Chao Hu
GlimpRouter: Efficient Collaborative Inference by Glimpsing One Token of Thoughts
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) achieve remarkable performance by explicitly generating multi-step chains of thought, but this capability incurs substantial inference latency and computational cost. Collaborative inference offers a promising solution by selectively allocating work between lightweight and large models, yet a fundamental challenge remains: determining when a reasoning step requires the capacity of a large model or the efficiency of a small model. Existing routing strategies either rely on local token probabilities or post-hoc verification, introducing significant inference overhead. In this work, we propose a novel perspective on step-wise collaboration: the difficulty of a reasoning step can be inferred from its very first token. Inspired by the "Aha Moment" phenomenon in LRMs, we show that the entropy of the initial token serves as a strong predictor of step difficulty. Building on this insight, we introduce GlimpRouter, a training-free step-wise collaboration framework. GlimpRouter employs a lightweight model to generate only the first token of each reasoning step and routes the step to a larger model only when the initial token entropy exceeds a threshold. Experiments on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our approach significantly reduces inference latency while preserving accuracy. For instance, GlimpRouter attains a substantial 10.7% improvement in accuracy while reducing inference latency by 25.9% compared to a standalone large model on AIME25. These results suggest a simple yet effective mechanism for reasoning: allocating computation based on a glimpse of thought rather than full-step evaluation.
In Line with Context: Repository-Level Code Generation via Context Inlining
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Repository-level code generation has attracted growing attention in recent years. Unlike function-level code generation, it requires the model to understand the entire repository, reasoning over complex dependencies across functions, classes, and modules. However, existing approaches such as retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) or context-based function selection often fall short: they primarily rely on surface-level similarity and struggle to capture the rich dependencies that govern repository-level semantics. In this paper, we introduce InlineCoder, a novel framework for repository-level code generation. InlineCoder enhances the understanding of repository context by inlining the unfinished function into its call graph, thereby reframing the challenging repository understanding as an easier function-level coding task. Given a function signature, InlineCoder first generates a draft completion, termed an anchor, which approximates downstream dependencies and enables perplexity-based confidence estimation. This anchor drives a bidirectional inlining process: (i) Upstream Inlining, which embeds the anchor into its callers to capture diverse usage scenarios; and (ii) Downstream Retrieval, which integrates the anchor's callees into the prompt to provide precise dependency context. The enriched context, combining draft completion with upstream and downstream perspectives, equips the LLM with a comprehensive repository view.
6D Channel Knowledge Map Construction via Bidirectional Wireless Gaussian Splatting
Oct 30, 2025
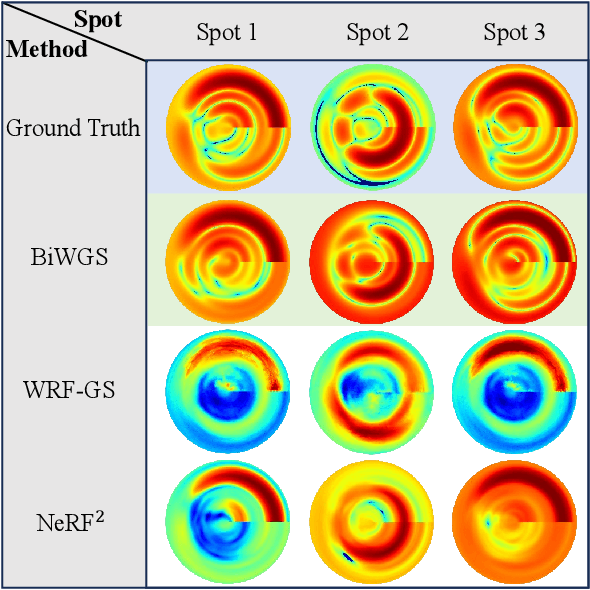
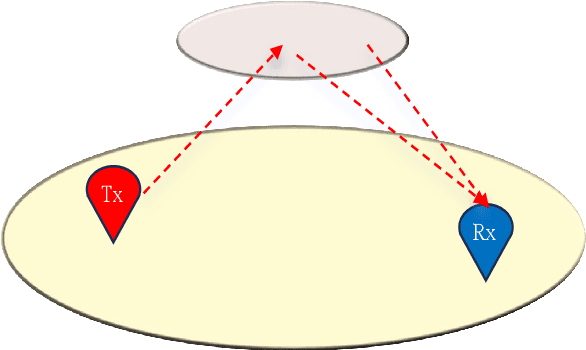
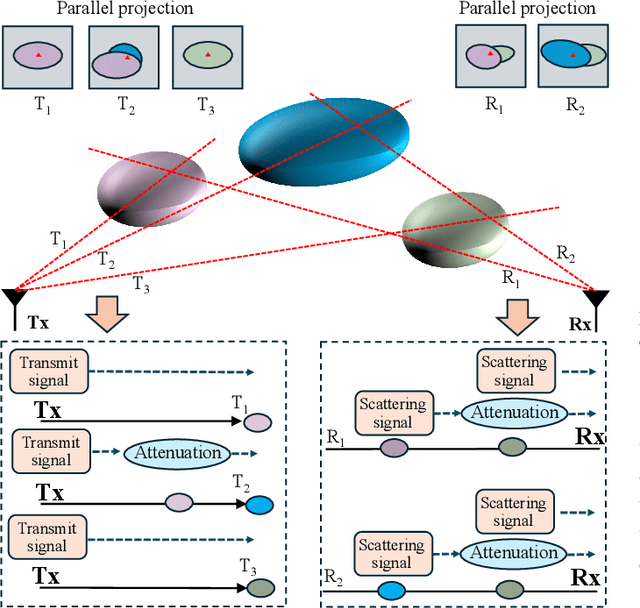
Abstract:This paper investigates the construction of channel knowledge map (CKM) from sparse channel measurements. Dif ferent from conventional two-/three-dimensional (2D/3D) CKM approaches assuming fixed base station configurations, we present a six-dimensional (6D) CKM framework named bidirectional wireless Gaussian splatting (BiWGS), which is capable of mod eling wireless channels across dynamic transmitter (Tx) and receiver (Rx) positions in 3D space. BiWGS uses Gaussian el lipsoids to represent virtual scatterer clusters and environmental obstacles in the wireless environment. By properly learning the bidirectional scattering patterns and complex attenuation profiles based on channel measurements, these ellipsoids inherently cap ture the electromagnetic transmission characteristics of wireless environments, thereby accurately modeling signal transmission under varying transceiver configurations. Experiment results show that BiWGS significantly outperforms classic multi-layer perception (MLP) for the construction of 6D channel power gain map with varying Tx-Rx positions, and achieves spatial spectrum prediction accuracy comparable to the state-of-the art wireless radiation field Gaussian splatting (WRF-GS) for 3D CKM construction. This validates the capability of the proposed BiWGS in accomplishing dimensional expansion of 6D CKM construction, without compromising fidelity.
Robust Multimodal Learning for Ophthalmic Disease Grading via Disentangled Representation
Mar 07, 2025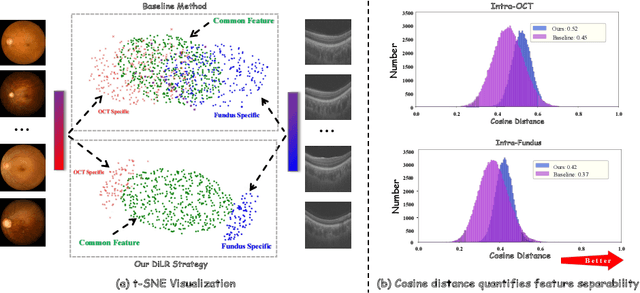
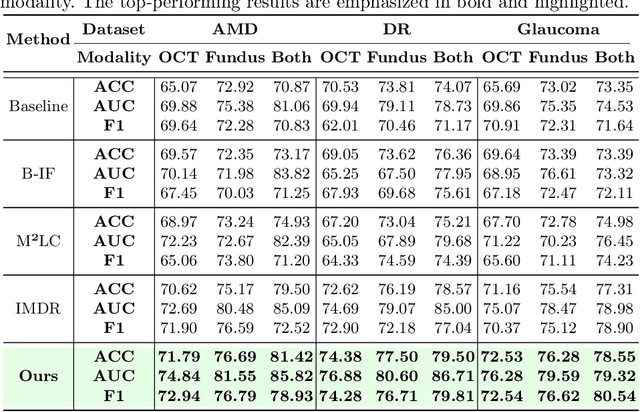
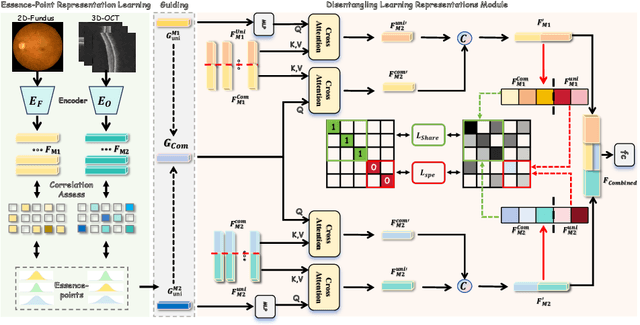

Abstract:This paper discusses how ophthalmologists often rely on multimodal data to improve diagnostic accuracy. However, complete multimodal data is rare in real-world applications due to a lack of medical equipment and concerns about data privacy. Traditional deep learning methods typically address these issues by learning representations in latent space. However, the paper highlights two key limitations of these approaches: (i) Task-irrelevant redundant information (e.g., numerous slices) in complex modalities leads to significant redundancy in latent space representations. (ii) Overlapping multimodal representations make it difficult to extract unique features for each modality. To overcome these challenges, the authors propose the Essence-Point and Disentangle Representation Learning (EDRL) strategy, which integrates a self-distillation mechanism into an end-to-end framework to enhance feature selection and disentanglement for more robust multimodal learning. Specifically, the Essence-Point Representation Learning module selects discriminative features that improve disease grading performance. The Disentangled Representation Learning module separates multimodal data into modality-common and modality-unique representations, reducing feature entanglement and enhancing both robustness and interpretability in ophthalmic disease diagnosis. Experiments on multimodal ophthalmology datasets show that the proposed EDRL strategy significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art methods.
Facial Identity Anonymization via Intrinsic and Extrinsic Attention Distraction
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:The unprecedented capture and application of face images raise increasing concerns on anonymization to fight against privacy disclosure. Most existing methods may suffer from the problem of excessive change of the identity-independent information or insufficient identity protection. In this paper, we present a new face anonymization approach by distracting the intrinsic and extrinsic identity attentions. On the one hand, we anonymize the identity information in the feature space by distracting the intrinsic identity attention. On the other, we anonymize the visual clues (i.e. appearance and geometry structure) by distracting the extrinsic identity attention. Our approach allows for flexible and intuitive manipulation of face appearance and geometry structure to produce diverse results, and it can also be used to instruct users to perform personalized anonymization. We conduct extensive experiments on multiple datasets and demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
Joint Angle and Delay Cramér-Rao Bound Optimization for Integrated Sensing and Communications
Nov 13, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we study a multi-input multi-output (MIMO) beamforming design in an integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system, in which an ISAC base station (BS) is used to communicate with multiple downlink users and simultaneously the communication signals are reused for sensing multiple targets. Our interested sensing parameters are the angle and delay information of the targets, which can be used to locate these targets. Under this consideration, we first derive the Cram\'{e}r-Rao bound (CRB) for angle and delay estimation. Then, we optimize the transmit beamforming at the BS to minimize the CRB, subject to communication rate and power constraints. In particular, we obtain the optimal solution in closed-form in the case of single-target and single-user, and in the case of multi-target and multi-user scenario, the sparsity of the optimal solution is proven, leading to a reduction in computational complexity during optimization. The numerical results demonstrate that the optimized beamforming yields excellent positioning performance and effectively reduces the requirement for a large number of antennas at the BS.
An interpretable deep learning method for bearing fault diagnosis
Aug 20, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning (DL) has gained popularity in recent years as an effective tool for classifying the current health and predicting the future of industrial equipment. However, most DL models have black-box components with an underlying structure that is too complex to be interpreted and explained to human users. This presents significant challenges when deploying these models for safety-critical maintenance tasks, where non-technical personnel often need to have complete trust in the recommendations these models give. To address these challenges, we utilize a convolutional neural network (CNN) with Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM) activation map visualizations to form an interpretable DL method for classifying bearing faults. After the model training process, we apply Grad-CAM to identify a training sample's feature importance and to form a library of diagnosis knowledge (or health library) containing training samples with annotated feature maps. During the model evaluation process, the proposed approach retrieves prediction basis samples from the health library according to the similarity of the feature importance. The proposed method can be easily applied to any CNN model without modifying the model architecture, and our experimental results show that this method can select prediction basis samples that are intuitively and physically meaningful, improving the model's trustworthiness for human users.
Predicting Battery Lifetime Under Varying Usage Conditions from Early Aging Data
Jul 17, 2023Abstract:Accurate battery lifetime prediction is important for preventative maintenance, warranties, and improved cell design and manufacturing. However, manufacturing variability and usage-dependent degradation make life prediction challenging. Here, we investigate new features derived from capacity-voltage data in early life to predict the lifetime of cells cycled under widely varying charge rates, discharge rates, and depths of discharge. Features were extracted from regularly scheduled reference performance tests (i.e., low rate full cycles) during cycling. The early-life features capture a cell's state of health and the rate of change of component-level degradation modes, some of which correlate strongly with cell lifetime. Using a newly generated dataset from 225 nickel-manganese-cobalt/graphite Li-ion cells aged under a wide range of conditions, we demonstrate a lifetime prediction of in-distribution cells with 15.1% mean absolute percentage error using no more than the first 15% of data, for most cells. Further testing using a hierarchical Bayesian regression model shows improved performance on extrapolation, achieving 21.8% mean absolute percentage error for out-of-distribution cells. Our approach highlights the importance of using domain knowledge of lithium-ion battery degradation modes to inform feature engineering. Further, we provide the community with a new publicly available battery aging dataset with cells cycled beyond 80% of their rated capacity.
When SAM Meets Sonar Images
Jun 25, 2023Abstract:Segment Anything Model (SAM) has revolutionized the way of segmentation. However, SAM's performance may decline when applied to tasks involving domains that differ from natural images. Nonetheless, by employing fine-tuning techniques, SAM exhibits promising capabilities in specific domains, such as medicine and planetary science. Notably, there is a lack of research on the application of SAM to sonar imaging. In this paper, we aim to address this gap by conducting a comprehensive investigation of SAM's performance on sonar images. Specifically, we evaluate SAM using various settings on sonar images. Additionally, we fine-tune SAM using effective methods both with prompts and for semantic segmentation, thereby expanding its applicability to tasks requiring automated segmentation. Experimental results demonstrate a significant improvement in the performance of the fine-tuned SAM.
Uncertainty Quantification in Machine Learning for Engineering Design and Health Prognostics: A Tutorial
May 07, 2023Abstract:On top of machine learning models, uncertainty quantification (UQ) functions as an essential layer of safety assurance that could lead to more principled decision making by enabling sound risk assessment and management. The safety and reliability improvement of ML models empowered by UQ has the potential to significantly facilitate the broad adoption of ML solutions in high-stakes decision settings, such as healthcare, manufacturing, and aviation, to name a few. In this tutorial, we aim to provide a holistic lens on emerging UQ methods for ML models with a particular focus on neural networks and the applications of these UQ methods in tackling engineering design as well as prognostics and health management problems. Toward this goal, we start with a comprehensive classification of uncertainty types, sources, and causes pertaining to UQ of ML models. Next, we provide a tutorial-style description of several state-of-the-art UQ methods: Gaussian process regression, Bayesian neural network, neural network ensemble, and deterministic UQ methods focusing on spectral-normalized neural Gaussian process. Established upon the mathematical formulations, we subsequently examine the soundness of these UQ methods quantitatively and qualitatively (by a toy regression example) to examine their strengths and shortcomings from different dimensions. Then, we review quantitative metrics commonly used to assess the quality of predictive uncertainty in classification and regression problems. Afterward, we discuss the increasingly important role of UQ of ML models in solving challenging problems in engineering design and health prognostics. Two case studies with source codes available on GitHub are used to demonstrate these UQ methods and compare their performance in the life prediction of lithium-ion batteries at the early stage and the remaining useful life prediction of turbofan engines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge