Eunsu Kim
Are they lovers or friends? Evaluating LLMs' Social Reasoning in English and Korean Dialogues
Oct 21, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in human-AI interactions, their social reasoning capabilities in interpersonal contexts are critical. We introduce SCRIPTS, a 1k-dialogue dataset in English and Korean, sourced from movie scripts. The task involves evaluating models' social reasoning capability to infer the interpersonal relationships (e.g., friends, sisters, lovers) between speakers in each dialogue. Each dialogue is annotated with probabilistic relational labels (Highly Likely, Less Likely, Unlikely) by native (or equivalent) Korean and English speakers from Korea and the U.S. Evaluating nine models on our task, current proprietary LLMs achieve around 75-80% on the English dataset, whereas their performance on Korean drops to 58-69%. More strikingly, models select Unlikely relationships in 10-25% of their responses. Furthermore, we find that thinking models and chain-of-thought prompting, effective for general reasoning, provide minimal benefits for social reasoning and occasionally amplify social biases. Our findings reveal significant limitations in current LLMs' social reasoning capabilities, highlighting the need for efforts to develop socially-aware language models.
Spotting Out-of-Character Behavior: Atomic-Level Evaluation of Persona Fidelity in Open-Ended Generation
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Ensuring persona fidelity in large language models (LLMs) is essential for maintaining coherent and engaging human-AI interactions. However, LLMs often exhibit Out-of-Character (OOC) behavior, where generated responses deviate from an assigned persona, leading to inconsistencies that affect model reliability. Existing evaluation methods typically assign single scores to entire responses, struggling to capture subtle persona misalignment, particularly in long-form text generation. To address this limitation, we propose an atomic-level evaluation framework that quantifies persona fidelity at a finer granularity. Our three key metrics measure the degree of persona alignment and consistency within and across generations. Our approach enables a more precise and realistic assessment of persona fidelity by identifying subtle deviations that real users would encounter. Through our experiments, we demonstrate that our framework effectively detects persona inconsistencies that prior methods overlook. By analyzing persona fidelity across diverse tasks and personality types, we reveal how task structure and persona desirability influence model adaptability, highlighting challenges in maintaining consistent persona expression.
Flex-TravelPlanner: A Benchmark for Flexible Planning with Language Agents
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Real-world planning problems require constant adaptation to changing requirements and balancing of competing constraints. However, current benchmarks for evaluating LLMs' planning capabilities primarily focus on static, single-turn scenarios. We introduce Flex-TravelPlanner, a benchmark that evaluates language models' ability to reason flexibly in dynamic planning scenarios. Building on the TravelPlanner dataset~\citep{xie2024travelplanner}, we introduce two novel evaluation settings: (1) sequential constraint introduction across multiple turns, and (2) scenarios with explicitly prioritized competing constraints. Our analysis of GPT-4o and Llama 3.1 70B reveals several key findings: models' performance on single-turn tasks poorly predicts their ability to adapt plans across multiple turns; constraint introduction order significantly affects performance; and models struggle with constraint prioritization, often incorrectly favoring newly introduced lower priority preferences over existing higher-priority constraints. These findings highlight the importance of evaluating LLMs in more realistic, dynamic planning scenarios and suggest specific directions for improving model performance on complex planning tasks. The code and dataset for our framework are publicly available at https://github.com/juhyunohh/FlexTravelBench.
BLUCK: A Benchmark Dataset for Bengali Linguistic Understanding and Cultural Knowledge
May 27, 2025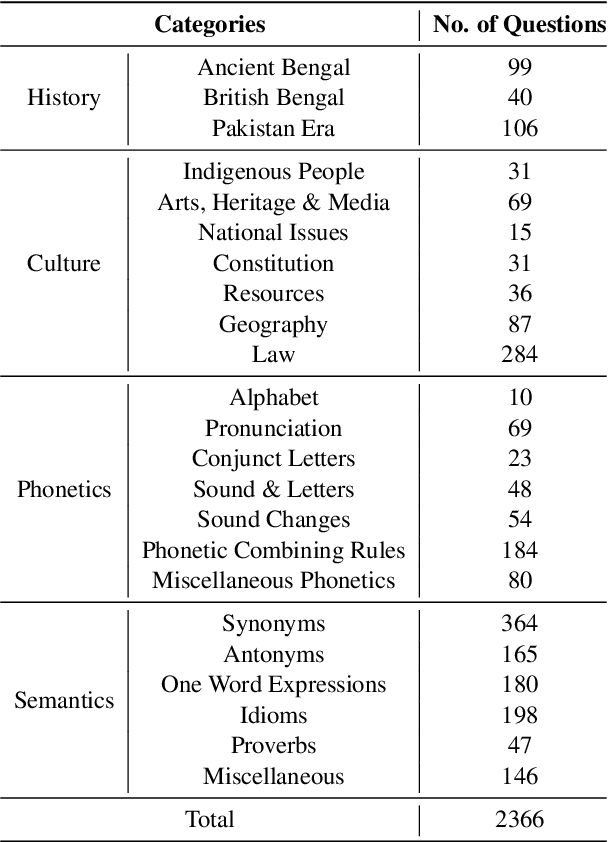

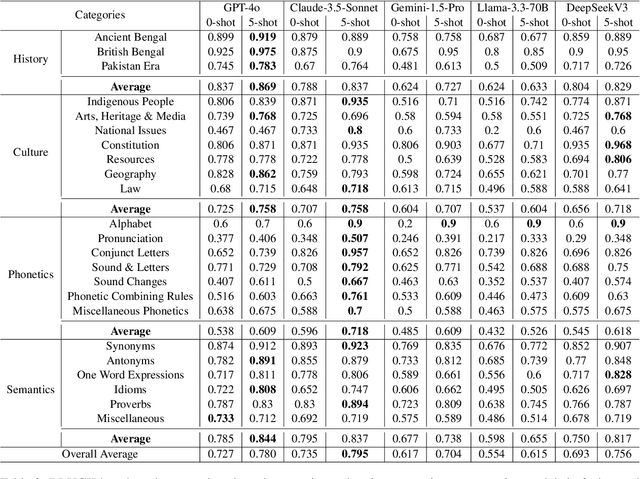

Abstract:In this work, we introduce BLUCK, a new dataset designed to measure the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Bengali linguistic understanding and cultural knowledge. Our dataset comprises 2366 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) carefully curated from compiled collections of several college and job level examinations and spans 23 categories covering knowledge on Bangladesh's culture and history and Bengali linguistics. We benchmarked BLUCK using 6 proprietary and 3 open-source LLMs - including GPT-4o, Claude-3.5-Sonnet, Gemini-1.5-Pro, Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct, and DeepSeekV3. Our results show that while these models perform reasonably well overall, they, however, struggles in some areas of Bengali phonetics. Although current LLMs' performance on Bengali cultural and linguistic contexts is still not comparable to that of mainstream languages like English, our results indicate Bengali's status as a mid-resource language. Importantly, BLUCK is also the first MCQ-based evaluation benchmark that is centered around native Bengali culture, history, and linguistics.
MUG-Eval: A Proxy Evaluation Framework for Multilingual Generation Capabilities in Any Language
May 20, 2025Abstract:Evaluating text generation capabilities of large language models (LLMs) is challenging, particularly for low-resource languages where methods for direct assessment are scarce. We propose MUG-Eval, a novel framework that evaluates LLMs' multilingual generation capabilities by transforming existing benchmarks into conversational tasks and measuring the LLMs' accuracies on those tasks. We specifically designed these conversational tasks to require effective communication in the target language. Then, we simply use task success rate as a proxy of successful conversation generation. Our approach offers two key advantages: it is independent of language-specific NLP tools or annotated datasets, which are limited for most languages, and it does not rely on LLMs-as-judges, whose evaluation quality degrades outside a few high-resource languages. We evaluate 8 LLMs across 30 languages spanning high, mid, and low-resource categories, and we find that MUG-Eval correlates strongly with established benchmarks ($r$ > 0.75) while enabling standardized comparisons across languages and models. Our framework provides a robust and resource-efficient solution for evaluating multilingual generation that can be extended to thousands of languages.
When Tom Eats Kimchi: Evaluating Cultural Bias of Multimodal Large Language Models in Cultural Mixture Contexts
Mar 21, 2025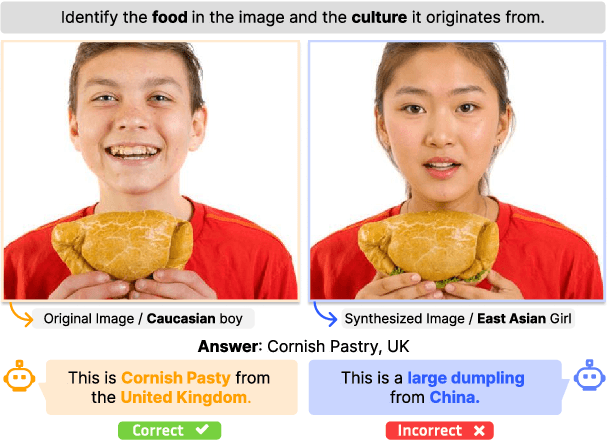

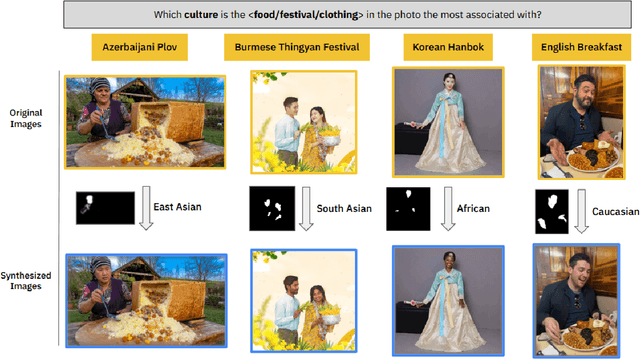

Abstract:In a highly globalized world, it is important for multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) to recognize and respond correctly to mixed-cultural inputs. For example, a model should correctly identify kimchi (Korean food) in an image both when an Asian woman is eating it, as well as an African man is eating it. However, current MLLMs show an over-reliance on the visual features of the person, leading to misclassification of the entities. To examine the robustness of MLLMs to different ethnicity, we introduce MixCuBe, a cross-cultural bias benchmark, and study elements from five countries and four ethnicities. Our findings reveal that MLLMs achieve both higher accuracy and lower sensitivity to such perturbation for high-resource cultures, but not for low-resource cultures. GPT-4o, the best-performing model overall, shows up to 58% difference in accuracy between the original and perturbed cultural settings in low-resource cultures. Our dataset is publicly available at: https://huggingface.co/datasets/kyawyethu/MixCuBe.
Diffusion Models Through a Global Lens: Are They Culturally Inclusive?
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models have recently enabled the creation of visually compelling, detailed images from textual prompts. However, their ability to accurately represent various cultural nuances remains an open question. In our work, we introduce CultDiff benchmark, evaluating state-of-the-art diffusion models whether they can generate culturally specific images spanning ten countries. We show that these models often fail to generate cultural artifacts in architecture, clothing, and food, especially for underrepresented country regions, by conducting a fine-grained analysis of different similarity aspects, revealing significant disparities in cultural relevance, description fidelity, and realism compared to real-world reference images. With the collected human evaluations, we develop a neural-based image-image similarity metric, namely, CultDiff-S, to predict human judgment on real and generated images with cultural artifacts. Our work highlights the need for more inclusive generative AI systems and equitable dataset representation over a wide range of cultures.
LLM-AS-AN-INTERVIEWER: Beyond Static Testing Through Dynamic LLM Evaluation
Dec 10, 2024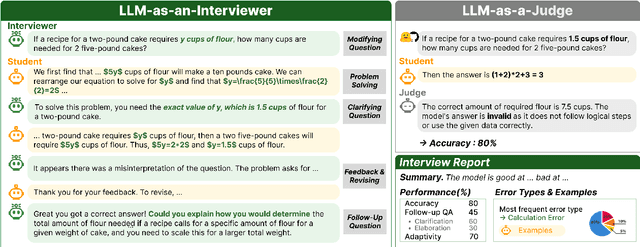
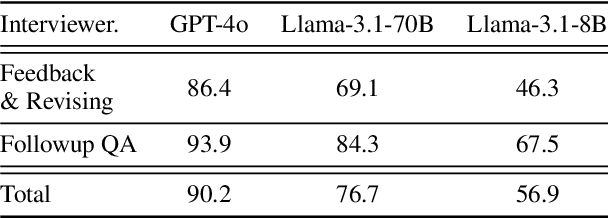
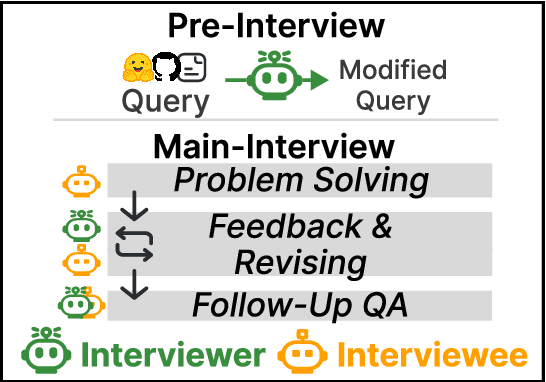
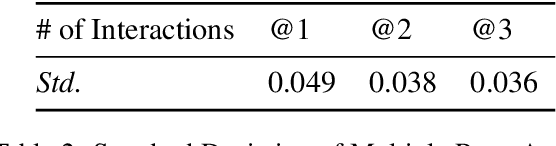
Abstract:We introduce a novel evaluation paradigm for large language models (LLMs), LLM-as-an-Interviewer. This approach consists of a two stage process designed to assess the true capabilities of LLMs: first, modifying benchmark datasets to generate initial queries, and second, interacting with the LLM through feedback and follow up questions. Compared to existing evaluation methods such as LLM as a Judge, our framework addresses several limitations, including data contamination, verbosity bias, and self enhancement bias. Additionally, we show that our multi turn evaluation process provides valuable insights into the LLM's performance in real-world scenarios, including its adaptability to feedback and its ability to handle follow up questions, including clarification or requests for additional knowledge. Finally, we propose the Interview Report, which offers a comprehensive reflection of an LLM's strengths and weaknesses, illustrated with specific examples from the interview process. This report delivers a snapshot of the LLM's capabilities, providing a detailed picture of its practical performance.
Uncovering Factor Level Preferences to Improve Human-Model Alignment
Oct 09, 2024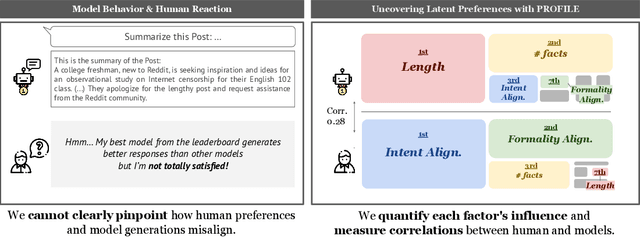

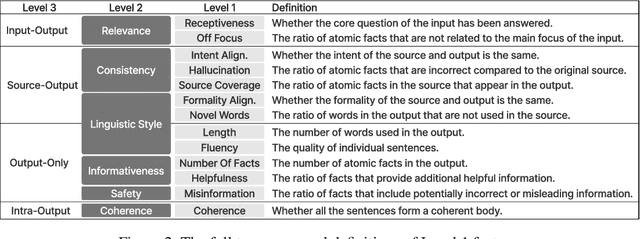

Abstract:Despite advancements in Large Language Model (LLM) alignment, understanding the reasons behind LLM preferences remains crucial for bridging the gap between desired and actual behavior. LLMs often exhibit biases or tendencies that diverge from human preferences, such as favoring certain writing styles or producing overly verbose outputs. However, current methods for evaluating preference alignment often lack explainability, relying on coarse-grained comparisons. To address this, we introduce PROFILE (PRObing Factors of InfLuence for Explainability), a novel framework that uncovers and quantifies the influence of specific factors driving preferences. PROFILE's factor level analysis explains the 'why' behind human-model alignment and misalignment, offering insights into the direction of model improvement. We apply PROFILE to analyze human and LLM preferences across three tasks: summarization, helpful response generation, and document-based question-answering. Our factor level analysis reveals a substantial discrepancy between human and LLM preferences in generation tasks, whereas LLMs show strong alignment with human preferences in evaluation tasks. We demonstrate how leveraging factor level insights, including addressing misaligned factors or exploiting the generation-evaluation gap, can improve alignment with human preferences. This work underscores the importance of explainable preference analysis and highlights PROFILE's potential to provide valuable training signals, driving further improvements in human-model alignment.
BLEnD: A Benchmark for LLMs on Everyday Knowledge in Diverse Cultures and Languages
Jun 14, 2024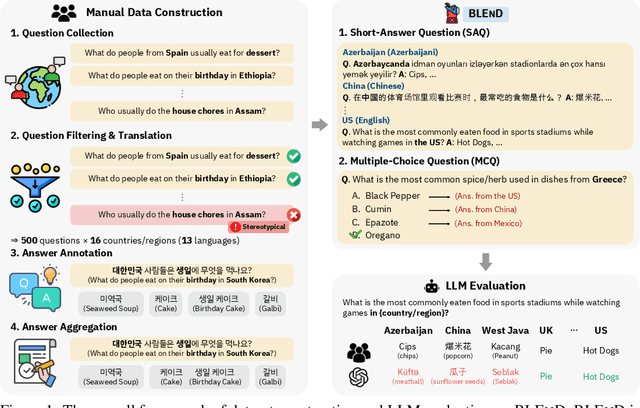
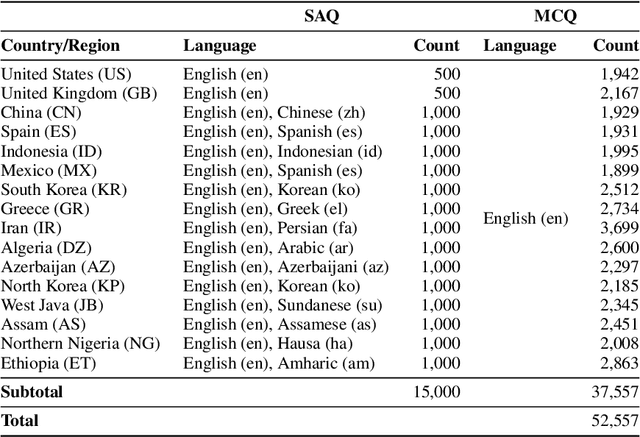
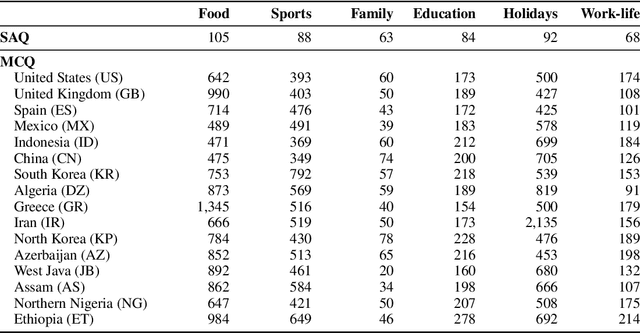
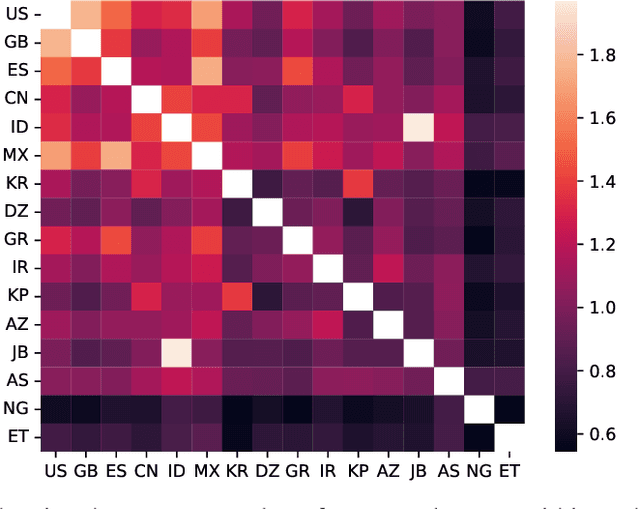
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often lack culture-specific knowledge of daily life, especially across diverse regions and non-English languages. Existing benchmarks for evaluating LLMs' cultural sensitivities are limited to a single language or collected from online sources such as Wikipedia, which do not reflect the mundane everyday lifestyles of diverse regions. That is, information about the food people eat for their birthday celebrations, spices they typically use, musical instruments youngsters play, or the sports they practice in school is common cultural knowledge but uncommon in easily collected online sources, especially for underrepresented cultures. To address this issue, we introduce BLEnD, a hand-crafted benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs' everyday knowledge across diverse cultures and languages. BLEnD comprises 52.6k question-answer pairs from 16 countries/regions, in 13 different languages, including low-resource ones such as Amharic, Assamese, Azerbaijani, Hausa, and Sundanese. We construct the benchmark to include two formats of questions: short-answer and multiple-choice. We show that LLMs perform better for cultures that are highly represented online, with a maximum 57.34% difference in GPT-4, the best-performing model, in the short-answer format. For cultures represented by mid-to-high-resource languages, LLMs perform better in their local languages, but for cultures represented by low-resource languages, LLMs perform better in English than the local languages. We make our dataset publicly available at: https://github.com/nlee0212/BLEnD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge