Masato Ishii
AutoRefiner: Improving Autoregressive Video Diffusion Models via Reflective Refinement Over the Stochastic Sampling Path
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive video diffusion models (AR-VDMs) show strong promise as scalable alternatives to bidirectional VDMs, enabling real-time and interactive applications. Yet there remains room for improvement in their sample fidelity. A promising solution is inference-time alignment, which optimizes the noise space to improve sample fidelity without updating model parameters. Yet, optimization- or search-based methods are computationally impractical for AR-VDMs. Recent text-to-image (T2I) works address this via feedforward noise refiners that modulate sampled noises in a single forward pass. Can such noise refiners be extended to AR-VDMs? We identify the failure of naively extending T2I noise refiners to AR-VDMs and propose AutoRefiner-a noise refiner tailored for AR-VDMs, with two key designs: pathwise noise refinement and a reflective KV-cache. Experiments demonstrate that AutoRefiner serves as an efficient plug-in for AR-VDMs, effectively enhancing sample fidelity by refining noise along stochastic denoising paths.
Schrodinger Audio-Visual Editor: Object-Level Audiovisual Removal
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Joint editing of audio and visual content is crucial for precise and controllable content creation. This new task poses challenges due to the limitations of paired audio-visual data before and after targeted edits, and the heterogeneity across modalities. To address the data and modeling challenges in joint audio-visual editing, we introduce SAVEBench, a paired audiovisual dataset with text and mask conditions to enable object-grounded source-to-target learning. With SAVEBench, we train the Schrodinger Audio-Visual Editor (SAVE), an end-to-end flow-matching model that edits audio and video in parallel while keeping them aligned throughout processing. SAVE incorporates a Schrodinger Bridge that learns a direct transport from source to target audiovisual mixtures. Our evaluation demonstrates that the proposed SAVE model is able to remove the target objects in audio and visual content while preserving the remaining content, with stronger temporal synchronization and audiovisual semantic correspondence compared with pairwise combinations of an audio editor and a video editor.
Coherent Audio-Visual Editing via Conditional Audio Generation Following Video Edits
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:We introduce a novel pipeline for joint audio-visual editing that enhances the coherence between edited video and its accompanying audio. Our approach first applies state-of-the-art video editing techniques to produce the target video, then performs audio editing to align with the visual changes. To achieve this, we present a new video-to-audio generation model that conditions on the source audio, target video, and a text prompt. We extend the model architecture to incorporate conditional audio input and propose a data augmentation strategy that improves training efficiency. Furthermore, our model dynamically adjusts the influence of the source audio based on the complexity of the edits, preserving the original audio structure where possible. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches in maintaining audio-visual alignment and content integrity.
SoundReactor: Frame-level Online Video-to-Audio Generation
Oct 02, 2025



Abstract:Prevailing Video-to-Audio (V2A) generation models operate offline, assuming an entire video sequence or chunks of frames are available beforehand. This critically limits their use in interactive applications such as live content creation and emerging generative world models. To address this gap, we introduce the novel task of frame-level online V2A generation, where a model autoregressively generates audio from video without access to future video frames. Furthermore, we propose SoundReactor, which, to the best of our knowledge, is the first simple yet effective framework explicitly tailored for this task. Our design enforces end-to-end causality and targets low per-frame latency with audio-visual synchronization. Our model's backbone is a decoder-only causal transformer over continuous audio latents. For vision conditioning, it leverages grid (patch) features extracted from the smallest variant of the DINOv2 vision encoder, which are aggregated into a single token per frame to maintain end-to-end causality and efficiency. The model is trained through a diffusion pre-training followed by consistency fine-tuning to accelerate the diffusion head decoding. On a benchmark of diverse gameplay videos from AAA titles, our model successfully generates semantically and temporally aligned, high-quality full-band stereo audio, validated by both objective and human evaluations. Furthermore, our model achieves low per-frame waveform-level latency (26.3ms with the head NFE=1, 31.5ms with NFE=4) on 30FPS, 480p videos using a single H100. Demo samples are available at https://koichi-saito-sony.github.io/soundreactor/.
TITAN-Guide: Taming Inference-Time AligNment for Guided Text-to-Video Diffusion Models
Aug 01, 2025



Abstract:In the recent development of conditional diffusion models still require heavy supervised fine-tuning for performing control on a category of tasks. Training-free conditioning via guidance with off-the-shelf models is a favorable alternative to avoid further fine-tuning on the base model. However, the existing training-free guidance frameworks either have heavy memory requirements or offer sub-optimal control due to rough estimation. These shortcomings limit the applicability to control diffusion models that require intense computation, such as Text-to-Video (T2V) diffusion models. In this work, we propose Taming Inference Time Alignment for Guided Text-to-Video Diffusion Model, so-called TITAN-Guide, which overcomes memory space issues, and provides more optimal control in the guidance process compared to the counterparts. In particular, we develop an efficient method for optimizing diffusion latents without backpropagation from a discriminative guiding model. In particular, we study forward gradient descents for guided diffusion tasks with various options on directional directives. In our experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in efficiently managing memory during latent optimization, while previous methods fall short. Our proposed approach not only minimizes memory requirements but also significantly enhances T2V performance across a range of diffusion guidance benchmarks. Code, models, and demo are available at https://titanguide.github.io.
Step-by-Step Video-to-Audio Synthesis via Negative Audio Guidance
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel step-by-step video-to-audio generation method that sequentially produces individual audio tracks, each corresponding to a specific sound event in the video. Our approach mirrors traditional Foley workflows, aiming to capture all sound events induced by a given video comprehensively. Each generation step is formulated as a guided video-to-audio synthesis task, conditioned on a target text prompt and previously generated audio tracks. This design is inspired by the idea of concept negation from prior compositional generation frameworks. To enable this guided generation, we introduce a training framework that leverages pre-trained video-to-audio models and eliminates the need for specialized paired datasets, allowing training on more accessible data. Experimental results demonstrate that our method generates multiple semantically distinct audio tracks for a single input video, leading to higher-quality composite audio synthesis than existing baselines.
Taming Multimodal Joint Training for High-Quality Video-to-Audio Synthesis
Dec 19, 2024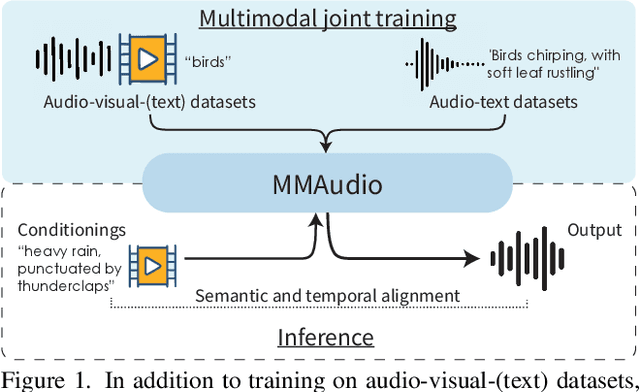
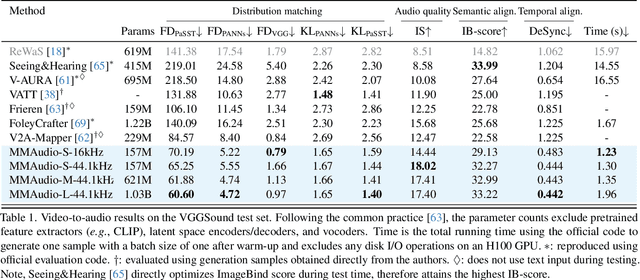
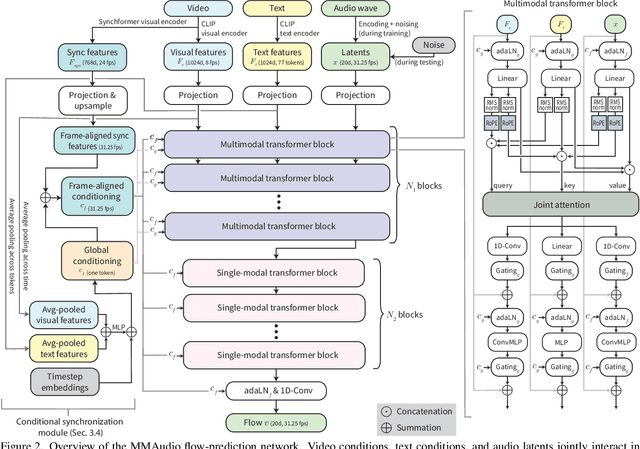
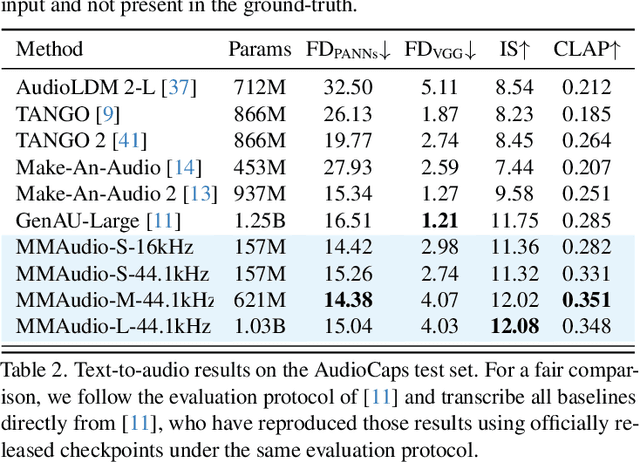
Abstract:We propose to synthesize high-quality and synchronized audio, given video and optional text conditions, using a novel multimodal joint training framework MMAudio. In contrast to single-modality training conditioned on (limited) video data only, MMAudio is jointly trained with larger-scale, readily available text-audio data to learn to generate semantically aligned high-quality audio samples. Additionally, we improve audio-visual synchrony with a conditional synchronization module that aligns video conditions with audio latents at the frame level. Trained with a flow matching objective, MMAudio achieves new video-to-audio state-of-the-art among public models in terms of audio quality, semantic alignment, and audio-visual synchronization, while having a low inference time (1.23s to generate an 8s clip) and just 157M parameters. MMAudio also achieves surprisingly competitive performance in text-to-audio generation, showing that joint training does not hinder single-modality performance. Code and demo are available at: https://hkchengrex.github.io/MMAudio
Mining Your Own Secrets: Diffusion Classifier Scores for Continual Personalization of Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Oct 02, 2024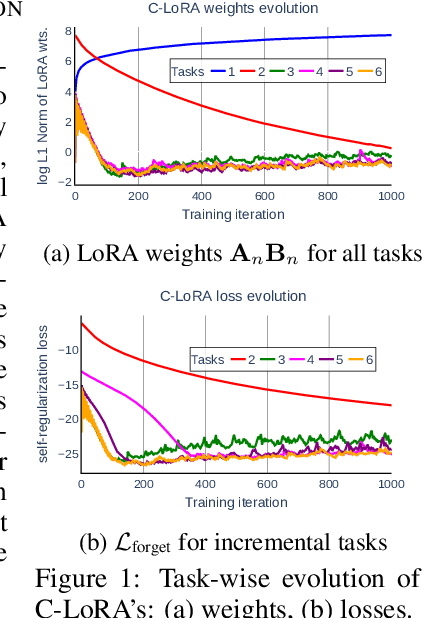
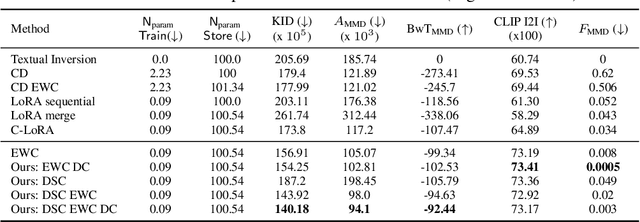
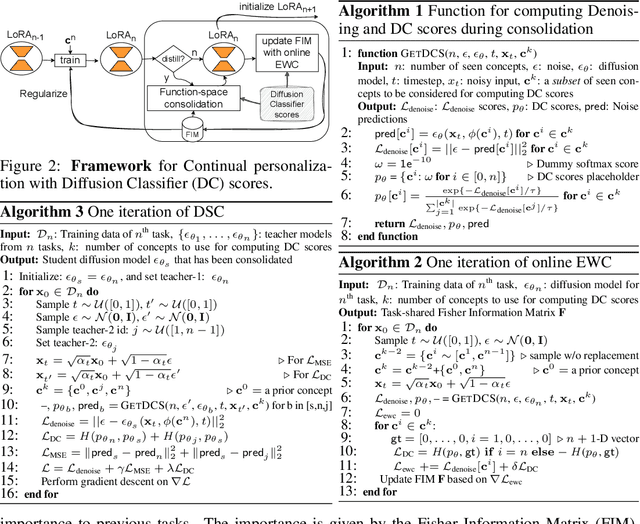
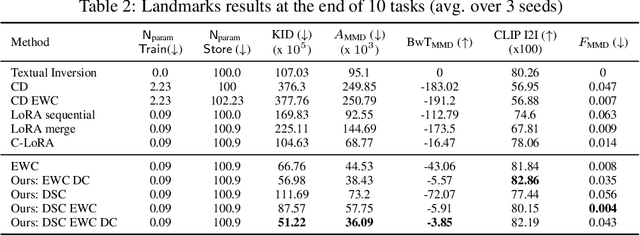
Abstract:Personalized text-to-image diffusion models have grown popular for their ability to efficiently acquire a new concept from user-defined text descriptions and a few images. However, in the real world, a user may wish to personalize a model on multiple concepts but one at a time, with no access to the data from previous concepts due to storage/privacy concerns. When faced with this continual learning (CL) setup, most personalization methods fail to find a balance between acquiring new concepts and retaining previous ones -- a challenge that continual personalization (CP) aims to solve. Inspired by the successful CL methods that rely on class-specific information for regularization, we resort to the inherent class-conditioned density estimates, also known as diffusion classifier (DC) scores, for continual personalization of text-to-image diffusion models. Namely, we propose using DC scores for regularizing the parameter-space and function-space of text-to-image diffusion models, to achieve continual personalization. Using several diverse evaluation setups, datasets, and metrics, we show that our proposed regularization-based CP methods outperform the state-of-the-art C-LoRA, and other baselines. Finally, by operating in the replay-free CL setup and on low-rank adapters, our method incurs zero storage and parameter overhead, respectively, over the state-of-the-art.
A Simple but Strong Baseline for Sounding Video Generation: Effective Adaptation of Audio and Video Diffusion Models for Joint Generation
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we build a simple but strong baseline for sounding video generation. Given base diffusion models for audio and video, we integrate them with additional modules into a single model and train it to make the model jointly generate audio and video. To enhance alignment between audio-video pairs, we introduce two novel mechanisms in our model. The first one is timestep adjustment, which provides different timestep information to each base model. It is designed to align how samples are generated along with timesteps across modalities. The second one is a new design of the additional modules, termed Cross-Modal Conditioning as Positional Encoding (CMC-PE). In CMC-PE, cross-modal information is embedded as if it represents temporal position information, and the embeddings are fed into the model like positional encoding. Compared with the popular cross-attention mechanism, CMC-PE provides a better inductive bias for temporal alignment in the generated data. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of the two newly introduced mechanisms and also demonstrate that our method outperforms existing methods.
Discriminator-Guided Cooperative Diffusion for Joint Audio and Video Generation
May 28, 2024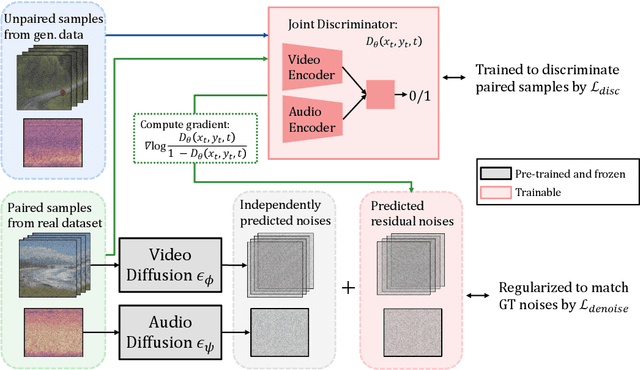
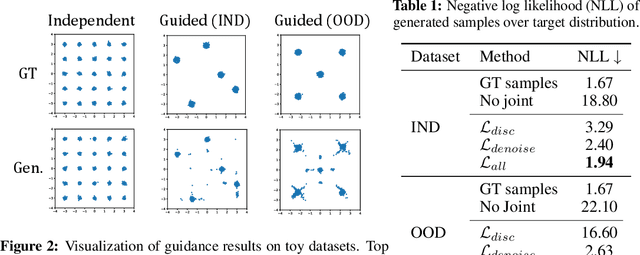
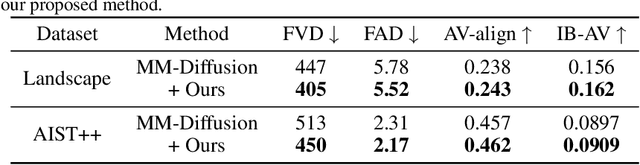
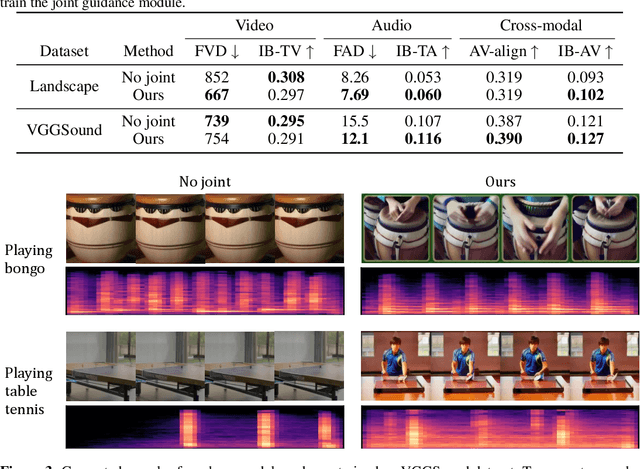
Abstract:In this study, we aim to construct an audio-video generative model with minimal computational cost by leveraging pre-trained single-modal generative models for audio and video. To achieve this, we propose a novel method that guides each single-modal model to cooperatively generate well-aligned samples across modalities. Specifically, given two pre-trained base diffusion models, we train a lightweight joint guidance module to adjust scores separately estimated by the base models to match the score of joint distribution over audio and video. We theoretically show that this guidance can be computed through the gradient of the optimal discriminator distinguishing real audio-video pairs from fake ones independently generated by the base models. On the basis of this analysis, we construct the joint guidance module by training this discriminator. Additionally, we adopt a loss function to make the gradient of the discriminator work as a noise estimator, as in standard diffusion models, stabilizing the gradient of the discriminator. Empirical evaluations on several benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method improves both single-modal fidelity and multi-modal alignment with a relatively small number of parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge