Jeongyeon Seo
Lossless Acceleration of Large Language Models with Hierarchical Drafting based on Temporal Locality in Speculative Decoding
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:Accelerating inference in Large Language Models (LLMs) is critical for real-time interactions, as they have been widely incorporated into real-world services. Speculative decoding, a fully algorithmic solution, has gained attention for improving inference speed by drafting and verifying tokens, thereby generating multiple tokens in a single forward pass. However, current drafting strategies usually require significant fine-tuning or have inconsistent performance across tasks. To address these challenges, we propose Hierarchy Drafting (HD), a novel lossless drafting approach that organizes various token sources into multiple databases in a hierarchical framework based on temporal locality. In the drafting step, HD sequentially accesses multiple databases to obtain draft tokens from the highest to the lowest locality, ensuring consistent acceleration across diverse tasks and minimizing drafting latency. Our experiments on Spec-Bench using LLMs with 7B and 13B parameters demonstrate that HD outperforms existing database drafting methods, achieving robust inference speedups across model sizes, tasks, and temperatures.
Different Bias Under Different Criteria: Assessing Bias in LLMs with a Fact-Based Approach
Nov 26, 2024
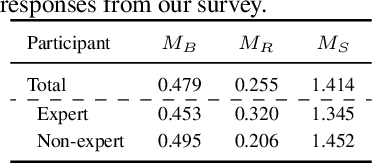
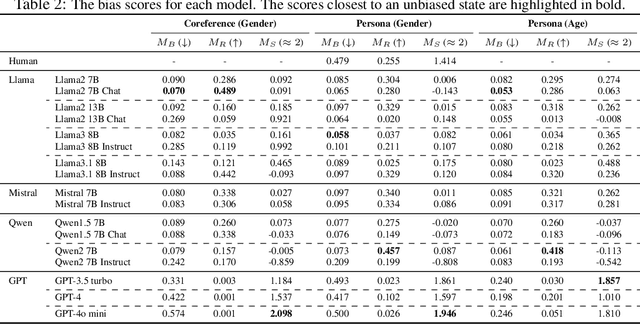
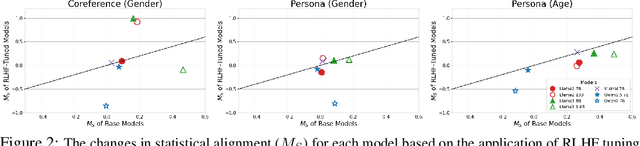
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often reflect real-world biases, leading to efforts to mitigate these effects and make the models unbiased. Achieving this goal requires defining clear criteria for an unbiased state, with any deviation from these criteria considered biased. Some studies define an unbiased state as equal treatment across diverse demographic groups, aiming for balanced outputs from LLMs. However, differing perspectives on equality and the importance of pluralism make it challenging to establish a universal standard. Alternatively, other approaches propose using fact-based criteria for more consistent and objective evaluations, though these methods have not yet been fully applied to LLM bias assessments. Thus, there is a need for a metric with objective criteria that offers a distinct perspective from equality-based approaches. Motivated by this need, we introduce a novel metric to assess bias using fact-based criteria and real-world statistics. In this paper, we conducted a human survey demonstrating that humans tend to perceive LLM outputs more positively when they align closely with real-world demographic distributions. Evaluating various LLMs with our proposed metric reveals that model bias varies depending on the criteria used, highlighting the need for multi-perspective assessment.
Typos that Broke the RAG's Back: Genetic Attack on RAG Pipeline by Simulating Documents in the Wild via Low-level Perturbations
Apr 22, 2024



Abstract:The robustness of recent Large Language Models (LLMs) has become increasingly crucial as their applicability expands across various domains and real-world applications. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a promising solution for addressing the limitations of LLMs, yet existing studies on the robustness of RAG often overlook the interconnected relationships between RAG components or the potential threats prevalent in real-world databases, such as minor textual errors. In this work, we investigate two underexplored aspects when assessing the robustness of RAG: 1) vulnerability to noisy documents through low-level perturbations and 2) a holistic evaluation of RAG robustness. Furthermore, we introduce a novel attack method, the Genetic Attack on RAG (\textit{GARAG}), which targets these aspects. Specifically, GARAG is designed to reveal vulnerabilities within each component and test the overall system functionality against noisy documents. We validate RAG robustness by applying our \textit{GARAG} to standard QA datasets, incorporating diverse retrievers and LLMs. The experimental results show that GARAG consistently achieves high attack success rates. Also, it significantly devastates the performance of each component and their synergy, highlighting the substantial risk that minor textual inaccuracies pose in disrupting RAG systems in the real world.
Improving Zero-shot Reader by Reducing Distractions from Irrelevant Documents in Open-Domain Question Answering
Nov 02, 2023

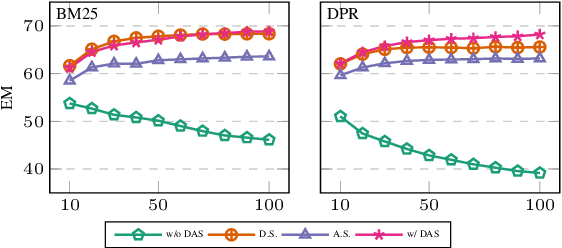

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) enable zero-shot approaches in open-domain question answering (ODQA), yet with limited advancements as the reader is compared to the retriever. This study aims at the feasibility of a zero-shot reader that addresses the challenges of computational cost and the need for labeled data. We find that LLMs are distracted due to irrelevant documents in the retrieved set and the overconfidence of the generated answers when they are exploited as zero-shot readers. To tackle these problems, we mitigate the impact of such documents via Distraction-aware Answer Selection (DAS) with a negation-based instruction and score adjustment for proper answer selection. Experimental results show that our approach successfully handles distraction across diverse scenarios, enhancing the performance of zero-shot readers. Furthermore, unlike supervised readers struggling with unseen data, zero-shot readers demonstrate outstanding transferability without any training.
Discrete Prompt Optimization via Constrained Generation for Zero-shot Re-ranker
May 23, 2023

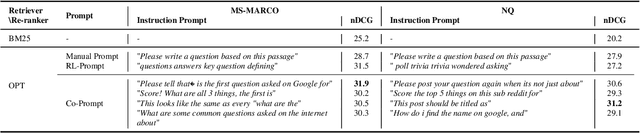

Abstract:Re-rankers, which order retrieved documents with respect to the relevance score on the given query, have gained attention for the information retrieval (IR) task. Rather than fine-tuning the pre-trained language model (PLM), the large-scale language model (LLM) is utilized as a zero-shot re-ranker with excellent results. While LLM is highly dependent on the prompts, the impact and the optimization of the prompts for the zero-shot re-ranker are not explored yet. Along with highlighting the impact of optimization on the zero-shot re-ranker, we propose a novel discrete prompt optimization method, Constrained Prompt generation (Co-Prompt), with the metric estimating the optimum for re-ranking. Co-Prompt guides the generated texts from PLM toward optimal prompts based on the metric without parameter update. The experimental results demonstrate that Co-Prompt leads to outstanding re-ranking performance against the baselines. Also, Co-Prompt generates more interpretable prompts for humans against other prompt optimization methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge