Yiping Bao
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
WorldVQA: Measuring Atomic World Knowledge in Multimodal Large Language Models
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:We introduce WorldVQA, a benchmark designed to evaluate the atomic visual world knowledge of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Unlike current evaluations, which often conflate visual knowledge retrieval with reasoning, WorldVQA decouples these capabilities to strictly measure "what the model memorizes." The benchmark assesses the atomic capability of grounding and naming visual entities across a stratified taxonomy, spanning from common head-class objects to long-tail rarities. We expect WorldVQA to serve as a rigorous test for visual factuality, thereby establishing a standard for assessing the encyclopedic breadth and hallucination rates of current and next-generation frontier models.
Towards Pixel-Level VLM Perception via Simple Points Prediction
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:We present SimpleSeg, a strikingly simple yet highly effective approach to endow Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with native pixel-level perception. Our method reframes segmentation as a simple sequence generation problem: the model directly predicts sequences of points (textual coordinates) delineating object boundaries, entirely within its language space. To achieve high fidelity, we introduce a two-stage SF$\to$RL training pipeline, where Reinforcement Learning with an IoU-based reward refines the point sequences to accurately match ground-truth contours. We find that the standard MLLM architecture possesses a strong, inherent capacity for low-level perception that can be unlocked without any specialized architecture. On segmentation benchmarks, SimpleSeg achieves performance that is comparable to, and often surpasses, methods relying on complex, task-specific designs. This work lays out that precise spatial understanding can emerge from simple point prediction, challenging the prevailing need for auxiliary components and paving the way for more unified and capable VLMs. Homepage: https://simpleseg.github.io/
BabyVision: Visual Reasoning Beyond Language
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:While humans develop core visual skills long before acquiring language, contemporary Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) still rely heavily on linguistic priors to compensate for their fragile visual understanding. We uncovered a crucial fact: state-of-the-art MLLMs consistently fail on basic visual tasks that humans, even 3-year-olds, can solve effortlessly. To systematically investigate this gap, we introduce BabyVision, a benchmark designed to assess core visual abilities independent of linguistic knowledge for MLLMs. BabyVision spans a wide range of tasks, with 388 items divided into 22 subclasses across four key categories. Empirical results and human evaluation reveal that leading MLLMs perform significantly below human baselines. Gemini3-Pro-Preview scores 49.7, lagging behind 6-year-old humans and falling well behind the average adult score of 94.1. These results show despite excelling in knowledge-heavy evaluations, current MLLMs still lack fundamental visual primitives. Progress in BabyVision represents a step toward human-level visual perception and reasoning capabilities. We also explore solving visual reasoning with generation models by proposing BabyVision-Gen and automatic evaluation toolkit. Our code and benchmark data are released at https://github.com/UniPat-AI/BabyVision for reproduction.
Kimi K2: Open Agentic Intelligence
Jul 28, 2025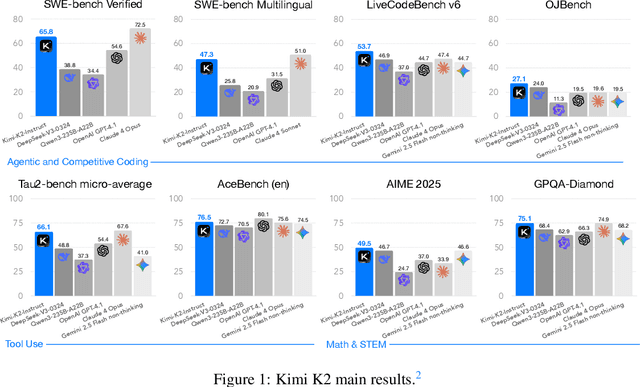
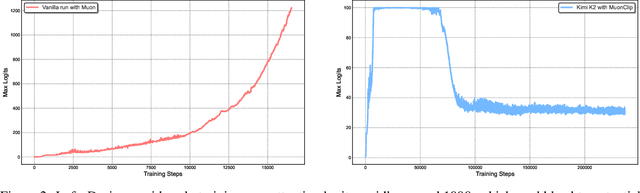
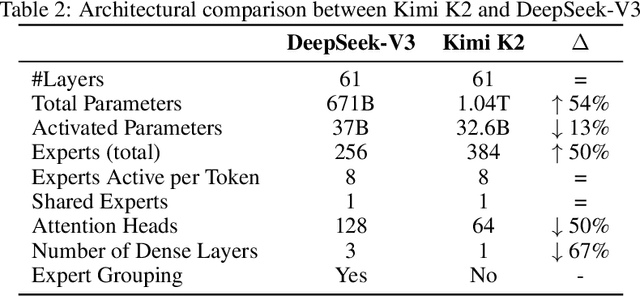
Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 32 billion activated parameters and 1 trillion total parameters. We propose the MuonClip optimizer, which improves upon Muon with a novel QK-clip technique to address training instability while enjoying the advanced token efficiency of Muon. Based on MuonClip, K2 was pre-trained on 15.5 trillion tokens with zero loss spike. During post-training, K2 undergoes a multi-stage post-training process, highlighted by a large-scale agentic data synthesis pipeline and a joint reinforcement learning (RL) stage, where the model improves its capabilities through interactions with real and synthetic environments. Kimi K2 achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source non-thinking models, with strengths in agentic capabilities. Notably, K2 obtains 66.1 on Tau2-Bench, 76.5 on ACEBench (En), 65.8 on SWE-Bench Verified, and 47.3 on SWE-Bench Multilingual -- surpassing most open and closed-sourced baselines in non-thinking settings. It also exhibits strong capabilities in coding, mathematics, and reasoning tasks, with a score of 53.7 on LiveCodeBench v6, 49.5 on AIME 2025, 75.1 on GPQA-Diamond, and 27.1 on OJBench, all without extended thinking. These results position Kimi K2 as one of the most capable open-source large language models to date, particularly in software engineering and agentic tasks. We release our base and post-trained model checkpoints to facilitate future research and applications of agentic intelligence.
Kimi-VL Technical Report
Apr 10, 2025
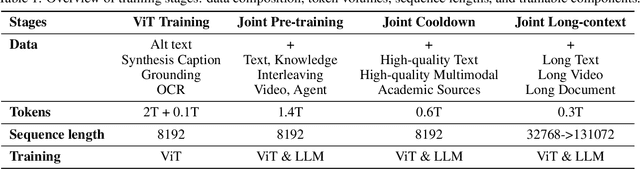
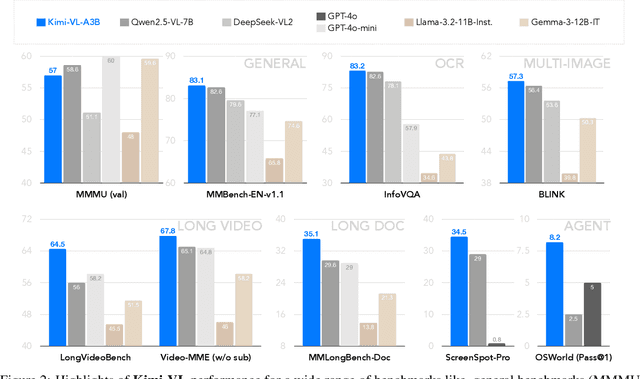
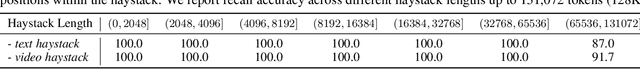
Abstract:We present Kimi-VL, an efficient open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) vision-language model (VLM) that offers advanced multimodal reasoning, long-context understanding, and strong agent capabilities - all while activating only 2.8B parameters in its language decoder (Kimi-VL-A3B). Kimi-VL demonstrates strong performance across challenging domains: as a general-purpose VLM, Kimi-VL excels in multi-turn agent tasks (e.g., OSWorld), matching flagship models. Furthermore, it exhibits remarkable capabilities across diverse challenging vision language tasks, including college-level image and video comprehension, OCR, mathematical reasoning, and multi-image understanding. In comparative evaluations, it effectively competes with cutting-edge efficient VLMs such as GPT-4o-mini, Qwen2.5-VL-7B, and Gemma-3-12B-IT, while surpassing GPT-4o in several key domains. Kimi-VL also advances in processing long contexts and perceiving clearly. With a 128K extended context window, Kimi-VL can process diverse long inputs, achieving impressive scores of 64.5 on LongVideoBench and 35.1 on MMLongBench-Doc. Its native-resolution vision encoder, MoonViT, further allows it to see and understand ultra-high-resolution visual inputs, achieving 83.2 on InfoVQA and 34.5 on ScreenSpot-Pro, while maintaining lower computational cost for common tasks. Building upon Kimi-VL, we introduce an advanced long-thinking variant: Kimi-VL-Thinking. Developed through long chain-of-thought (CoT) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL), this model exhibits strong long-horizon reasoning capabilities. It achieves scores of 61.7 on MMMU, 36.8 on MathVision, and 71.3 on MathVista while maintaining the compact 2.8B activated LLM parameters, setting a new standard for efficient multimodal thinking models. Code and models are publicly accessible at https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-VL.
Multi-modal Relation Distillation for Unified 3D Representation Learning
Jul 19, 2024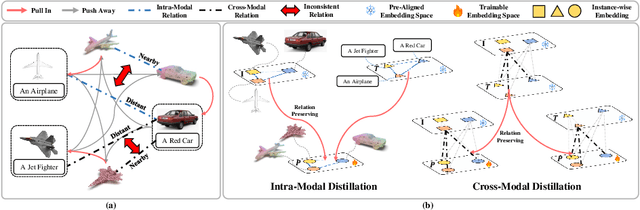

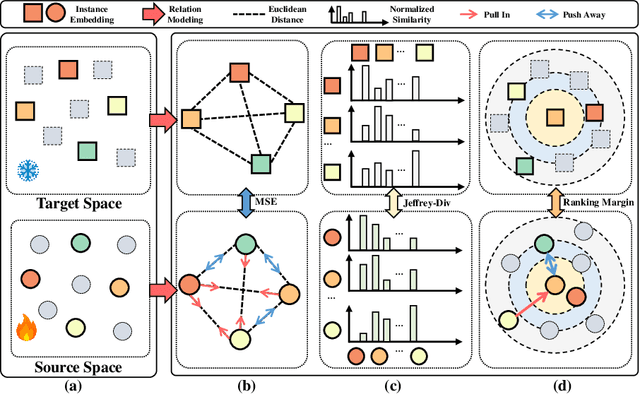

Abstract:Recent advancements in multi-modal pre-training for 3D point clouds have demonstrated promising results by aligning heterogeneous features across 3D shapes and their corresponding 2D images and language descriptions. However, current straightforward solutions often overlook intricate structural relations among samples, potentially limiting the full capabilities of multi-modal learning. To address this issue, we introduce Multi-modal Relation Distillation (MRD), a tri-modal pre-training framework, which is designed to effectively distill reputable large Vision-Language Models (VLM) into 3D backbones. MRD aims to capture both intra-relations within each modality as well as cross-relations between different modalities and produce more discriminative 3D shape representations. Notably, MRD achieves significant improvements in downstream zero-shot classification tasks and cross-modality retrieval tasks, delivering new state-of-the-art performance.
W2N:Switching From Weak Supervision to Noisy Supervision for Object Detection
Jul 25, 2022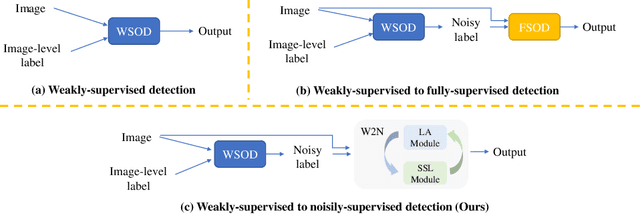
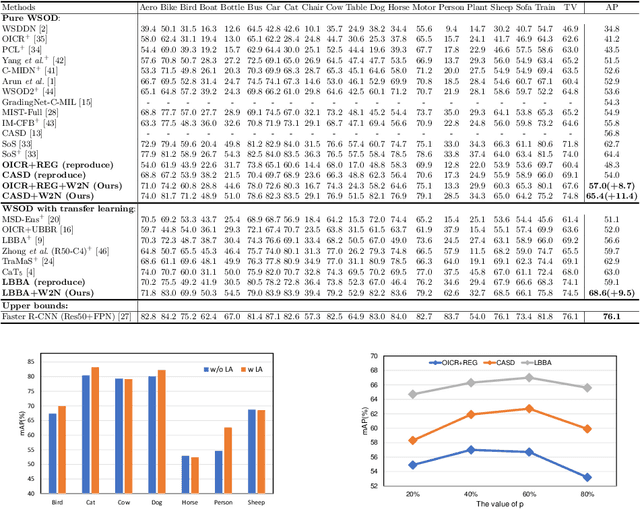
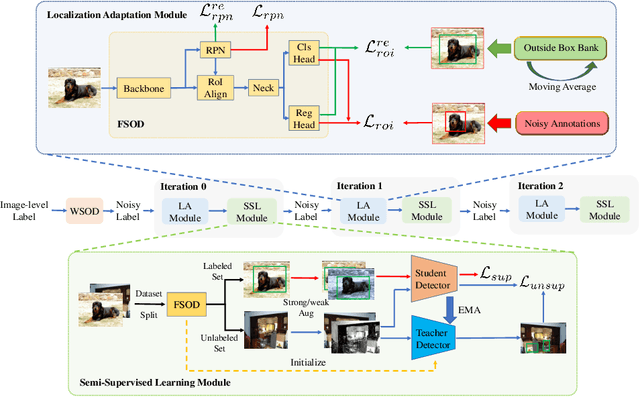
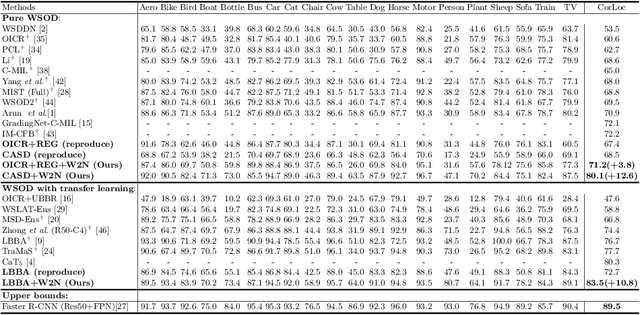
Abstract:Weakly-supervised object detection (WSOD) aims to train an object detector only requiring the image-level annotations. Recently, some works have managed to select the accurate boxes generated from a well-trained WSOD network to supervise a semi-supervised detection framework for better performance. However, these approaches simply divide the training set into labeled and unlabeled sets according to the image-level criteria, such that sufficient mislabeled or wrongly localized box predictions are chosen as pseudo ground-truths, resulting in a sub-optimal solution of detection performance. To overcome this issue, we propose a novel WSOD framework with a new paradigm that switches from weak supervision to noisy supervision (W2N). Generally, with given pseudo ground-truths generated from the well-trained WSOD network, we propose a two-module iterative training algorithm to refine pseudo labels and supervise better object detector progressively. In the localization adaptation module, we propose a regularization loss to reduce the proportion of discriminative parts in original pseudo ground-truths, obtaining better pseudo ground-truths for further training. In the semi-supervised module, we propose a two tasks instance-level split method to select high-quality labels for training a semi-supervised detector. Experimental results on different benchmarks verify the effectiveness of W2N, and our W2N outperforms all existing pure WSOD methods and transfer learning methods. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/1170300714/w2n_wsod.
Prototypical Contrastive Language Image Pretraining
Jun 22, 2022



Abstract:Contrastive Language Image Pretraining (CLIP) received widespread attention since its learned representations can be transferred well to various downstream tasks. During CLIP training, the InfoNCE objective aims to align positive image-text pairs and separate negative ones. In this paper, we show a representation grouping effect during this process: the InfoNCE objective indirectly groups semantically similar representations together via randomly emerged within-modal anchors. We introduce Prototypical Contrastive Language Image Pretraining (ProtoCLIP) to enhance such grouping by boosting its efficiency and increasing its robustness against modality gap. Specifically, ProtoCLIP sets up prototype-level discrimination between image and text spaces, which efficiently transfers higher-level structural knowledge. We further propose Prototypical Back Translation (PBT) to decouple representation grouping from representation alignment, resulting in effective learning of meaningful representations under large modality gap. PBT also enables us to introduce additional external teachers with richer prior knowledge. ProtoCLIP is trained with an online episodic training strategy, which makes it can be scaled up to unlimited amounts of data. Combining the above novel designs, we train our ProtoCLIP on Conceptual Captions and achieved an +5.81% ImageNet linear probing improvement and an +2.01% ImageNet zero-shot classification improvement. Codes are available at https://github.com/megvii-research/protoclip.
Attend to Who You Are: Supervising Self-Attention for Keypoint Detection and Instance-Aware Association
Nov 25, 2021
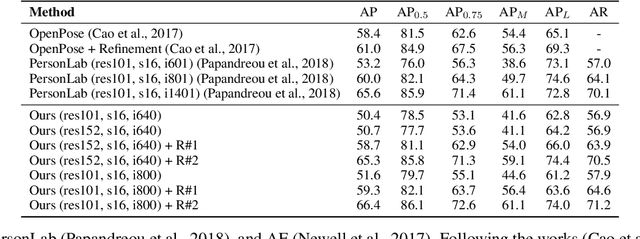
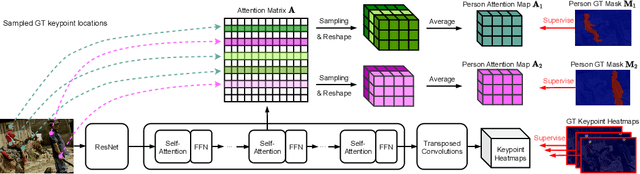
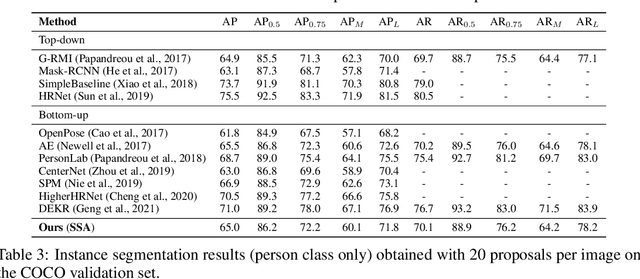
Abstract:This paper presents a new method to solve keypoint detection and instance association by using Transformer. For bottom-up multi-person pose estimation models, they need to detect keypoints and learn associative information between keypoints. We argue that these problems can be entirely solved by Transformer. Specifically, the self-attention in Transformer measures dependencies between any pair of locations, which can provide association information for keypoints grouping. However, the naive attention patterns are still not subjectively controlled, so there is no guarantee that the keypoints will always attend to the instances to which they belong. To address it we propose a novel approach of supervising self-attention for multi-person keypoint detection and instance association. By using instance masks to supervise self-attention to be instance-aware, we can assign the detected keypoints to their corresponding instances based on the pairwise attention scores, without using pre-defined offset vector fields or embedding like CNN-based bottom-up models. An additional benefit of our method is that the instance segmentation results of any number of people can be directly obtained from the supervised attention matrix, thereby simplifying the pixel assignment pipeline. The experiments on the COCO multi-person keypoint detection challenge and person instance segmentation task demonstrate the effectiveness and simplicity of the proposed method and show a promising way to control self-attention behavior for specific purposes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge