Patrick Pantel
Preserving Integrity in Online Social Networks
Sep 25, 2020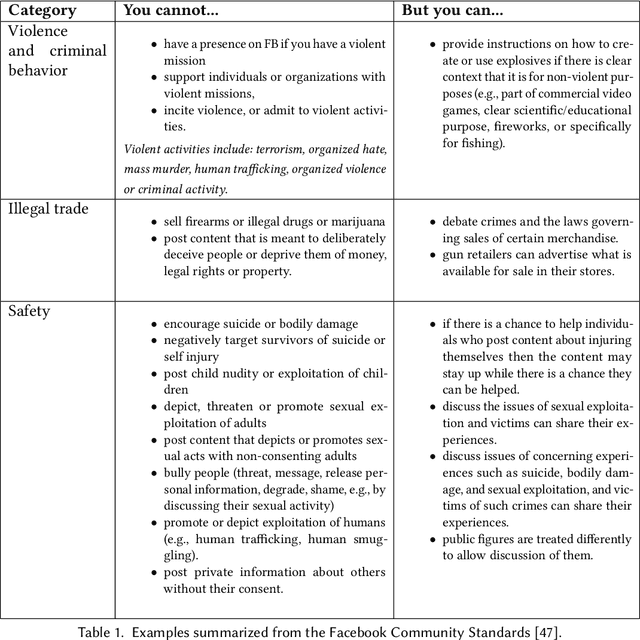
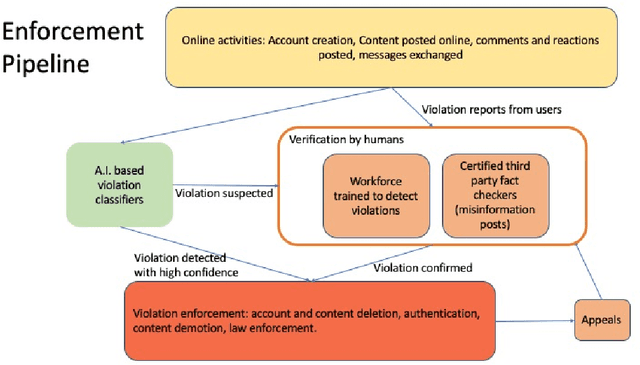
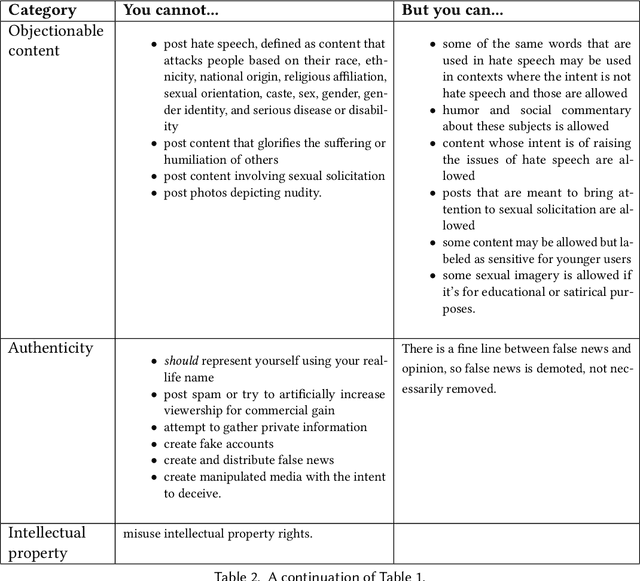
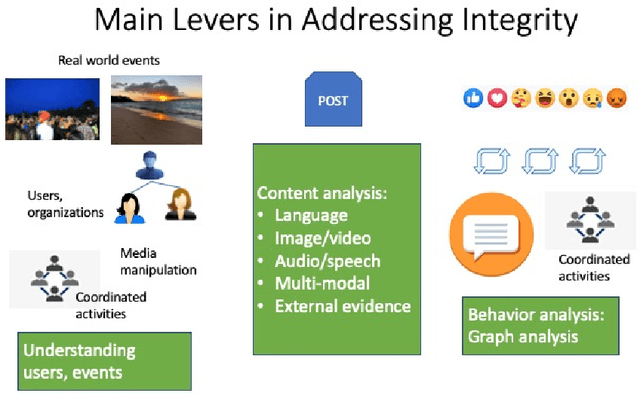
Abstract:Online social networks provide a platform for sharing information and free expression. However, these networks are also used for malicious purposes, such as distributing misinformation and hate speech, selling illegal drugs, and coordinating sex trafficking or child exploitation. This paper surveys the state of the art in keeping online platforms and their users safe from such harm, also known as the problem of preserving integrity. This survey comes from the perspective of having to combat a broad spectrum of integrity violations at Facebook. We highlight the techniques that have been proven useful in practice and that deserve additional attention from the academic community. Instead of discussing the many individual violation types, we identify key aspects of the social-media eco-system, each of which is common to a wide variety violation types. Furthermore, each of these components represents an area for research and development, and the innovations that are found can be applied widely.
Neural Task Representations as Weak Supervision for Model Agnostic Cross-Lingual Transfer
Nov 02, 2018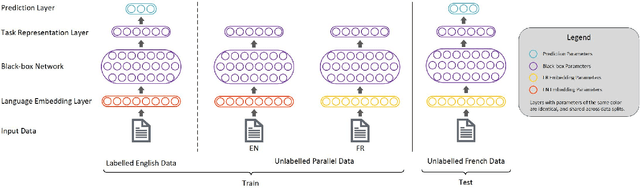
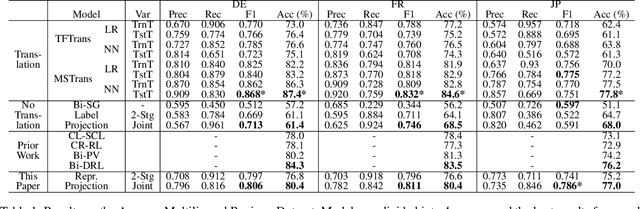
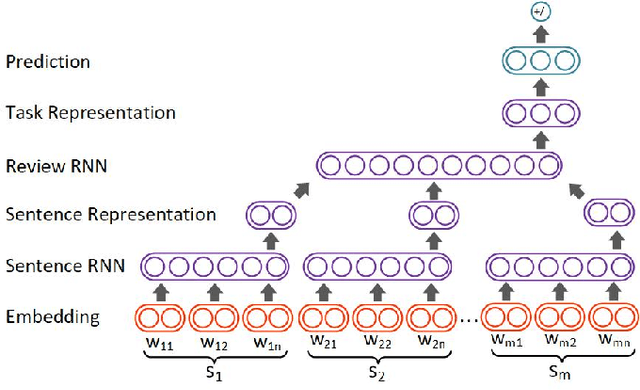
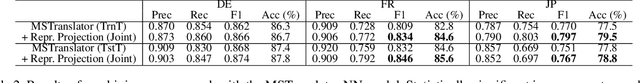
Abstract:Natural language processing is heavily Anglo-centric, while the demand for models that work in languages other than English is greater than ever. Yet, the task of transferring a model from one language to another can be expensive in terms of annotation costs, engineering time and effort. In this paper, we present a general framework for easily and effectively transferring neural models from English to other languages. The framework, which relies on task representations as a form of weak supervision, is model and task agnostic, meaning that many existing neural architectures can be ported to other languages with minimal effort. The only requirement is unlabeled parallel data, and a loss defined over task representations. We evaluate our framework by transferring an English sentiment classifier to three different languages. On a battery of tests, we show that our models outperform a number of strong baselines and rival state-of-the-art results, which rely on more complex approaches and significantly more resources and data. Additionally, we find that the framework proposed in this paper is able to capture semantically rich and meaningful representations across languages, despite the lack of direct supervision.
Actionable Email Intent Modeling with Reparametrized RNNs
Dec 26, 2017
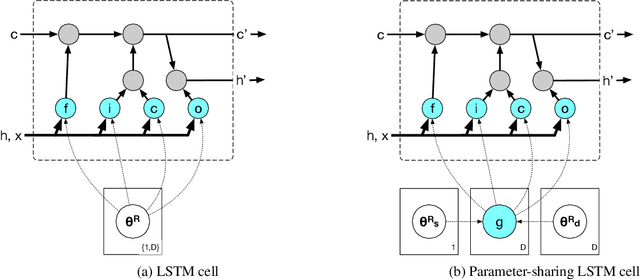
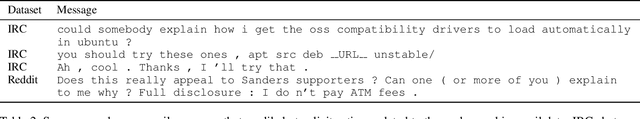
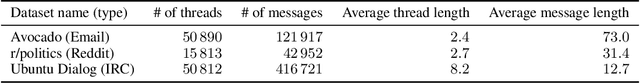
Abstract:Emails in the workplace are often intentional calls to action for its recipients. We propose to annotate these emails for what action its recipient will take. We argue that our approach of action-based annotation is more scalable and theory-agnostic than traditional speech-act-based email intent annotation, while still carrying important semantic and pragmatic information. We show that our action-based annotation scheme achieves good inter-annotator agreement. We also show that we can leverage threaded messages from other domains, which exhibit comparable intents in their conversation, with domain adaptive RAINBOW (Recurrently AttentIve Neural Bag-Of-Words). On a collection of datasets consisting of IRC, Reddit, and email, our reparametrized RNNs outperform common multitask/multidomain approaches on several speech act related tasks. We also experiment with a minimally supervised scenario of email recipient action classification, and find the reparametrized RNNs learn a useful representation.
From Frequency to Meaning: Vector Space Models of Semantics
Mar 04, 2010

Abstract:Computers understand very little of the meaning of human language. This profoundly limits our ability to give instructions to computers, the ability of computers to explain their actions to us, and the ability of computers to analyse and process text. Vector space models (VSMs) of semantics are beginning to address these limits. This paper surveys the use of VSMs for semantic processing of text. We organize the literature on VSMs according to the structure of the matrix in a VSM. There are currently three broad classes of VSMs, based on term-document, word-context, and pair-pattern matrices, yielding three classes of applications. We survey a broad range of applications in these three categories and we take a detailed look at a specific open source project in each category. Our goal in this survey is to show the breadth of applications of VSMs for semantics, to provide a new perspective on VSMs for those who are already familiar with the area, and to provide pointers into the literature for those who are less familiar with the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge