Andreas Opedal
MathGAP: Out-of-Distribution Evaluation on Problems with Arbitrarily Complex Proofs
Oct 17, 2024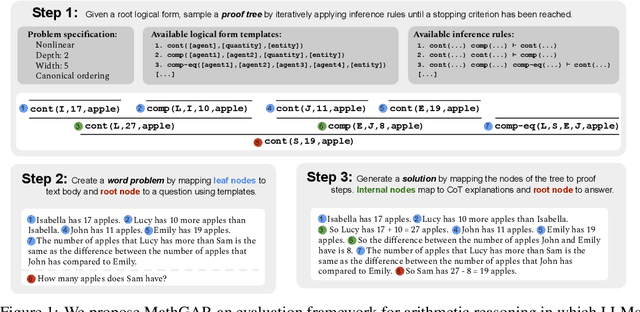

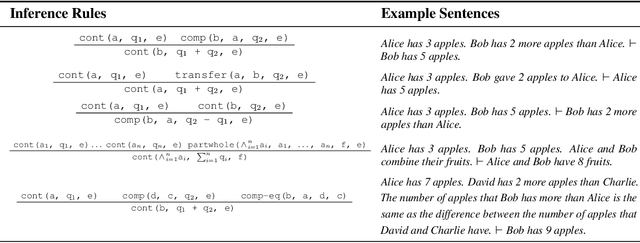
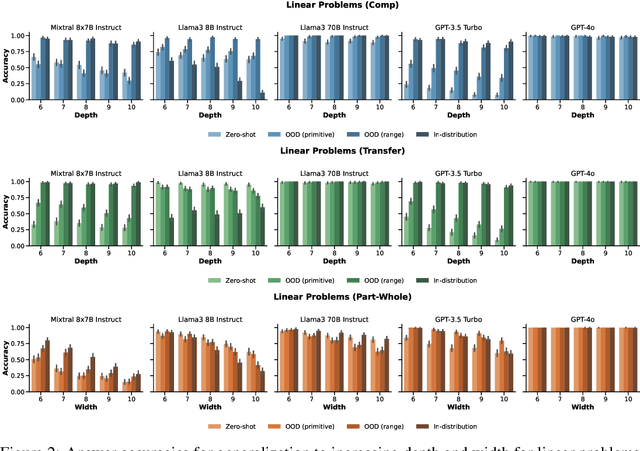
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can solve arithmetic word problems with high accuracy, but little is known about how well they generalize to problems that are more complex than the ones on which they have been trained. Empirical investigations of such questions are impeded by two major flaws of current evaluations: (i) much of the evaluation data is contaminated, in the sense that it has already been seen during training, and (ii) benchmark datasets do not capture how problem proofs may be arbitrarily complex in various ways. As a step towards addressing these issues, we present a framework for evaluating LLMs on problems that have arbitrarily complex arithmetic proofs, called MathGAP. MathGAP generates problems that follow fixed proof specifications -- along with chain-of-thought reasoning annotations -- enabling systematic studies on generalization with respect to arithmetic proof complexity. We apply MathGAP to analyze how in-context learning interacts with generalization to problems that have more complex proofs. We find that among the models tested, most show a significant decrease in performance as proofs get deeper and wider. This effect is more pronounced in complex, nonlinear proof structures, which are challenging even for GPT-4o. Surprisingly, providing in-context examples from the same distribution as the test set is not always beneficial for performance. In particular, zero-shot prompting as well as demonstrating a diverse range of examples that are less complex than the test data sometimes yield similar or higher accuracies.
Generalized Measures of Anticipation and Responsivity in Online Language Processing
Sep 16, 2024



Abstract:We introduce a generalization of classic information-theoretic measures of predictive uncertainty in online language processing, based on the simulation of expected continuations of incremental linguistic contexts. Our framework provides a formal definition of anticipatory and responsive measures, and it equips experimenters with the tools to define new, more expressive measures beyond standard next-symbol entropy and surprisal. While extracting these standard quantities from language models is convenient, we demonstrate that using Monte Carlo simulation to estimate alternative responsive and anticipatory measures pays off empirically: New special cases of our generalized formula exhibit enhanced predictive power compared to surprisal for human cloze completion probability as well as ELAN, LAN, and N400 amplitudes, and greater complementarity with surprisal in predicting reading times.
On the Role of Context in Reading Time Prediction
Sep 12, 2024



Abstract:We present a new perspective on how readers integrate context during real-time language comprehension. Our proposals build on surprisal theory, which posits that the processing effort of a linguistic unit (e.g., a word) is an affine function of its in-context information content. We first observe that surprisal is only one out of many potential ways that a contextual predictor can be derived from a language model. Another one is the pointwise mutual information (PMI) between a unit and its context, which turns out to yield the same predictive power as surprisal when controlling for unigram frequency. Moreover, both PMI and surprisal are correlated with frequency. This means that neither PMI nor surprisal contains information about context alone. In response to this, we propose a technique where we project surprisal onto the orthogonal complement of frequency, yielding a new contextual predictor that is uncorrelated with frequency. Our experiments show that the proportion of variance in reading times explained by context is a lot smaller when context is represented by the orthogonalized predictor. From an interpretability standpoint, this indicates that previous studies may have overstated the role that context has in predicting reading times.
Do Language Models Exhibit the Same Cognitive Biases in Problem Solving as Human Learners?
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:There is increasing interest in employing large language models (LLMs) as cognitive models. For such purposes, it is central to understand which cognitive properties are well-modeled by LLMs, and which are not. In this work, we study the biases of LLMs in relation to those known in children when solving arithmetic word problems. Surveying the learning science literature, we posit that the problem-solving process can be split into three distinct steps: text comprehension, solution planning and solution execution. We construct tests for each one in order to understand which parts of this process can be faithfully modeled by current state-of-the-art LLMs. We generate a novel set of word problems for each of these tests, using a neuro-symbolic method that enables fine-grained control over the problem features. We find evidence that LLMs, with and without instruction-tuning, exhibit human-like biases in both the text-comprehension and the solution-planning steps of the solving process, but not during the final step which relies on the problem's arithmetic expressions (solution execution).
An Exploration of Left-Corner Transformations
Nov 27, 2023



Abstract:The left-corner transformation (Rosenkrantz and Lewis, 1970) is used to remove left recursion from context-free grammars, which is an important step towards making the grammar parsable top-down with simple techniques. This paper generalizes prior left-corner transformations to support semiring-weighted production rules and to provide finer-grained control over which left corners may be moved. Our generalized left-corner transformation (GLCT) arose from unifying the left-corner transformation and speculation transformation (Eisner and Blatz, 2007), originally for logic programming. Our new transformation and speculation define equivalent weighted languages. Yet, their derivation trees are structurally different in an important way: GLCT replaces left recursion with right recursion, and speculation does not. We also provide several technical results regarding the formal relationships between the outputs of GLCT, speculation, and the original grammar. Lastly, we empirically investigate the efficiency of GLCT for left-recursion elimination from grammars of nine languages.
Efficient Semiring-Weighted Earley Parsing
Jul 06, 2023
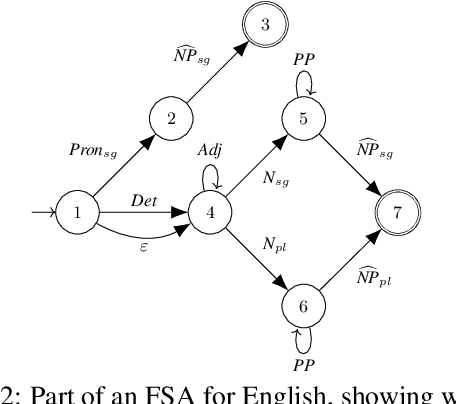

Abstract:This paper provides a reference description, in the form of a deduction system, of Earley's (1970) context-free parsing algorithm with various speed-ups. Our presentation includes a known worst-case runtime improvement from Earley's $O (N^3|G||R|)$, which is unworkable for the large grammars that arise in natural language processing, to $O (N^3|G|)$, which matches the runtime of CKY on a binarized version of the grammar $G$. Here $N$ is the length of the sentence, $|R|$ is the number of productions in $G$, and $|G|$ is the total length of those productions. We also provide a version that achieves runtime of $O (N^3|M|)$ with $|M| \leq |G|$ when the grammar is represented compactly as a single finite-state automaton $M$ (this is partly novel). We carefully treat the generalization to semiring-weighted deduction, preprocessing the grammar like Stolcke (1995) to eliminate deduction cycles, and further generalize Stolcke's method to compute the weights of sentence prefixes. We also provide implementation details for efficient execution, ensuring that on a preprocessed grammar, the semiring-weighted versions of our methods have the same asymptotic runtime and space requirements as the unweighted methods, including sub-cubic runtime on some grammars.
World Models for Math Story Problems
Jun 07, 2023
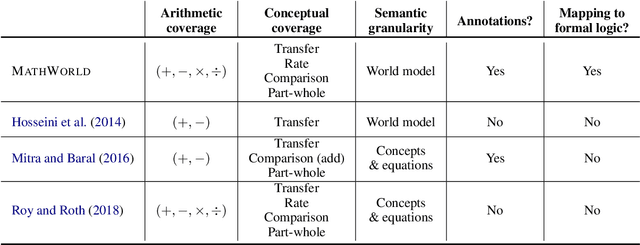
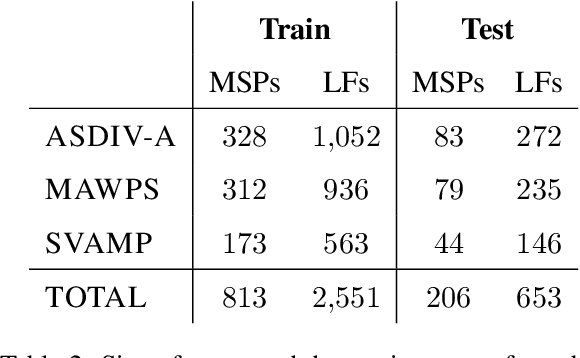
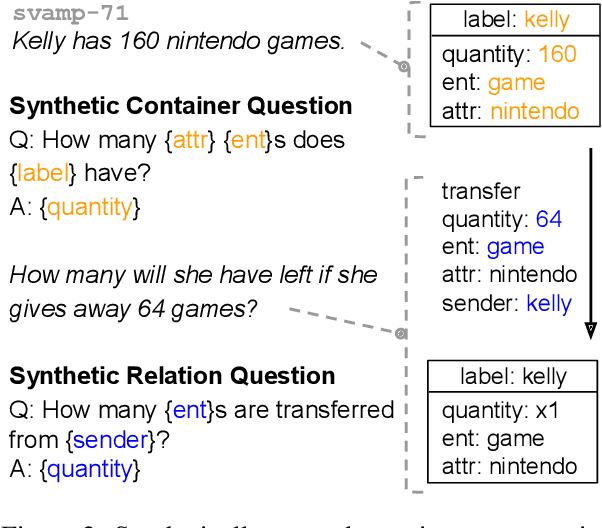
Abstract:Solving math story problems is a complex task for students and NLP models alike, requiring them to understand the world as described in the story and reason over it to compute an answer. Recent years have seen impressive performance on automatically solving these problems with large pre-trained language models and innovative techniques to prompt them. However, it remains unclear if these models possess accurate representations of mathematical concepts. This leads to lack of interpretability and trustworthiness which impedes their usefulness in various applications. In this paper, we consolidate previous work on categorizing and representing math story problems and develop MathWorld, which is a graph-based semantic formalism specific for the domain of math story problems. With MathWorld, we can assign world models to math story problems which represent the situations and actions introduced in the text and their mathematical relationships. We combine math story problems from several existing datasets and annotate a corpus of 1,019 problems and 3,204 logical forms with MathWorld. Using this data, we demonstrate the following use cases of MathWorld: (1) prompting language models with synthetically generated question-answer pairs to probe their reasoning and world modeling abilities, and (2) generating new problems by using the world models as a design space.
On the Intersection of Context-Free and Regular Languages
Sep 14, 2022
Abstract:The Bar-Hillel construction is a classic result in formal language theory. It shows, by construction, that the intersection between a context-free language and a regular language is itself context-free. However, neither its original formulation (Bar-Hillel et al., 1961) nor its weighted extension (Nederhof and Satta, 2003) can handle automata with $\epsilon$-arcs. In this short note, we generalize the Bar-Hillel construction to correctly compute the intersection even when the automaton contains $\epsilon$-arcs. We further prove that our generalized construction leads to a grammar that encodes the structure of both the input automaton and grammar while retaining the asymptotic size of the original construction.
Slangvolution: A Causal Analysis of Semantic Change and Frequency Dynamics in Slang
Mar 09, 2022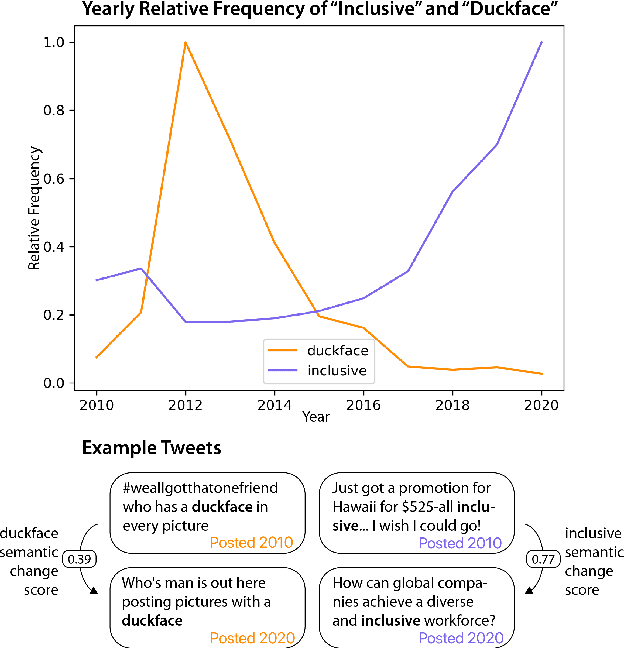

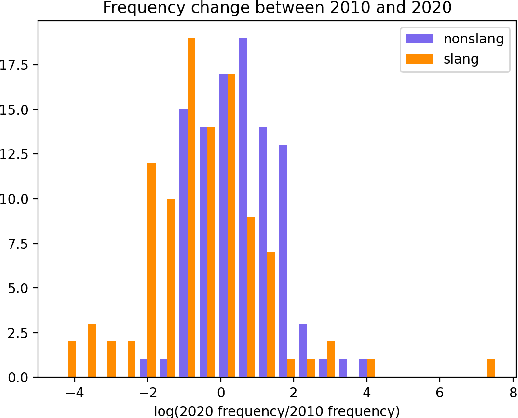
Abstract:Languages are continuously undergoing changes, and the mechanisms that underlie these changes are still a matter of debate. In this work, we approach language evolution through the lens of causality in order to model not only how various distributional factors associate with language change, but how they causally affect it. In particular, we study slang, which is an informal language that is typically restricted to a specific group or social setting. We analyze the semantic change and frequency shift of slang words and compare them to those of standard, nonslang words. With causal discovery and causal inference techniques, we measure the effect that word type (slang/nonslang) has on both semantic change and frequency shift, as well as its relationship to frequency, polysemy and part of speech. Our analysis provides some new insights in the study of semantic change, e.g., we show that slang words undergo less semantic change but tend to have larger frequency shifts over time.
Recovering Barabási-Albert Parameters of Graphs through Disentanglement
May 04, 2021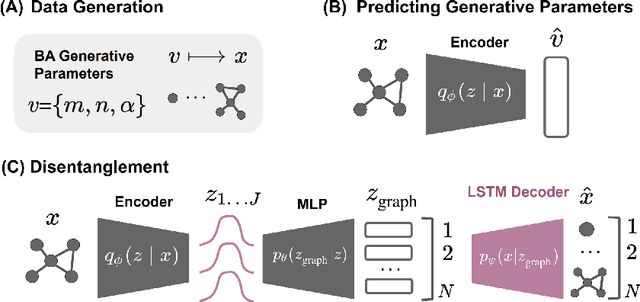
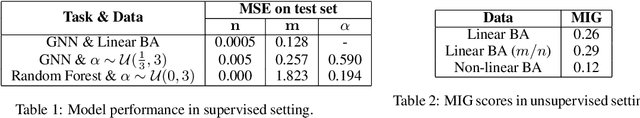

Abstract:Classical graph modeling approaches such as Erd\H{o}s R\'{e}nyi (ER) random graphs or Barab\'asi-Albert (BA) graphs, here referred to as stylized models, aim to reproduce properties of real-world graphs in an interpretable way. While useful, graph generation with stylized models requires domain knowledge and iterative trial and error simulation. Previous work by Stoehr et al. (2019) addresses these issues by learning the generation process from graph data, using a disentanglement-focused deep autoencoding framework, more specifically, a $\beta$-Variational Autoencoder ($\beta$-VAE). While they successfully recover the generative parameters of ER graphs through the model's latent variables, their model performs badly on sequentially generated graphs such as BA graphs, due to their oversimplified decoder. We focus on recovering the generative parameters of BA graphs by replacing their $\beta$-VAE decoder with a sequential one. We first learn the generative BA parameters in a supervised fashion using a Graph Neural Network (GNN) and a Random Forest Regressor, by minimizing the squared loss between the true generative parameters and the latent variables. Next, we train a $\beta$-VAE model, combining the GNN encoder from the first stage with an LSTM-based decoder with a customized loss.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge