Imed Zitouni
Adapting Decoder-Based Language Models for Diverse Encoder Downstream Tasks
Mar 04, 2025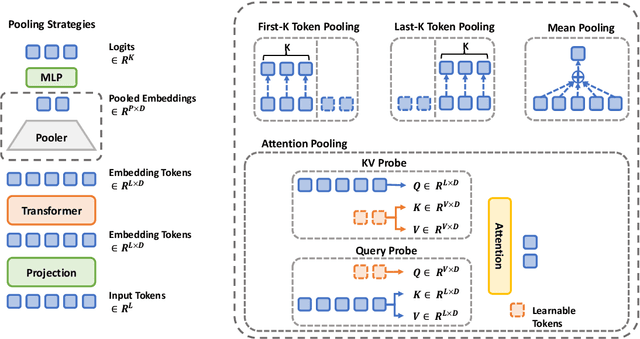
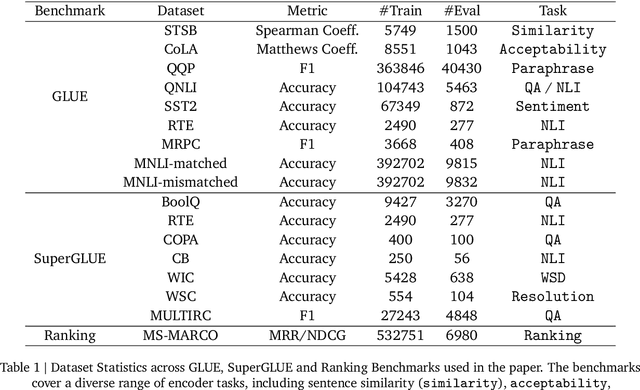
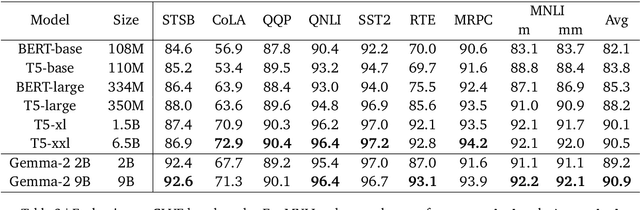
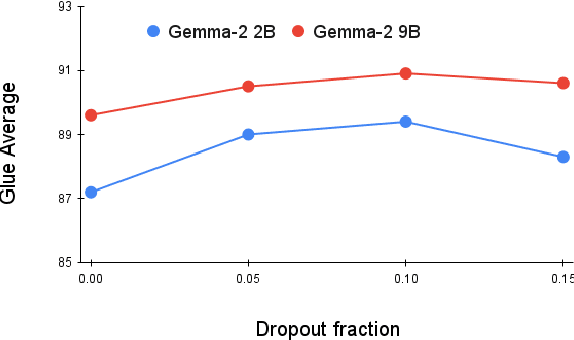
Abstract:Decoder-based transformers, while revolutionizing language modeling and scaling to immense sizes, have not completely overtaken encoder-heavy architectures in natural language processing. Specifically, encoder-only models remain dominant in tasks like classification, regression, and ranking. This is primarily due to the inherent structure of decoder-based models, which limits their direct applicability to these tasks. In this paper, we introduce Gemma Encoder, adapting the powerful Gemma decoder model to an encoder architecture, thereby unlocking its potential for a wider range of non-generative applications. To optimize the adaptation from decoder to encoder, we systematically analyze various pooling strategies, attention mechanisms, and hyperparameters (e.g., dropout rate). Furthermore, we benchmark Gemma Encoder against established approaches on the GLUE benchmarks, and MS MARCO ranking benchmark, demonstrating its effectiveness and versatility.
ArabicNLU 2024: The First Arabic Natural Language Understanding Shared Task
Jul 30, 2024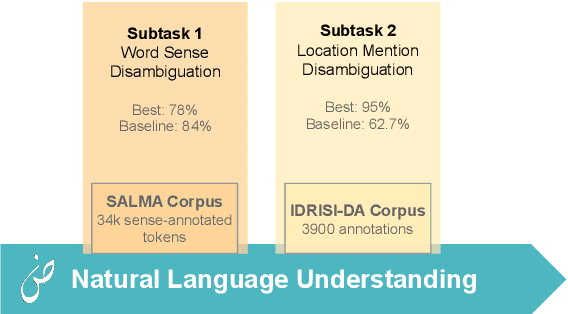
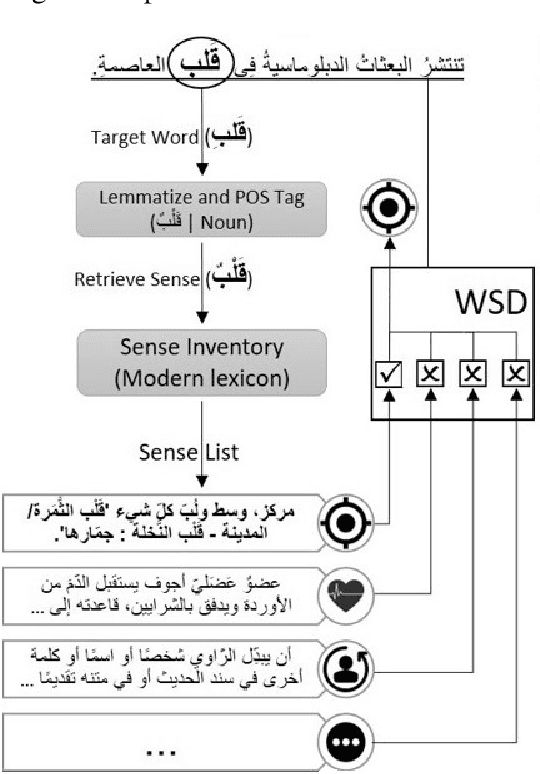
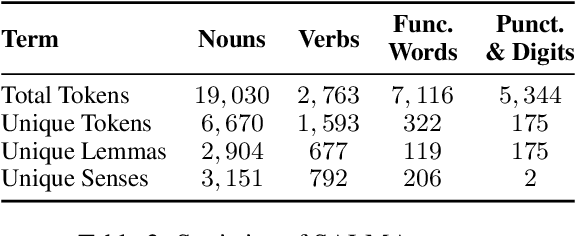
Abstract:This paper presents an overview of the Arabic Natural Language Understanding (ArabicNLU 2024) shared task, focusing on two subtasks: Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) and Location Mention Disambiguation (LMD). The task aimed to evaluate the ability of automated systems to resolve word ambiguity and identify locations mentioned in Arabic text. We provided participants with novel datasets, including a sense-annotated corpus for WSD, called SALMA with approximately 34k annotated tokens, and the IDRISI-DA dataset with 3,893 annotations and 763 unique location mentions. These are challenging tasks. Out of the 38 registered teams, only three teams participated in the final evaluation phase, with the highest accuracy being 77.8% for WSD and the highest MRR@1 being 95.0% for LMD. The shared task not only facilitated the evaluation and comparison of different techniques, but also provided valuable insights and resources for the continued advancement of Arabic NLU technologies.
The FIGNEWS Shared Task on News Media Narratives
Jul 25, 2024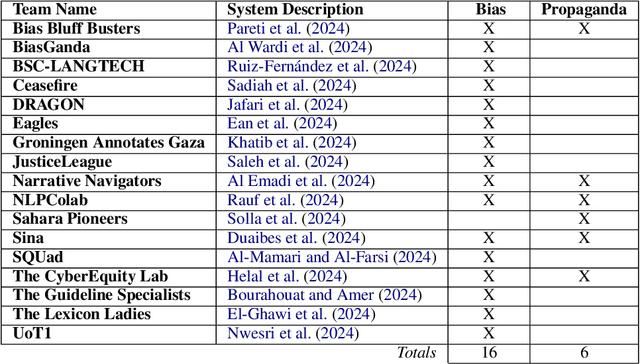
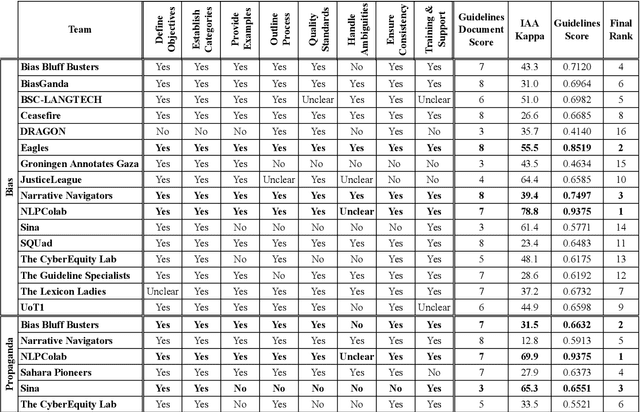
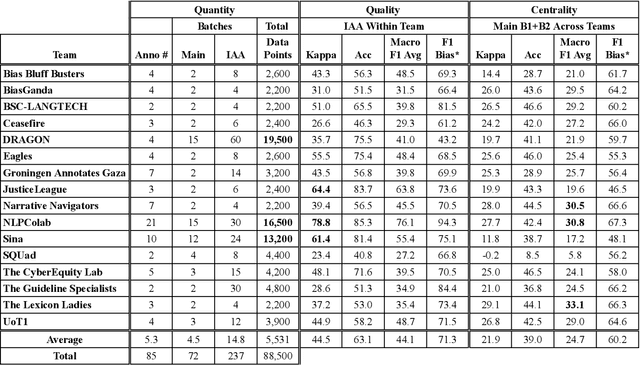
Abstract:We present an overview of the FIGNEWS shared task, organized as part of the ArabicNLP 2024 conference co-located with ACL 2024. The shared task addresses bias and propaganda annotation in multilingual news posts. We focus on the early days of the Israel War on Gaza as a case study. The task aims to foster collaboration in developing annotation guidelines for subjective tasks by creating frameworks for analyzing diverse narratives highlighting potential bias and propaganda. In a spirit of fostering and encouraging diversity, we address the problem from a multilingual perspective, namely within five languages: English, French, Arabic, Hebrew, and Hindi. A total of 17 teams participated in two annotation subtasks: bias (16 teams) and propaganda (6 teams). The teams competed in four evaluation tracks: guidelines development, annotation quality, annotation quantity, and consistency. Collectively, the teams produced 129,800 data points. Key findings and implications for the field are discussed.
SamToNe: Improving Contrastive Loss for Dual Encoder Retrieval Models with Same Tower Negatives
Jun 05, 2023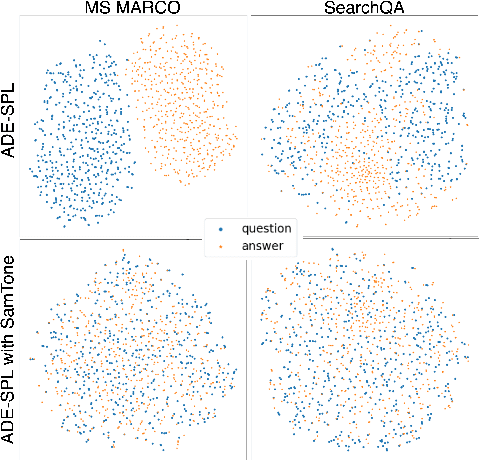
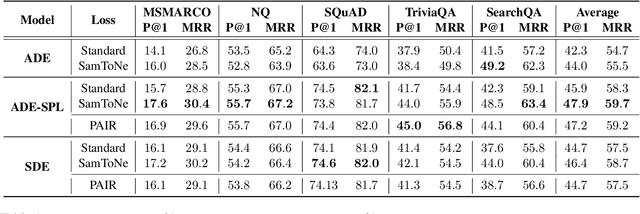
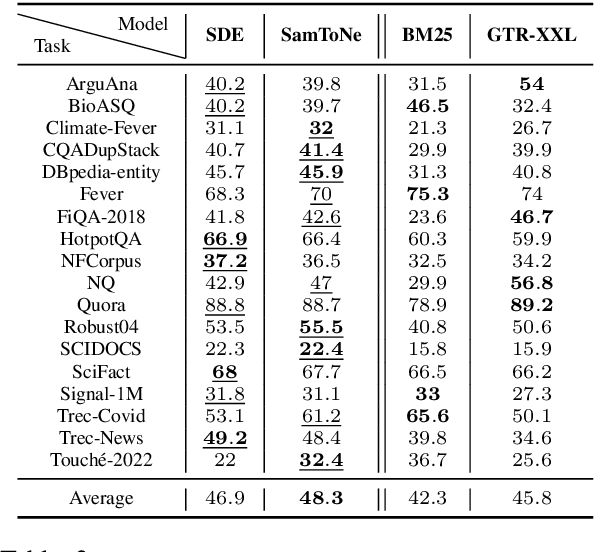
Abstract:Dual encoders have been used for retrieval tasks and representation learning with good results. A standard way to train dual encoders is using a contrastive loss with in-batch negatives. In this work, we propose an improved contrastive learning objective by adding queries or documents from the same encoder towers to the negatives, for which we name it as "contrastive loss with SAMe TOwer NEgatives" (SamToNe). By evaluating on question answering retrieval benchmarks from MS MARCO and MultiReQA, and heterogenous zero-shot information retrieval benchmarks (BEIR), we demonstrate that SamToNe can effectively improve the retrieval quality for both symmetric and asymmetric dual encoders. By directly probing the embedding spaces of the two encoding towers via the t-SNE algorithm (van der Maaten and Hinton, 2008), we observe that SamToNe ensures the alignment between the embedding spaces from the two encoder towers. Based on the analysis of the embedding distance distributions of the top-$1$ retrieved results, we further explain the efficacy of the method from the perspective of regularisation.
Exploring Dual Encoder Architectures for Question Answering
Apr 14, 2022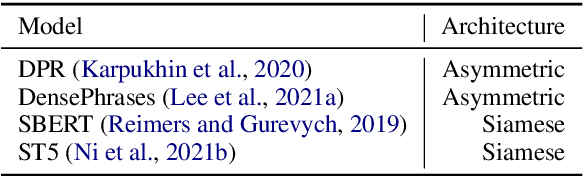
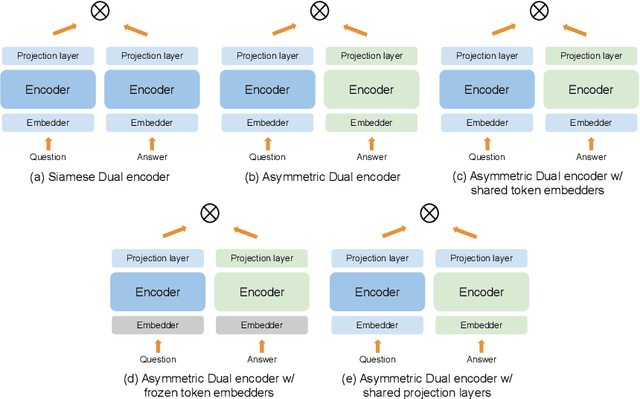
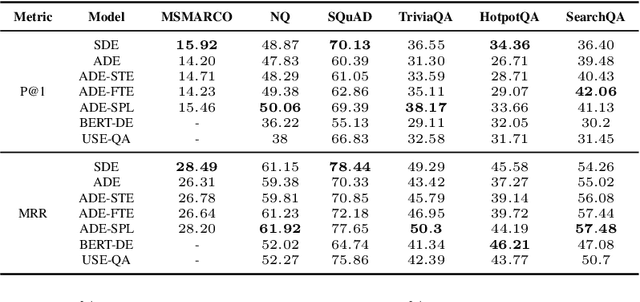
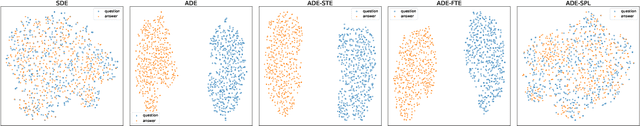
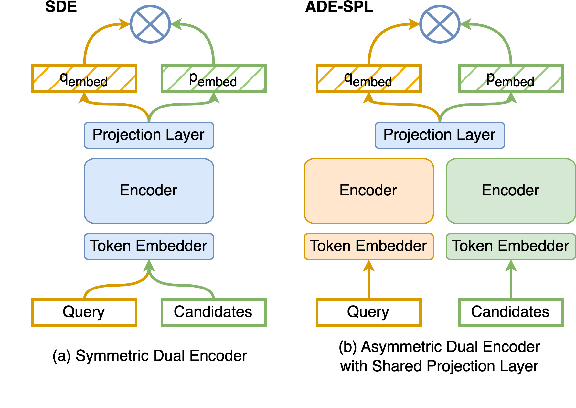
Abstract:Dual encoders have been used for question-answering (QA) and information retrieval (IR) tasks with good results. There are two major types of dual encoders, Siamese Dual Encoders (SDE), with parameters shared across two encoders, and Asymmetric Dual Encoder (ADE), with two distinctly parameterized encoders. In this work, we explore the dual encoder architectures for QA retrieval tasks. By evaluating on MS MARCO and the MultiReQA benchmark, we show that SDE performs significantly better than ADE. We further propose three different improved versions of ADEs. Based on the evaluation of QA retrieval tasks and direct analysis of the embeddings, we demonstrate that sharing parameters in projection layers would enable ADEs to perform competitively with SDEs.
Off-policy evaluation for slate recommendation
Nov 06, 2017



Abstract:This paper studies the evaluation of policies that recommend an ordered set of items (e.g., a ranking) based on some context---a common scenario in web search, ads, and recommendation. We build on techniques from combinatorial bandits to introduce a new practical estimator that uses logged data to estimate a policy's performance. A thorough empirical evaluation on real-world data reveals that our estimator is accurate in a variety of settings, including as a subroutine in a learning-to-rank task, where it achieves competitive performance. We derive conditions under which our estimator is unbiased---these conditions are weaker than prior heuristics for slate evaluation---and experimentally demonstrate a smaller bias than parametric approaches, even when these conditions are violated. Finally, our theory and experiments also show exponential savings in the amount of required data compared with general unbiased estimators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge