David Anugraha
CommonLID: Re-evaluating State-of-the-Art Language Identification Performance on Web Data
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Language identification (LID) is a fundamental step in curating multilingual corpora. However, LID models still perform poorly for many languages, especially on the noisy and heterogeneous web data often used to train multilingual language models. In this paper, we introduce CommonLID, a community-driven, human-annotated LID benchmark for the web domain, covering 109 languages. Many of the included languages have been previously under-served, making CommonLID a key resource for developing more representative high-quality text corpora. We show CommonLID's value by using it, alongside five other common evaluation sets, to test eight popular LID models. We analyse our results to situate our contribution and to provide an overview of the state of the art. In particular, we highlight that existing evaluations overestimate LID accuracy for many languages in the web domain. We make CommonLID and the code used to create it available under an open, permissive license.
Can Large Language Models Understand, Reason About, and Generate Code-Switched Text?
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Code-switching is a pervasive phenomenon in multilingual communication, yet the robustness of large language models (LLMs) in mixed-language settings remains insufficiently understood. In this work, we present a comprehensive evaluation of LLM capabilities in understanding, reasoning over, and generating code-switched text. We introduce CodeMixQA a novel benchmark with high-quality human annotations, comprising 16 diverse parallel code-switched language-pair variants that span multiple geographic regions and code-switching patterns, and include both original scripts and their transliterated forms. Using this benchmark, we analyze the reasoning behavior of LLMs on code-switched question-answering tasks, shedding light on how models process and reason over mixed-language inputs. We further conduct a systematic evaluation of LLM-generated synthetic code-switched text, focusing on both naturalness and semantic fidelity, and uncover key limitations in current generation capabilities. Our findings reveal persistent challenges in both reasoning and generation under code-switching conditions and provide actionable insights for building more robust multilingual LLMs. We release the dataset and code as open source.
Rethinking what Matters: Effective and Robust Multilingual Realignment for Low-Resource Languages
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Realignment is a promising strategy to improve cross-lingual transfer in multilingual language models. However, empirical results are mixed and often unreliable, particularly for typologically distant or low-resource languages (LRLs) compared to English. Moreover, word realignment tools often rely on high-quality parallel data, which can be scarce or noisy for many LRLs. In this work, we conduct an extensive empirical study to investigate whether realignment truly benefits from using all available languages, or if strategically selected subsets can offer comparable or even improved cross-lingual transfer, and study the impact on LRLs. Our controlled experiments show that realignment can be particularly effective for LRLs and that using carefully selected, linguistically diverse subsets can match full multilingual alignment, and even outperform it for unseen LRLs. This indicates that effective realignment does not require exhaustive language coverage and can reduce data collection overhead, while remaining both efficient and robust when guided by informed language selection.
IndoPref: A Multi-Domain Pairwise Preference Dataset for Indonesian
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:Over 200 million people speak Indonesian, yet the language remains significantly underrepresented in preference-based research for large language models (LLMs). Most existing multilingual datasets are derived from English translations, often resulting in content that lacks cultural and linguistic authenticity. To address this gap, we introduce IndoPref, the first fully human-authored and multi-domain Indonesian preference dataset specifically designed to evaluate the naturalness and quality of LLM-generated text. All annotations are natively written in Indonesian and evaluated using Krippendorff's alpha, demonstrating strong inter-annotator agreement. Additionally, we benchmark the dataset across multiple LLMs and assess the output quality of each model.
R3: Robust Rubric-Agnostic Reward Models
May 19, 2025Abstract:Reward models are essential for aligning language model outputs with human preferences, yet existing approaches often lack both controllability and interpretability. These models are typically optimized for narrow objectives, limiting their generalizability to broader downstream tasks. Moreover, their scalar outputs are difficult to interpret without contextual reasoning. To address these limitations, we introduce R3, a novel reward modeling framework that is rubric-agnostic, generalizable across evaluation dimensions, and provides interpretable, reasoned score assignments. R3 enables more transparent and flexible evaluation of language models, supporting robust alignment with diverse human values and use cases. Our models, data, and code are available as open source at https://github.com/rubricreward/r3
Crowdsource, Crawl, or Generate? Creating SEA-VL, a Multicultural Vision-Language Dataset for Southeast Asia
Mar 10, 2025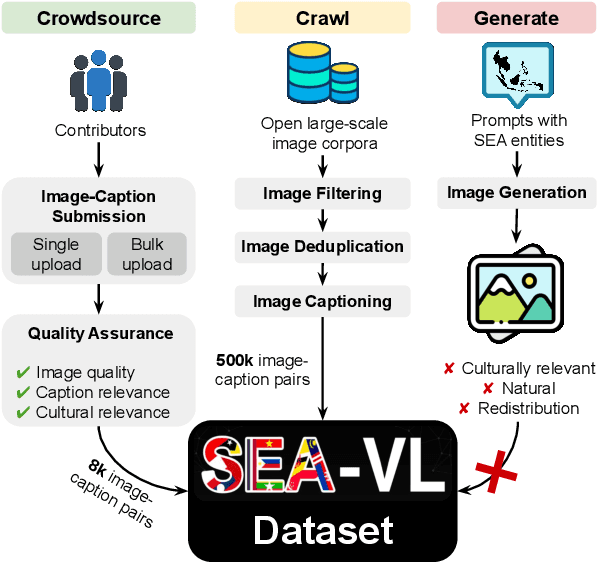
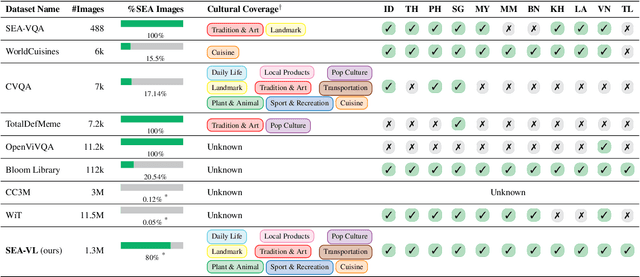
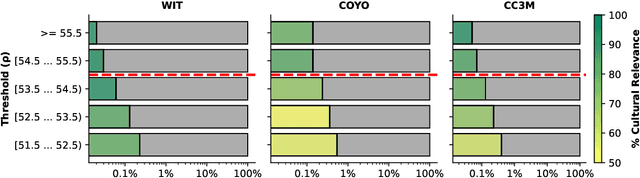

Abstract:Southeast Asia (SEA) is a region of extraordinary linguistic and cultural diversity, yet it remains significantly underrepresented in vision-language (VL) research. This often results in artificial intelligence (AI) models that fail to capture SEA cultural nuances. To fill this gap, we present SEA-VL, an open-source initiative dedicated to developing high-quality, culturally relevant data for SEA languages. By involving contributors from SEA countries, SEA-VL aims to ensure better cultural relevance and diversity, fostering greater inclusivity of underrepresented languages in VL research. Beyond crowdsourcing, our initiative goes one step further in the exploration of the automatic collection of culturally relevant images through crawling and image generation. First, we find that image crawling achieves approximately ~85% cultural relevance while being more cost- and time-efficient than crowdsourcing. Second, despite the substantial progress in generative vision models, synthetic images remain unreliable in accurately reflecting SEA cultures. The generated images often fail to reflect the nuanced traditions and cultural contexts of the region. Collectively, we gather 1.28M SEA culturally-relevant images, more than 50 times larger than other existing datasets. Through SEA-VL, we aim to bridge the representation gap in SEA, fostering the development of more inclusive AI systems that authentically represent diverse cultures across SEA.
MetaMetrics-MT: Tuning Meta-Metrics for Machine Translation via Human Preference Calibration
Nov 01, 2024Abstract:We present MetaMetrics-MT, an innovative metric designed to evaluate machine translation (MT) tasks by aligning closely with human preferences through Bayesian optimization with Gaussian Processes. MetaMetrics-MT enhances existing MT metrics by optimizing their correlation with human judgments. Our experiments on the WMT24 metric shared task dataset demonstrate that MetaMetrics-MT outperforms all existing baselines, setting a new benchmark for state-of-the-art performance in the reference-based setting. Furthermore, it achieves comparable results to leading metrics in the reference-free setting, offering greater efficiency.
WorldCuisines: A Massive-Scale Benchmark for Multilingual and Multicultural Visual Question Answering on Global Cuisines
Oct 16, 2024
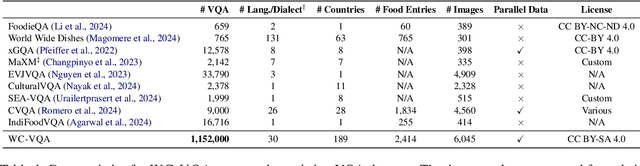
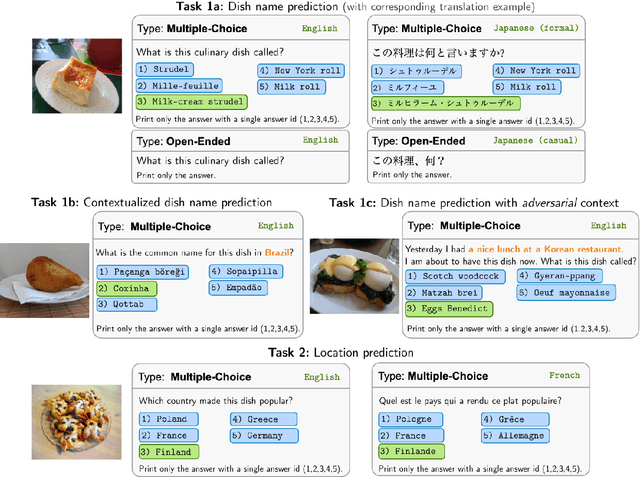
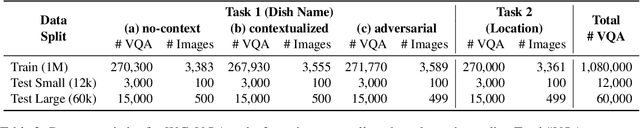
Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) often struggle with culture-specific knowledge, particularly in languages other than English and in underrepresented cultural contexts. To evaluate their understanding of such knowledge, we introduce WorldCuisines, a massive-scale benchmark for multilingual and multicultural, visually grounded language understanding. This benchmark includes a visual question answering (VQA) dataset with text-image pairs across 30 languages and dialects, spanning 9 language families and featuring over 1 million data points, making it the largest multicultural VQA benchmark to date. It includes tasks for identifying dish names and their origins. We provide evaluation datasets in two sizes (12k and 60k instances) alongside a training dataset (1 million instances). Our findings show that while VLMs perform better with correct location context, they struggle with adversarial contexts and predicting specific regional cuisines and languages. To support future research, we release a knowledge base with annotated food entries and images along with the VQA data.
MetaMetrics: Calibrating Metrics For Generation Tasks Using Human Preferences
Oct 03, 2024Abstract:Understanding the quality of a performance evaluation metric is crucial for ensuring that model outputs align with human preferences. However, it remains unclear how well each metric captures the diverse aspects of these preferences, as metrics often excel in one particular area but not across all dimensions. To address this, it is essential to systematically calibrate metrics to specific aspects of human preference, catering to the unique characteristics of each aspect. We introduce MetaMetrics, a calibrated meta-metric designed to evaluate generation tasks across different modalities in a supervised manner. MetaMetrics optimizes the combination of existing metrics to enhance their alignment with human preferences. Our metric demonstrates flexibility and effectiveness in both language and vision downstream tasks, showing significant benefits across various multilingual and multi-domain scenarios. MetaMetrics aligns closely with human preferences and is highly extendable and easily integrable into any application. This makes MetaMetrics a powerful tool for improving the evaluation of generation tasks, ensuring that metrics are more representative of human judgment across diverse contexts.
URIEL+: Enhancing Linguistic Inclusion and Usability in a Typological and Multilingual Knowledge Base
Sep 27, 2024



Abstract:URIEL is a knowledge base offering geographical, phylogenetic, and typological vector representations for 7970 languages. It includes distance measures between these vectors for 4005 languages, which are accessible via the lang2vec tool. Despite being frequently cited, URIEL is limited in terms of linguistic inclusion and overall usability. To tackle these challenges, we introduce URIEL+, an enhanced version of URIEL and lang2vec addressing these limitations. In addition to expanding typological feature coverage for 2898 languages, URIEL+ improves user experience with robust, customizable distance calculations to better suit the needs of the users. These upgrades also offer competitive performance on downstream tasks and provide distances that better align with linguistic distance studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge