available data consists of regular English news headlines paired with versions of the same headlines that contain simple replacement edits designed to make them funny. We carefully curated crowdsourced editors to create funny headlines and judges to score a to a total of 15,095 edited headlines, with five judges per headline. The simple edits, usually just a single word replacement, mean we can apply straightforward analysis techniques to determine what makes our edited headlines humorous. We show how the data support classic theories of humor, such as incongruity, superiority, and setup/punchline. Finally, we develop baseline classifiers that can predict whether or not an edited headline is funny, which is a first step toward automatically generating humorous headlines as an approach to creating topical humor.
Neural Task Representations as Weak Supervision for Model Agnostic Cross-Lingual Transfer
Nov 02, 2018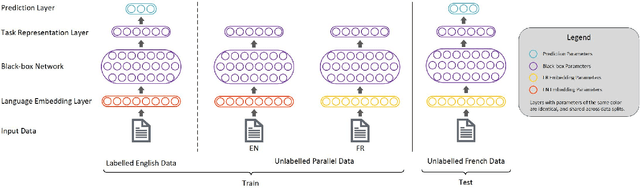
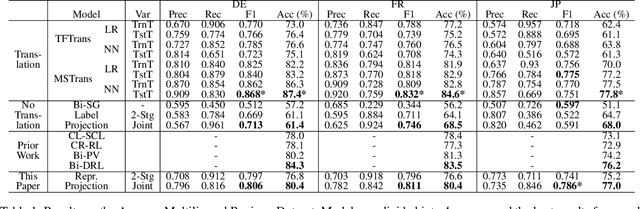
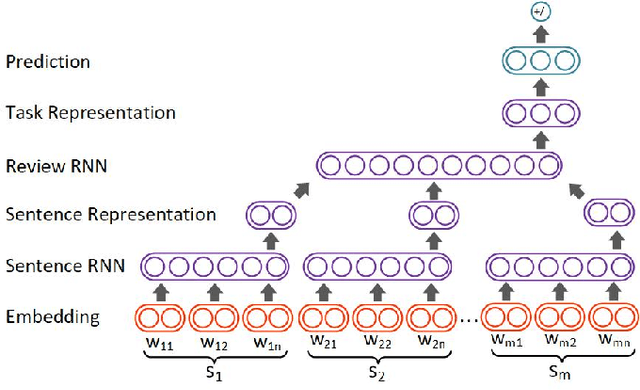
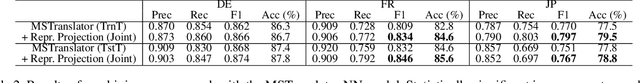
Abstract:Natural language processing is heavily Anglo-centric, while the demand for models that work in languages other than English is greater than ever. Yet, the task of transferring a model from one language to another can be expensive in terms of annotation costs, engineering time and effort. In this paper, we present a general framework for easily and effectively transferring neural models from English to other languages. The framework, which relies on task representations as a form of weak supervision, is model and task agnostic, meaning that many existing neural architectures can be ported to other languages with minimal effort. The only requirement is unlabeled parallel data, and a loss defined over task representations. We evaluate our framework by transferring an English sentiment classifier to three different languages. On a battery of tests, we show that our models outperform a number of strong baselines and rival state-of-the-art results, which rely on more complex approaches and significantly more resources and data. Additionally, we find that the framework proposed in this paper is able to capture semantically rich and meaningful representations across languages, despite the lack of direct supervision.
Actionable Email Intent Modeling with Reparametrized RNNs
Dec 26, 2017
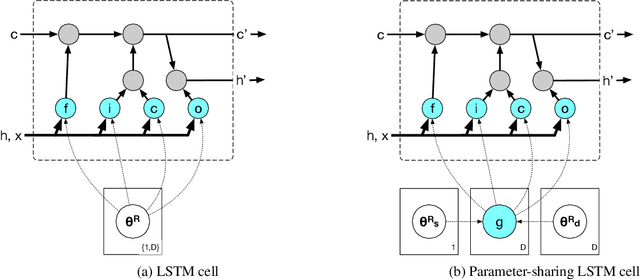
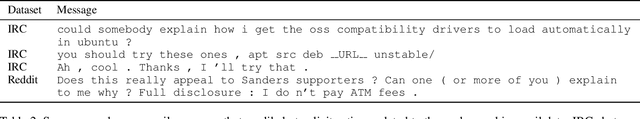
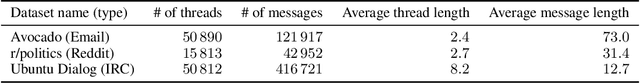
Abstract:Emails in the workplace are often intentional calls to action for its recipients. We propose to annotate these emails for what action its recipient will take. We argue that our approach of action-based annotation is more scalable and theory-agnostic than traditional speech-act-based email intent annotation, while still carrying important semantic and pragmatic information. We show that our action-based annotation scheme achieves good inter-annotator agreement. We also show that we can leverage threaded messages from other domains, which exhibit comparable intents in their conversation, with domain adaptive RAINBOW (Recurrently AttentIve Neural Bag-Of-Words). On a collection of datasets consisting of IRC, Reddit, and email, our reparametrized RNNs outperform common multitask/multidomain approaches on several speech act related tasks. We also experiment with a minimally supervised scenario of email recipient action classification, and find the reparametrized RNNs learn a useful representation.
Mark My Words! Linguistic Style Accommodation in Social Media
May 03, 2011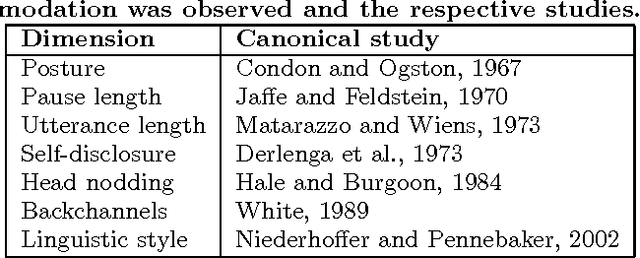
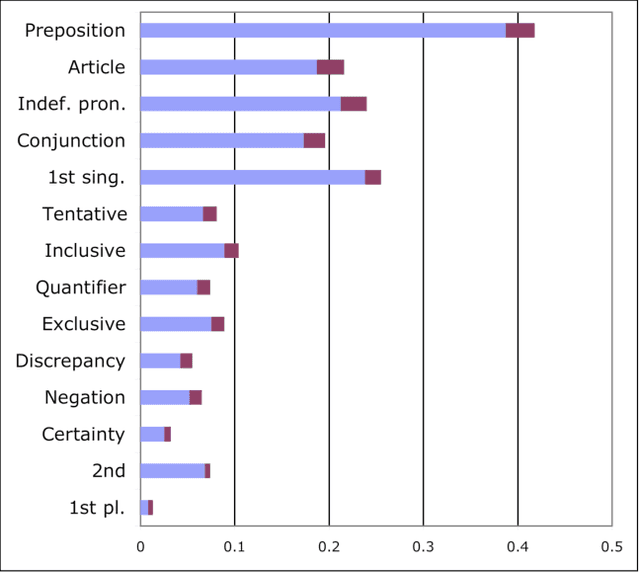
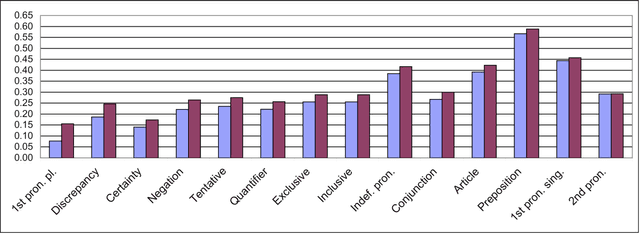
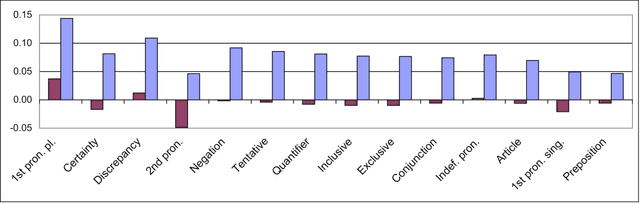
Abstract:The psycholinguistic theory of communication accommodation accounts for the general observation that participants in conversations tend to converge to one another's communicative behavior: they coordinate in a variety of dimensions including choice of words, syntax, utterance length, pitch and gestures. In its almost forty years of existence, this theory has been empirically supported exclusively through small-scale or controlled laboratory studies. Here we address this phenomenon in the context of Twitter conversations. Undoubtedly, this setting is unlike any other in which accommodation was observed and, thus, challenging to the theory. Its novelty comes not only from its size, but also from the non real-time nature of conversations, from the 140 character length restriction, from the wide variety of social relation types, and from a design that was initially not geared towards conversation at all. Given such constraints, it is not clear a priori whether accommodation is robust enough to occur given the constraints of this new environment. To investigate this, we develop a probabilistic framework that can model accommodation and measure its effects. We apply it to a large Twitter conversational dataset specifically developed for this task. This is the first time the hypothesis of linguistic style accommodation has been examined (and verified) in a large scale, real world setting. Furthermore, when investigating concepts such as stylistic influence and symmetry of accommodation, we discover a complexity of the phenomenon which was never observed before. We also explore the potential relation between stylistic influence and network features commonly associated with social status.
* Talk slides available at http://www.cs.cornell.edu/~cristian/www2011
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge