Can LLM Generate Culturally Relevant Commonsense QA Data? Case Study in Indonesian and Sundanese
Paper and Code
Feb 27, 2024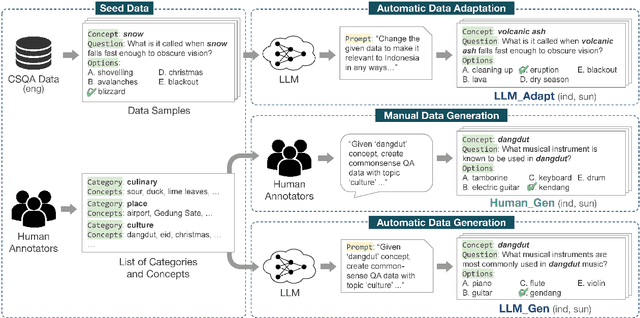
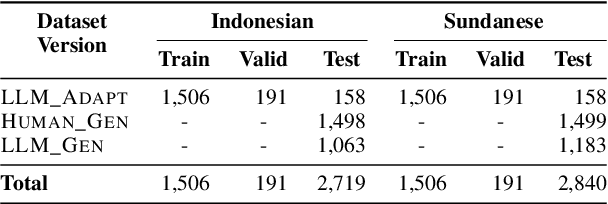
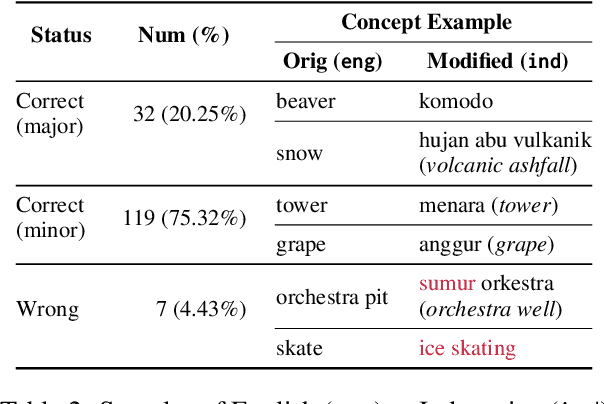
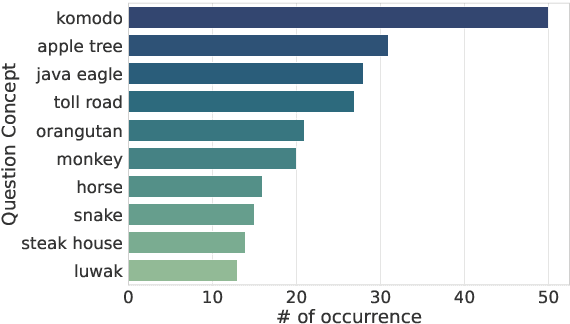
Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly being used to generate synthetic data for training and evaluating models. However, it is unclear whether they can generate a good quality of question answering (QA) dataset that incorporates knowledge and cultural nuance embedded in a language, especially for low-resource languages. In this study, we investigate the effectiveness of using LLMs in generating culturally relevant commonsense QA datasets for Indonesian and Sundanese languages. To do so, we create datasets for these languages using various methods involving both LLMs and human annotators. Our experiments show that the current best-performing LLM, GPT-4 Turbo, is capable of generating questions with adequate knowledge in Indonesian but not in Sundanese, highlighting the performance discrepancy between medium- and lower-resource languages. We also benchmark various LLMs on our generated datasets and find that they perform better on the LLM-generated datasets compared to those created by humans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge