Yu
Kevin
Occult: Optimizing Collaborative Communication across Experts for Accelerated Parallel MoE Training and Inference
May 19, 2025Abstract:Mixture-of-experts (MoE) architectures could achieve impressive computational efficiency with expert parallelism, which relies heavily on all-to-all communication across devices. Unfortunately, such communication overhead typically constitutes a significant portion of the total runtime, hampering the scalability of distributed training and inference for modern MoE models (consuming over $40\%$ runtime in large-scale training). In this paper, we first define collaborative communication to illustrate this intrinsic limitation, and then propose system- and algorithm-level innovations to reduce communication costs. Specifically, given a pair of experts co-activated by one token, we call them "collaborated", which comprises $2$ cases as intra- and inter-collaboration, depending on whether they are kept on the same device. Our pilot investigations reveal that augmenting the proportion of intra-collaboration can accelerate expert parallelism at scale. It motivates us to strategically optimize collaborative communication for accelerated MoE training and inference, dubbed Occult. Our designs are capable of either delivering exact results with reduced communication cost or controllably minimizing the cost with collaboration pruning, materialized by modified fine-tuning. Comprehensive experiments on various MoE-LLMs demonstrate that Occult can be faster than popular state-of-the-art inference or training frameworks (more than $1.5\times$ speed up across multiple tasks and models) with comparable or superior quality compared to the standard fine-tuning. Code is available at $\href{https://github.com/UNITES-Lab/Occult}{https://github.com/UNITES-Lab/Occult}$.
Hydra: An Agentic Reasoning Approach for Enhancing Adversarial Robustness and Mitigating Hallucinations in Vision-Language Models
Apr 19, 2025



Abstract:To develop trustworthy Vision-Language Models (VLMs), it is essential to address adversarial robustness and hallucination mitigation, both of which impact factual accuracy in high-stakes applications such as defense and healthcare. Existing methods primarily focus on either adversarial defense or hallucination post-hoc correction, leaving a gap in unified robustness strategies. We introduce \textbf{Hydra}, an adaptive agentic framework that enhances plug-in VLMs through iterative reasoning, structured critiques, and cross-model verification, improving both resilience to adversarial perturbations and intrinsic model errors. Hydra employs an Action-Critique Loop, where it retrieves and critiques visual information, leveraging Chain-of-Thought (CoT) and In-Context Learning (ICL) techniques to refine outputs dynamically. Unlike static post-hoc correction methods, Hydra adapts to both adversarial manipulations and intrinsic model errors, making it robust to malicious perturbations and hallucination-related inaccuracies. We evaluate Hydra on four VLMs, three hallucination benchmarks, two adversarial attack strategies, and two adversarial defense methods, assessing performance on both clean and adversarial inputs. Results show that Hydra surpasses plug-in VLMs and state-of-the-art (SOTA) dehallucination methods, even without explicit adversarial defenses, demonstrating enhanced robustness and factual consistency. By bridging adversarial resistance and hallucination mitigation, Hydra provides a scalable, training-free solution for improving the reliability of VLMs in real-world applications.
TranSplat: Lighting-Consistent Cross-Scene Object Transfer with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:We present TranSplat, a 3D scene rendering algorithm that enables realistic cross-scene object transfer (from a source to a target scene) based on the Gaussian Splatting framework. Our approach addresses two critical challenges: (1) precise 3D object extraction from the source scene, and (2) faithful relighting of the transferred object in the target scene without explicit material property estimation. TranSplat fits a splatting model to the source scene, using 2D object masks to drive fine-grained 3D segmentation. Following user-guided insertion of the object into the target scene, along with automatic refinement of position and orientation, TranSplat derives per-Gaussian radiance transfer functions via spherical harmonic analysis to adapt the object's appearance to match the target scene's lighting environment. This relighting strategy does not require explicitly estimating physical scene properties such as BRDFs. Evaluated on several synthetic and real-world scenes and objects, TranSplat yields excellent 3D object extractions and relighting performance compared to recent baseline methods and visually convincing cross-scene object transfers. We conclude by discussing the limitations of the approach.
From Model Explanation to Data Misinterpretation: Uncovering the Pitfalls of Post Hoc Explainers in Business Research
Aug 30, 2024



Abstract:Machine learning models have been increasingly used in business research. However, most state-of-the-art machine learning models, such as deep neural networks and XGBoost, are black boxes in nature. Therefore, post hoc explainers that provide explanations for machine learning models by, for example, estimating numerical importance of the input features, have been gaining wide usage. Despite the intended use of post hoc explainers being explaining machine learning models, we found a growing trend in business research where post hoc explanations are used to draw inferences about the data. In this work, we investigate the validity of such use. Specifically, we investigate with extensive experiments whether the explanations obtained by the two most popular post hoc explainers, SHAP and LIME, provide correct information about the true marginal effects of X on Y in the data, which we call data-alignment. We then identify what factors influence the alignment of explanations. Finally, we propose a set of mitigation strategies to improve the data-alignment of explanations and demonstrate their effectiveness with real-world data in an econometric context. In spite of this effort, we nevertheless conclude that it is often not appropriate to infer data insights from post hoc explanations. We articulate appropriate alternative uses, the most important of which is to facilitate the proposition and subsequent empirical investigation of hypotheses. The ultimate goal of this paper is to caution business researchers against translating post hoc explanations of machine learning models into potentially false insights and understanding of data.
The Llama 3 Herd of Models
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Modern artificial intelligence (AI) systems are powered by foundation models. This paper presents a new set of foundation models, called Llama 3. It is a herd of language models that natively support multilinguality, coding, reasoning, and tool usage. Our largest model is a dense Transformer with 405B parameters and a context window of up to 128K tokens. This paper presents an extensive empirical evaluation of Llama 3. We find that Llama 3 delivers comparable quality to leading language models such as GPT-4 on a plethora of tasks. We publicly release Llama 3, including pre-trained and post-trained versions of the 405B parameter language model and our Llama Guard 3 model for input and output safety. The paper also presents the results of experiments in which we integrate image, video, and speech capabilities into Llama 3 via a compositional approach. We observe this approach performs competitively with the state-of-the-art on image, video, and speech recognition tasks. The resulting models are not yet being broadly released as they are still under development.
N-Grammer: Augmenting Transformers with latent n-grams
Jul 13, 2022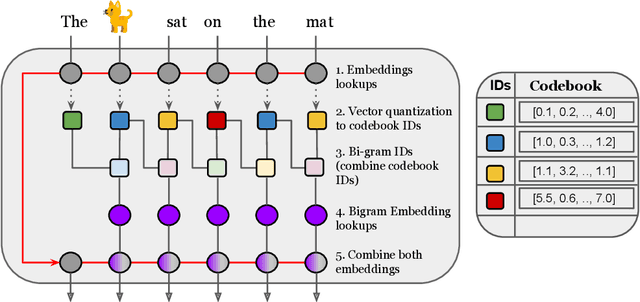
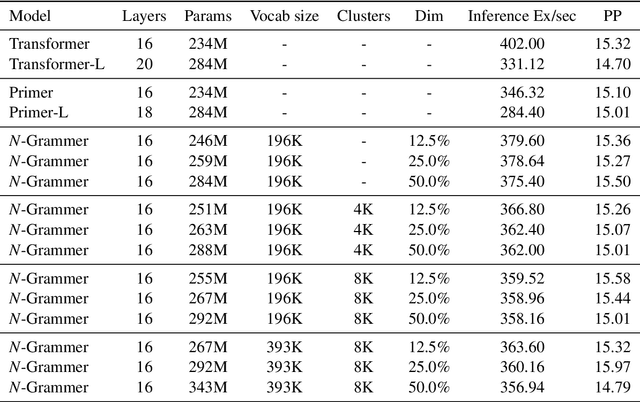
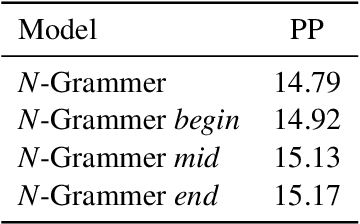
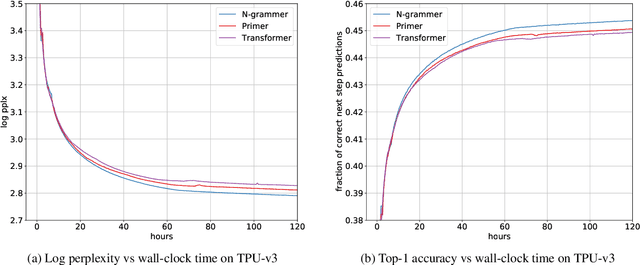
Abstract:Transformer models have recently emerged as one of the foundational models in natural language processing, and as a byproduct, there is significant recent interest and investment in scaling these models. However, the training and inference costs of these large Transformer language models are prohibitive, thus necessitating more research in identifying more efficient variants. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective modification to the Transformer architecture inspired by the literature in statistical language modeling, by augmenting the model with n-grams that are constructed from a discrete latent representation of the text sequence. We evaluate our model, the N-Grammer on language modeling on the C4 data-set as well as text classification on the SuperGLUE data-set, and find that it outperforms several strong baselines such as the Transformer and the Primer. We open-source our model for reproducibility purposes in Jax.
Data-Free Point Cloud Network for 3D Face Recognition
Nov 12, 2019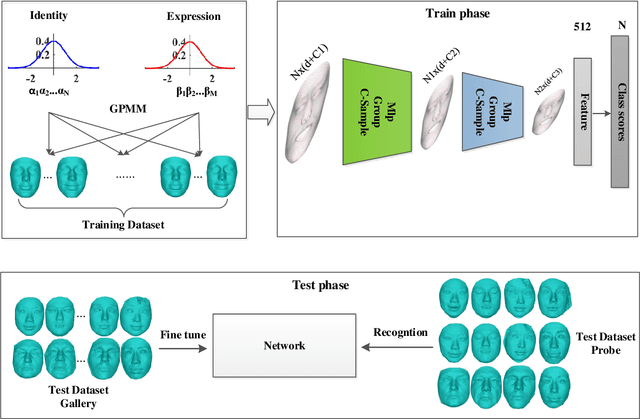
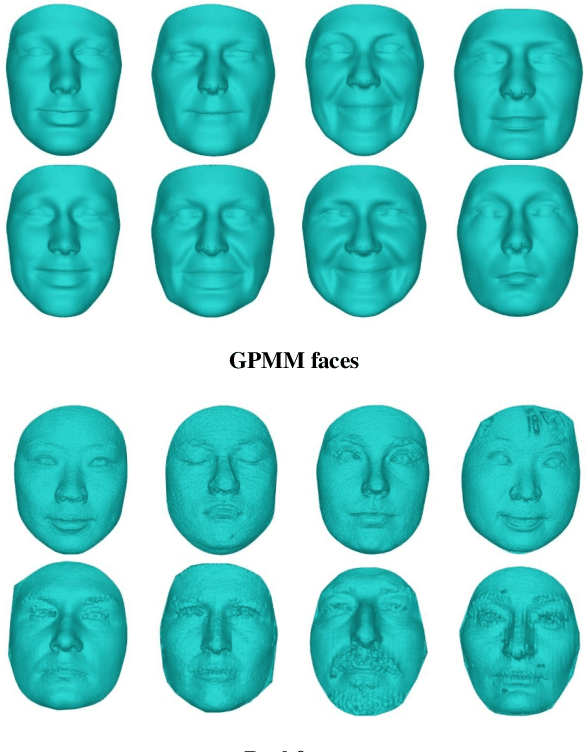
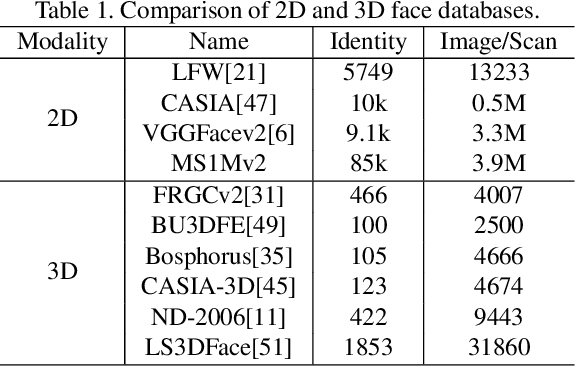

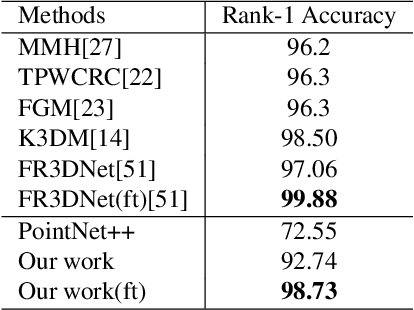
Abstract:Point clouds-based Networks have achieved great attention in 3D object classification, segmentation and indoor scene semantic parsing. In terms of face recognition, 3D face recognition method which directly consume point clouds as input is still under study. Two main factors account for this: One is how to get discriminative face representations from 3D point clouds using deep network; the other is the lack of large 3D training dataset. To address these problems, a data-free 3D face recognition method is proposed only using synthesized unreal data from statistical 3D Morphable Model to train a deep point cloud network. To ease the inconsistent distribution between model data and real faces, different point sampling methods are used in train and test phase. In this paper, we propose a curvature-aware point sampling(CPS) strategy replacing the original furthest point sampling(FPS) to hierarchically down-sample feature-sensitive points which are crucial to pass and aggregate features deeply. A PointNet++ like Network is used to extract face features directly from point clouds. The experimental results show that the network trained on generated data generalizes well for real 3D faces. Fine tuning on a small part of FRGCv2.0 and Bosphorus, which include real faces in different poses and expressions, further improves recognition accuracy.
Early Predictions for Medical Crowdfunding: A Deep Learning Approach Using Diverse Inputs
Nov 09, 2019



Abstract:Medical crowdfunding is a popular channel for people needing financial help paying medical bills to collect donations from large numbers of people. However, large heterogeneity exists in donations across cases, and fundraisers face significant uncertainty in whether their crowdfunding campaigns can meet fundraising goals. Therefore, it is important to provide early warnings for fundraisers if such a channel will eventually fail. In this study, we aim to develop novel algorithms to provide accurate and timely predictions of fundraising performance, to better inform fundraisers. In particular, we propose a new approach to combine time-series features and time-invariant features in the deep learning model, to process diverse sources of input data. Compared with baseline models, our model achieves better accuracy and requires a shorter observation window of the time-varying features from the campaign launch to provide robust predictions with high confidence. To extract interpretable insights, we further conduct a multivariate time-series clustering analysis and identify four typical temporal donation patterns. This demonstrates the heterogeneity in the features and how they relate to the fundraising outcome. The prediction model and the interpretable insights can be applied to assist fundraisers with better promoting their fundraising campaigns and can potentially help crowdfunding platforms to provide more timely feedback to all fundraisers. Our proposed framework is also generalizable to other fields where diverse structured and unstructured data are valuable for predictions.
GLAD: Group Anomaly Detection in Social Media Analysis- Extended Abstract
Oct 07, 2014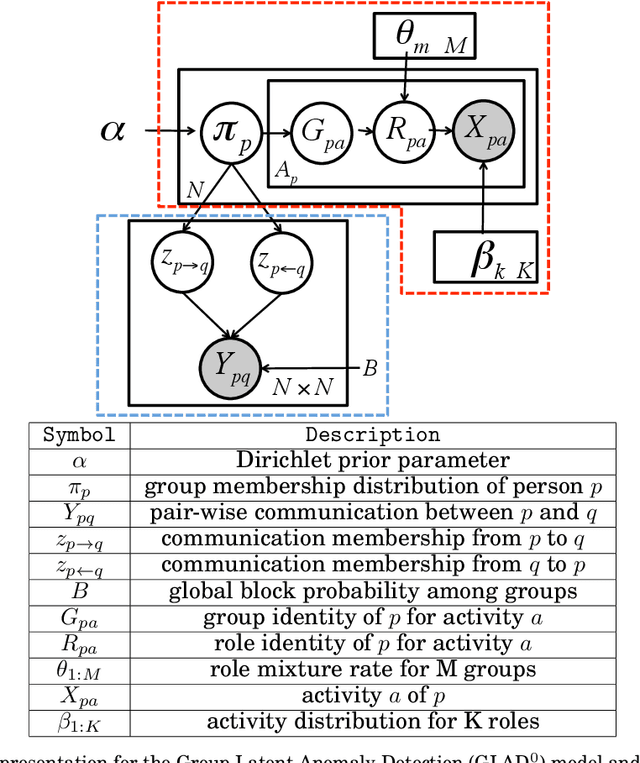
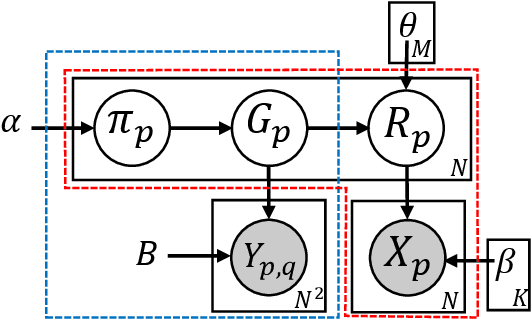
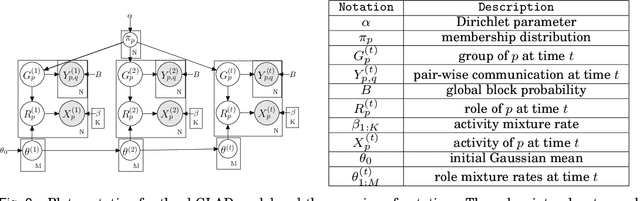
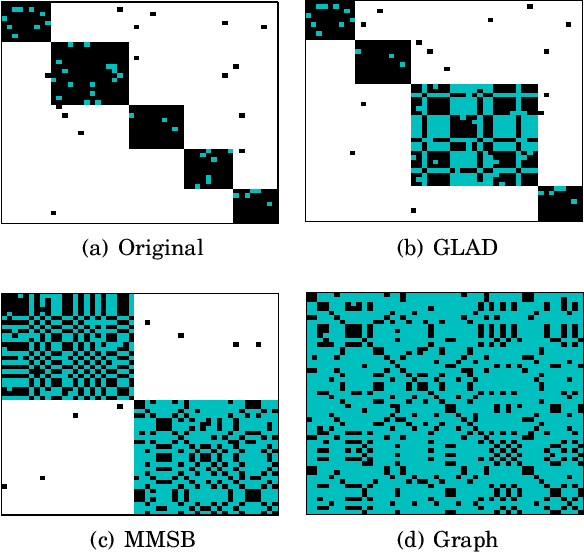
Abstract:Traditional anomaly detection on social media mostly focuses on individual point anomalies while anomalous phenomena usually occur in groups. Therefore it is valuable to study the collective behavior of individuals and detect group anomalies. Existing group anomaly detection approaches rely on the assumption that the groups are known, which can hardly be true in real world social media applications. In this paper, we take a generative approach by proposing a hierarchical Bayes model: Group Latent Anomaly Detection (GLAD) model. GLAD takes both pair-wise and point-wise data as input, automatically infers the groups and detects group anomalies simultaneously. To account for the dynamic properties of the social media data, we further generalize GLAD to its dynamic extension d-GLAD. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate our models on both synthetic and real world datasets. The empirical results demonstrate that our approach is effective and robust in discovering latent groups and detecting group anomalies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge