Changyoon Lee
Learning from Teaching Assistants to Program with Subgoals: Exploring the Potential for AI Teaching Assistants
Sep 19, 2023



Abstract:With recent advances in generative AI, conversational models like ChatGPT have become feasible candidates for TAs. We investigate the practicality of using generative AI as TAs in introductory programming education by examining novice learners' interaction with TAs in a subgoal learning environment. To compare the learners' interaction and perception of the AI and human TAs, we conducted a between-subject study with 20 novice programming learners. Learners solve programming tasks by producing subgoals and subsolutions with the guidance of a TA. Our study shows that learners can solve tasks faster with comparable scores with AI TAs. Learners' perception of the AI TA is on par with that of human TAs in terms of speed and comprehensiveness of the replies and helpfulness, difficulty, and satisfaction of the conversation. Finally, we suggest guidelines to better design and utilize generative AI as TAs in programming education from the result of our chat log analysis.
CS1QA: A Dataset for Assisting Code-based Question Answering in an Introductory Programming Course
Oct 26, 2022Abstract:We introduce CS1QA, a dataset for code-based question answering in the programming education domain. CS1QA consists of 9,237 question-answer pairs gathered from chat logs in an introductory programming class using Python, and 17,698 unannotated chat data with code. Each question is accompanied with the student's code, and the portion of the code relevant to answering the question. We carefully design the annotation process to construct CS1QA, and analyze the collected dataset in detail. The tasks for CS1QA are to predict the question type, the relevant code snippet given the question and the code and retrieving an answer from the annotated corpus. Results for the experiments on several baseline models are reported and thoroughly analyzed. The tasks for CS1QA challenge models to understand both the code and natural language. This unique dataset can be used as a benchmark for source code comprehension and question answering in the educational setting.
Rethinking Annotation: Can Language Learners Contribute?
Oct 13, 2022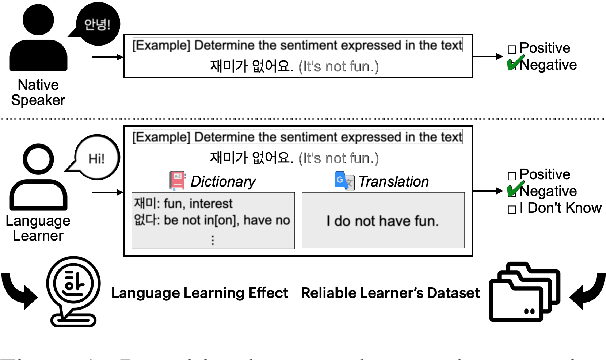
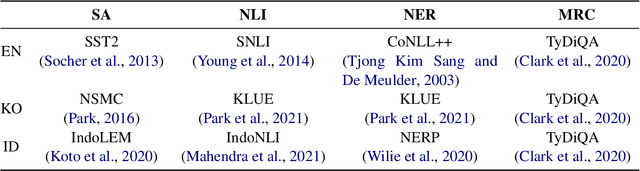
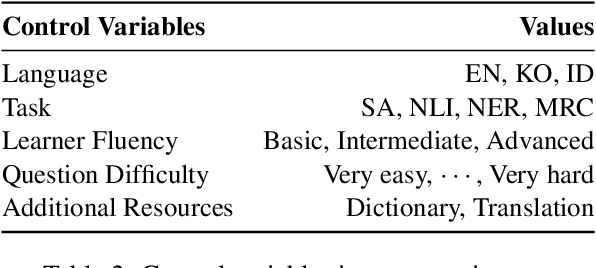
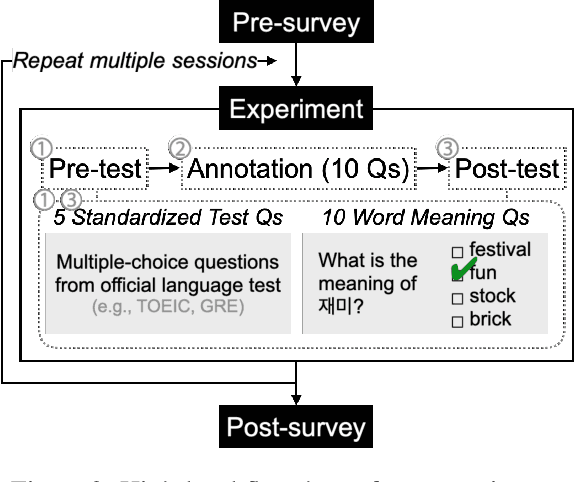
Abstract:Researchers have traditionally recruited native speakers to provide annotations for the widely used benchmark datasets. But there are languages for which recruiting native speakers is difficult, and it would help to get learners of those languages to annotate the data. In this paper, we investigate whether language learners can contribute annotations to the benchmark datasets. In a carefully controlled annotation experiment, we recruit 36 language learners, provide two types of additional resources (dictionaries and machine-translated sentences), and perform mini-tests to measure their language proficiency. We target three languages, English, Korean, and Indonesian, and four NLP tasks, sentiment analysis, natural language inference, named entity recognition, and machine reading comprehension. We find that language learners, especially those with intermediate or advanced language proficiency, are able to provide fairly accurate labels with the help of additional resources. Moreover, we show that data annotation improves learners' language proficiency in terms of vocabulary and grammar. The implication of our findings is that broadening the annotation task to include language learners can open up the opportunity to build benchmark datasets for languages for which it is difficult to recruit native speakers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge