Bryan Perozzi
Position: Graph Learning Will Lose Relevance Due To Poor Benchmarks
Feb 20, 2025
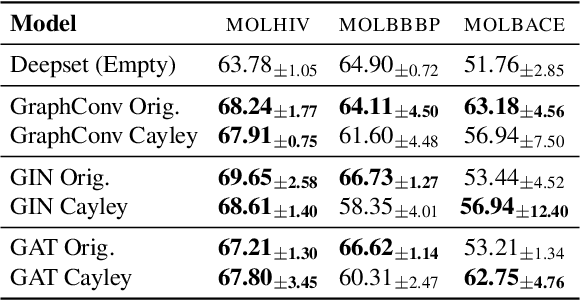
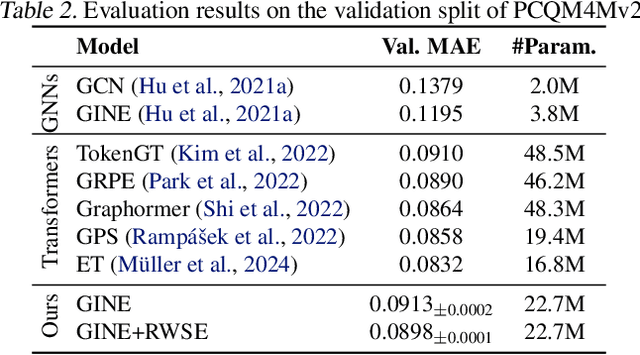
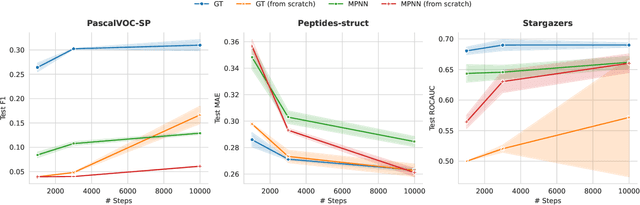
Abstract:While machine learning on graphs has demonstrated promise in drug design and molecular property prediction, significant benchmarking challenges hinder its further progress and relevance. Current benchmarking practices often lack focus on transformative, real-world applications, favoring narrow domains like two-dimensional molecular graphs over broader, impactful areas such as combinatorial optimization, relational databases, or chip design. Additionally, many benchmark datasets poorly represent the underlying data, leading to inadequate abstractions and misaligned use cases. Fragmented evaluations and an excessive focus on accuracy further exacerbate these issues, incentivizing overfitting rather than fostering generalizable insights. These limitations have prevented the development of truly useful graph foundation models. This position paper calls for a paradigm shift toward more meaningful benchmarks, rigorous evaluation protocols, and stronger collaboration with domain experts to drive impactful and reliable advances in graph learning research, unlocking the potential of graph learning.
Best of Both Worlds: Advantages of Hybrid Graph Sequence Models
Nov 23, 2024Abstract:Modern sequence models (e.g., Transformers, linear RNNs, etc.) emerged as dominant backbones of recent deep learning frameworks, mainly due to their efficiency, representational power, and/or ability to capture long-range dependencies. Adopting these sequence models for graph-structured data has recently gained popularity as the alternative to Message Passing Neural Networks (MPNNs). There is, however, a lack of a common foundation about what constitutes a good graph sequence model, and a mathematical description of the benefits and deficiencies in adopting different sequence models for learning on graphs. To this end, we first present Graph Sequence Model (GSM), a unifying framework for adopting sequence models for graphs, consisting of three main steps: (1) Tokenization, which translates the graph into a set of sequences; (2) Local Encoding, which encodes local neighborhoods around each node; and (3) Global Encoding, which employs a scalable sequence model to capture long-range dependencies within the sequences. This framework allows us to understand, evaluate, and compare the power of different sequence model backbones in graph tasks. Our theoretical evaluations of the representation power of Transformers and modern recurrent models through the lens of global and local graph tasks show that there are both negative and positive sides for both types of models. Building on this observation, we present GSM++, a fast hybrid model that uses the Hierarchical Affinity Clustering (HAC) algorithm to tokenize the graph into hierarchical sequences, and then employs a hybrid architecture of Transformer to encode these sequences. Our theoretical and experimental results support the design of GSM++, showing that GSM++ outperforms baselines in most benchmark evaluations.
General Geospatial Inference with a Population Dynamics Foundation Model
Nov 13, 2024



Abstract:Supporting the health and well-being of dynamic populations around the world requires governmental agencies, organizations and researchers to understand and reason over complex relationships between human behavior and local contexts in order to identify high-risk groups and strategically allocate limited resources. Traditional approaches to these classes of problems often entail developing manually curated, task-specific features and models to represent human behavior and the natural and built environment, which can be challenging to adapt to new, or even, related tasks. To address this, we introduce a Population Dynamics Foundation Model (PDFM) that aims to capture the relationships between diverse data modalities and is applicable to a broad range of geospatial tasks. We first construct a geo-indexed dataset for postal codes and counties across the United States, capturing rich aggregated information on human behavior from maps, busyness, and aggregated search trends, and environmental factors such as weather and air quality. We then model this data and the complex relationships between locations using a graph neural network, producing embeddings that can be adapted to a wide range of downstream tasks using relatively simple models. We evaluate the effectiveness of our approach by benchmarking it on 27 downstream tasks spanning three distinct domains: health indicators, socioeconomic factors, and environmental measurements. The approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on all 27 geospatial interpolation tasks, and on 25 out of the 27 extrapolation and super-resolution tasks. We combined the PDFM with a state-of-the-art forecasting foundation model, TimesFM, to predict unemployment and poverty, achieving performance that surpasses fully supervised forecasting. The full set of embeddings and sample code are publicly available for researchers.
Text-space Graph Foundation Models: Comprehensive Benchmarks and New Insights
Jun 15, 2024



Abstract:Given the ubiquity of graph data and its applications in diverse domains, building a Graph Foundation Model (GFM) that can work well across different graphs and tasks with a unified backbone has recently garnered significant interests. A major obstacle to achieving this goal stems from the fact that graphs from different domains often exhibit diverse node features. Inspired by multi-modal models that align different modalities with natural language, the text has recently been adopted to provide a unified feature space for diverse graphs. Despite the great potential of these text-space GFMs, current research in this field is hampered by two problems. First, the absence of a comprehensive benchmark with unified problem settings hinders a clear understanding of the comparative effectiveness and practical value of different text-space GFMs. Second, there is a lack of sufficient datasets to thoroughly explore the methods' full potential and verify their effectiveness across diverse settings. To address these issues, we conduct a comprehensive benchmark providing novel text-space datasets and comprehensive evaluation under unified problem settings. Empirical results provide new insights and inspire future research directions. Our code and data are publicly available from \url{https://github.com/CurryTang/TSGFM}.
Test of Time: A Benchmark for Evaluating LLMs on Temporal Reasoning
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have showcased remarkable reasoning capabilities, yet they remain susceptible to errors, particularly in temporal reasoning tasks involving complex temporal logic. Existing research has explored LLM performance on temporal reasoning using diverse datasets and benchmarks. However, these studies often rely on real-world data that LLMs may have encountered during pre-training or employ anonymization techniques that can inadvertently introduce factual inconsistencies. In this work, we address these limitations by introducing novel synthetic datasets specifically designed to assess LLM temporal reasoning abilities in various scenarios. The diversity of question types across these datasets enables systematic investigation into the impact of the problem structure, size, question type, fact order, and other factors on LLM performance. Our findings provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of current LLMs in temporal reasoning tasks. To foster further research in this area, we are open-sourcing the datasets and evaluation framework used in our experiments: https://huggingface.co/datasets/baharef/ToT.
Understanding Transformer Reasoning Capabilities via Graph Algorithms
May 28, 2024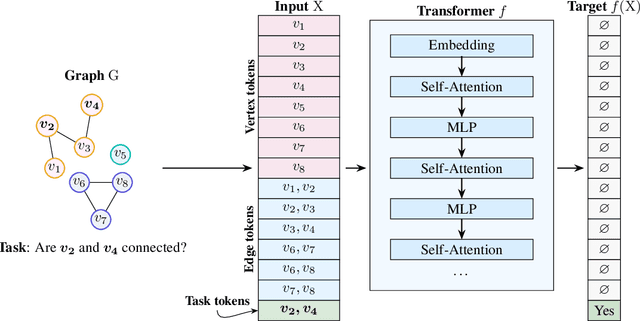

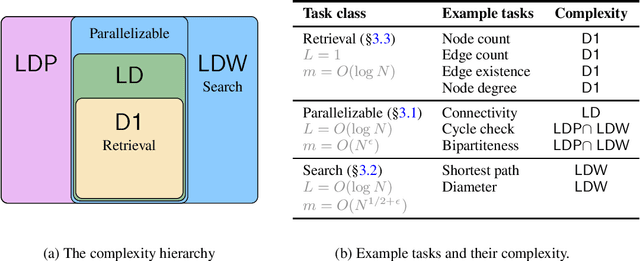
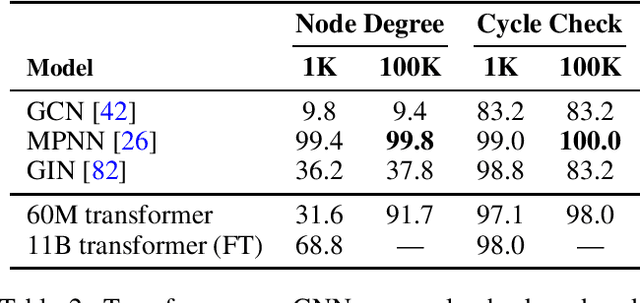
Abstract:Which transformer scaling regimes are able to perfectly solve different classes of algorithmic problems? While tremendous empirical advances have been attained by transformer-based neural networks, a theoretical understanding of their algorithmic reasoning capabilities in realistic parameter regimes is lacking. We investigate this question in terms of the network's depth, width, and number of extra tokens for algorithm execution. Our novel representational hierarchy separates 9 algorithmic reasoning problems into classes solvable by transformers in different realistic parameter scaling regimes. We prove that logarithmic depth is necessary and sufficient for tasks like graph connectivity, while single-layer transformers with small embedding dimensions can solve contextual retrieval tasks. We also support our theoretical analysis with ample empirical evidence using the GraphQA benchmark. These results show that transformers excel at many graph reasoning tasks, even outperforming specialized graph neural networks.
Don't Forget to Connect! Improving RAG with Graph-based Reranking
May 28, 2024Abstract:Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) has greatly improved the performance of Large Language Model (LLM) responses by grounding generation with context from existing documents. These systems work well when documents are clearly relevant to a question context. But what about when a document has partial information, or less obvious connections to the context? And how should we reason about connections between documents? In this work, we seek to answer these two core questions about RAG generation. We introduce G-RAG, a reranker based on graph neural networks (GNNs) between the retriever and reader in RAG. Our method combines both connections between documents and semantic information (via Abstract Meaning Representation graphs) to provide a context-informed ranker for RAG. G-RAG outperforms state-of-the-art approaches while having smaller computational footprint. Additionally, we assess the performance of PaLM 2 as a reranker and find it to significantly underperform G-RAG. This result emphasizes the importance of reranking for RAG even when using Large Language Models.
Let Your Graph Do the Talking: Encoding Structured Data for LLMs
Feb 08, 2024Abstract:How can we best encode structured data into sequential form for use in large language models (LLMs)? In this work, we introduce a parameter-efficient method to explicitly represent structured data for LLMs. Our method, GraphToken, learns an encoding function to extend prompts with explicit structured information. Unlike other work which focuses on limited domains (e.g. knowledge graph representation), our work is the first effort focused on the general encoding of structured data to be used for various reasoning tasks. We show that explicitly representing the graph structure allows significant improvements to graph reasoning tasks. Specifically, we see across the board improvements - up to 73% points - on node, edge and, graph-level tasks from the GraphQA benchmark.
The Graph Lottery Ticket Hypothesis: Finding Sparse, Informative Graph Structure
Dec 08, 2023Abstract:Graph learning methods help utilize implicit relationships among data items, thereby reducing training label requirements and improving task performance. However, determining the optimal graph structure for a particular learning task remains a challenging research problem. In this work, we introduce the Graph Lottery Ticket (GLT) Hypothesis - that there is an extremely sparse backbone for every graph, and that graph learning algorithms attain comparable performance when trained on that subgraph as on the full graph. We identify and systematically study 8 key metrics of interest that directly influence the performance of graph learning algorithms. Subsequently, we define the notion of a "winning ticket" for graph structure - an extremely sparse subset of edges that can deliver a robust approximation of the entire graph's performance. We propose a straightforward and efficient algorithm for finding these GLTs in arbitrary graphs. Empirically, we observe that performance of different graph learning algorithms can be matched or even exceeded on graphs with the average degree as low as 5.
Talk like a Graph: Encoding Graphs for Large Language Models
Oct 06, 2023Abstract:Graphs are a powerful tool for representing and analyzing complex relationships in real-world applications such as social networks, recommender systems, and computational finance. Reasoning on graphs is essential for drawing inferences about the relationships between entities in a complex system, and to identify hidden patterns and trends. Despite the remarkable progress in automated reasoning with natural text, reasoning on graphs with large language models (LLMs) remains an understudied problem. In this work, we perform the first comprehensive study of encoding graph-structured data as text for consumption by LLMs. We show that LLM performance on graph reasoning tasks varies on three fundamental levels: (1) the graph encoding method, (2) the nature of the graph task itself, and (3) interestingly, the very structure of the graph considered. These novel results provide valuable insight on strategies for encoding graphs as text. Using these insights we illustrate how the correct choice of encoders can boost performance on graph reasoning tasks inside LLMs by 4.8% to 61.8%, depending on the task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge