Yong Cui
NetMamba+: A Framework of Pre-trained Models for Efficient and Accurate Network Traffic Classification
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:With the rapid growth of encrypted network traffic, effective traffic classification has become essential for network security and quality of service management. Current machine learning and deep learning approaches for traffic classification face three critical challenges: computational inefficiency of Transformer architectures, inadequate traffic representations with loss of crucial byte-level features while retaining detrimental biases, and poor handling of long-tail distributions in real-world data. We propose NetMamba+, a framework that addresses these challenges through three key innovations: (1) an efficient architecture considering Mamba and Flash Attention mechanisms, (2) a multimodal traffic representation scheme that preserves essential traffic information while eliminating biases, and (3) a label distribution-aware fine-tuning strategy. Evaluation experiments on massive datasets encompassing four main classification tasks showcase NetMamba+'s superior classification performance compared to state-of-the-art baselines, with improvements of up to 6.44\% in F1 score. Moreover, NetMamba+ demonstrates excellent efficiency, achieving 1.7x higher inference throughput than the best baseline while maintaining comparably low memory usage. Furthermore, NetMamba+ exhibits superior few-shot learning abilities, achieving better classification performance with fewer labeled data. Additionally, we implement an online traffic classification system that demonstrates robust real-world performance with a throughput of 261.87 Mb/s. As the first framework to adapt Mamba architecture for network traffic classification, NetMamba+ opens new possibilities for efficient and accurate traffic analysis in complex network environments.
Bias in the Shadows: Explore Shortcuts in Encrypted Network Traffic Classification
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Pre-trained models operating directly on raw bytes have achieved promising performance in encrypted network traffic classification (NTC), but often suffer from shortcut learning-relying on spurious correlations that fail to generalize to real-world data. Existing solutions heavily rely on model-specific interpretation techniques, which lack adaptability and generality across different model architectures and deployment scenarios. In this paper, we propose BiasSeeker, the first semi-automated framework that is both model-agnostic and data-driven for detecting dataset-specific shortcut features in encrypted traffic. By performing statistical correlation analysis directly on raw binary traffic, BiasSeeker identifies spurious or environment-entangled features that may compromise generalization, independent of any classifier. To address the diverse nature of shortcut features, we introduce a systematic categorization and apply category-specific validation strategies that reduce bias while preserving meaningful information. We evaluate BiasSeeker on 19 public datasets across three NTC tasks. By emphasizing context-aware feature selection and dataset-specific diagnosis, BiasSeeker offers a novel perspective for understanding and addressing shortcut learning in encrypted network traffic classification, raising awareness that feature selection should be an intentional and scenario-sensitive step prior to model training.
Sample Efficient Experience Replay in Non-stationary Environments
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) in non-stationary environments is challenging, as changing dynamics and rewards quickly make past experiences outdated. Traditional experience replay (ER) methods, especially those using TD-error prioritization, struggle to distinguish between changes caused by the agent's policy and those from the environment, resulting in inefficient learning under dynamic conditions. To address this challenge, we propose the Discrepancy of Environment Dynamics (DoE), a metric that isolates the effects of environment shifts on value functions. Building on this, we introduce Discrepancy of Environment Prioritized Experience Replay (DEER), an adaptive ER framework that prioritizes transitions based on both policy updates and environmental changes. DEER uses a binary classifier to detect environment changes and applies distinct prioritization strategies before and after each shift, enabling more sample-efficient learning. Experiments on four non-stationary benchmarks demonstrate that DEER further improves the performance of off-policy algorithms by 11.54 percent compared to the best-performing state-of-the-art ER methods.
LEED: A Highly Efficient and Scalable LLM-Empowered Expert Demonstrations Framework for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) holds substantial promise for intelligent decision-making in complex environments. However, it suffers from a coordination and scalability bottleneck as the number of agents increases. To address these issues, we propose the LLM-empowered expert demonstrations framework for multi-agent reinforcement learning (LEED). LEED consists of two components: a demonstration generation (DG) module and a policy optimization (PO) module. Specifically, the DG module leverages large language models to generate instructions for interacting with the environment, thereby producing high-quality demonstrations. The PO module adopts a decentralized training paradigm, where each agent utilizes the generated demonstrations to construct an expert policy loss, which is then integrated with its own policy loss. This enables each agent to effectively personalize and optimize its local policy based on both expert knowledge and individual experience. Experimental results show that LEED achieves superior sample efficiency, time efficiency, and robust scalability compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
KeepKV: Eliminating Output Perturbation in KV Cache Compression for Efficient LLMs Inference
Apr 14, 2025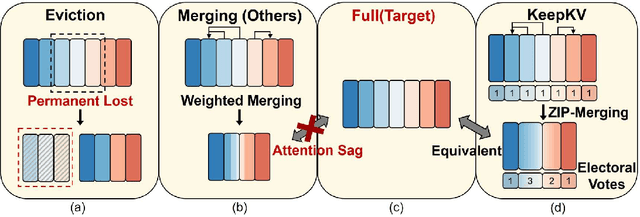
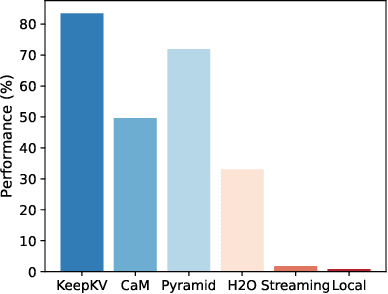
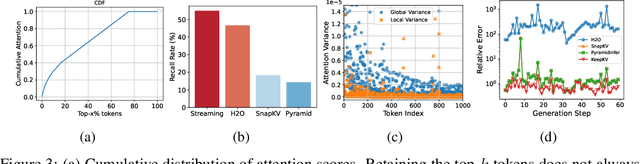
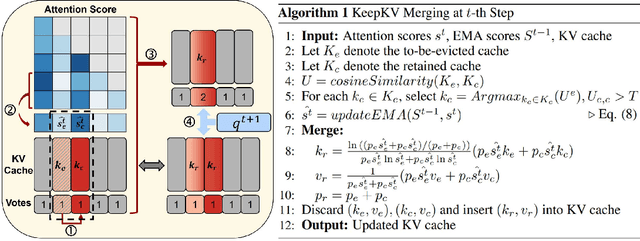
Abstract:Efficient inference of large language models (LLMs) is hindered by an ever-growing key-value (KV) cache, making KV cache compression a critical research direction. Traditional methods selectively evict less important KV cache entries based on attention scores or position heuristics, which leads to information loss and hallucinations. Recently, merging-based strategies have been explored to retain more information by merging KV pairs that would be discarded; however, these existing approaches inevitably introduce inconsistencies in attention distributions before and after merging, causing output perturbation and degraded generation quality. To overcome this challenge, we propose KeepKV, a novel adaptive KV cache merging method designed to eliminate output perturbation while preserving performance under strict memory constraints. KeepKV introduces the Electoral Votes mechanism that records merging history and adaptively adjusts attention scores. Moreover, it further leverages a novel Zero Inference-Perturbation Merging methods, keeping attention consistency and compensating for attention loss resulting from cache merging. KeepKV successfully retains essential context information within a significantly compressed cache. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks and LLM architectures demonstrate that KeepKV substantially reduces memory usage, enhances inference throughput by more than 2x and keeps superior generation quality even with 10% KV cache budgets.
Robust Deep Reinforcement Learning in Robotics via Adaptive Gradient-Masked Adversarial Attacks
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has emerged as a promising approach for robotic control, but its realworld deployment remains challenging due to its vulnerability to environmental perturbations. Existing white-box adversarial attack methods, adapted from supervised learning, fail to effectively target DRL agents as they overlook temporal dynamics and indiscriminately perturb all state dimensions, limiting their impact on long-term rewards. To address these challenges, we propose the Adaptive Gradient-Masked Reinforcement (AGMR) Attack, a white-box attack method that combines DRL with a gradient-based soft masking mechanism to dynamically identify critical state dimensions and optimize adversarial policies. AGMR selectively allocates perturbations to the most impactful state features and incorporates a dynamic adjustment mechanism to balance exploration and exploitation during training. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AGMR outperforms state-of-the-art adversarial attack methods in degrading the performance of the victim agent and enhances the victim agent's robustness through adversarial defense mechanisms.
State-Aware Perturbation Optimization for Robust Deep Reinforcement Learning
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Recently, deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has emerged as a promising approach for robotic control. However, the deployment of DRL in real-world robots is hindered by its sensitivity to environmental perturbations. While existing whitebox adversarial attacks rely on local gradient information and apply uniform perturbations across all states to evaluate DRL robustness, they fail to account for temporal dynamics and state-specific vulnerabilities. To combat the above challenge, we first conduct a theoretical analysis of white-box attacks in DRL by establishing the adversarial victim-dynamics Markov decision process (AVD-MDP), to derive the necessary and sufficient conditions for a successful attack. Based on this, we propose a selective state-aware reinforcement adversarial attack method, named STAR, to optimize perturbation stealthiness and state visitation dispersion. STAR first employs a soft mask-based state-targeting mechanism to minimize redundant perturbations, enhancing stealthiness and attack effectiveness. Then, it incorporates an information-theoretic optimization objective to maximize mutual information between perturbations, environmental states, and victim actions, ensuring a dispersed state-visitation distribution that steers the victim agent into vulnerable states for maximum return reduction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that STAR outperforms state-of-the-art benchmarks.
LLM-Sketch: Enhancing Network Sketches with LLM
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Network stream mining is fundamental to many network operations. Sketches, as compact data structures that offer low memory overhead with bounded accuracy, have emerged as a promising solution for network stream mining. Recent studies attempt to optimize sketches using machine learning; however, these approaches face the challenges of lacking adaptivity to dynamic networks and incurring high training costs. In this paper, we propose LLM-Sketch, based on the insight that fields beyond the flow IDs in packet headers can also help infer flow sizes. By using a two-tier data structure and separately recording large and small flows, LLM-Sketch improves accuracy while minimizing memory usage. Furthermore, it leverages fine-tuned large language models (LLMs) to reliably estimate flow sizes. We evaluate LLM-Sketch on three representative tasks, and the results demonstrate that LLM-Sketch outperforms state-of-the-art methods by achieving a $7.5\times$ accuracy improvement.
Leveraging LLM Agents for Translating Network Configurations
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:Configuration translation is a critical and frequent task in network operations. When a network device is damaged or outdated, administrators need to replace it to maintain service continuity. The replacement devices may originate from different vendors, necessitating configuration translation to ensure seamless network operation. However, translating configurations manually is a labor-intensive and error-prone process. In this paper, we propose an intent-based framework for translating network configuration with Large Language Model (LLM) Agents. The core of our approach is an Intent-based Retrieval Augmented Generation (IRAG) module that systematically splits a configuration file into fragments, extracts intents, and generates accurate translations. We also design a two-stage verification method to validate the syntax and semantics correctness of the translated configurations. We implement and evaluate the proposed method on real-world network configurations. Experimental results show that our method achieves 97.74% syntax correctness, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in translation accuracy.
Rethinking Adversarial Attacks in Reinforcement Learning from Policy Distribution Perspective
Jan 08, 2025Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) suffers from uncertainties and inaccuracies in the observation signal in realworld applications. Adversarial attack is an effective method for evaluating the robustness of DRL agents. However, existing attack methods targeting individual sampled actions have limited impacts on the overall policy distribution, particularly in continuous action spaces. To address these limitations, we propose the Distribution-Aware Projected Gradient Descent attack (DAPGD). DAPGD uses distribution similarity as the gradient perturbation input to attack the policy network, which leverages the entire policy distribution rather than relying on individual samples. We utilize the Bhattacharyya distance in DAPGD to measure policy similarity, enabling sensitive detection of subtle but critical differences between probability distributions. Our experiment results demonstrate that DAPGD achieves SOTA results compared to the baselines in three robot navigation tasks, achieving an average 22.03% higher reward drop compared to the best baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge