Min-Gyu Park
CanonicalFusion: Generating Drivable 3D Human Avatars from Multiple Images
Jul 05, 2024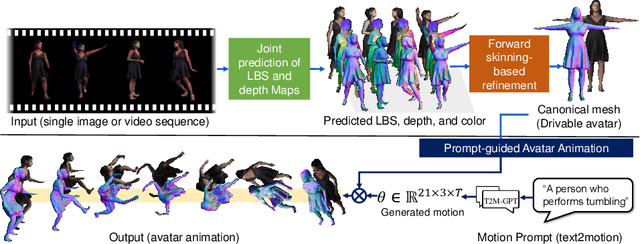
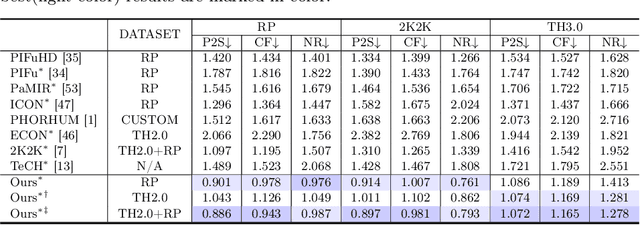
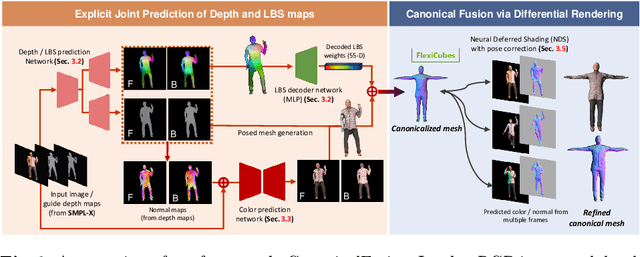
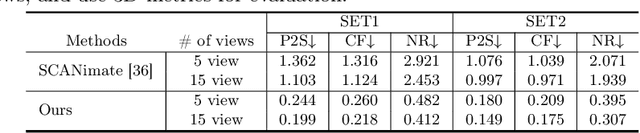
Abstract:We present a novel framework for reconstructing animatable human avatars from multiple images, termed CanonicalFusion. Our central concept involves integrating individual reconstruction results into the canonical space. To be specific, we first predict Linear Blend Skinning (LBS) weight maps and depth maps using a shared-encoder-dual-decoder network, enabling direct canonicalization of the 3D mesh from the predicted depth maps. Here, instead of predicting high-dimensional skinning weights, we infer compressed skinning weights, i.e., 3-dimensional vector, with the aid of pre-trained MLP networks. We also introduce a forward skinning-based differentiable rendering scheme to merge the reconstructed results from multiple images. This scheme refines the initial mesh by reposing the canonical mesh via the forward skinning and by minimizing photometric and geometric errors between the rendered and the predicted results. Our optimization scheme considers the position and color of vertices as well as the joint angles for each image, thereby mitigating the negative effects of pose errors. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method and compare our CanonicalFusion with state-of-the-art methods. Our source codes are available at https://github.com/jsshin98/CanonicalFusion.
High-fidelity 3D Human Digitization from Single 2K Resolution Images
Mar 27, 2023Abstract:High-quality 3D human body reconstruction requires high-fidelity and large-scale training data and appropriate network design that effectively exploits the high-resolution input images. To tackle these problems, we propose a simple yet effective 3D human digitization method called 2K2K, which constructs a large-scale 2K human dataset and infers 3D human models from 2K resolution images. The proposed method separately recovers the global shape of a human and its details. The low-resolution depth network predicts the global structure from a low-resolution image, and the part-wise image-to-normal network predicts the details of the 3D human body structure. The high-resolution depth network merges the global 3D shape and the detailed structures to infer the high-resolution front and back side depth maps. Finally, an off-the-shelf mesh generator reconstructs the full 3D human model, which are available at https://github.com/SangHunHan92/2K2K. In addition, we also provide 2,050 3D human models, including texture maps, 3D joints, and SMPL parameters for research purposes. In experiments, we demonstrate competitive performance over the recent works on various datasets.
Monocular Human Digitization via Implicit Re-projection Networks
May 16, 2022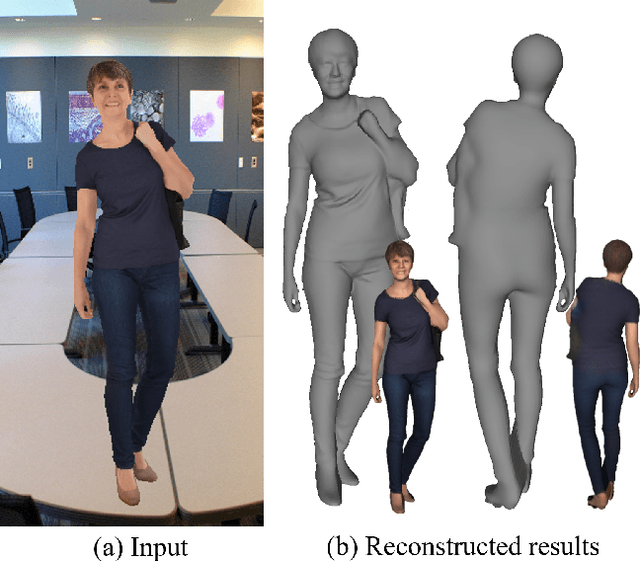
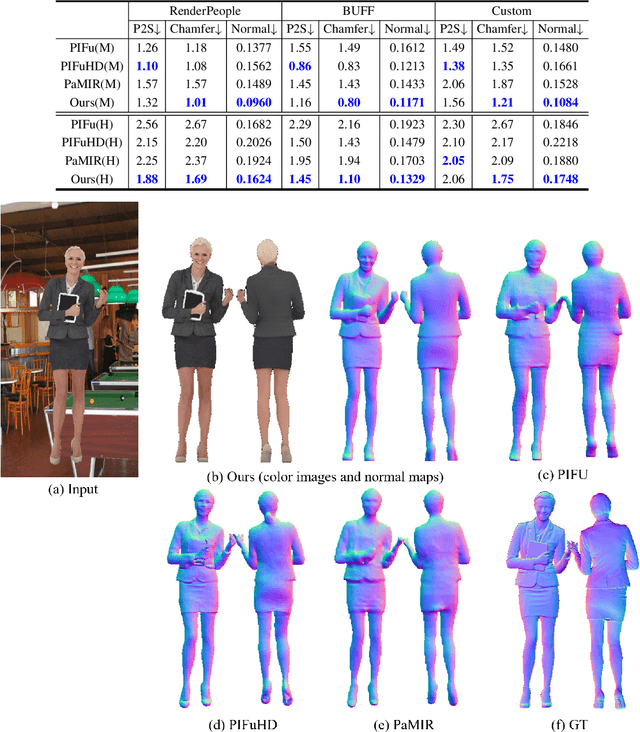
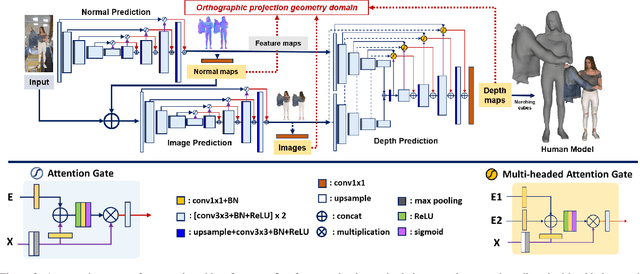
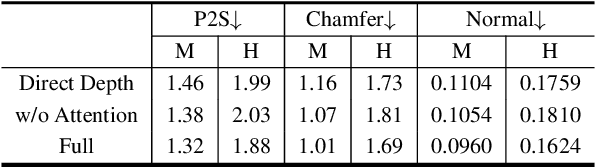
Abstract:We present an approach to generating 3D human models from images. The key to our framework is that we predict double-sided orthographic depth maps and color images from a single perspective projected image. Our framework consists of three networks. The first network predicts normal maps to recover geometric details such as wrinkles in the clothes and facial regions. The second network predicts shade-removed images for the front and back views by utilizing the predicted normal maps. The last multi-headed network takes both normal maps and shade-free images and predicts depth maps while selectively fusing photometric and geometric information through multi-headed attention gates. Experimental results demonstrate that our method shows visually plausible results and competitive performance in terms of various evaluation metrics over state-of-the-art methods.
Gyroscope-aided Relative Pose Estimation for Rolling Shutter Cameras
Apr 14, 2019
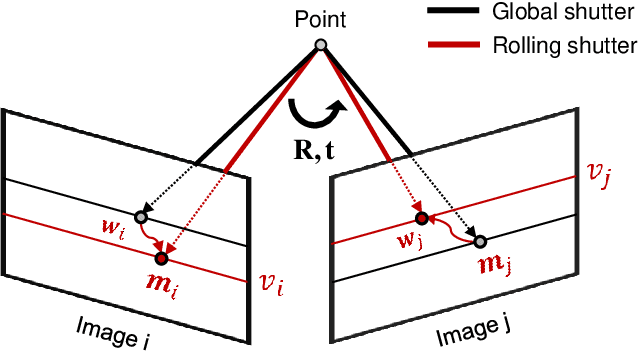
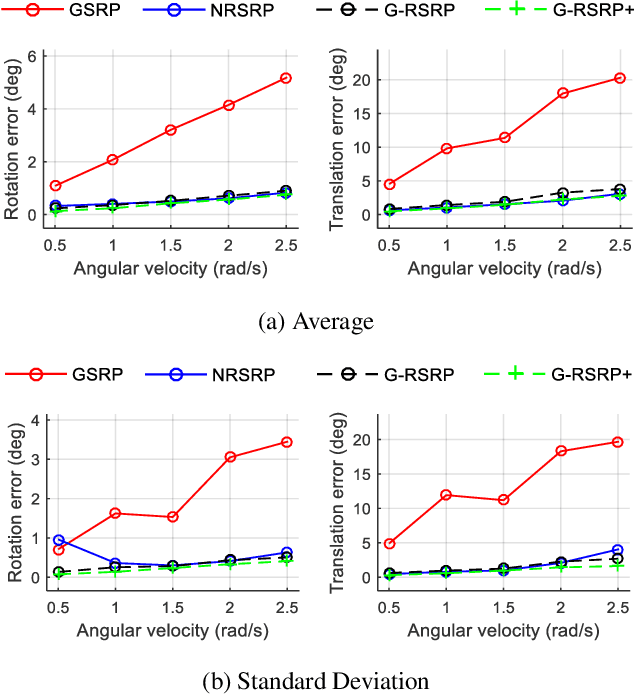
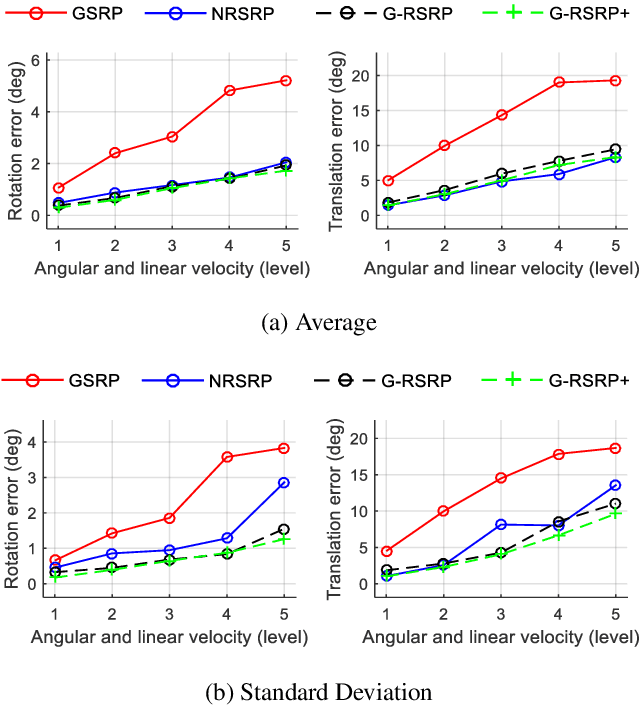
Abstract:The rolling shutter camera has received great attention due to its low cost imaging capability, however, the estimation of relative pose between rolling shutter cameras still remains a difficult problem owing to its line-by-line image capturing characteristics. To alleviate this problem, we exploit gyroscope measurements, angular velocity, along with image measurement to compute the relative pose between rolling shutter cameras. The gyroscope measurements provide the information about instantaneous motion that causes the rolling shutter distortion. Having gyroscope measurements in one hand, we simplify the relative pose estimation problem and find a minimal solution for the problem based on the Grobner basis polynomial solver. The proposed method requires only five points to compute relative pose between rolling shutter cameras, whereas previous methods require 20 or 44 corresponding points for linear and uniform rolling shutter geometry models, respectively. Experimental results on synthetic and real data verify the superiority of the proposed method over existing relative pose estimation methods.
Joint Layout Estimation and Global Multi-View Registration for Indoor Reconstruction
Sep 06, 2017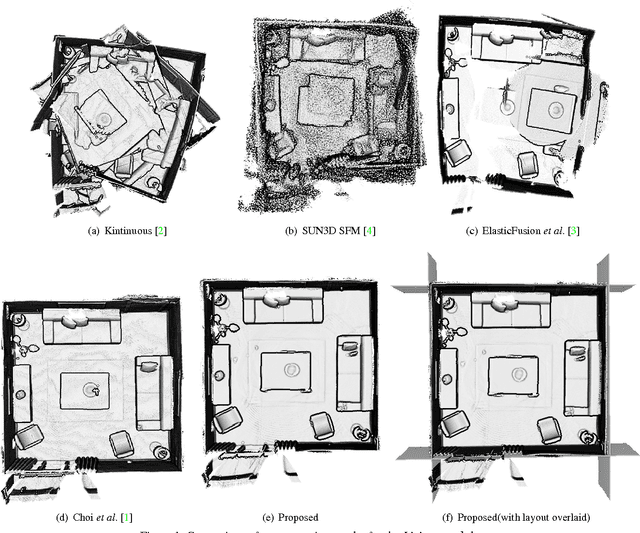
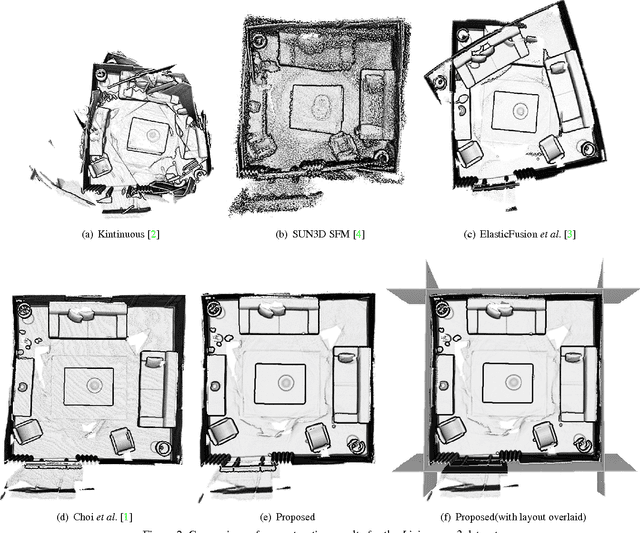
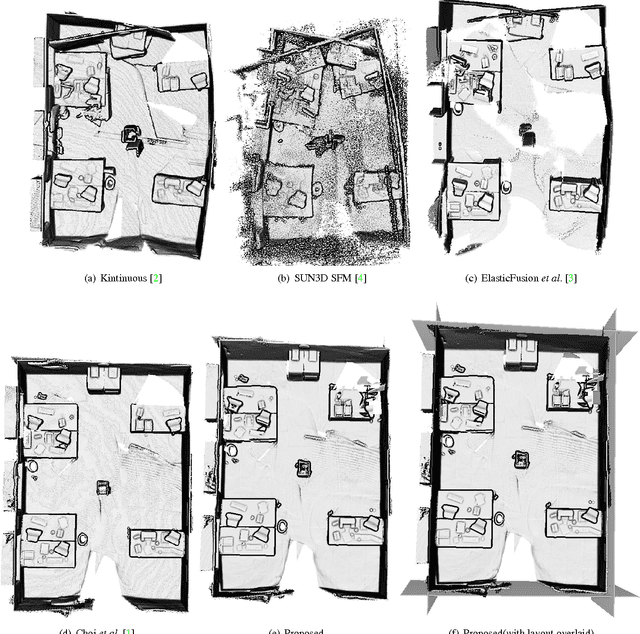
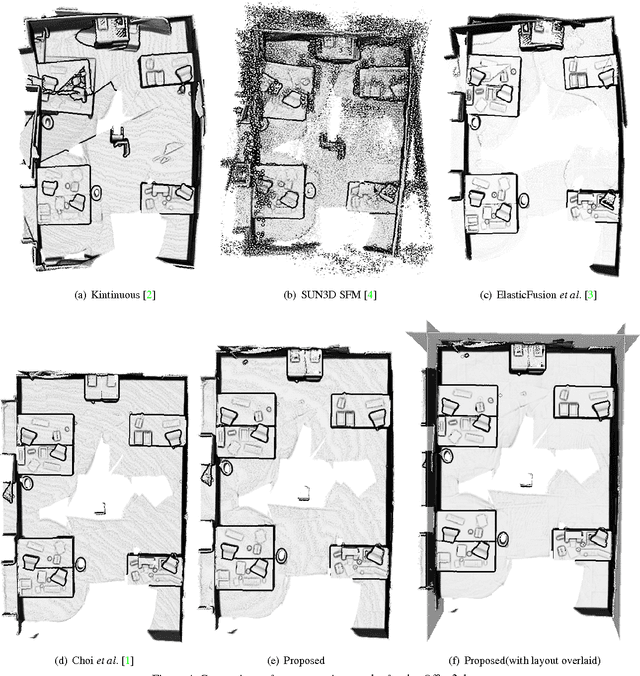
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel method to jointly solve scene layout estimation and global registration problems for accurate indoor 3D reconstruction. Given a sequence of range data, we first build a set of scene fragments using KinectFusion and register them through pose graph optimization. Afterwards, we alternate between layout estimation and layout-based global registration processes in iterative fashion to complement each other. We extract the scene layout through hierarchical agglomerative clustering and energy-based multi-model fitting in consideration of noisy measurements. Having the estimated scene layout in one hand, we register all the range data through the global iterative closest point algorithm where the positions of 3D points that belong to the layout such as walls and a ceiling are constrained to be close to the layout. We experimentally verify the proposed method with the publicly available synthetic and real-world datasets in both quantitative and qualitative ways.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge