Mark My Words! Linguistic Style Accommodation in Social Media
Paper and Code
May 03, 2011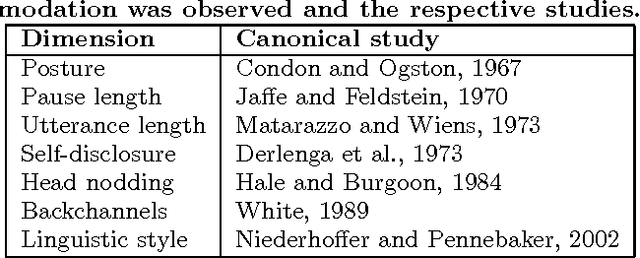
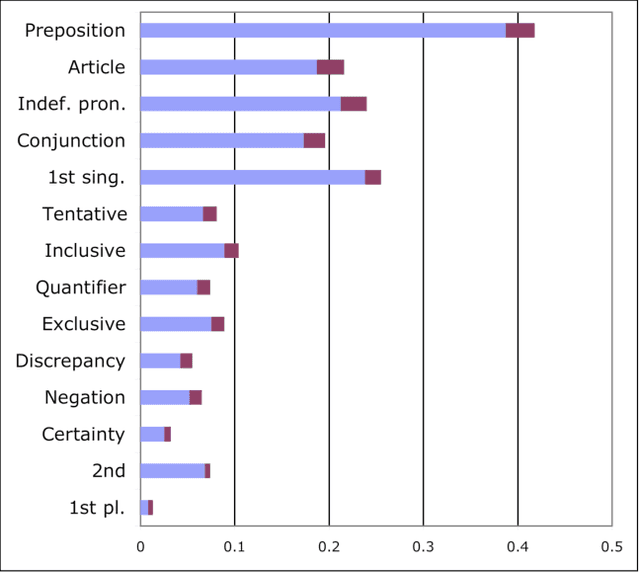
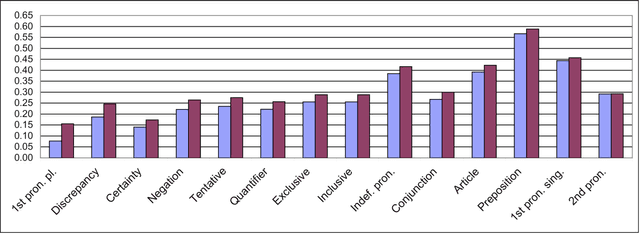
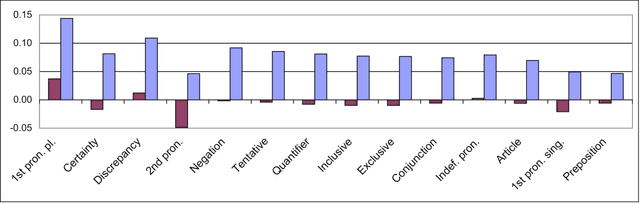
The psycholinguistic theory of communication accommodation accounts for the general observation that participants in conversations tend to converge to one another's communicative behavior: they coordinate in a variety of dimensions including choice of words, syntax, utterance length, pitch and gestures. In its almost forty years of existence, this theory has been empirically supported exclusively through small-scale or controlled laboratory studies. Here we address this phenomenon in the context of Twitter conversations. Undoubtedly, this setting is unlike any other in which accommodation was observed and, thus, challenging to the theory. Its novelty comes not only from its size, but also from the non real-time nature of conversations, from the 140 character length restriction, from the wide variety of social relation types, and from a design that was initially not geared towards conversation at all. Given such constraints, it is not clear a priori whether accommodation is robust enough to occur given the constraints of this new environment. To investigate this, we develop a probabilistic framework that can model accommodation and measure its effects. We apply it to a large Twitter conversational dataset specifically developed for this task. This is the first time the hypothesis of linguistic style accommodation has been examined (and verified) in a large scale, real world setting. Furthermore, when investigating concepts such as stylistic influence and symmetry of accommodation, we discover a complexity of the phenomenon which was never observed before. We also explore the potential relation between stylistic influence and network features commonly associated with social status.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge