Bohan Zhang
NetEase
ContextBench: A Benchmark for Context Retrieval in Coding Agents
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:LLM-based coding agents have shown strong performance on automated issue resolution benchmarks, yet existing evaluations largely focus on final task success, providing limited insight into how agents retrieve and use code context during problem solving. We introduce ContextBench, a process-oriented evaluation of context retrieval in coding agents. ContextBench consists of 1,136 issue-resolution tasks from 66 repositories across eight programming languages, each augmented with human-annotated gold contexts. We further implement an automated evaluation framework that tracks agent trajectories and measures context recall, precision, and efficiency throughout issue resolution. Using ContextBench, we evaluate four frontier LLMs and five coding agents. Our results show that sophisticated agent scaffolding yields only marginal gains in context retrieval ("The Bitter Lesson" of coding agents), LLMs consistently favor recall over precision, and substantial gaps exist between explored and utilized context. ContextBench augments existing end-to-end benchmarks with intermediate gold-context metrics that unbox the issue-resolution process. These contexts offer valuable intermediate signals for guiding LLM reasoning in software tasks. Data and code are available at: https://cioutn.github.io/context-bench/.
CoSA: Compressed Sensing-Based Adaptation of Large Language Models
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) has emerged as a practical paradigm for adapting large language models (LLMs) without updating all parameters. Most existing approaches, such as LoRA and PiSSA, rely on low-rank decompositions of weight updates. However, the low-rank assumption may restrict expressivity, particularly in task-specific adaptation scenarios where singular values are distributed relatively uniformly. To address this limitation, we propose CoSA (Compressed Sensing-Based Adaptation), a new PEFT method extended from compressed sensing theory. Instead of constraining weight updates to a low-rank subspace, CoSA expresses them through fixed random projection matrices and a compact learnable core. We provide a formal theoretical analysis of CoSA as a synthesis process, proving that weight updates can be compactly encoded into a low-dimensional space and mapped back through random projections. Extensive experimental results show that CoSA provides a principled perspective for efficient and expressive multi-scale model adaptation. Specifically, we evaluate CoSA on 10 diverse tasks, including natural language understanding and generation, employing 5 models of different scales from RoBERTa, Llama, and Qwen families. Across these settings, CoSA consistently matches or outperforms state-of-the-art PEFT methods.
Sparse-RL: Breaking the Memory Wall in LLM Reinforcement Learning via Stable Sparse Rollouts
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) has become essential for eliciting complex reasoning capabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs). However, the substantial memory overhead of storing Key-Value (KV) caches during long-horizon rollouts acts as a critical bottleneck, often prohibiting efficient training on limited hardware. While existing KV compression techniques offer a remedy for inference, directly applying them to RL training induces a severe policy mismatch, leading to catastrophic performance collapse. To address this, we introduce Sparse-RL empowers stable RL training under sparse rollouts. We show that instability arises from a fundamental policy mismatch among the dense old policy, the sparse sampler policy, and the learner policy. To mitigate this issue, Sparse-RL incorporates Sparsity-Aware Rejection Sampling and Importance-based Reweighting to correct the off-policy bias introduced by compression-induced information loss. Experimental results show that Sparse-RL reduces rollout overhead compared to dense baselines while preserving the performance. Furthermore, Sparse-RL inherently implements sparsity-aware training, significantly enhancing model robustness during sparse inference deployment.
Who Owns the Text? Design Patterns for Preserving Authorship in AI-Assisted Writing
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:AI writing assistants can reduce effort and improve fluency, but they may also weaken writers' sense of authorship. We study this tension with an ownership-aware co-writing editor that offers on-demand, sentence-level suggestions and tests two common design choices: persona-based coaching and style personalization. In an online study (N=176), participants completed three professional writing tasks: an email without AI help, a proposal with generic AI suggestions, and a cover letter with persona-based coaching, while half received suggestions tailored to a brief sample of their prior writing. Across the two AI-assisted tasks, psychological ownership dropped relative to unassisted writing (about 0.85-1.0 points on a 7-point scale), even as cognitive load decreased (about 0.9 points) and quality ratings stayed broadly similar overall. Persona coaching did not prevent the ownership decline. Style personalization partially restored ownership (about +0.43) and increased AI incorporation in text (+5 percentage points). We distill five design patterns: on-demand initiation, micro-suggestions, voice anchoring, audience scaffolds, and point-of-decision provenance, to guide authorship-preserving writing tools.
Neural Networks Learn Generic Multi-Index Models Near Information-Theoretic Limit
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:In deep learning, a central issue is to understand how neural networks efficiently learn high-dimensional features. To this end, we explore the gradient descent learning of a general Gaussian Multi-index model $f(\boldsymbol{x})=g(\boldsymbol{U}\boldsymbol{x})$ with hidden subspace $\boldsymbol{U}\in \mathbb{R}^{r\times d}$, which is the canonical setup to study representation learning. We prove that under generic non-degenerate assumptions on the link function, a standard two-layer neural network trained via layer-wise gradient descent can agnostically learn the target with $o_d(1)$ test error using $\widetilde{\mathcal{O}}(d)$ samples and $\widetilde{\mathcal{O}}(d^2)$ time. The sample and time complexity both align with the information-theoretic limit up to leading order and are therefore optimal. During the first stage of gradient descent learning, the proof proceeds via showing that the inner weights can perform a power-iteration process. This process implicitly mimics a spectral start for the whole span of the hidden subspace and eventually eliminates finite-sample noise and recovers this span. It surprisingly indicates that optimal results can only be achieved if the first layer is trained for more than $\mathcal{O}(1)$ steps. This work demonstrates the ability of neural networks to effectively learn hierarchical functions with respect to both sample and time efficiency.
ArchMap: Arch-Flattening and Knowledge-Guided Vision Language Model for Tooth Counting and Structured Dental Understanding
Nov 18, 2025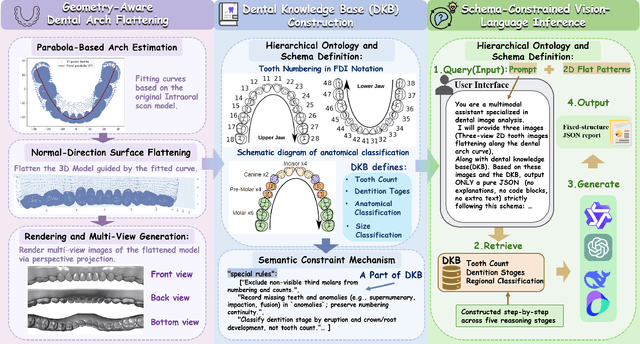
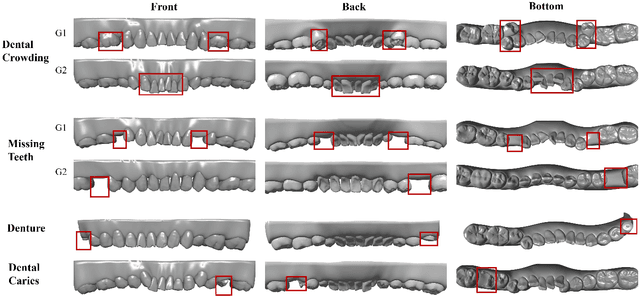
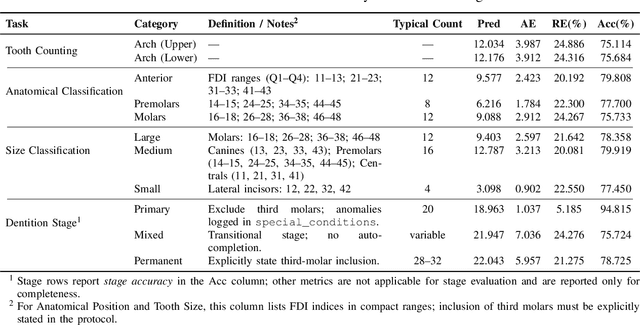
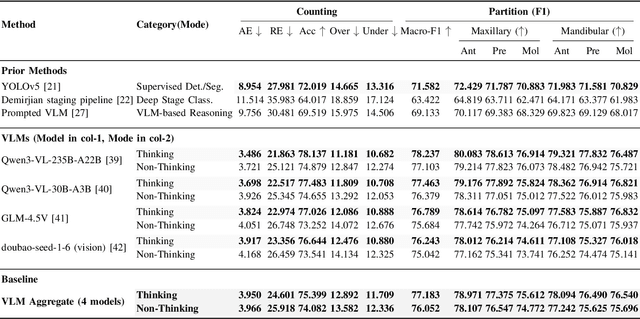
Abstract:A structured understanding of intraoral 3D scans is essential for digital orthodontics. However, existing deep-learning approaches rely heavily on modality-specific training, large annotated datasets, and controlled scanning conditions, which limit generalization across devices and hinder deployment in real clinical workflows. Moreover, raw intraoral meshes exhibit substantial variation in arch pose, incomplete geometry caused by occlusion or tooth contact, and a lack of texture cues, making unified semantic interpretation highly challenging. To address these limitations, we propose ArchMap, a training-free and knowledge-guided framework for robust structured dental understanding. ArchMap first introduces a geometry-aware arch-flattening module that standardizes raw 3D meshes into spatially aligned, continuity-preserving multi-view projections. We then construct a Dental Knowledge Base (DKB) encoding hierarchical tooth ontology, dentition-stage policies, and clinical semantics to constrain the symbolic reasoning space. We validate ArchMap on 1060 pre-/post-orthodontic cases, demonstrating robust performance in tooth counting, anatomical partitioning, dentition-stage classification, and the identification of clinical conditions such as crowding, missing teeth, prosthetics, and caries. Compared with supervised pipelines and prompted VLM baselines, ArchMap achieves higher accuracy, reduced semantic drift, and superior stability under sparse or artifact-prone conditions. As a fully training-free system, ArchMap demonstrates that combining geometric normalization with ontology-guided multimodal reasoning offers a practical and scalable solution for the structured analysis of 3D intraoral scans in modern digital orthodontics.
GLM-4.5: Agentic, Reasoning, and Coding (ARC) Foundation Models
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:We present GLM-4.5, an open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 355B total parameters and 32B activated parameters, featuring a hybrid reasoning method that supports both thinking and direct response modes. Through multi-stage training on 23T tokens and comprehensive post-training with expert model iteration and reinforcement learning, GLM-4.5 achieves strong performance across agentic, reasoning, and coding (ARC) tasks, scoring 70.1% on TAU-Bench, 91.0% on AIME 24, and 64.2% on SWE-bench Verified. With much fewer parameters than several competitors, GLM-4.5 ranks 3rd overall among all evaluated models and 2nd on agentic benchmarks. We release both GLM-4.5 (355B parameters) and a compact version, GLM-4.5-Air (106B parameters), to advance research in reasoning and agentic AI systems. Code, models, and more information are available at https://github.com/zai-org/GLM-4.5.
ExAnte: A Benchmark for Ex-Ante Inference in Large Language Models
May 26, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) face significant challenges in ex-ante reasoning, where analysis, inference, or predictions must be made without access to information from future events. Even with explicit prompts enforcing temporal cutoffs, LLMs often generate outputs influenced by internalized knowledge of events beyond the specified cutoff. This paper introduces a novel task and benchmark designed to evaluate the ability of LLMs to reason while adhering to such temporal constraints. The benchmark includes a variety of tasks: stock prediction, Wikipedia event prediction, scientific publication prediction, and Question Answering (QA), designed to assess factual knowledge under temporal cutoff constraints. We use leakage rate to quantify models' reliance on future information beyond cutoff timestamps. Experimental results reveal that LLMs struggle to consistently adhere to temporal cutoffs across common prompting strategies and tasks, demonstrating persistent challenges in ex-ante reasoning. This benchmark provides a potential evaluation framework to advance the development of LLMs' temporal reasoning ability for time-sensitive applications.
NurValues: Real-World Nursing Values Evaluation for Large Language Models in Clinical Context
May 13, 2025Abstract:This work introduces the first benchmark for nursing value alignment, consisting of five core value dimensions distilled from international nursing codes: Altruism, Human Dignity, Integrity, Justice, and Professionalism. The benchmark comprises 1,100 real-world nursing behavior instances collected through a five-month longitudinal field study across three hospitals of varying tiers. These instances are annotated by five clinical nurses and then augmented with LLM-generated counterfactuals with reversed ethic polarity. Each original case is paired with a value-aligned and a value-violating version, resulting in 2,200 labeled instances that constitute the Easy-Level dataset. To increase adversarial complexity, each instance is further transformed into a dialogue-based format that embeds contextual cues and subtle misleading signals, yielding a Hard-Level dataset. We evaluate 23 state-of-the-art (SoTA) LLMs on their alignment with nursing values. Our findings reveal three key insights: (1) DeepSeek-V3 achieves the highest performance on the Easy-Level dataset (94.55), where Claude 3.5 Sonnet outperforms other models on the Hard-Level dataset (89.43), significantly surpassing the medical LLMs; (2) Justice is consistently the most difficult nursing value dimension to evaluate; and (3) in-context learning significantly improves alignment. This work aims to provide a foundation for value-sensitive LLMs development in clinical settings. The dataset and the code are available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/Ben012345/NurValues.
PHYBench: Holistic Evaluation of Physical Perception and Reasoning in Large Language Models
Apr 22, 2025



Abstract:We introduce PHYBench, a novel, high-quality benchmark designed for evaluating reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in physical contexts. PHYBench consists of 500 meticulously curated physics problems based on real-world physical scenarios, designed to assess the ability of models to understand and reason about realistic physical processes. Covering mechanics, electromagnetism, thermodynamics, optics, modern physics, and advanced physics, the benchmark spans difficulty levels from high school exercises to undergraduate problems and Physics Olympiad challenges. Additionally, we propose the Expression Edit Distance (EED) Score, a novel evaluation metric based on the edit distance between mathematical expressions, which effectively captures differences in model reasoning processes and results beyond traditional binary scoring methods. We evaluate various LLMs on PHYBench and compare their performance with human experts. Our results reveal that even state-of-the-art reasoning models significantly lag behind human experts, highlighting their limitations and the need for improvement in complex physical reasoning scenarios. Our benchmark results and dataset are publicly available at https://phybench-official.github.io/phybench-demo/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge