Ali Shahin Shamsabadi
SPILLage: Agentic Oversharing on the Web
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:LLM-powered agents are beginning to automate user's tasks across the open web, often with access to user resources such as emails and calendars. Unlike standard LLMs answering questions in a controlled ChatBot setting, web agents act "in the wild", interacting with third parties and leaving behind an action trace. Therefore, we ask the question: how do web agents handle user resources when accomplishing tasks on their behalf across live websites? In this paper, we formalize Natural Agentic Oversharing -- the unintentional disclosure of task-irrelevant user information through an agent trace of actions on the web. We introduce SPILLage, a framework that characterizes oversharing along two dimensions: channel (content vs. behavior) and directness (explicit vs. implicit). This taxonomy reveals a critical blind spot: while prior work focuses on text leakage, web agents also overshare behaviorally through clicks, scrolls, and navigation patterns that can be monitored. We benchmark 180 tasks on live e-commerce sites with ground-truth annotations separating task-relevant from task-irrelevant attributes. Across 1,080 runs spanning two agentic frameworks and three backbone LLMs, we demonstrate that oversharing is pervasive with behavioral oversharing dominates content oversharing by 5x. This effect persists -- and can even worsen -- under prompt-level mitigation. However, removing task-irrelevant information before execution improves task success by up to 17.9%, demonstrating that reducing oversharing improves task success. Our findings underscore that protecting privacy in web agents is a fundamental challenge, requiring a broader view of "output" that accounts for what agents do on the web, not just what they type. Our datasets and code are available at https://github.com/jrohsc/SPILLage.
Membership and Memorization in LLM Knowledge Distillation
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Knowledge Distillation (KD) aim to mitigate the high computational demands of Large Language Models (LLMs) by transferring knowledge from a large ''teacher'' to a smaller ''student'' model. However, students may inherit the teacher's privacy when the teacher is trained on private data. In this work, we systematically characterize and investigate membership and memorization privacy risks inherent in six LLM KD techniques. Using instruction-tuning settings that span seven NLP tasks, together with three teacher model families (GPT-2, LLAMA-2, and OPT), and various size student models, we demonstrate that all existing LLM KD approaches carry membership and memorization privacy risks from the teacher to its students. However, the extent of privacy risks varies across different KD techniques. We systematically analyse how key LLM KD components (KD objective functions, student training data and NLP tasks) impact such privacy risks. We also demonstrate a significant disagreement between memorization and membership privacy risks of LLM KD techniques. Finally, we characterize per-block privacy risk and demonstrate that the privacy risk varies across different blocks by a large margin.
Confidential Guardian: Cryptographically Prohibiting the Abuse of Model Abstention
May 29, 2025Abstract:Cautious predictions -- where a machine learning model abstains when uncertain -- are crucial for limiting harmful errors in safety-critical applications. In this work, we identify a novel threat: a dishonest institution can exploit these mechanisms to discriminate or unjustly deny services under the guise of uncertainty. We demonstrate the practicality of this threat by introducing an uncertainty-inducing attack called Mirage, which deliberately reduces confidence in targeted input regions, thereby covertly disadvantaging specific individuals. At the same time, Mirage maintains high predictive performance across all data points. To counter this threat, we propose Confidential Guardian, a framework that analyzes calibration metrics on a reference dataset to detect artificially suppressed confidence. Additionally, it employs zero-knowledge proofs of verified inference to ensure that reported confidence scores genuinely originate from the deployed model. This prevents the provider from fabricating arbitrary model confidence values while protecting the model's proprietary details. Our results confirm that Confidential Guardian effectively prevents the misuse of cautious predictions, providing verifiable assurances that abstention reflects genuine model uncertainty rather than malicious intent.
NoEsis: Differentially Private Knowledge Transfer in Modular LLM Adaptation
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLM) are typically trained on vast amounts of data from various sources. Even when designed modularly (e.g., Mixture-of-Experts), LLMs can leak privacy on their sources. Conversely, training such models in isolation arguably prohibits generalization. To this end, we propose a framework, NoEsis, which builds upon the desired properties of modularity, privacy, and knowledge transfer. NoEsis integrates differential privacy with a hybrid two-staged parameter-efficient fine-tuning that combines domain-specific low-rank adapters, acting as experts, with common prompt tokens, acting as a knowledge-sharing backbone. Results from our evaluation on CodeXGLUE showcase that NoEsis can achieve provable privacy guarantees with tangible knowledge transfer across domains, and empirically show protection against Membership Inference Attacks. Finally, on code completion tasks, NoEsis bridges at least 77% of the accuracy gap between the non-shared and the non-private baseline.
* ICLR 2025 MCDC workshop
P4: Towards private, personalized, and Peer-to-Peer learning
May 27, 2024Abstract:Personalized learning is a proposed approach to address the problem of data heterogeneity in collaborative machine learning. In a decentralized setting, the two main challenges of personalization are client clustering and data privacy. In this paper, we address these challenges by developing P4 (Personalized Private Peer-to-Peer) a method that ensures that each client receives a personalized model while maintaining differential privacy guarantee of each client's local dataset during and after the training. Our approach includes the design of a lightweight algorithm to identify similar clients and group them in a private, peer-to-peer (P2P) manner. Once grouped, we develop differentially-private knowledge distillation for clients to co-train with minimal impact on accuracy. We evaluate our proposed method on three benchmark datasets (FEMNIST or Federated EMNIST, CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100) and two different neural network architectures (Linear and CNN-based networks) across a range of privacy parameters. The results demonstrate the potential of P4, as it outperforms the state-of-the-art of differential private P2P by up to 40 percent in terms of accuracy. We also show the practicality of P4 by implementing it on resource constrained devices, and validating that it has minimal overhead, e.g., about 7 seconds to run collaborative training between two clients.
Identifying and Mitigating Privacy Risks Stemming from Language Models: A Survey
Sep 27, 2023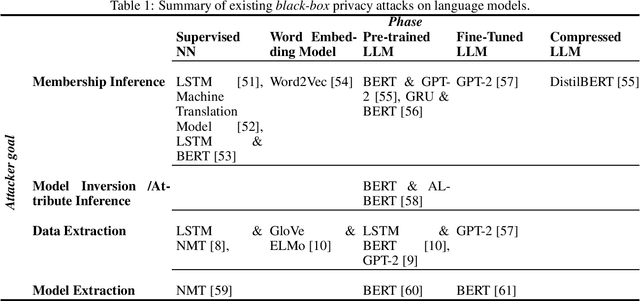
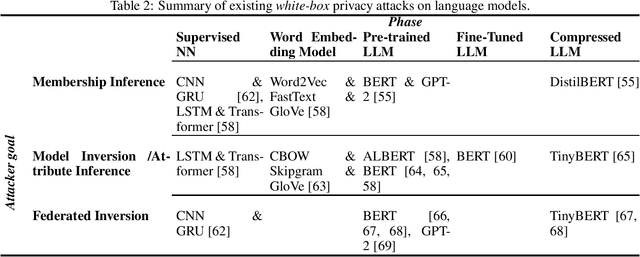
Abstract:Rapid advancements in language models (LMs) have led to their adoption across many sectors. Alongside the potential benefits, such models present a range of risks, including around privacy. In particular, as LMs have grown in size, the potential to memorise aspects of their training data has increased, resulting in the risk of leaking private information. As LMs become increasingly widespread, it is vital that we understand such privacy risks and how they might be mitigated. To help researchers and policymakers understand the state of knowledge around privacy attacks and mitigations, including where more work is needed, we present the first technical survey on LM privacy. We (i) identify a taxonomy of salient dimensions where attacks differ on LMs, (ii) survey existing attacks and use our taxonomy of dimensions to highlight key trends, (iii) discuss existing mitigation strategies, highlighting their strengths and limitations, identifying key gaps and demonstrating open problems and areas for concern.
Is Federated Learning a Practical PET Yet?
Jan 09, 2023



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a framework for users to jointly train a machine learning model. FL is promoted as a privacy-enhancing technology (PET) that provides data minimization: data never "leaves" personal devices and users share only model updates with a server (e.g., a company) coordinating the distributed training. We assess the realistic (i.e., worst-case) privacy guarantees that are provided to users who are unable to trust the server. To this end, we propose an attack against FL protected with distributed differential privacy (DDP) and secure aggregation (SA). The attack method is based on the introduction of Sybil devices that deviate from the protocol to expose individual users' data for reconstruction by the server. The underlying root cause for the vulnerability to our attack is the power imbalance. The server orchestrates the whole protocol and users are given little guarantees about the selection of other users participating in the protocol. Moving forward, we discuss requirements for an FL protocol to guarantee DDP without asking users to trust the server. We conclude that such systems are not yet practical.
Private Multi-Winner Voting for Machine Learning
Nov 23, 2022



Abstract:Private multi-winner voting is the task of revealing $k$-hot binary vectors satisfying a bounded differential privacy (DP) guarantee. This task has been understudied in machine learning literature despite its prevalence in many domains such as healthcare. We propose three new DP multi-winner mechanisms: Binary, $\tau$, and Powerset voting. Binary voting operates independently per label through composition. $\tau$ voting bounds votes optimally in their $\ell_2$ norm for tight data-independent guarantees. Powerset voting operates over the entire binary vector by viewing the possible outcomes as a power set. Our theoretical and empirical analysis shows that Binary voting can be a competitive mechanism on many tasks unless there are strong correlations between labels, in which case Powerset voting outperforms it. We use our mechanisms to enable privacy-preserving multi-label learning in the central setting by extending the canonical single-label technique: PATE. We find that our techniques outperform current state-of-the-art approaches on large, real-world healthcare data and standard multi-label benchmarks. We further enable multi-label confidential and private collaborative (CaPC) learning and show that model performance can be significantly improved in the multi-site setting.
On the reversibility of adversarial attacks
Jun 01, 2022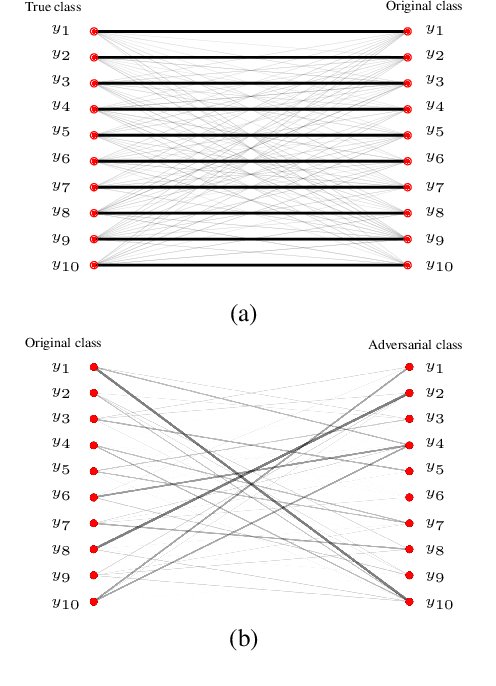
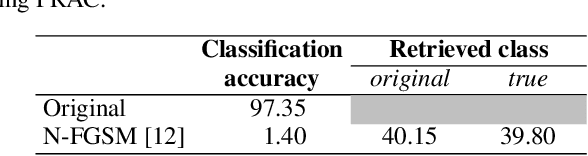
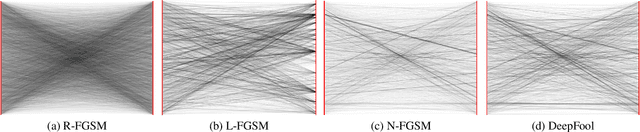
Abstract:Adversarial attacks modify images with perturbations that change the prediction of classifiers. These modified images, known as adversarial examples, expose the vulnerabilities of deep neural network classifiers. In this paper, we investigate the predictability of the mapping between the classes predicted for original images and for their corresponding adversarial examples. This predictability relates to the possibility of retrieving the original predictions and hence reversing the induced misclassification. We refer to this property as the reversibility of an adversarial attack, and quantify reversibility as the accuracy in retrieving the original class or the true class of an adversarial example. We present an approach that reverses the effect of an adversarial attack on a classifier using a prior set of classification results. We analyse the reversibility of state-of-the-art adversarial attacks on benchmark classifiers and discuss the factors that affect the reversibility.
GAP: Differentially Private Graph Neural Networks with Aggregation Perturbation
Mar 02, 2022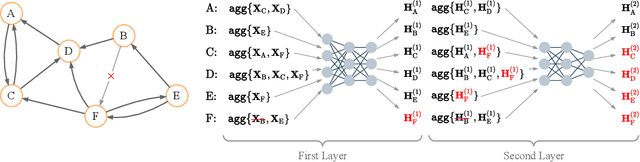

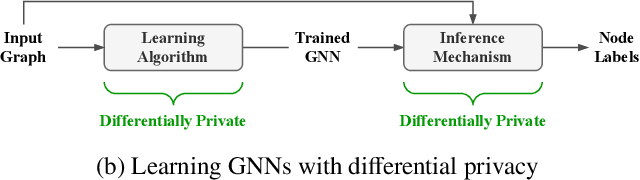

Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are powerful models designed for graph data that learn node representation by recursively aggregating information from each node's local neighborhood. However, despite their state-of-the-art performance in predictive graph-based applications, recent studies have shown that GNNs can raise significant privacy concerns when graph data contain sensitive information. As a result, in this paper, we study the problem of learning GNNs with Differential Privacy (DP). We propose GAP, a novel differentially private GNN that safeguards the privacy of nodes and edges using aggregation perturbation, i.e., adding calibrated stochastic noise to the output of the GNN's aggregation function, which statistically obfuscates the presence of a single edge (edge-level privacy) or a single node and all its adjacent edges (node-level privacy). To circumvent the accumulation of privacy cost at every forward pass of the model, we tailor the GNN architecture to the specifics of private learning. In particular, we first precompute private aggregations by recursively applying neighborhood aggregation and perturbing the output of each aggregation step. Then, we privately train a deep neural network on the resulting perturbed aggregations for any node-wise classification task. A major advantage of GAP over previous approaches is that we guarantee edge-level and node-level DP not only for training, but also at inference time with no additional costs beyond the training's privacy budget. We theoretically analyze the formal privacy guarantees of GAP using R\'enyi DP. Empirical experiments conducted over three real-world graph datasets demonstrate that GAP achieves a favorable privacy-accuracy trade-off and significantly outperforms existing approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge