Zhe Dong
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
CroBIM-U: Uncertainty-Driven Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Referring remote sensing image segmentation aims to localize specific targets described by natural language within complex overhead imagery. However, due to extreme scale variations, dense similar distractors, and intricate boundary structures, the reliability of cross-modal alignment exhibits significant \textbf{spatial non-uniformity}. Existing methods typically employ uniform fusion and refinement strategies across the entire image, which often introduces unnecessary linguistic perturbations in visually clear regions while failing to provide sufficient disambiguation in confused areas. To address this, we propose an \textbf{uncertainty-guided framework} that explicitly leverages a pixel-wise \textbf{referring uncertainty map} as a spatial prior to orchestrate adaptive inference. Specifically, we introduce a plug-and-play \textbf{Referring Uncertainty Scorer (RUS)}, which is trained via an online error-consistency supervision strategy to interpretably predict the spatial distribution of referential ambiguity. Building on this prior, we design two plug-and-play modules: 1) \textbf{Uncertainty-Gated Fusion (UGF)}, which dynamically modulates language injection strength to enhance constraints in high-uncertainty regions while suppressing noise in low-uncertainty ones; and 2) \textbf{Uncertainty-Driven Local Refinement (UDLR)}, which utilizes uncertainty-derived soft masks to focus refinement on error-prone boundaries and fine details. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method functions as a unified, plug-and-play solution that significantly improves robustness and geometric fidelity in complex remote sensing scenes without altering the backbone architecture.
EarthMapper: Visual Autoregressive Models for Controllable Bidirectional Satellite-Map Translation
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Satellite imagery and maps, as two fundamental data modalities in remote sensing, offer direct observations of the Earth's surface and human-interpretable geographic abstractions, respectively. The task of bidirectional translation between satellite images and maps (BSMT) holds significant potential for applications in urban planning and disaster response. However, this task presents two major challenges: first, the absence of precise pixel-wise alignment between the two modalities substantially complicates the translation process; second, it requires achieving both high-level abstraction of geographic features and high-quality visual synthesis, which further elevates the technical complexity. To address these limitations, we introduce EarthMapper, a novel autoregressive framework for controllable bidirectional satellite-map translation. EarthMapper employs geographic coordinate embeddings to anchor generation, ensuring region-specific adaptability, and leverages multi-scale feature alignment within a geo-conditioned joint scale autoregression (GJSA) process to unify bidirectional translation in a single training cycle. A semantic infusion (SI) mechanism is introduced to enhance feature-level consistency, while a key point adaptive guidance (KPAG) mechanism is proposed to dynamically balance diversity and precision during inference. We further contribute CNSatMap, a large-scale dataset comprising 302,132 precisely aligned satellite-map pairs across 38 Chinese cities, enabling robust benchmarking. Extensive experiments on CNSatMap and the New York dataset demonstrate EarthMapper's superior performance, achieving significant improvements in visual realism, semantic consistency, and structural fidelity over state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, EarthMapper excels in zero-shot tasks like in-painting, out-painting and coordinate-conditional generation, underscoring its versatility.
Encoder-Decoder Gemma: Improving the Quality-Efficiency Trade-Off via Adaptation
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:While decoder-only large language models (LLMs) have shown impressive results, encoder-decoder models are still widely adopted in real-world applications for their inference efficiency and richer encoder representation. In this paper, we study a novel problem: adapting pretrained decoder-only LLMs to encoder-decoder, with the goal of leveraging the strengths of both approaches to achieve a more favorable quality-efficiency trade-off. We argue that adaptation not only enables inheriting the capability of decoder-only LLMs but also reduces the demand for computation compared to pretraining from scratch. We rigorously explore different pretraining objectives and parameter initialization/optimization techniques. Through extensive experiments based on Gemma 2 (2B and 9B) and a suite of newly pretrained mT5-sized models (up to 1.6B), we demonstrate the effectiveness of adaptation and the advantage of encoder-decoder LLMs. Under similar inference budget, encoder-decoder LLMs achieve comparable (often better) pretraining performance but substantially better finetuning performance than their decoder-only counterpart. For example, Gemma 2B-2B outperforms Gemma 2B by $\sim$7\% after instruction tuning. Encoder-decoder adaptation also allows for flexible combination of different-sized models, where Gemma 9B-2B significantly surpasses Gemma 2B-2B by $>$3\%. The adapted encoder representation also yields better results on SuperGLUE. We will release our checkpoints to facilitate future research.
Gemini Embedding: Generalizable Embeddings from Gemini
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:In this report, we introduce Gemini Embedding, a state-of-the-art embedding model leveraging the power of Gemini, Google's most capable large language model. Capitalizing on Gemini's inherent multilingual and code understanding capabilities, Gemini Embedding produces highly generalizable embeddings for text spanning numerous languages and textual modalities. The representations generated by Gemini Embedding can be precomputed and applied to a variety of downstream tasks including classification, similarity, clustering, ranking, and retrieval. Evaluated on the Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark (MMTEB), which includes over one hundred tasks across 250+ languages, Gemini Embedding substantially outperforms prior state-of-the-art models, demonstrating considerable improvements in embedding quality. Achieving state-of-the-art performance across MMTEB's multilingual, English, and code benchmarks, our unified model demonstrates strong capabilities across a broad selection of tasks and surpasses specialized domain-specific models.
Adapting Decoder-Based Language Models for Diverse Encoder Downstream Tasks
Mar 04, 2025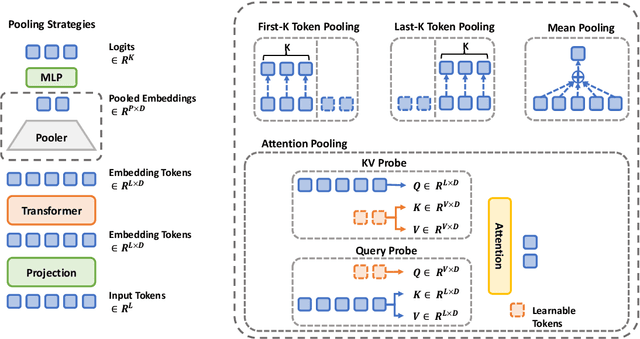
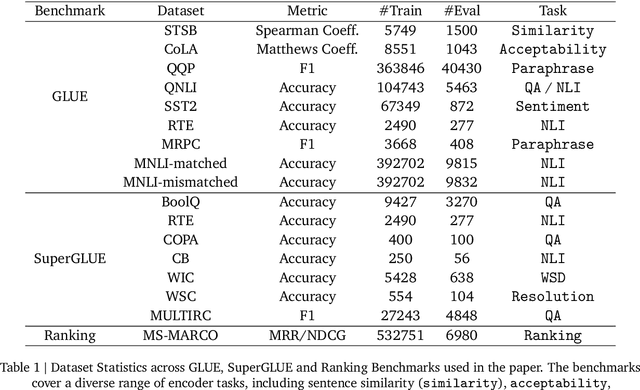
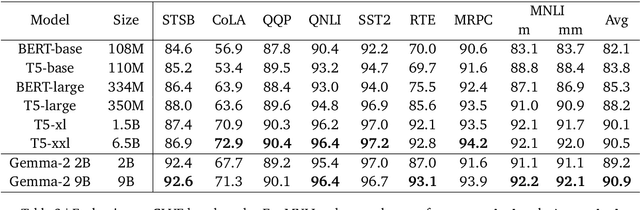
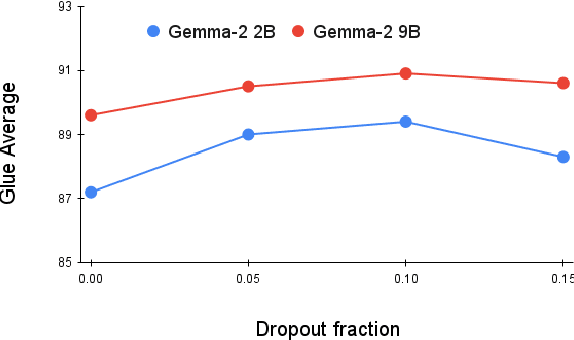
Abstract:Decoder-based transformers, while revolutionizing language modeling and scaling to immense sizes, have not completely overtaken encoder-heavy architectures in natural language processing. Specifically, encoder-only models remain dominant in tasks like classification, regression, and ranking. This is primarily due to the inherent structure of decoder-based models, which limits their direct applicability to these tasks. In this paper, we introduce Gemma Encoder, adapting the powerful Gemma decoder model to an encoder architecture, thereby unlocking its potential for a wider range of non-generative applications. To optimize the adaptation from decoder to encoder, we systematically analyze various pooling strategies, attention mechanisms, and hyperparameters (e.g., dropout rate). Furthermore, we benchmark Gemma Encoder against established approaches on the GLUE benchmarks, and MS MARCO ranking benchmark, demonstrating its effectiveness and versatility.
Cross-Modal Bidirectional Interaction Model for Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:Given a natural language expression and a remote sensing image, the goal of referring remote sensing image segmentation (RRSIS) is to generate a pixel-level mask of the target object identified by the referring expression. In contrast to natural scenarios, expressions in RRSIS often involve complex geospatial relationships, with target objects of interest that vary significantly in scale and lack visual saliency, thereby increasing the difficulty of achieving precise segmentation. To address the aforementioned challenges, a novel RRSIS framework is proposed, termed the cross-modal bidirectional interaction model (CroBIM). Specifically, a context-aware prompt modulation (CAPM) module is designed to integrate spatial positional relationships and task-specific knowledge into the linguistic features, thereby enhancing the ability to capture the target object. Additionally, a language-guided feature aggregation (LGFA) module is introduced to integrate linguistic information into multi-scale visual features, incorporating an attention deficit compensation mechanism to enhance feature aggregation. Finally, a mutual-interaction decoder (MID) is designed to enhance cross-modal feature alignment through cascaded bidirectional cross-attention, thereby enabling precise segmentation mask prediction. To further forster the research of RRSIS, we also construct RISBench, a new large-scale benchmark dataset comprising 52,472 image-language-label triplets. Extensive benchmarking on RISBench and two other prevalent datasets demonstrates the superior performance of the proposed CroBIM over existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. The source code for CroBIM and the RISBench dataset will be publicly available at https://github.com/HIT-SIRS/CroBIM
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Context-Enhanced Detector For Building Detection From Remote Sensing Images
Oct 11, 2023Abstract:The field of building detection from remote sensing images has made significant progress, but faces challenges in achieving high-accuracy detection due to the diversity in building appearances and the complexity of vast scenes. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach called Context-Enhanced Detector (CEDet). Our approach utilizes a three-stage cascade structure to enhance the extraction of contextual information and improve building detection accuracy. Specifically, we introduce two modules: the Semantic Guided Contextual Mining (SGCM) module, which aggregates multi-scale contexts and incorporates an attention mechanism to capture long-range interactions, and the Instance Context Mining Module (ICMM), which captures instance-level relationship context by constructing a spatial relationship graph and aggregating instance features. Additionally, we introduce a semantic segmentation loss based on pseudo-masks to guide contextual information extraction. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on three building detection benchmarks, including CNBuilding-9P, CNBuilding-23P, and SpaceNet.
SamToNe: Improving Contrastive Loss for Dual Encoder Retrieval Models with Same Tower Negatives
Jun 05, 2023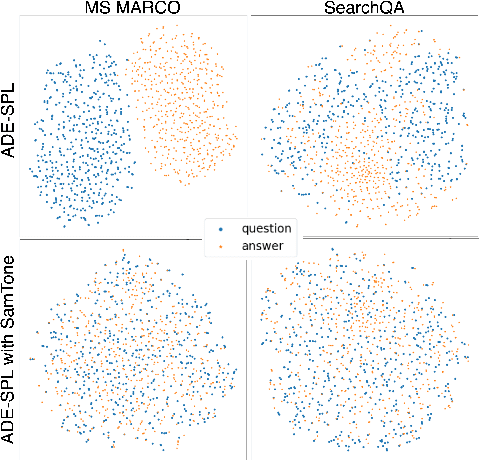
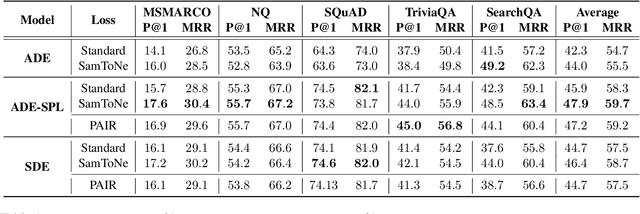
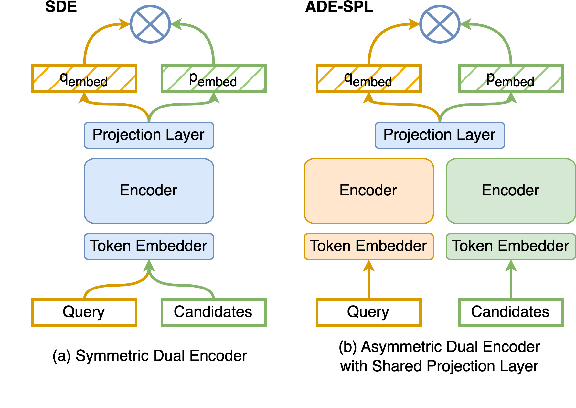
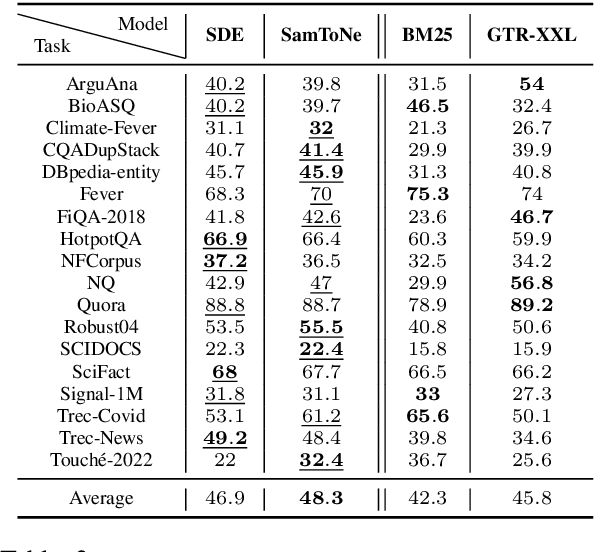
Abstract:Dual encoders have been used for retrieval tasks and representation learning with good results. A standard way to train dual encoders is using a contrastive loss with in-batch negatives. In this work, we propose an improved contrastive learning objective by adding queries or documents from the same encoder towers to the negatives, for which we name it as "contrastive loss with SAMe TOwer NEgatives" (SamToNe). By evaluating on question answering retrieval benchmarks from MS MARCO and MultiReQA, and heterogenous zero-shot information retrieval benchmarks (BEIR), we demonstrate that SamToNe can effectively improve the retrieval quality for both symmetric and asymmetric dual encoders. By directly probing the embedding spaces of the two encoding towers via the t-SNE algorithm (van der Maaten and Hinton, 2008), we observe that SamToNe ensures the alignment between the embedding spaces from the two encoder towers. Based on the analysis of the embedding distance distributions of the top-$1$ retrieved results, we further explain the efficacy of the method from the perspective of regularisation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge