DREsS: Dataset for Rubric-based Essay Scoring on EFL Writing
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2024


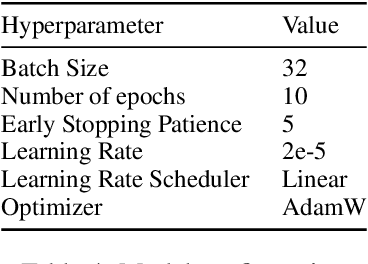
Automated essay scoring (AES) is a useful tool in English as a Foreign Language (EFL) writing education, offering real-time essay scores for students and instructors. However, previous AES models were trained on essays and scores irrelevant to the practical scenarios of EFL writing education and usually provided a single holistic score due to the lack of appropriate datasets. In this paper, we release DREsS, a large-scale, standard dataset for rubric-based automated essay scoring. DREsS comprises three sub-datasets: DREsS_New, DREsS_Std., and DREsS_CASE. We collect DREsS_New, a real-classroom dataset with 1.7K essays authored by EFL undergraduate students and scored by English education experts. We also standardize existing rubric-based essay scoring datasets as DREsS_Std. We suggest CASE, a corruption-based augmentation strategy for essays, which generates 20K synthetic samples of DREsS_CASE and improves the baseline results by 45.44%. DREsS will enable further research to provide a more accurate and practical AES system for EFL writing education.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge