Ziwei Wu
Language in the Flow of Time: Time-Series-Paired Texts Weaved into a Unified Temporal Narrative
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:While many advances in time series models focus exclusively on numerical data, research on multimodal time series, particularly those involving contextual textual information commonly encountered in real-world scenarios, remains in its infancy. Consequently, effectively integrating the text modality remains challenging. In this work, we highlight an intuitive yet significant observation that has been overlooked by existing works: time-series-paired texts exhibit periodic properties that closely mirror those of the original time series. Building on this insight, we propose a novel framework, Texts as Time Series (TaTS), which considers the time-series-paired texts to be auxiliary variables of the time series. TaTS can be plugged into any existing numerical-only time series models and enable them to handle time series data with paired texts effectively. Through extensive experiments on both multimodal time series forecasting and imputation tasks across benchmark datasets with various existing time series models, we demonstrate that TaTS can enhance predictive performance and achieve outperformance without modifying model architectures.
Fair Anomaly Detection For Imbalanced Groups
Sep 17, 2024



Abstract:Anomaly detection (AD) has been widely studied for decades in many real-world applications, including fraud detection in finance, and intrusion detection for cybersecurity, etc. Due to the imbalanced nature between protected and unprotected groups and the imbalanced distributions of normal examples and anomalies, the learning objectives of most existing anomaly detection methods tend to solely concentrate on the dominating unprotected group. Thus, it has been recognized by many researchers about the significance of ensuring model fairness in anomaly detection. However, the existing fair anomaly detection methods tend to erroneously label most normal examples from the protected group as anomalies in the imbalanced scenario where the unprotected group is more abundant than the protected group. This phenomenon is caused by the improper design of learning objectives, which statistically focus on learning the frequent patterns (i.e., the unprotected group) while overlooking the under-represented patterns (i.e., the protected group). To address these issues, we propose FairAD, a fairness-aware anomaly detection method targeting the imbalanced scenario. It consists of a fairness-aware contrastive learning module and a rebalancing autoencoder module to ensure fairness and handle the imbalanced data issue, respectively. Moreover, we provide the theoretical analysis that shows our proposed contrastive learning regularization guarantees group fairness. Empirical studies demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of FairAD across multiple real-world datasets.
Neural Active Learning Beyond Bandits
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:We study both stream-based and pool-based active learning with neural network approximations. A recent line of works proposed bandit-based approaches that transformed active learning into a bandit problem, achieving both theoretical and empirical success. However, the performance and computational costs of these methods may be susceptible to the number of classes, denoted as $K$, due to this transformation. Therefore, this paper seeks to answer the question: "How can we mitigate the adverse impacts of $K$ while retaining the advantages of principled exploration and provable performance guarantees in active learning?" To tackle this challenge, we propose two algorithms based on the newly designed exploitation and exploration neural networks for stream-based and pool-based active learning. Subsequently, we provide theoretical performance guarantees for both algorithms in a non-parametric setting, demonstrating a slower error-growth rate concerning $K$ for the proposed approaches. We use extensive experiments to evaluate the proposed algorithms, which consistently outperform state-of-the-art baselines.
Taiyi-Diffusion-XL: Advancing Bilingual Text-to-Image Generation with Large Vision-Language Model Support
Jan 26, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in text-to-image models have significantly enhanced image generation capabilities, yet a notable gap of open-source models persists in bilingual or Chinese language support. To address this need, we present Taiyi-Diffusion-XL, a new Chinese and English bilingual text-to-image model which is developed by extending the capabilities of CLIP and Stable-Diffusion-XL through a process of bilingual continuous pre-training. This approach includes the efficient expansion of vocabulary by integrating the most frequently used Chinese characters into CLIP's tokenizer and embedding layers, coupled with an absolute position encoding expansion. Additionally, we enrich text prompts by large vision-language model, leading to better images captions and possess higher visual quality. These enhancements are subsequently applied to downstream text-to-image models. Our empirical results indicate that the developed CLIP model excels in bilingual image-text retrieval.Furthermore, the bilingual image generation capabilities of Taiyi-Diffusion-XL surpass previous models. This research leads to the development and open-sourcing of the Taiyi-Diffusion-XL model, representing a notable advancement in the field of image generation, particularly for Chinese language applications. This contribution is a step forward in addressing the need for more diverse language support in multimodal research. The model and demonstration are made publicly available at \href{https://huggingface.co/IDEA-CCNL/Taiyi-Stable-Diffusion-XL-3.5B/}{this https URL}, fostering further research and collaboration in this domain.
iDesigner: A High-Resolution and Complex-Prompt Following Text-to-Image Diffusion Model for Interior Design
Dec 19, 2023
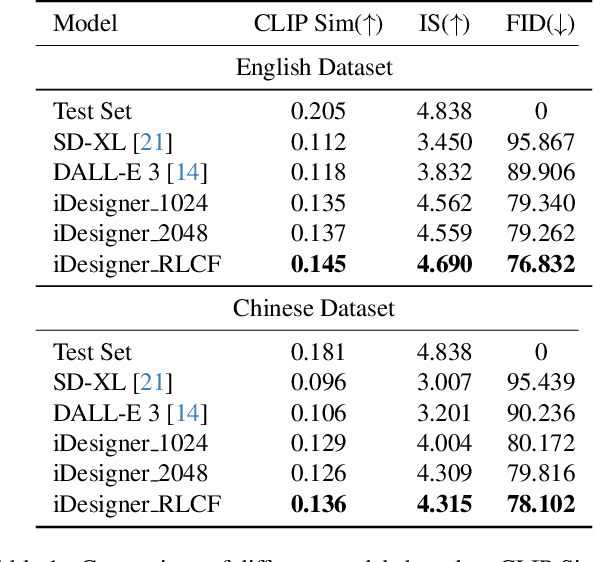
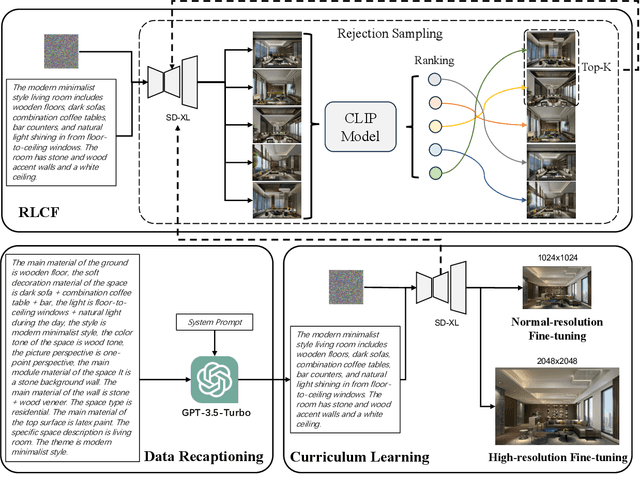
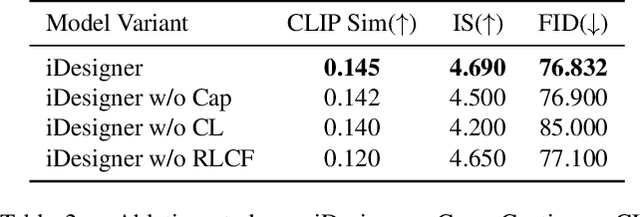
Abstract:With the open-sourcing of text-to-image models (T2I) such as stable diffusion (SD) and stable diffusion XL (SD-XL), there is an influx of models fine-tuned in specific domains based on the open-source SD model, such as in anime, character portraits, etc. However, there are few specialized models in certain domains, such as interior design, which is attributed to the complex textual descriptions and detailed visual elements inherent in design, alongside the necessity for adaptable resolution. Therefore, text-to-image models for interior design are required to have outstanding prompt-following capabilities, as well as iterative collaboration with design professionals to achieve the desired outcome. In this paper, we collect and optimize text-image data in the design field and continue training in both English and Chinese on the basis of the open-source CLIP model. We also proposed a fine-tuning strategy with curriculum learning and reinforcement learning from CLIP feedback to enhance the prompt-following capabilities of our approach so as to improve the quality of image generation. The experimental results on the collected dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, which achieves impressive results and outperforms strong baselines.
Lyrics: Boosting Fine-grained Language-Vision Alignment and Comprehension via Semantic-aware Visual Objects
Dec 08, 2023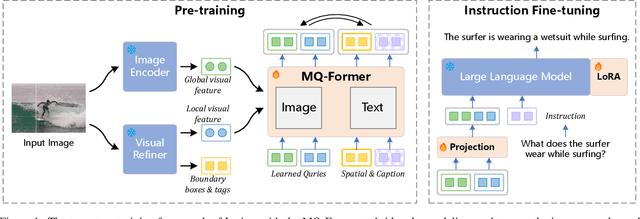
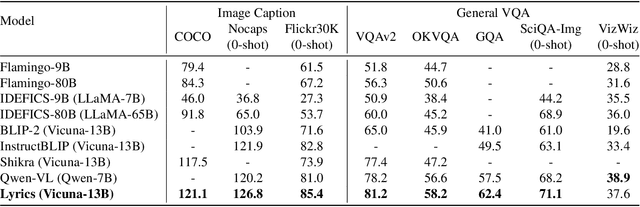
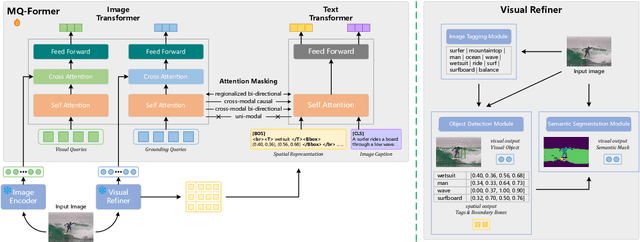
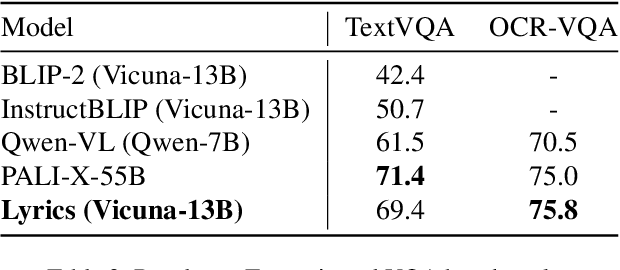
Abstract:Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) have demonstrated impressive zero-shot capabilities in various vision-language dialogue scenarios. However, the absence of fine-grained visual object detection hinders the model from understanding the details of images, leading to irreparable visual hallucinations and factual errors. In this paper, we propose Lyrics, a novel multi-modal pre-training and instruction fine-tuning paradigm that bootstraps vision-language alignment from fine-grained cross-modal collaboration. Building on the foundation of BLIP-2, Lyrics infuses local visual features extracted from a visual refiner that includes image tagging, object detection and semantic segmentation modules into the Querying Transformer, while on the text side, the language inputs equip the boundary boxes and tags derived from the visual refiner. We further introduce a two-stage training scheme, in which the pre-training stage bridges the modality gap through explicit and comprehensive vision-language alignment targets. During the instruction fine-tuning stage, we introduce semantic-aware visual feature extraction, a crucial method that enables the model to extract informative features from concrete visual objects. Our approach achieves strong performance on 13 held-out datasets across various vision-language tasks, and demonstrates promising multi-modal understanding and detailed depiction capabilities in real dialogue scenarios.
Ziya2: Data-centric Learning is All LLMs Need
Nov 06, 2023



Abstract:Various large language models (LLMs) have been proposed in recent years, including closed- and open-source ones, continually setting new records on multiple benchmarks. However, the development of LLMs still faces several issues, such as high cost of training models from scratch, and continual pre-training leading to catastrophic forgetting, etc. Although many such issues are addressed along the line of research on LLMs, an important yet practical limitation is that many studies overly pursue enlarging model sizes without comprehensively analyzing and optimizing the use of pre-training data in their learning process, as well as appropriate organization and leveraging of such data in training LLMs under cost-effective settings. In this work, we propose Ziya2, a model with 13 billion parameters adopting LLaMA2 as the foundation model, and further pre-trained on 700 billion tokens, where we focus on pre-training techniques and use data-centric optimization to enhance the learning process of Ziya2 on different stages. Experiments show that Ziya2 significantly outperforms other models in multiple benchmarks especially with promising results compared to representative open-source ones. Ziya2 (Base) is released at https://huggingface.co/IDEA-CCNL/Ziya2-13B-Base and https://modelscope.cn/models/Fengshenbang/Ziya2-13B-Base/summary.
Zero-Shot Learners for Natural Language Understanding via a Unified Multiple Choice Perspective
Oct 18, 2022



Abstract:We propose a new paradigm for zero-shot learners that is format agnostic, i.e., it is compatible with any format and applicable to a list of language tasks, such as text classification, commonsense reasoning, coreference resolution, and sentiment analysis. Zero-shot learning aims to train a model on a given task such that it can address new learning tasks without any additional training. Our approach converts zero-shot learning into multiple-choice tasks, avoiding problems in commonly used large-scale generative models such as FLAN. It not only adds generalization ability to models but also significantly reduces the number of parameters. Our method shares the merits of efficient training and deployment. Our approach shows state-of-the-art performance on several benchmarks and produces satisfactory results on tasks such as natural language inference and text classification. Our model achieves this success with only 235M parameters, which is substantially smaller than state-of-the-art models with billions of parameters. The code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/IDEA-CCNL/Fengshenbang-LM .
Fengshenbang 1.0: Being the Foundation of Chinese Cognitive Intelligence
Sep 07, 2022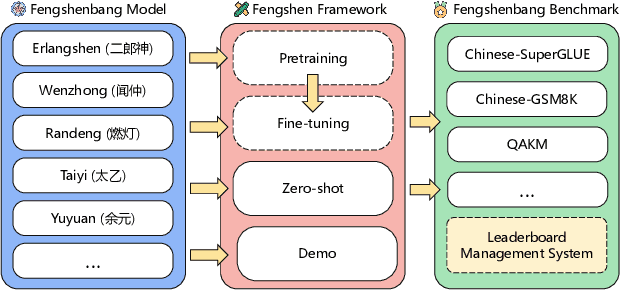
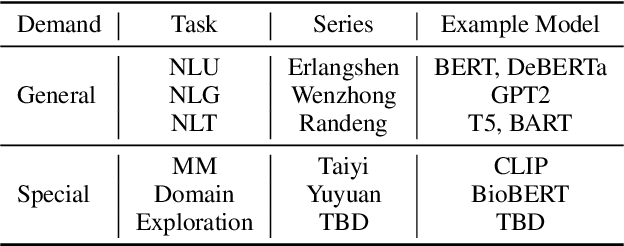
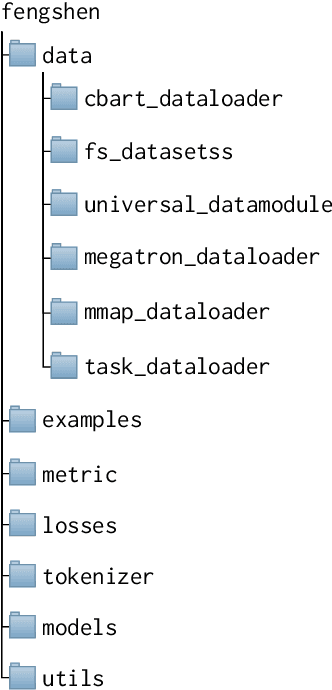
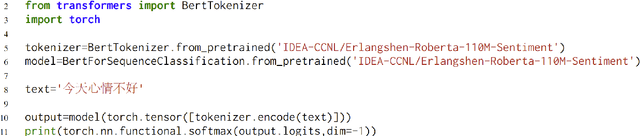
Abstract:Nowadays, foundation models become one of fundamental infrastructures in artificial intelligence, paving ways to the general intelligence. However, the reality presents two urgent challenges: existing foundation models are dominated by the English-language community; users are often given limited resources and thus cannot always use foundation models. To support the development of the Chinese-language community, we introduce an open-source project, called Fengshenbang, which leads by the research center for Cognitive Computing and Natural Language (CCNL). Our project has comprehensive capabilities, including large pre-trained models, user-friendly APIs, benchmarks, datasets, and others. We wrap all these in three sub-projects: the Fengshenbang Model, the Fengshen Framework, and the Fengshen Benchmark. An open-source roadmap, Fengshenbang, aims to re-evaluate the open-source community of Chinese pre-trained large-scale models, prompting the development of the entire Chinese large-scale model community. We also want to build a user-centered open-source ecosystem to allow individuals to access the desired models to match their computing resources. Furthermore, we invite companies, colleges, and research institutions to collaborate with us to build the large-scale open-source model-based ecosystem. We hope that this project will be the foundation of Chinese cognitive intelligence.
Fairness-aware Model-agnostic Positive and Unlabeled Learning
Jun 19, 2022



Abstract:With the increasing application of machine learning in high-stake decision-making problems, potential algorithmic bias towards people from certain social groups poses negative impacts on individuals and our society at large. In the real-world scenario, many such problems involve positive and unlabeled data such as medical diagnosis, criminal risk assessment and recommender systems. For instance, in medical diagnosis, only the diagnosed diseases will be recorded (positive) while others will not (unlabeled). Despite the large amount of existing work on fairness-aware machine learning in the (semi-)supervised and unsupervised settings, the fairness issue is largely under-explored in the aforementioned Positive and Unlabeled Learning (PUL) context, where it is usually more severe. In this paper, to alleviate this tension, we propose a fairness-aware PUL method named FairPUL. In particular, for binary classification over individuals from two populations, we aim to achieve similar true positive rates and false positive rates in both populations as our fairness metric. Based on the analysis of the optimal fair classifier for PUL, we design a model-agnostic post-processing framework, leveraging both the positive examples and unlabeled ones. Our framework is proven to be statistically consistent in terms of both the classification error and the fairness metric. Experiments on the synthetic and real-world data sets demonstrate that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art in both PUL and fair classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge