Haneul Yoo
Can Large Language Models Understand, Reason About, and Generate Code-Switched Text?
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Code-switching is a pervasive phenomenon in multilingual communication, yet the robustness of large language models (LLMs) in mixed-language settings remains insufficiently understood. In this work, we present a comprehensive evaluation of LLM capabilities in understanding, reasoning over, and generating code-switched text. We introduce CodeMixQA a novel benchmark with high-quality human annotations, comprising 16 diverse parallel code-switched language-pair variants that span multiple geographic regions and code-switching patterns, and include both original scripts and their transliterated forms. Using this benchmark, we analyze the reasoning behavior of LLMs on code-switched question-answering tasks, shedding light on how models process and reason over mixed-language inputs. We further conduct a systematic evaluation of LLM-generated synthetic code-switched text, focusing on both naturalness and semantic fidelity, and uncover key limitations in current generation capabilities. Our findings reveal persistent challenges in both reasoning and generation under code-switching conditions and provide actionable insights for building more robust multilingual LLMs. We release the dataset and code as open source.
From National Curricula to Cultural Awareness: Constructing Open-Ended Culture-Specific Question Answering Dataset
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) achieve strong performance on many tasks, but their progress remains uneven across languages and cultures, often reflecting values latent in English-centric training data. To enable practical cultural alignment, we propose a scalable approach that leverages national social studies curricula as a foundation for culture-aware supervision. We introduce CuCu, an automated multi-agent LLM framework that transforms national textbook curricula into open-ended, culture-specific question-answer pairs. Applying CuCu to the Korean national social studies curriculum, we construct KCaQA, comprising 34.1k open-ended QA pairs. Our quantitative and qualitative analyses suggest that KCaQA covers culture-specific topics and produces responses grounded in local sociocultural contexts.
OLA: Output Language Alignment in Code-Switched LLM Interactions
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Code-switching, alternating between languages within a conversation, is natural for multilingual users, yet poses fundamental challenges for large language models (LLMs). When a user code-switches in their prompt to an LLM, they typically do not specify the expected language of the LLM response, and thus LLMs must infer the output language from contextual and pragmatic cues. We find that current LLMs systematically fail to align with this expectation, responding in undesired languages even when cues are clear to humans. We introduce OLA, a benchmark to evaluate LLMs' Output Language Alignment in code-switched interactions. OLA focuses on Korean--English code-switching and spans simple intra-sentential mixing to instruction-content mismatches. Even frontier models frequently misinterpret implicit language expectation, exhibiting a bias toward non-English responses. We further show this bias generalizes beyond Korean to Chinese and Indonesian pairs. Models also show instability through mid-response switching and language intrusions. Chain-of-Thought prompting fails to resolve these errors, indicating weak pragmatic reasoning about output language. However, Code-Switching Aware DPO with minimal data (about 1K examples) substantially reduces misalignment, suggesting these failures stem from insufficient alignment rather than fundamental limitations. Our results highlight the need to align multilingual LLMs with users' implicit expectations in real-world code-switched interactions.
One-Topic-Doesn't-Fit-All: Transcreating Reading Comprehension Test for Personalized Learning
Nov 12, 2025


Abstract:Personalized learning has gained attention in English as a Foreign Language (EFL) education, where engagement and motivation play crucial roles in reading comprehension. We propose a novel approach to generating personalized English reading comprehension tests tailored to students' interests. We develop a structured content transcreation pipeline using OpenAI's gpt-4o, where we start with the RACE-C dataset, and generate new passages and multiple-choice reading comprehension questions that are linguistically similar to the original passages but semantically aligned with individual learners' interests. Our methodology integrates topic extraction, question classification based on Bloom's taxonomy, linguistic feature analysis, and content transcreation to enhance student engagement. We conduct a controlled experiment with EFL learners in South Korea to examine the impact of interest-aligned reading materials on comprehension and motivation. Our results show students learning with personalized reading passages demonstrate improved comprehension and motivation retention compared to those learning with non-personalized materials.
On the Effect of Uncertainty on Layer-wise Inference Dynamics
Jul 09, 2025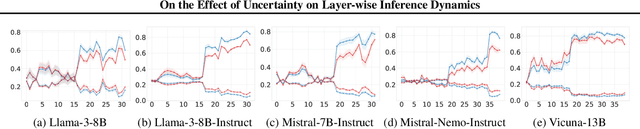
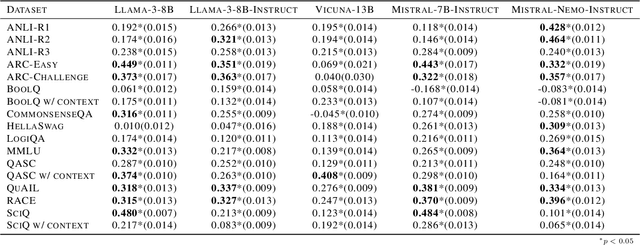
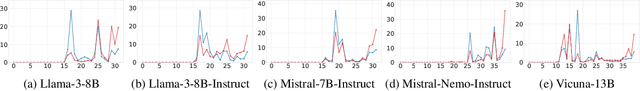
Abstract:Understanding how large language models (LLMs) internally represent and process their predictions is central to detecting uncertainty and preventing hallucinations. While several studies have shown that models encode uncertainty in their hidden states, it is underexplored how this affects the way they process such hidden states. In this work, we demonstrate that the dynamics of output token probabilities across layers for certain and uncertain outputs are largely aligned, revealing that uncertainty does not seem to affect inference dynamics. Specifically, we use the Tuned Lens, a variant of the Logit Lens, to analyze the layer-wise probability trajectories of final prediction tokens across 11 datasets and 5 models. Using incorrect predictions as those with higher epistemic uncertainty, our results show aligned trajectories for certain and uncertain predictions that both observe abrupt increases in confidence at similar layers. We balance this finding by showing evidence that more competent models may learn to process uncertainty differently. Our findings challenge the feasibility of leveraging simplistic methods for detecting uncertainty at inference. More broadly, our work demonstrates how interpretability methods may be used to investigate the way uncertainty affects inference.
HERITAGE: An End-to-End Web Platform for Processing Korean Historical Documents in Hanja
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:While Korean historical documents are invaluable cultural heritage, understanding those documents requires in-depth Hanja expertise. Hanja is an ancient language used in Korea before the 20th century, whose characters were borrowed from old Chinese but had evolved in Korea for centuries. Modern Koreans and Chinese cannot understand Korean historical documents without substantial additional help, and while previous efforts have produced some Korean and English translations, this requires in-depth expertise, and so most of the documents are not translated into any modern language. To address this gap, we present HERITAGE, the first open-source Hanja NLP toolkit to assist in understanding and translating the unexplored Korean historical documents written in Hanja. HERITAGE is a web-based platform providing model predictions of three critical tasks in historical document understanding via Hanja language models: punctuation restoration, named entity recognition, and machine translation (MT). HERITAGE also provides an interactive glossary, which provides the character-level reading of the Hanja characters in modern Korean, as well as character-level English definition. HERITAGE serves two purposes. First, anyone interested in these documents can get a general understanding from the model predictions and the interactive glossary, especially MT outputs in Korean and English. Second, since the model outputs are not perfect, Hanja experts can revise them to produce better annotations and translations. This would boost the translation efficiency and potentially lead to most of the historical documents being translated into modern languages, lowering the barrier on unexplored Korean historical documents.
When Does Classical Chinese Help? Quantifying Cross-Lingual Transfer in Hanja and Kanbun
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:Historical and linguistic connections within the Sinosphere have led researchers to use Classical Chinese resources for cross-lingual transfer when processing historical documents from Korea and Japan. In this paper, we question the assumption of cross-lingual transferability from Classical Chinese to Hanja and Kanbun, the ancient written languages of Korea and Japan, respectively. Our experiments across machine translation, named entity recognition, and punctuation restoration tasks show minimal impact of Classical Chinese datasets on language model performance for ancient Korean documents written in Hanja, with performance differences within $\pm{}0.0068$ F1-score for sequence labeling tasks and up to $+0.84$ BLEU score for translation. These limitations persist consistently across various model sizes, architectures, and domain-specific datasets. Our analysis reveals that the benefits of Classical Chinese resources diminish rapidly as local language data increases for Hanja, while showing substantial improvements only in extremely low-resource scenarios for both Korean and Japanese historical documents. These mixed results emphasize the need for careful empirical validation rather than assuming benefits from indiscriminate cross-lingual transfer.
Code-Switching Curriculum Learning for Multilingual Transfer in LLMs
Nov 04, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) now exhibit near human-level performance in various tasks, but their performance drops drastically after a handful of high-resource languages due to the imbalance in pre-training data. Inspired by the human process of second language acquisition, particularly code-switching (the practice of language alternation in a conversation), we propose code-switching curriculum learning (CSCL) to enhance cross-lingual transfer for LLMs. CSCL mimics the stages of human language learning by progressively training models with a curriculum consisting of 1) token-level code-switching, 2) sentence-level code-switching, and 3) monolingual corpora. Using Qwen 2 as our underlying model, we demonstrate the efficacy of the CSCL in improving language transfer to Korean, achieving significant performance gains compared to monolingual continual pre-training methods. Ablation studies reveal that both token- and sentence-level code-switching significantly enhance cross-lingual transfer and that curriculum learning amplifies these effects. We also extend our findings into various languages, including Japanese (high-resource) and Indonesian (low-resource), and using two additional models (Gemma 2 and Phi 3.5). We further show that CSCL mitigates spurious correlations between language resources and safety alignment, presenting a robust, efficient framework for more equitable language transfer in LLMs. We observe that CSCL is effective for low-resource settings where high-quality, monolingual corpora for language transfer are hardly available.
LLM-Driven Learning Analytics Dashboard for Teachers in EFL Writing Education
Oct 19, 2024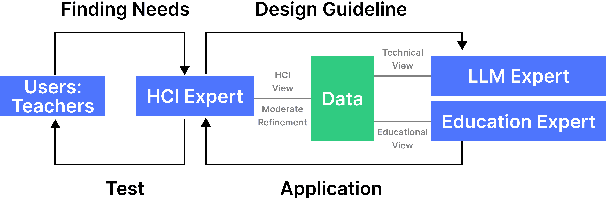
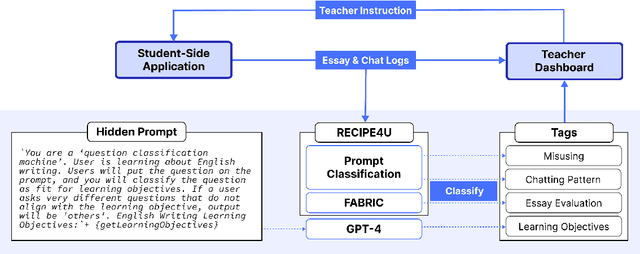
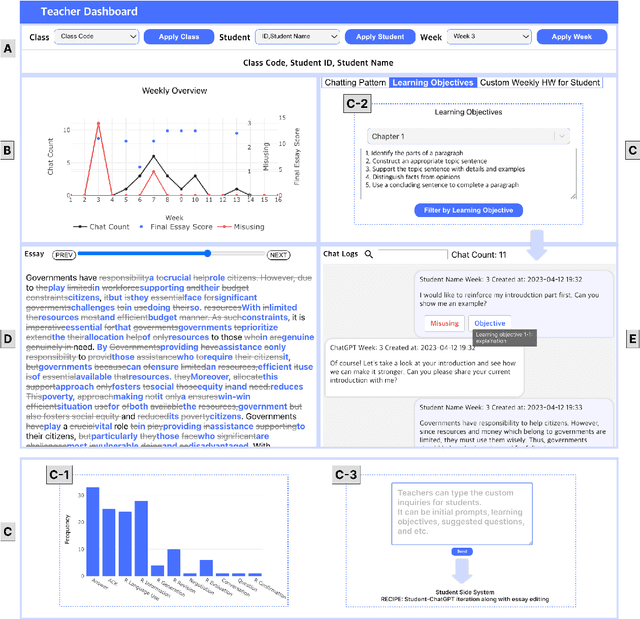
Abstract:This paper presents the development of a dashboard designed specifically for teachers in English as a Foreign Language (EFL) writing education. Leveraging LLMs, the dashboard facilitates the analysis of student interactions with an essay writing system, which integrates ChatGPT for real-time feedback. The dashboard aids teachers in monitoring student behavior, identifying noneducational interaction with ChatGPT, and aligning instructional strategies with learning objectives. By combining insights from NLP and Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), this study demonstrates how a human-centered approach can enhance the effectiveness of teacher dashboards, particularly in ChatGPT-integrated learning.
MAQA: Evaluating Uncertainty Quantification in LLMs Regarding Data Uncertainty
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:Although large language models (LLMs) are capable of performing various tasks, they still suffer from producing plausible but incorrect responses. To improve the reliability of LLMs, recent research has focused on uncertainty quantification to predict whether a response is correct or not. However, most uncertainty quantification methods have been evaluated on questions requiring a single clear answer, ignoring the existence of data uncertainty that arises from irreducible randomness. Instead, these methods only consider model uncertainty, which arises from a lack of knowledge. In this paper, we investigate previous uncertainty quantification methods under the presence of data uncertainty. Our contributions are two-fold: 1) proposing a new Multi-Answer Question Answering dataset, MAQA, consisting of world knowledge, mathematical reasoning, and commonsense reasoning tasks to evaluate uncertainty quantification regarding data uncertainty, and 2) assessing 5 uncertainty quantification methods of diverse white- and black-box LLMs. Our findings show that entropy and consistency-based methods estimate the model uncertainty well even under data uncertainty, while other methods for white- and black-box LLMs struggle depending on the tasks. Additionally, methods designed for white-box LLMs suffer from overconfidence in reasoning tasks compared to simple knowledge queries. We believe our observations will pave the way for future work on uncertainty quantification in realistic setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge