Yi
Grace
Mobile Distributed MIMO (MD-MIMO) for NextG: Mobility Meets Cooperation in Distributed Arrays
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Distributed multiple-input multiple-output (D\mbox{-}MIMO) is a promising technology to realize the promise of massive MIMO gains by fiber-connecting the distributed antenna arrays, thereby overcoming the form factor limitations of co-located MIMO. In this paper, we introduce the concept of mobile D-MIMO (MD-MIMO) network, a further extension of the D-MIMO technology where distributed antenna arrays are connected to the base station with a wireless link allowing all radio network nodes to be mobile. This approach significantly improves deployment flexibility and reduces operating costs, enabling the network to adapt to the highly dynamic nature of next-generation (NextG) networks. We discuss use cases, system design, network architecture, and the key enabling technologies for MD-MIMO. Furthermore, we investigate a case study of MD-MIMO for vehicular networks, presenting detailed performance evaluations for both downlink and uplink. The results show that an MD-MIMO network can provide substantial improvements in network throughput and reliability.
HyperCam: Low-Power Onboard Computer Vision for IoT Cameras
Jan 17, 2025Abstract:We present HyperCam, an energy-efficient image classification pipeline that enables computer vision tasks onboard low-power IoT camera systems. HyperCam leverages hyperdimensional computing to perform training and inference efficiently on low-power microcontrollers. We implement a low-power wireless camera platform using off-the-shelf hardware and demonstrate that HyperCam can achieve an accuracy of 93.60%, 84.06%, 92.98%, and 72.79% for MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, Face Detection, and Face Identification tasks, respectively, while significantly outperforming other classifiers in resource efficiency. Specifically, it delivers inference latency of 0.08-0.27s while using 42.91-63.00KB flash memory and 22.25KB RAM at peak. Among other machine learning classifiers such as SVM, xgBoost, MicroNets, MobileNetV3, and MCUNetV3, HyperCam is the only classifier that achieves competitive accuracy while maintaining competitive memory footprint and inference latency that meets the resource requirements of low-power camera systems.
Adversarial Classification of the Attacks on Smart Grids Using Game Theory and Deep Learning
Jun 06, 2021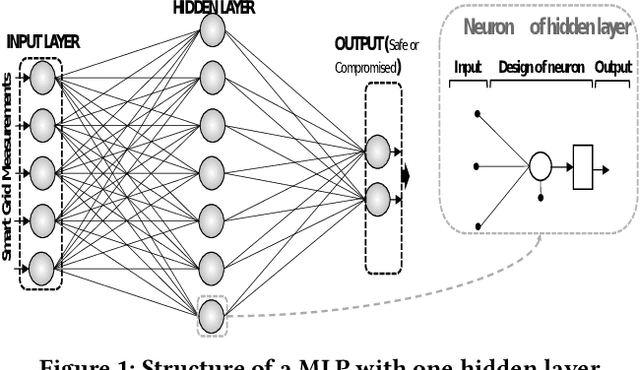
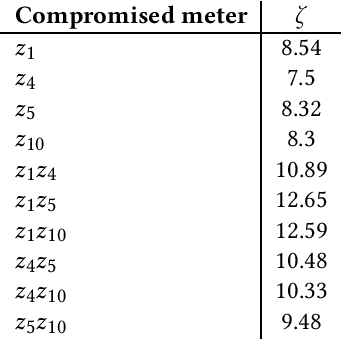
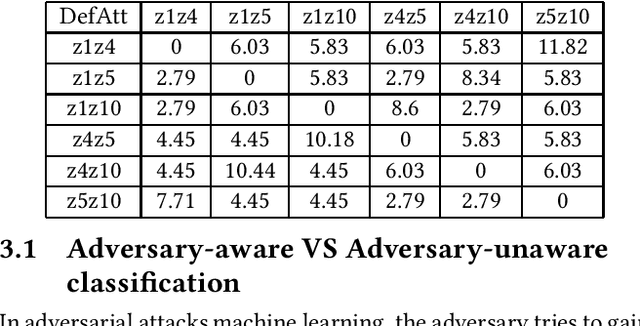
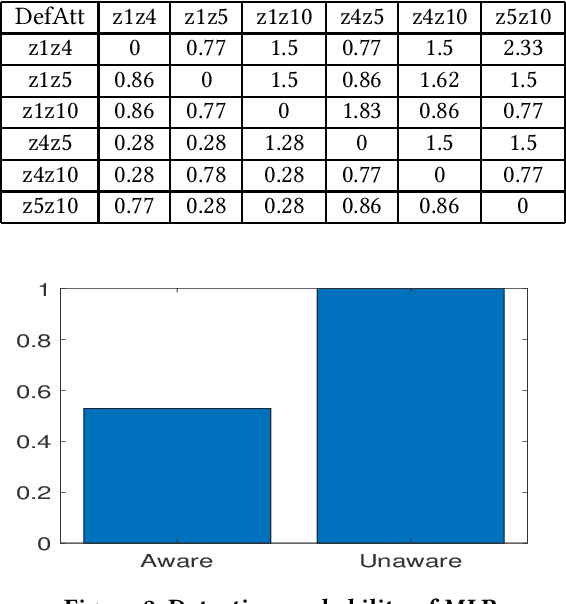
Abstract:Smart grids are vulnerable to cyber-attacks. This paper proposes a game-theoretic approach to evaluate the variations caused by an attacker on the power measurements. Adversaries can gain financial benefits through the manipulation of the meters of smart grids. On the other hand, there is a defender that tries to maintain the accuracy of the meters. A zero-sum game is used to model the interactions between the attacker and defender. In this paper, two different defenders are used and the effectiveness of each defender in different scenarios is evaluated. Multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs) and traditional state estimators are the two defenders that are studied in this paper. The utility of the defender is also investigated in adversary-aware and adversary-unaware situations. Our simulations suggest that the utility which is gained by the adversary drops significantly when the MLP is used as the defender. It will be shown that the utility of the defender is variant in different scenarios, based on the defender that is being used. In the end, we will show that this zero-sum game does not yield a pure strategy, and the mixed strategy of the game is calculated.
Data-Free Point Cloud Network for 3D Face Recognition
Nov 12, 2019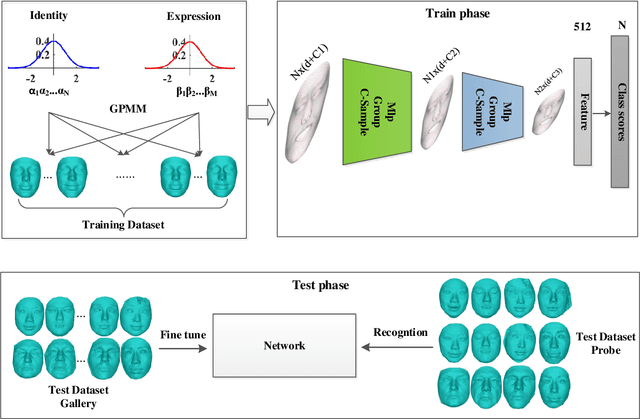
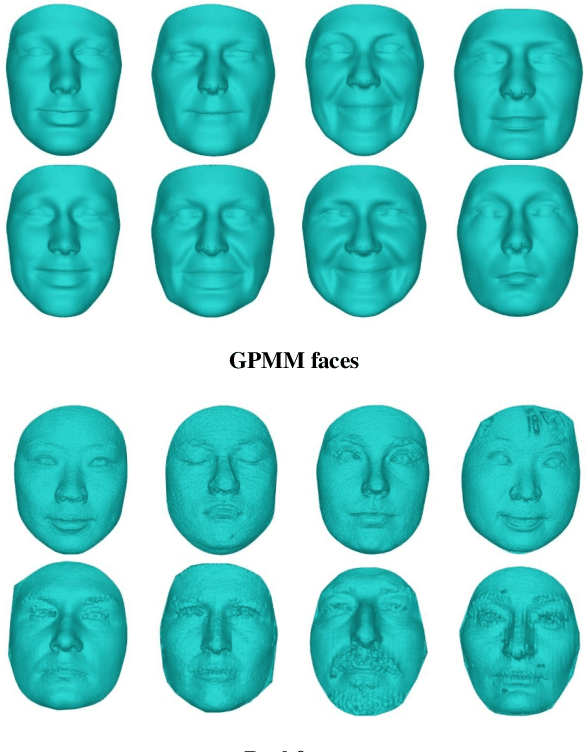
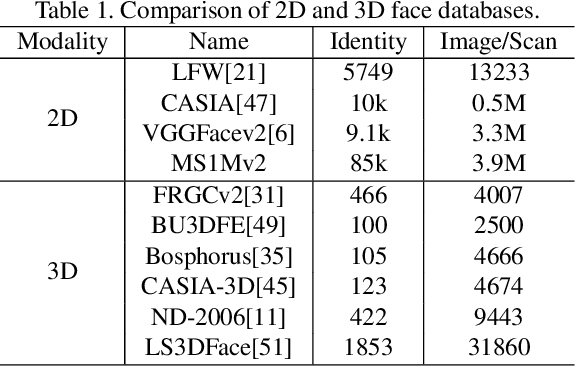

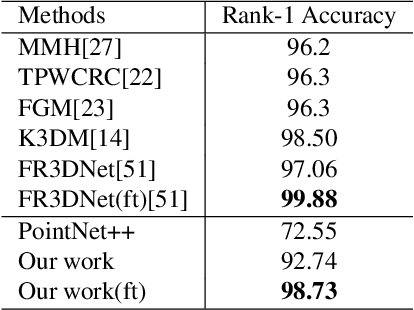
Abstract:Point clouds-based Networks have achieved great attention in 3D object classification, segmentation and indoor scene semantic parsing. In terms of face recognition, 3D face recognition method which directly consume point clouds as input is still under study. Two main factors account for this: One is how to get discriminative face representations from 3D point clouds using deep network; the other is the lack of large 3D training dataset. To address these problems, a data-free 3D face recognition method is proposed only using synthesized unreal data from statistical 3D Morphable Model to train a deep point cloud network. To ease the inconsistent distribution between model data and real faces, different point sampling methods are used in train and test phase. In this paper, we propose a curvature-aware point sampling(CPS) strategy replacing the original furthest point sampling(FPS) to hierarchically down-sample feature-sensitive points which are crucial to pass and aggregate features deeply. A PointNet++ like Network is used to extract face features directly from point clouds. The experimental results show that the network trained on generated data generalizes well for real 3D faces. Fine tuning on a small part of FRGCv2.0 and Bosphorus, which include real faces in different poses and expressions, further improves recognition accuracy.
High Dimensional Data Modeling Techniques for Detection of Chemical Plumes and Anomalies in Hyperspectral Images and Movies
Jan 29, 2016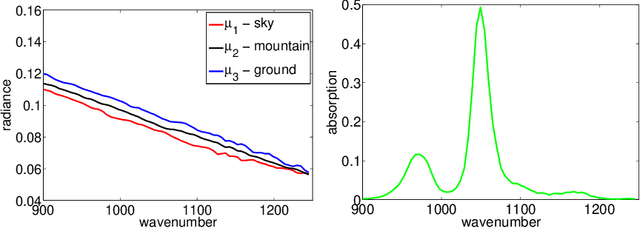
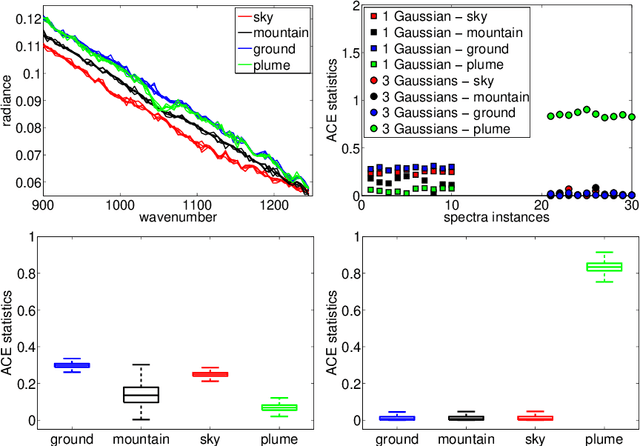
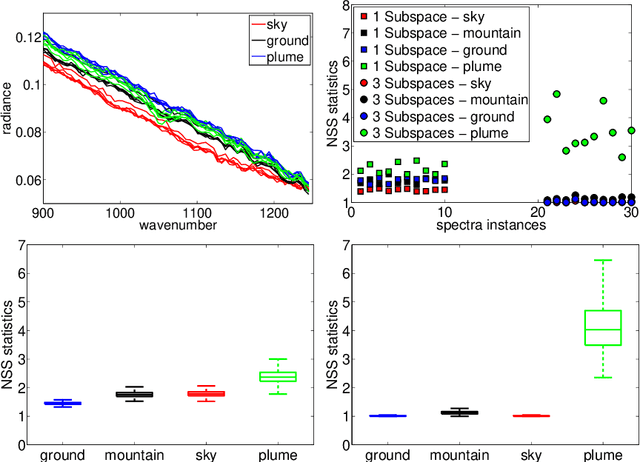
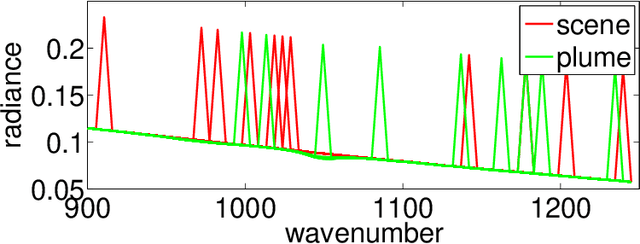
Abstract:We briefly review recent progress in techniques for modeling and analyzing hyperspectral images and movies, in particular for detecting plumes of both known and unknown chemicals. For detecting chemicals of known spectrum, we extend the technique of using a single subspace for modeling the background to a "mixture of subspaces" model to tackle more complicated background. Furthermore, we use partial least squares regression on a resampled training set to boost performance. For the detection of unknown chemicals we view the problem as an anomaly detection problem, and use novel estimators with low-sampled complexity for intrinsically low-dimensional data in high-dimensions that enable us to model the "normal" spectra and detect anomalies. We apply these algorithms to benchmark data sets made available by the Automated Target Detection program co-funded by NSF, DTRA and NGA, and compare, when applicable, to current state-of-the-art algorithms, with favorable results.
An Efficient and Integrated Algorithm for Video Enhancement in Challenging Lighting Conditions
Feb 16, 2011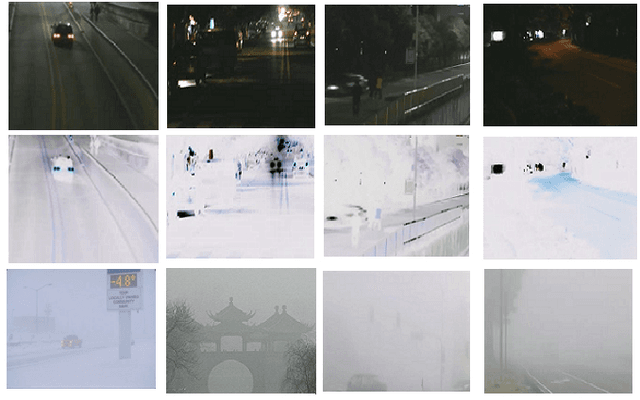
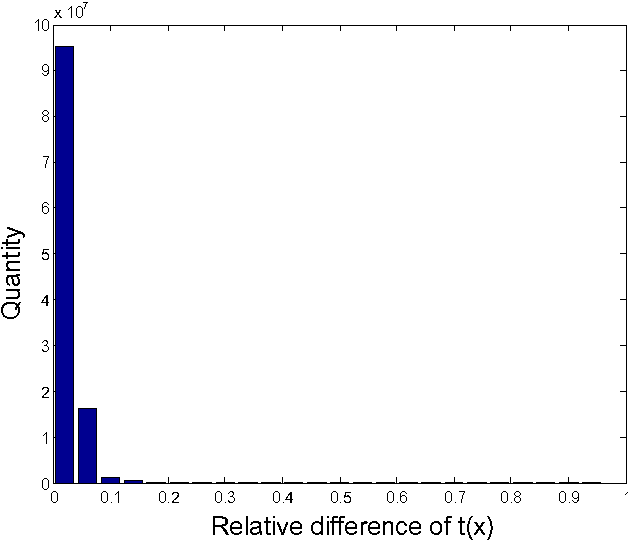
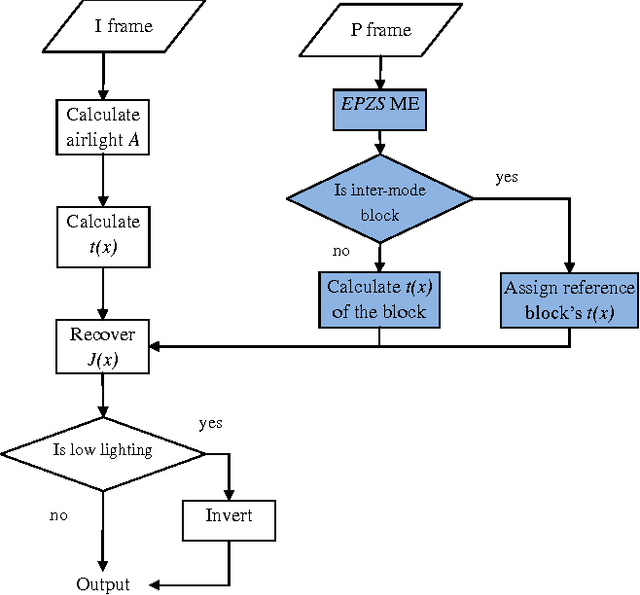
Abstract:We describe a novel integrated algorithm for real-time enhancement of video acquired under challenging lighting conditions. Such conditions include low lighting, haze, and high dynamic range situations. The algorithm automatically detects the dominate source of impairment, then depending on whether it is low lighting, haze or others, a corresponding pre-processing is applied to the input video, followed by the core enhancement algorithm. Temporal and spatial redundancies in the video input are utilized to facilitate real-time processing and to improve temporal and spatial consistency of the output. The proposed algorithm can be used as an independent module, or be integrated in either a video encoder or a video decoder for further optimizations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge