Jisu Shin
Mi:dm 2.0 Korea-centric Bilingual Language Models
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:We introduce Mi:dm 2.0, a bilingual large language model (LLM) specifically engineered to advance Korea-centric AI. This model goes beyond Korean text processing by integrating the values, reasoning patterns, and commonsense knowledge inherent to Korean society, enabling nuanced understanding of cultural contexts, emotional subtleties, and real-world scenarios to generate reliable and culturally appropriate responses. To address limitations of existing LLMs, often caused by insufficient or low-quality Korean data and lack of cultural alignment, Mi:dm 2.0 emphasizes robust data quality through a comprehensive pipeline that includes proprietary data cleansing, high-quality synthetic data generation, strategic data mixing with curriculum learning, and a custom Korean-optimized tokenizer to improve efficiency and coverage. To realize this vision, we offer two complementary configurations: Mi:dm 2.0 Base (11.5B parameters), built with a depth-up scaling strategy for general-purpose use, and Mi:dm 2.0 Mini (2.3B parameters), optimized for resource-constrained environments and specialized tasks. Mi:dm 2.0 achieves state-of-the-art performance on Korean-specific benchmarks, with top-tier zero-shot results on KMMLU and strong internal evaluation results across language, humanities, and social science tasks. The Mi:dm 2.0 lineup is released under the MIT license to support extensive research and commercial use. By offering accessible and high-performance Korea-centric LLMs, KT aims to accelerate AI adoption across Korean industries, public services, and education, strengthen the Korean AI developer community, and lay the groundwork for the broader vision of K-intelligence. Our models are available at https://huggingface.co/K-intelligence. For technical inquiries, please contact midm-llm@kt.com.
Off The Grid: Detection of Primitives for Feed-Forward 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 17, 2025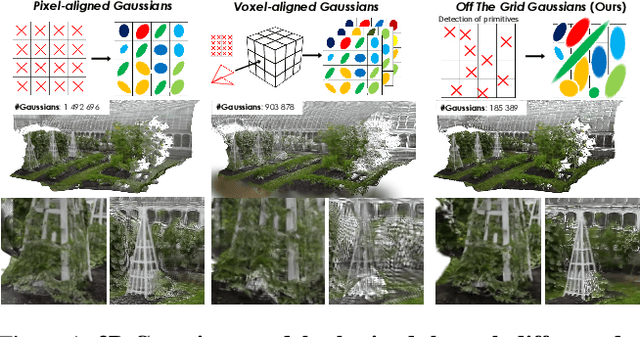
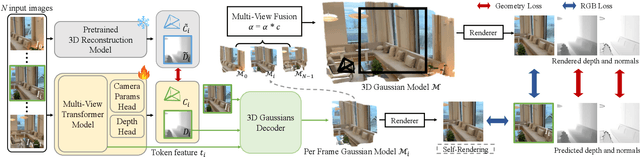

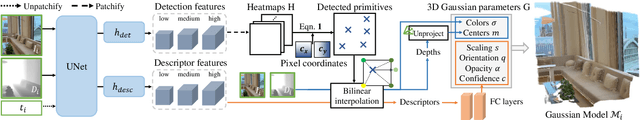
Abstract:Feed-forward 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) models enable real-time scene generation but are hindered by suboptimal pixel-aligned primitive placement, which relies on a dense, rigid grid and limits both quality and efficiency. We introduce a new feed-forward architecture that detects 3D Gaussian primitives at a sub-pixel level, replacing the pixel grid with an adaptive, "Off The Grid" distribution. Inspired by keypoint detection, our multi-resolution decoder learns to distribute primitives across image patches. This module is trained end-to-end with a 3D reconstruction backbone using self-supervised learning. Our resulting pose-free model generates photorealistic scenes in seconds, achieving state-of-the-art novel view synthesis for feed-forward models. It outperforms competitors while using far fewer primitives, demonstrating a more accurate and efficient allocation that captures fine details and reduces artifacts. Moreover, we observe that by learning to render 3D Gaussians, our 3D reconstruction backbone improves camera pose estimation, suggesting opportunities to train these foundational models without labels.
Diagnose Like A REAL Pathologist: An Uncertainty-Focused Approach for Trustworthy Multi-Resolution Multiple Instance Learning
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:With the increasing demand for histopathological specimen examination and diagnostic reporting, Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) has received heightened research focus as a viable solution for AI-centric diagnostic aid. Recently, to improve its performance and make it work more like a pathologist, several MIL approaches based on the use of multiple-resolution images have been proposed, delivering often higher performance than those that use single-resolution images. Despite impressive recent developments of multiple-resolution MIL, previous approaches only focus on improving performance, thereby lacking research on well-calibrated MIL that clinical experts can rely on for trustworthy diagnostic results. In this study, we propose Uncertainty-Focused Calibrated MIL (UFC-MIL), which more closely mimics the pathologists' examination behaviors while providing calibrated diagnostic predictions, using multiple images with different resolutions. UFC-MIL includes a novel patch-wise loss that learns the latent patterns of instances and expresses their uncertainty for classification. Also, the attention-based architecture with a neighbor patch aggregation module collects features for the classifier. In addition, aggregated predictions are calibrated through patch-level uncertainty without requiring multiple iterative inferences, which is a key practical advantage. Against challenging public datasets, UFC-MIL shows superior performance in model calibration while achieving classification accuracy comparable to that of state-of-the-art methods.
Entangled in Representations: Mechanistic Investigation of Cultural Biases in Large Language Models
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:The growing deployment of large language models (LLMs) across diverse cultural contexts necessitates a better understanding of how the overgeneralization of less documented cultures within LLMs' representations impacts their cultural understanding. Prior work only performs extrinsic evaluation of LLMs' cultural competence, without accounting for how LLMs' internal mechanisms lead to cultural (mis)representation. To bridge this gap, we propose Culturescope, the first mechanistic interpretability-based method that probes the internal representations of LLMs to elicit the underlying cultural knowledge space. CultureScope utilizes a patching method to extract the cultural knowledge. We introduce a cultural flattening score as a measure of the intrinsic cultural biases. Additionally, we study how LLMs internalize Western-dominance bias and cultural flattening, which allows us to trace how cultural biases emerge within LLMs. Our experimental results reveal that LLMs encode Western-dominance bias and cultural flattening in their cultural knowledge space. We find that low-resource cultures are less susceptible to cultural biases, likely due to their limited training resources. Our work provides a foundation for future research on mitigating cultural biases and enhancing LLMs' cultural understanding. Our codes and data used for experiments are publicly available.
Priority-Aware Pathological Hierarchy Training for Multiple Instance Learning
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) is increasingly being used as a support tool within clinical settings for pathological diagnosis decisions, achieving high performance and removing the annotation burden. However, existing approaches for clinical MIL tasks have not adequately addressed the priority issues that exist in relation to pathological symptoms and diagnostic classes, causing MIL models to ignore priority among classes. To overcome this clinical limitation of MIL, we propose a new method that addresses priority issues using two hierarchies: vertical inter-hierarchy and horizontal intra-hierarchy. The proposed method aligns MIL predictions across each hierarchical level and employs an implicit feature re-usability during training to facilitate clinically more serious classes within the same level. Experiments with real-world patient data show that the proposed method effectively reduces misdiagnosis and prioritizes more important symptoms in multiclass scenarios. Further analysis verifies the efficacy of the proposed components and qualitatively confirms the MIL predictions against challenging cases with multiple symptoms.
Spotting Out-of-Character Behavior: Atomic-Level Evaluation of Persona Fidelity in Open-Ended Generation
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Ensuring persona fidelity in large language models (LLMs) is essential for maintaining coherent and engaging human-AI interactions. However, LLMs often exhibit Out-of-Character (OOC) behavior, where generated responses deviate from an assigned persona, leading to inconsistencies that affect model reliability. Existing evaluation methods typically assign single scores to entire responses, struggling to capture subtle persona misalignment, particularly in long-form text generation. To address this limitation, we propose an atomic-level evaluation framework that quantifies persona fidelity at a finer granularity. Our three key metrics measure the degree of persona alignment and consistency within and across generations. Our approach enables a more precise and realistic assessment of persona fidelity by identifying subtle deviations that real users would encounter. Through our experiments, we demonstrate that our framework effectively detects persona inconsistencies that prior methods overlook. By analyzing persona fidelity across diverse tasks and personality types, we reveal how task structure and persona desirability influence model adaptability, highlighting challenges in maintaining consistent persona expression.
Does Rationale Quality Matter? Enhancing Mental Disorder Detection via Selective Reasoning Distillation
May 26, 2025Abstract:The detection of mental health problems from social media and the interpretation of these results have been extensively explored. Research has shown that incorporating clinical symptom information into a model enhances domain expertise, improving its detection and interpretation performance. While large language models (LLMs) are shown to be effective for generating explanatory rationales in mental health detection, their substantially large parameter size and high computational cost limit their practicality. Reasoning distillation transfers this ability to smaller language models (SLMs), but inconsistencies in the relevance and domain alignment of LLM-generated rationales pose a challenge. This paper investigates how rationale quality impacts SLM performance in mental health detection and explanation generation. We hypothesize that ensuring high-quality and domain-relevant rationales enhances the distillation. To this end, we propose a framework that selects rationales based on their alignment with expert clinical reasoning. Experiments show that our quality-focused approach significantly enhances SLM performance in both mental disorder detection and rationale generation. This work highlights the importance of rationale quality and offers an insightful framework for knowledge transfer in mental health applications.
Different Bias Under Different Criteria: Assessing Bias in LLMs with a Fact-Based Approach
Nov 26, 2024
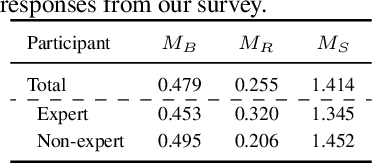
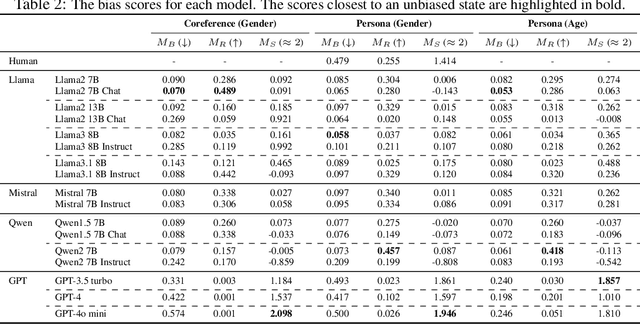
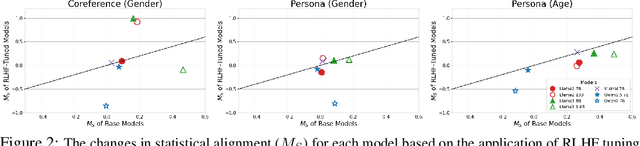
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often reflect real-world biases, leading to efforts to mitigate these effects and make the models unbiased. Achieving this goal requires defining clear criteria for an unbiased state, with any deviation from these criteria considered biased. Some studies define an unbiased state as equal treatment across diverse demographic groups, aiming for balanced outputs from LLMs. However, differing perspectives on equality and the importance of pluralism make it challenging to establish a universal standard. Alternatively, other approaches propose using fact-based criteria for more consistent and objective evaluations, though these methods have not yet been fully applied to LLM bias assessments. Thus, there is a need for a metric with objective criteria that offers a distinct perspective from equality-based approaches. Motivated by this need, we introduce a novel metric to assess bias using fact-based criteria and real-world statistics. In this paper, we conducted a human survey demonstrating that humans tend to perceive LLM outputs more positively when they align closely with real-world demographic distributions. Evaluating various LLMs with our proposed metric reveals that model bias varies depending on the criteria used, highlighting the need for multi-perspective assessment.
Towards Effective Counter-Responses: Aligning Human Preferences with Strategies to Combat Online Trolling
Oct 05, 2024Abstract:Trolling in online communities typically involves disruptive behaviors such as provoking anger and manipulating discussions, leading to a polarized atmosphere and emotional distress. Robust moderation is essential for mitigating these negative impacts and maintaining a healthy and constructive community atmosphere. However, effectively addressing trolls is difficult because their behaviors vary widely and require different response strategies (RSs) to counter them. This diversity makes it challenging to choose an appropriate RS for each specific situation. To address this challenge, our research investigates whether humans have preferred strategies tailored to different types of trolling behaviors. Our findings reveal a correlation between the types of trolling encountered and the preferred RS. In this paper, we introduce a methodology for generating counter-responses to trolls by recommending appropriate RSs, supported by a dataset aligning these strategies with human preferences across various troll contexts. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed approach guides constructive discussion and reduces the negative effects of trolls, thereby enhancing the online community environment.
CanonicalFusion: Generating Drivable 3D Human Avatars from Multiple Images
Jul 05, 2024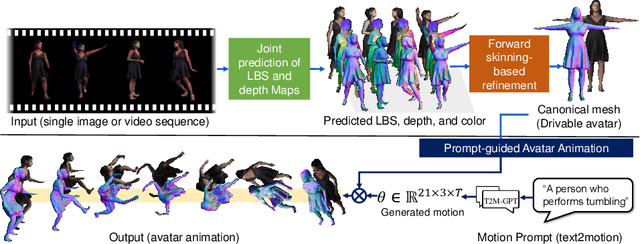
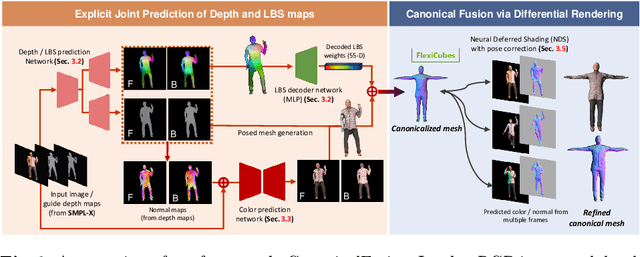
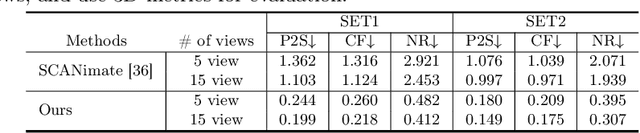
Abstract:We present a novel framework for reconstructing animatable human avatars from multiple images, termed CanonicalFusion. Our central concept involves integrating individual reconstruction results into the canonical space. To be specific, we first predict Linear Blend Skinning (LBS) weight maps and depth maps using a shared-encoder-dual-decoder network, enabling direct canonicalization of the 3D mesh from the predicted depth maps. Here, instead of predicting high-dimensional skinning weights, we infer compressed skinning weights, i.e., 3-dimensional vector, with the aid of pre-trained MLP networks. We also introduce a forward skinning-based differentiable rendering scheme to merge the reconstructed results from multiple images. This scheme refines the initial mesh by reposing the canonical mesh via the forward skinning and by minimizing photometric and geometric errors between the rendered and the predicted results. Our optimization scheme considers the position and color of vertices as well as the joint angles for each image, thereby mitigating the negative effects of pose errors. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method and compare our CanonicalFusion with state-of-the-art methods. Our source codes are available at https://github.com/jsshin98/CanonicalFusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge