Rifki Afina Putri
Adapting Language Models to Indonesian Local Languages: An Empirical Study of Language Transferability on Zero-Shot Settings
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the transferability of pre-trained language models to low-resource Indonesian local languages through the task of sentiment analysis. We evaluate both zero-shot performance and adapter-based transfer on ten local languages using models of different types: a monolingual Indonesian BERT, multilingual models such as mBERT and XLM-R, and a modular adapter-based approach called MAD-X. To better understand model behavior, we group the target languages into three categories: seen (included during pre-training), partially seen (not included but linguistically related to seen languages), and unseen (absent and unrelated in pre-training data). Our results reveal clear performance disparities across these groups: multilingual models perform best on seen languages, moderately on partially seen ones, and poorly on unseen languages. We find that MAD-X significantly improves performance, especially for seen and partially seen languages, without requiring labeled data in the target language. Additionally, we conduct a further analysis on tokenization and show that while subword fragmentation and vocabulary overlap with Indonesian correlate weakly with prediction quality, they do not fully explain the observed performance. Instead, the most consistent predictor of transfer success is the model's prior exposure to the language, either directly or through a related language.
WorldCuisines: A Massive-Scale Benchmark for Multilingual and Multicultural Visual Question Answering on Global Cuisines
Oct 16, 2024
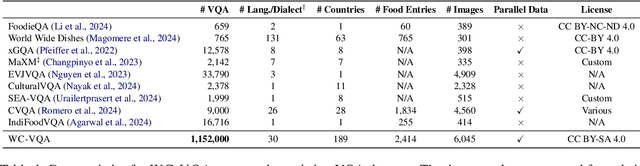
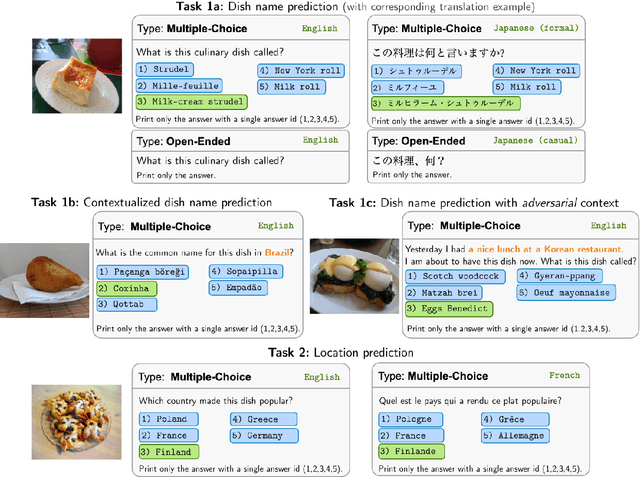
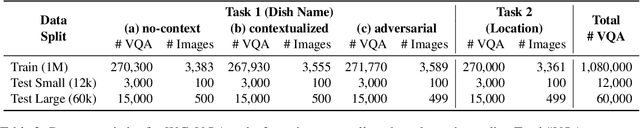
Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) often struggle with culture-specific knowledge, particularly in languages other than English and in underrepresented cultural contexts. To evaluate their understanding of such knowledge, we introduce WorldCuisines, a massive-scale benchmark for multilingual and multicultural, visually grounded language understanding. This benchmark includes a visual question answering (VQA) dataset with text-image pairs across 30 languages and dialects, spanning 9 language families and featuring over 1 million data points, making it the largest multicultural VQA benchmark to date. It includes tasks for identifying dish names and their origins. We provide evaluation datasets in two sizes (12k and 60k instances) alongside a training dataset (1 million instances). Our findings show that while VLMs perform better with correct location context, they struggle with adversarial contexts and predicting specific regional cuisines and languages. To support future research, we release a knowledge base with annotated food entries and images along with the VQA data.
BLEnD: A Benchmark for LLMs on Everyday Knowledge in Diverse Cultures and Languages
Jun 14, 2024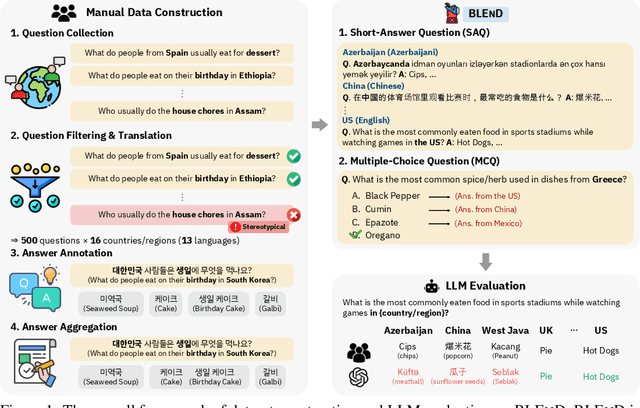
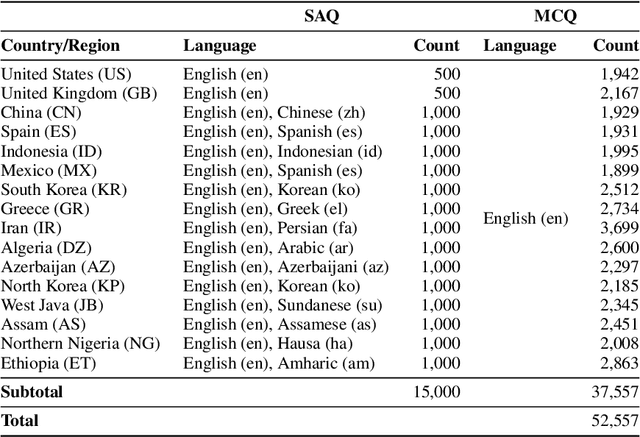
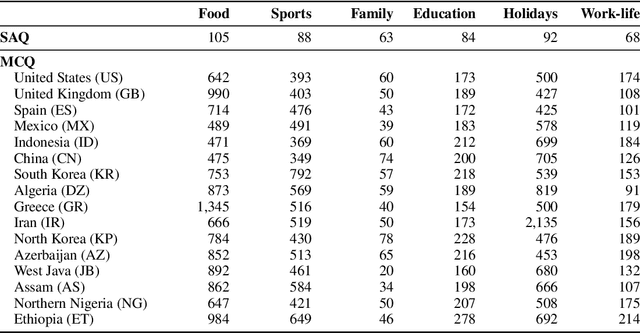
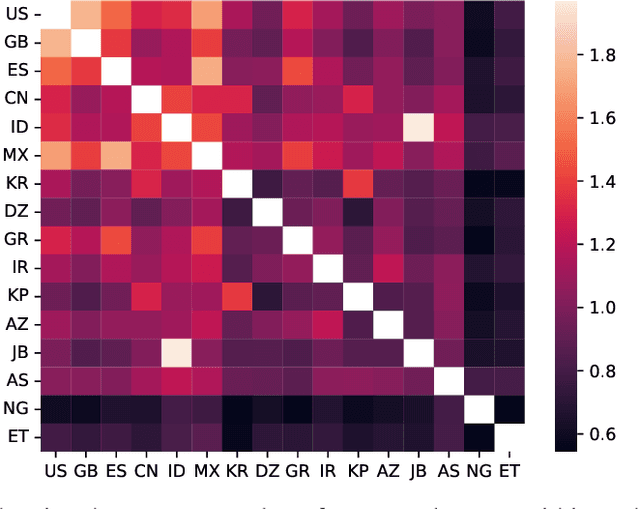
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often lack culture-specific knowledge of daily life, especially across diverse regions and non-English languages. Existing benchmarks for evaluating LLMs' cultural sensitivities are limited to a single language or collected from online sources such as Wikipedia, which do not reflect the mundane everyday lifestyles of diverse regions. That is, information about the food people eat for their birthday celebrations, spices they typically use, musical instruments youngsters play, or the sports they practice in school is common cultural knowledge but uncommon in easily collected online sources, especially for underrepresented cultures. To address this issue, we introduce BLEnD, a hand-crafted benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs' everyday knowledge across diverse cultures and languages. BLEnD comprises 52.6k question-answer pairs from 16 countries/regions, in 13 different languages, including low-resource ones such as Amharic, Assamese, Azerbaijani, Hausa, and Sundanese. We construct the benchmark to include two formats of questions: short-answer and multiple-choice. We show that LLMs perform better for cultures that are highly represented online, with a maximum 57.34% difference in GPT-4, the best-performing model, in the short-answer format. For cultures represented by mid-to-high-resource languages, LLMs perform better in their local languages, but for cultures represented by low-resource languages, LLMs perform better in English than the local languages. We make our dataset publicly available at: https://github.com/nlee0212/BLEnD.
Cendol: Open Instruction-tuned Generative Large Language Models for Indonesian Languages
Apr 09, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) show remarkable human-like capability in various domains and languages. However, a notable quality gap arises in low-resource languages, e.g., Indonesian indigenous languages, rendering them ineffective and inefficient in such linguistic contexts. To bridge this quality gap, we introduce Cendol, a collection of Indonesian LLMs encompassing both decoder-only and encoder-decoder architectures across a range of model sizes. We highlight Cendol's effectiveness across a diverse array of tasks, attaining 20% improvement, and demonstrate its capability to generalize to unseen tasks and indigenous languages of Indonesia. Furthermore, Cendol models showcase improved human favorability despite their limitations in capturing indigenous knowledge and cultural values in Indonesia. In addition, we discuss the shortcomings of parameter-efficient tunings, such as LoRA, for language adaptation. Alternatively, we propose the usage of vocabulary adaptation to enhance efficiency. Lastly, we evaluate the safety of Cendol and showcase that safety in pre-training in one language such as English is transferable to low-resource languages, such as Indonesian, even without RLHF and safety fine-tuning.
BEnQA: A Question Answering and Reasoning Benchmark for Bengali and English
Mar 16, 2024Abstract:In this study, we introduce BEnQA, a dataset comprising parallel Bengali and English exam questions for middle and high school levels in Bangladesh. Our dataset consists of approximately 5K questions covering several subjects in science with different types of questions, including factual, application, and reasoning-based questions. We benchmark several Large Language Models (LLMs) with our parallel dataset and observe a notable performance disparity between the models in Bengali and English. We also investigate some prompting methods, and find that Chain-of-Thought prompting is beneficial mostly on reasoning questions, but not so much on factual ones. We also find that appending English translation helps to answer questions in Bengali. Our findings point to promising future research directions for improving the performance of LLMs in Bengali and more generally in low-resource languages.
Can LLM Generate Culturally Relevant Commonsense QA Data? Case Study in Indonesian and Sundanese
Feb 27, 2024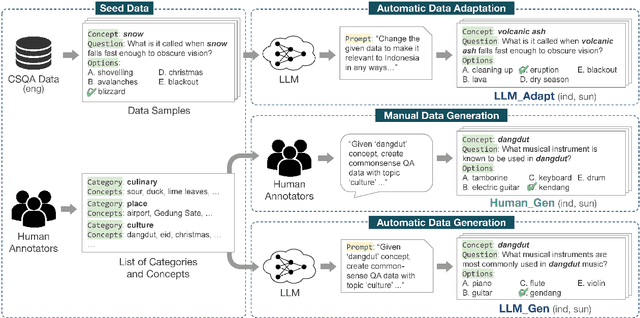
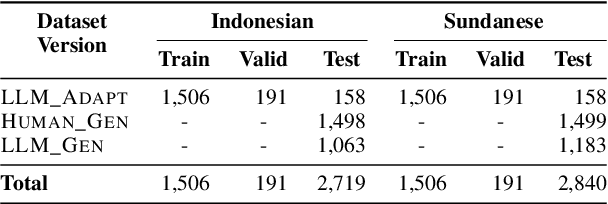
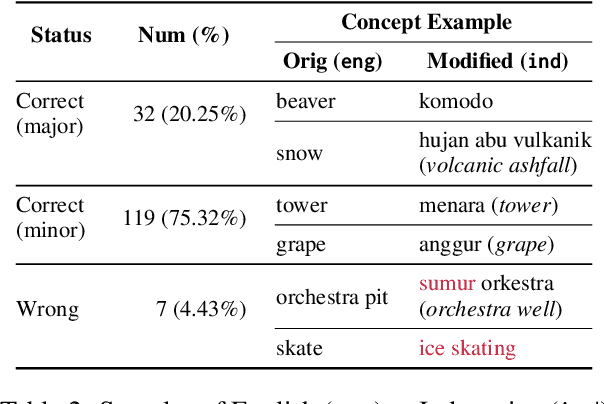
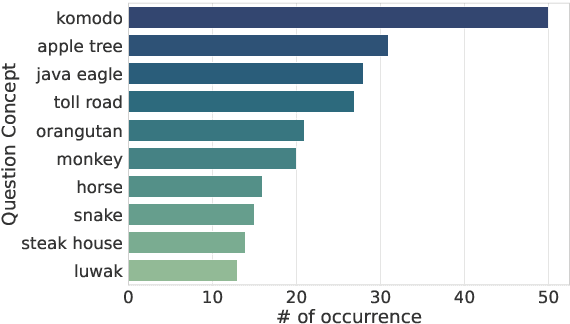
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly being used to generate synthetic data for training and evaluating models. However, it is unclear whether they can generate a good quality of question answering (QA) dataset that incorporates knowledge and cultural nuance embedded in a language, especially for low-resource languages. In this study, we investigate the effectiveness of using LLMs in generating culturally relevant commonsense QA datasets for Indonesian and Sundanese languages. To do so, we create datasets for these languages using various methods involving both LLMs and human annotators. Our experiments show that the current best-performing LLM, GPT-4 Turbo, is capable of generating questions with adequate knowledge in Indonesian but not in Sundanese, highlighting the performance discrepancy between medium- and lower-resource languages. We also benchmark various LLMs on our generated datasets and find that they perform better on the LLM-generated datasets compared to those created by humans.
NusaCrowd: Open Source Initiative for Indonesian NLP Resources
Dec 20, 2022Abstract:We present NusaCrowd, a collaborative initiative to collect and unite existing resources for Indonesian languages, including opening access to previously non-public resources. Through this initiative, we have has brought together 137 datasets and 117 standardized data loaders. The quality of the datasets has been assessed manually and automatically, and their effectiveness has been demonstrated in multiple experiments. NusaCrowd's data collection enables the creation of the first zero-shot benchmarks for natural language understanding and generation in Indonesian and its local languages. Furthermore, NusaCrowd brings the creation of the first multilingual automatic speech recognition benchmark in Indonesian and its local languages. Our work is intended to help advance natural language processing research in under-represented languages.
IDK-MRC: Unanswerable Questions for Indonesian Machine Reading Comprehension
Oct 25, 2022



Abstract:Machine Reading Comprehension (MRC) has become one of the essential tasks in Natural Language Understanding (NLU) as it is often included in several NLU benchmarks (Liang et al., 2020; Wilie et al., 2020). However, most MRC datasets only have answerable question type, overlooking the importance of unanswerable questions. MRC models trained only on answerable questions will select the span that is most likely to be the answer, even when the answer does not actually exist in the given passage (Rajpurkar et al., 2018). This problem especially remains in medium- to low-resource languages like Indonesian. Existing Indonesian MRC datasets (Purwarianti et al., 2007; Clark et al., 2020) are still inadequate because of the small size and limited question types, i.e., they only cover answerable questions. To fill this gap, we build a new Indonesian MRC dataset called I(n)don'tKnow- MRC (IDK-MRC) by combining the automatic and manual unanswerable question generation to minimize the cost of manual dataset construction while maintaining the dataset quality. Combined with the existing answerable questions, IDK-MRC consists of more than 10K questions in total. Our analysis shows that our dataset significantly improves the performance of Indonesian MRC models, showing a large improvement for unanswerable questions.
Rethinking Annotation: Can Language Learners Contribute?
Oct 13, 2022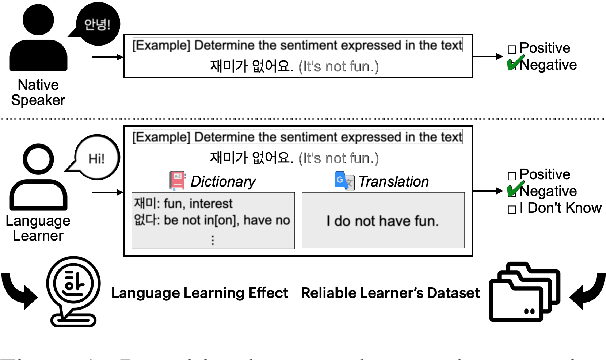
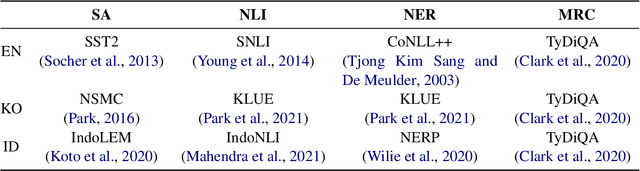
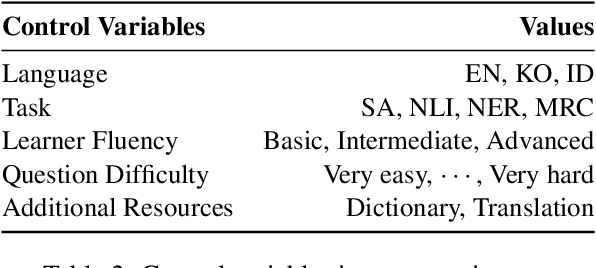
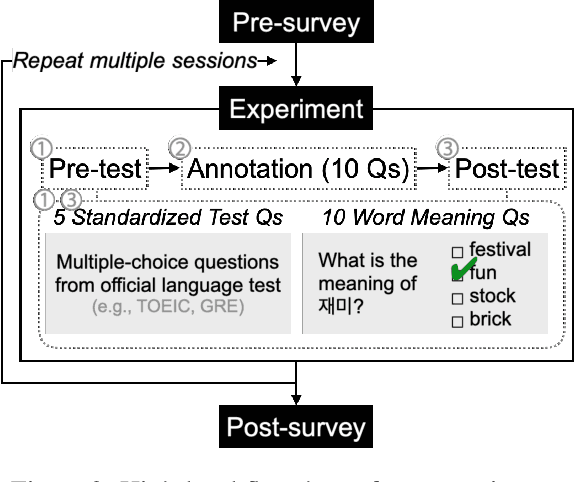
Abstract:Researchers have traditionally recruited native speakers to provide annotations for the widely used benchmark datasets. But there are languages for which recruiting native speakers is difficult, and it would help to get learners of those languages to annotate the data. In this paper, we investigate whether language learners can contribute annotations to the benchmark datasets. In a carefully controlled annotation experiment, we recruit 36 language learners, provide two types of additional resources (dictionaries and machine-translated sentences), and perform mini-tests to measure their language proficiency. We target three languages, English, Korean, and Indonesian, and four NLP tasks, sentiment analysis, natural language inference, named entity recognition, and machine reading comprehension. We find that language learners, especially those with intermediate or advanced language proficiency, are able to provide fairly accurate labels with the help of additional resources. Moreover, we show that data annotation improves learners' language proficiency in terms of vocabulary and grammar. The implication of our findings is that broadening the annotation task to include language learners can open up the opportunity to build benchmark datasets for languages for which it is difficult to recruit native speakers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge