Christian Simon
LIM\&BIO
SoundReactor: Frame-level Online Video-to-Audio Generation
Oct 02, 2025



Abstract:Prevailing Video-to-Audio (V2A) generation models operate offline, assuming an entire video sequence or chunks of frames are available beforehand. This critically limits their use in interactive applications such as live content creation and emerging generative world models. To address this gap, we introduce the novel task of frame-level online V2A generation, where a model autoregressively generates audio from video without access to future video frames. Furthermore, we propose SoundReactor, which, to the best of our knowledge, is the first simple yet effective framework explicitly tailored for this task. Our design enforces end-to-end causality and targets low per-frame latency with audio-visual synchronization. Our model's backbone is a decoder-only causal transformer over continuous audio latents. For vision conditioning, it leverages grid (patch) features extracted from the smallest variant of the DINOv2 vision encoder, which are aggregated into a single token per frame to maintain end-to-end causality and efficiency. The model is trained through a diffusion pre-training followed by consistency fine-tuning to accelerate the diffusion head decoding. On a benchmark of diverse gameplay videos from AAA titles, our model successfully generates semantically and temporally aligned, high-quality full-band stereo audio, validated by both objective and human evaluations. Furthermore, our model achieves low per-frame waveform-level latency (26.3ms with the head NFE=1, 31.5ms with NFE=4) on 30FPS, 480p videos using a single H100. Demo samples are available at https://koichi-saito-sony.github.io/soundreactor/.
TITAN-Guide: Taming Inference-Time AligNment for Guided Text-to-Video Diffusion Models
Aug 01, 2025



Abstract:In the recent development of conditional diffusion models still require heavy supervised fine-tuning for performing control on a category of tasks. Training-free conditioning via guidance with off-the-shelf models is a favorable alternative to avoid further fine-tuning on the base model. However, the existing training-free guidance frameworks either have heavy memory requirements or offer sub-optimal control due to rough estimation. These shortcomings limit the applicability to control diffusion models that require intense computation, such as Text-to-Video (T2V) diffusion models. In this work, we propose Taming Inference Time Alignment for Guided Text-to-Video Diffusion Model, so-called TITAN-Guide, which overcomes memory space issues, and provides more optimal control in the guidance process compared to the counterparts. In particular, we develop an efficient method for optimizing diffusion latents without backpropagation from a discriminative guiding model. In particular, we study forward gradient descents for guided diffusion tasks with various options on directional directives. In our experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in efficiently managing memory during latent optimization, while previous methods fall short. Our proposed approach not only minimizes memory requirements but also significantly enhances T2V performance across a range of diffusion guidance benchmarks. Code, models, and demo are available at https://titanguide.github.io.
Crowdsource, Crawl, or Generate? Creating SEA-VL, a Multicultural Vision-Language Dataset for Southeast Asia
Mar 10, 2025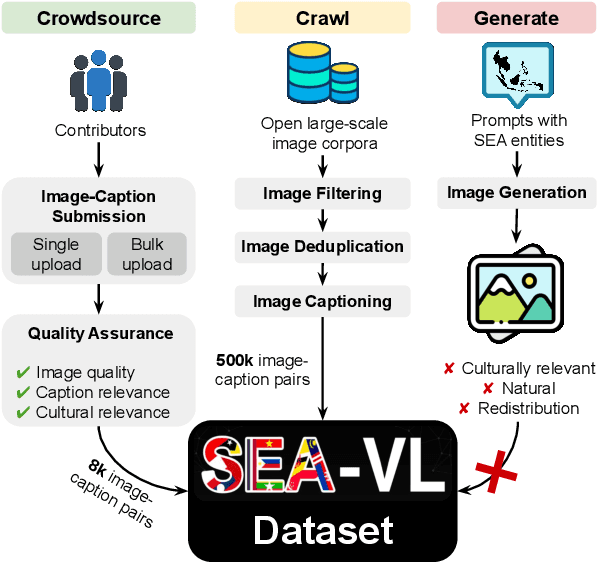
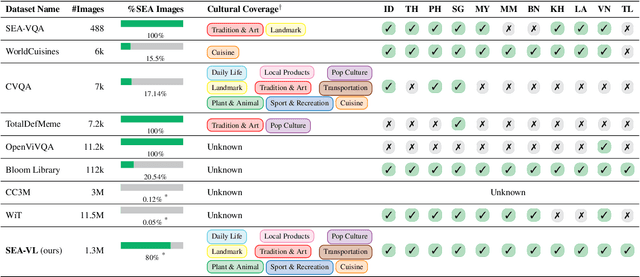
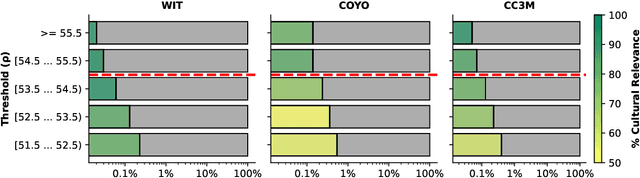

Abstract:Southeast Asia (SEA) is a region of extraordinary linguistic and cultural diversity, yet it remains significantly underrepresented in vision-language (VL) research. This often results in artificial intelligence (AI) models that fail to capture SEA cultural nuances. To fill this gap, we present SEA-VL, an open-source initiative dedicated to developing high-quality, culturally relevant data for SEA languages. By involving contributors from SEA countries, SEA-VL aims to ensure better cultural relevance and diversity, fostering greater inclusivity of underrepresented languages in VL research. Beyond crowdsourcing, our initiative goes one step further in the exploration of the automatic collection of culturally relevant images through crawling and image generation. First, we find that image crawling achieves approximately ~85% cultural relevance while being more cost- and time-efficient than crowdsourcing. Second, despite the substantial progress in generative vision models, synthetic images remain unreliable in accurately reflecting SEA cultures. The generated images often fail to reflect the nuanced traditions and cultural contexts of the region. Collectively, we gather 1.28M SEA culturally-relevant images, more than 50 times larger than other existing datasets. Through SEA-VL, we aim to bridge the representation gap in SEA, fostering the development of more inclusive AI systems that authentically represent diverse cultures across SEA.
CCStereo: Audio-Visual Contextual and Contrastive Learning for Binaural Audio Generation
Jan 06, 2025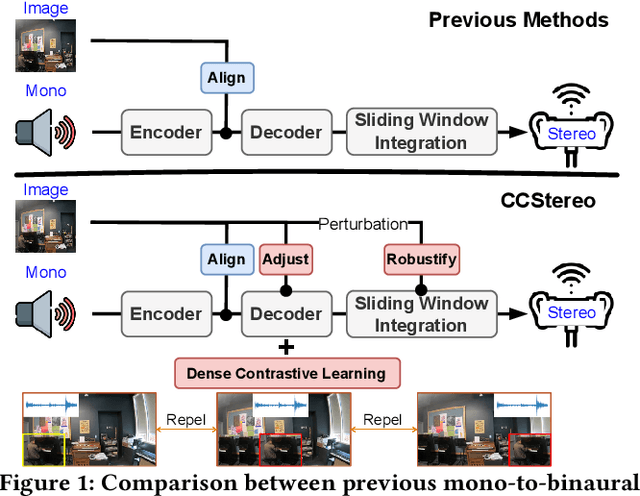
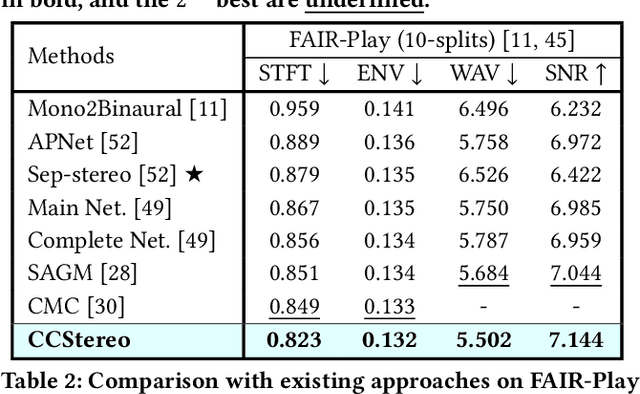
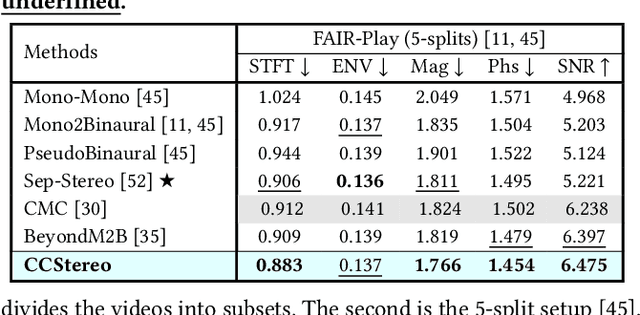
Abstract:Binaural audio generation (BAG) aims to convert monaural audio to stereo audio using visual prompts, requiring a deep understanding of spatial and semantic information. However, current models risk overfitting to room environments and lose fine-grained spatial details. In this paper, we propose a new audio-visual binaural generation model incorporating an audio-visual conditional normalisation layer that dynamically aligns the mean and variance of the target difference audio features using visual context, along with a new contrastive learning method to enhance spatial sensitivity by mining negative samples from shuffled visual features. We also introduce a cost-efficient way to utilise test-time augmentation in video data to enhance performance. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art generation accuracy on the FAIR-Play and MUSIC-Stereo benchmarks.
SAVGBench: Benchmarking Spatially Aligned Audio-Video Generation
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:This work addresses the lack of multimodal generative models capable of producing high-quality videos with spatially aligned audio. While recent advancements in generative models have been successful in video generation, they often overlook the spatial alignment between audio and visuals, which is essential for immersive experiences. To tackle this problem, we establish a new research direction in benchmarking Spatially Aligned Audio-Video Generation (SAVG). We propose three key components for the benchmark: dataset, baseline, and metrics. We introduce a spatially aligned audio-visual dataset, derived from an audio-visual dataset consisting of multichannel audio, video, and spatiotemporal annotations of sound events. We propose a baseline audio-visual diffusion model focused on stereo audio-visual joint learning to accommodate spatial sound. Finally, we present metrics to evaluate video and spatial audio quality, including a new spatial audio-visual alignment metric. Our experimental result demonstrates that gaps exist between the baseline model and ground truth in terms of video and audio quality, and spatial alignment between both modalities.
Mining Your Own Secrets: Diffusion Classifier Scores for Continual Personalization of Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Oct 02, 2024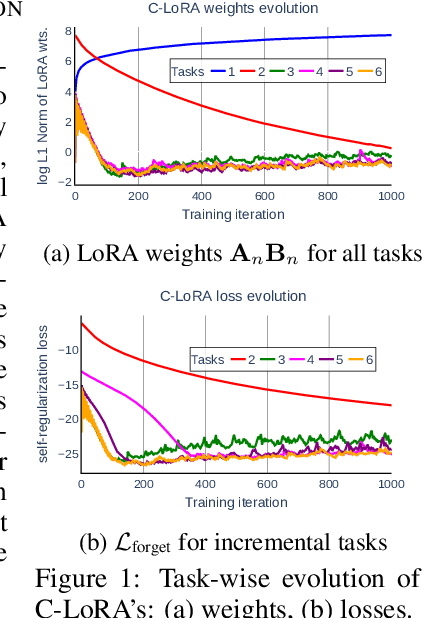
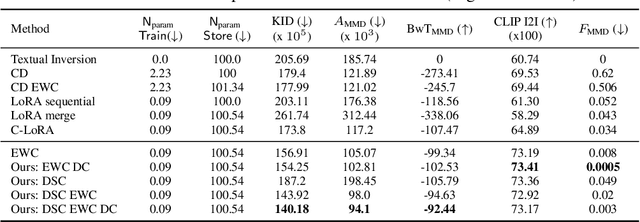
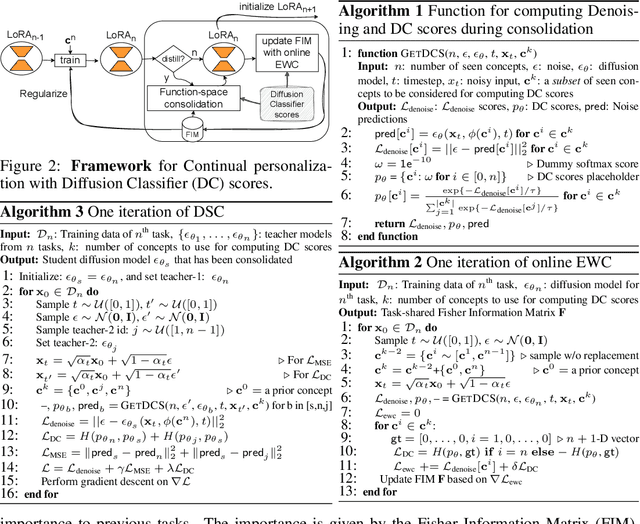
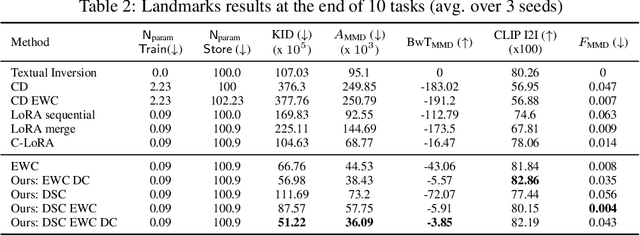
Abstract:Personalized text-to-image diffusion models have grown popular for their ability to efficiently acquire a new concept from user-defined text descriptions and a few images. However, in the real world, a user may wish to personalize a model on multiple concepts but one at a time, with no access to the data from previous concepts due to storage/privacy concerns. When faced with this continual learning (CL) setup, most personalization methods fail to find a balance between acquiring new concepts and retaining previous ones -- a challenge that continual personalization (CP) aims to solve. Inspired by the successful CL methods that rely on class-specific information for regularization, we resort to the inherent class-conditioned density estimates, also known as diffusion classifier (DC) scores, for continual personalization of text-to-image diffusion models. Namely, we propose using DC scores for regularizing the parameter-space and function-space of text-to-image diffusion models, to achieve continual personalization. Using several diverse evaluation setups, datasets, and metrics, we show that our proposed regularization-based CP methods outperform the state-of-the-art C-LoRA, and other baselines. Finally, by operating in the replay-free CL setup and on low-rank adapters, our method incurs zero storage and parameter overhead, respectively, over the state-of-the-art.
A randomized simulation trial evaluating ABiMed, a clinical decision support system for medication reviews and polypharmacy management
Sep 03, 2024



Abstract:Background: Medication review is a structured interview of the patient, performed by the pharmacist and aimed at optimizing drug treatments. In practice, medication review is a long and cognitively-demanding task that requires specific knowledge. Clinical practice guidelines have been proposed, but their application is tedious. Methods: We designed ABiMed, a clinical decision support system for medication reviews, based on the implementation of the STOPP/START v2 guidelines and on the visual presentation of aggregated drug knowledge using tables, graphs and flower glyphs. We evaluated ABiMed with 39 community pharmacists during a randomized simulation trial, each pharmacist performing a medication review for two fictitious patients without ABiMed, and two others with ABiMed. We recorded the problems identified by the pharmacists, the interventions proposed, the response time, the perceived usability and the comments. Pharmacists' medication reviews were compared to an expert-designed gold standard. Results: With ABiMed, pharmacists found 1.6 times more relevant drug-related problems during the medication review (p=1.1e-12) and proposed better interventions (p=9.8e-9), without needing more time (p=0.56). The System Usability Scale score is 82.7, which is ranked "excellent". In their comments, pharmacists appreciated the visual aspect of ABiMed and its ability to compare the current treatment with the proposed one. A multifactor analysis showed no difference in the support offered by ABiMed according to the pharmacist's age or sex, in terms of percentage of problems identified or quality of the proposed interventions. Conclusions: The use of an intelligent and visual clinical decision support system can help pharmacists when they perform medication reviews. Our main perspective is the validation of the system in clinical conditions.
Hyper-VolTran: Fast and Generalizable One-Shot Image to 3D Object Structure via HyperNetworks
Jan 05, 2024



Abstract:Solving image-to-3D from a single view is an ill-posed problem, and current neural reconstruction methods addressing it through diffusion models still rely on scene-specific optimization, constraining their generalization capability. To overcome the limitations of existing approaches regarding generalization and consistency, we introduce a novel neural rendering technique. Our approach employs the signed distance function as the surface representation and incorporates generalizable priors through geometry-encoding volumes and HyperNetworks. Specifically, our method builds neural encoding volumes from generated multi-view inputs. We adjust the weights of the SDF network conditioned on an input image at test-time to allow model adaptation to novel scenes in a feed-forward manner via HyperNetworks. To mitigate artifacts derived from the synthesized views, we propose the use of a volume transformer module to improve the aggregation of image features instead of processing each viewpoint separately. Through our proposed method, dubbed as Hyper-VolTran, we avoid the bottleneck of scene-specific optimization and maintain consistency across the images generated from multiple viewpoints. Our experiments show the advantages of our proposed approach with consistent results and rapid generation.
ABiMed: An intelligent and visual clinical decision support system for medication reviews and polypharmacy management
Dec 13, 2023Abstract:Background: Polypharmacy, i.e. taking five drugs or more, is both a public health and an economic issue. Medication reviews are structured interviews of the patient by the community pharmacist, aiming at optimizing the drug treatment and deprescribing useless, redundant or dangerous drugs. However, they remain difficult to perform and time-consuming. Several clinical decision support systems were developed for helping clinicians to manage polypharmacy. However, most were limited to the implementation of clinical practice guidelines. In this work, our objective is to design an innovative clinical decision support system for medication reviews and polypharmacy management, named ABiMed. Methods: ABiMed associates several approaches: guidelines implementation, but the automatic extraction of patient data from the GP's electronic health record and its transfer to the pharmacist, and the visual presentation of contextualized drug knowledge using visual analytics. We performed an ergonomic assessment and qualitative evaluations involving pharmacists and GPs during focus groups and workshops. Results: We describe the proposed architecture, which allows a collaborative multi-user usage. We present the various screens of ABiMed for entering or verifying patient data, for accessing drug knowledge (posology, adverse effects, interactions), for viewing STOPP/START rules and for suggesting modification to the treatment. Qualitative evaluations showed that health professionals were highly interested by our approach, associating the automatic guidelines execution with the visual presentation of drug knowledge. Conclusions: The association of guidelines implementation with visual presentation of knowledge is a promising approach for managing polypharmacy. Future works will focus on the improvement and the evaluation of ABiMed.
On Manipulating Scene Text in the Wild with Diffusion Models
Nov 03, 2023
Abstract:Diffusion models have gained attention for image editing yielding impressive results in text-to-image tasks. On the downside, one might notice that generated images of stable diffusion models suffer from deteriorated details. This pitfall impacts image editing tasks that require information preservation e.g., scene text editing. As a desired result, the model must show the capability to replace the text on the source image to the target text while preserving the details e.g., color, font size, and background. To leverage the potential of diffusion models, in this work, we introduce Diffusion-BasEd Scene Text manipulation Network so-called DBEST. Specifically, we design two adaptation strategies, namely one-shot style adaptation and text-recognition guidance. In experiments, we thoroughly assess and compare our proposed method against state-of-the-arts on various scene text datasets, then provide extensive ablation studies for each granularity to analyze our performance gain. Also, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method to synthesize scene text indicated by competitive Optical Character Recognition (OCR) accuracy. Our method achieves 94.15% and 98.12% on COCO-text and ICDAR2013 datasets for character-level evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge