Marc Tommasi
LIFL, INRIA Futurs, GRAPPA
Privacy Amplification Persists under Unlimited Synthetic Data Release
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:We study privacy amplification by synthetic data release, a phenomenon in which differential privacy guarantees are improved by releasing only synthetic data rather than the private generative model itself. Recent work by Pierquin et al. (2025) established the first formal amplification guarantees for a linear generator, but they apply only in asymptotic regimes where the model dimension far exceeds the number of released synthetic records, limiting their practical relevance. In this work, we show a surprising result: under a bounded-parameter assumption, privacy amplification persists even when releasing an unbounded number of synthetic records, thereby improving upon the bounds of Pierquin et al. (2025). Our analysis provides structural insights that may guide the development of tighter privacy guarantees for more complex release mechanisms.
Federated Learning for MRI-based BrainAGE: a multicenter study on post-stroke functional outcome prediction
Jun 18, 2025
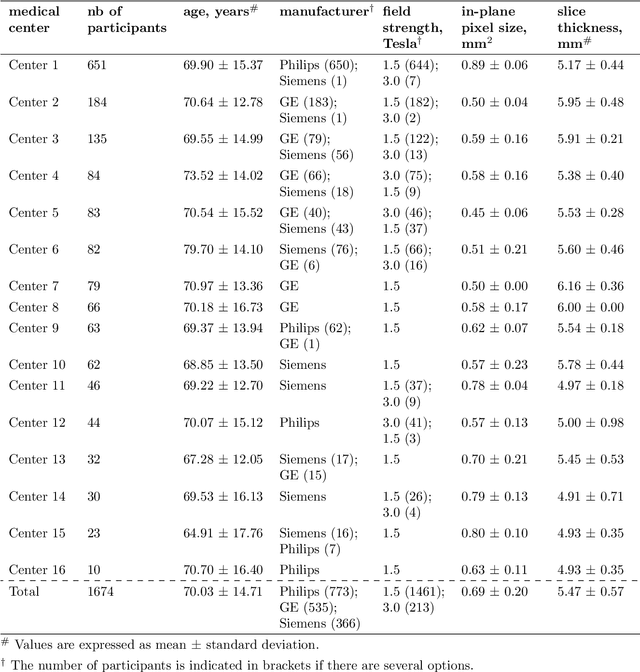
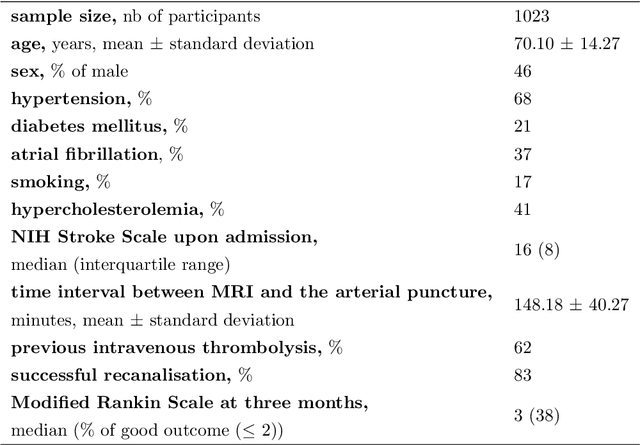
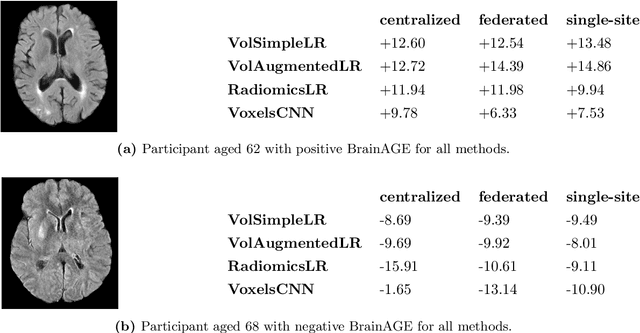
Abstract:$\textbf{Objective:}$ Brain-predicted age difference (BrainAGE) is a neuroimaging biomarker reflecting brain health. However, training robust BrainAGE models requires large datasets, often restricted by privacy concerns. This study evaluates the performance of federated learning (FL) for BrainAGE estimation in ischemic stroke patients treated with mechanical thrombectomy, and investigates its association with clinical phenotypes and functional outcomes. $\textbf{Methods:}$ We used FLAIR brain images from 1674 stroke patients across 16 hospital centers. We implemented standard machine learning and deep learning models for BrainAGE estimates under three data management strategies: centralized learning (pooled data), FL (local training at each site), and single-site learning. We reported prediction errors and examined associations between BrainAGE and vascular risk factors (e.g., diabetes mellitus, hypertension, smoking), as well as functional outcomes at three months post-stroke. Logistic regression evaluated BrainAGE's predictive value for these outcomes, adjusting for age, sex, vascular risk factors, stroke severity, time between MRI and arterial puncture, prior intravenous thrombolysis, and recanalisation outcome. $\textbf{Results:}$ While centralized learning yielded the most accurate predictions, FL consistently outperformed single-site models. BrainAGE was significantly higher in patients with diabetes mellitus across all models. Comparisons between patients with good and poor functional outcomes, and multivariate predictions of these outcomes showed the significance of the association between BrainAGE and post-stroke recovery. $\textbf{Conclusion:}$ FL enables accurate age predictions without data centralization. The strong association between BrainAGE, vascular risk factors, and post-stroke recovery highlights its potential for prognostic modeling in stroke care.
Tau-Eval: A Unified Evaluation Framework for Useful and Private Text Anonymization
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Text anonymization is the process of removing or obfuscating information from textual data to protect the privacy of individuals. This process inherently involves a complex trade-off between privacy protection and information preservation, where stringent anonymization methods can significantly impact the text's utility for downstream applications. Evaluating the effectiveness of text anonymization proves challenging from both privacy and utility perspectives, as there is no universal benchmark that can comprehensively assess anonymization techniques across diverse, and sometimes contradictory contexts. We present Tau-Eval, an open-source framework for benchmarking text anonymization methods through the lens of privacy and utility task sensitivity. A Python library, code, documentation and tutorials are publicly available.
Privacy Amplification Through Synthetic Data: Insights from Linear Regression
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Synthetic data inherits the differential privacy guarantees of the model used to generate it. Additionally, synthetic data may benefit from privacy amplification when the generative model is kept hidden. While empirical studies suggest this phenomenon, a rigorous theoretical understanding is still lacking. In this paper, we investigate this question through the well-understood framework of linear regression. First, we establish negative results showing that if an adversary controls the seed of the generative model, a single synthetic data point can leak as much information as releasing the model itself. Conversely, we show that when synthetic data is generated from random inputs, releasing a limited number of synthetic data points amplifies privacy beyond the model's inherent guarantees. We believe our findings in linear regression can serve as a foundation for deriving more general bounds in the future.
TAMIS: Tailored Membership Inference Attacks on Synthetic Data
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Membership Inference Attacks (MIA) enable to empirically assess the privacy of a machine learning algorithm. In this paper, we propose TAMIS, a novel MIA against differentially-private synthetic data generation methods that rely on graphical models. This attack builds upon MAMA-MIA, a recently-published state-of-the-art method. It lowers its computational cost and requires less attacker knowledge. Our attack is the product of a two-fold improvement. First, we recover the graphical model having generated a synthetic dataset by using solely that dataset, rather than shadow-modeling over an auxiliary one. This proves less costly and more performant. Second, we introduce a more mathematically-grounded attack score, that provides a natural threshold for binary predictions. In our experiments, TAMIS achieves better or similar performance as MAMA-MIA on replicas of the SNAKE challenge.
Analysis of Speech Temporal Dynamics in the Context of Speaker Verification and Voice Anonymization
Dec 22, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the impact of speech temporal dynamics in application to automatic speaker verification and speaker voice anonymization tasks. We propose several metrics to perform automatic speaker verification based only on phoneme durations. Experimental results demonstrate that phoneme durations leak some speaker information and can reveal speaker identity from both original and anonymized speech. Thus, this work emphasizes the importance of taking into account the speaker's speech rate and, more importantly, the speaker's phonetic duration characteristics, as well as the need to modify them in order to develop anonymization systems with strong privacy protection capacity.
TAROT: Task-Oriented Authorship Obfuscation Using Policy Optimization Methods
Jul 31, 2024



Abstract:Authorship obfuscation aims to disguise the identity of an author within a text by altering the writing style, vocabulary, syntax, and other linguistic features associated with the text author. This alteration needs to balance privacy and utility. While strong obfuscation techniques can effectively hide the author's identity, they often degrade the quality and usefulness of the text for its intended purpose. Conversely, maintaining high utility tends to provide insufficient privacy, making it easier for an adversary to de-anonymize the author. Thus, achieving an optimal trade-off between these two conflicting objectives is crucial. In this paper, we propose TAROT: Task-Oriented Authorship Obfuscation Using Policy Optimization, a new unsupervised authorship obfuscation method whose goal is to optimize the privacy-utility trade-off by regenerating the entire text considering its downstream utility. Our approach leverages policy optimization as a fine-tuning paradigm over small language models in order to rewrite texts by preserving author identity and downstream task utility. We show that our approach largely reduce the accuracy of attackers while preserving utility. We make our code and models publicly available.
Rényi Pufferfish Privacy: General Additive Noise Mechanisms and Privacy Amplification by Iteration
Dec 21, 2023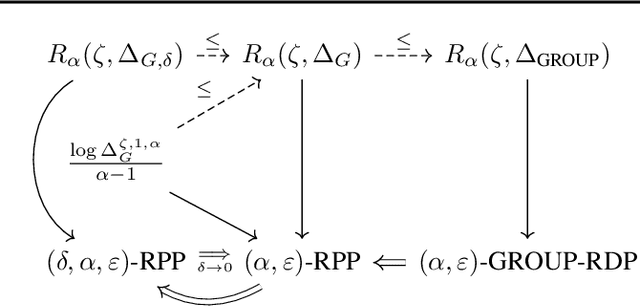
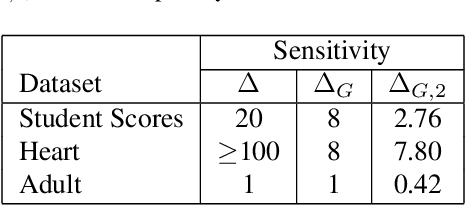
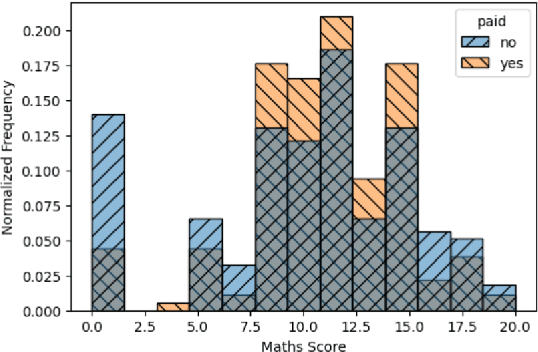
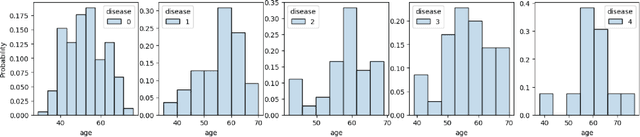
Abstract:Pufferfish privacy is a flexible generalization of differential privacy that allows to model arbitrary secrets and adversary's prior knowledge about the data. Unfortunately, designing general and tractable Pufferfish mechanisms that do not compromise utility is challenging. Furthermore, this framework does not provide the composition guarantees needed for a direct use in iterative machine learning algorithms. To mitigate these issues, we introduce a R\'enyi divergence-based variant of Pufferfish and show that it allows us to extend the applicability of the Pufferfish framework. We first generalize the Wasserstein mechanism to cover a wide range of noise distributions and introduce several ways to improve its utility. We also derive stronger guarantees against out-of-distribution adversaries. Finally, as an alternative to composition, we prove privacy amplification results for contractive noisy iterations and showcase the first use of Pufferfish in private convex optimization. A common ingredient underlying our results is the use and extension of shift reduction lemmas.
Improved Stability and Generalization Analysis of the Decentralized SGD Algorithm
Jun 05, 2023

Abstract:This paper presents a new generalization error analysis for the Decentralized Stochastic Gradient Descent (D-SGD) algorithm based on algorithmic stability. The obtained results largely improve upon state-of-the-art results, and even invalidate their claims that the communication graph has a detrimental effect on generalization. For instance, we show that in convex settings, D-SGD has the same generalization bounds as the classical SGD algorithm, no matter the choice of graph. We exhibit that this counter-intuitive result comes from considering the average of local parameters, which hides a final global averaging step incompatible with the decentralized scenario. In light of this observation, we advocate to analyze the supremum over local parameters and show that in this case, the graph does have an impact on the generalization. Unlike prior results, our analysis yields non-vacuous bounds even for non-connected graphs.
Fairness Certificates for Differentially Private Classification
Oct 28, 2022



Abstract:In this work, we theoretically study the impact of differential privacy on fairness in binary classification. We prove that, given a class of models, popular group fairness measures are pointwise Lipschitz-continuous with respect to the parameters of the model. This result is a consequence of a more general statement on the probability that a decision function makes a negative prediction conditioned on an arbitrary event (such as membership to a sensitive group), which may be of independent interest. We use the aforementioned Lipschitz property to prove a high probability bound showing that, given enough examples, the fairness level of private models is close to the one of their non-private counterparts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge