Yuxing Peng
GenMol: A Drug Discovery Generalist with Discrete Diffusion
Jan 10, 2025



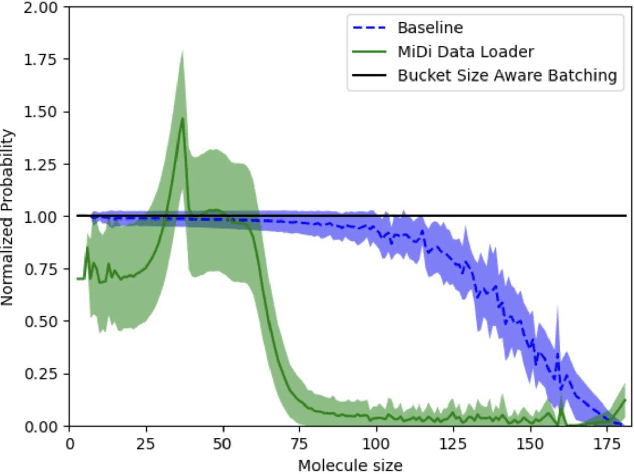
Abstract:Drug discovery is a complex process that involves multiple scenarios and stages, such as fragment-constrained molecule generation, hit generation and lead optimization. However, existing molecular generative models can only tackle one or two of these scenarios and lack the flexibility to address various aspects of the drug discovery pipeline. In this paper, we present Generalist Molecular generative model (GenMol), a versatile framework that addresses these limitations by applying discrete diffusion to the Sequential Attachment-based Fragment Embedding (SAFE) molecular representation. GenMol generates SAFE sequences through non-autoregressive bidirectional parallel decoding, thereby allowing utilization of a molecular context that does not rely on the specific token ordering and enhanced computational efficiency. Moreover, under the discrete diffusion framework, we introduce fragment remasking, a strategy that optimizes molecules by replacing fragments with masked tokens and regenerating them, enabling effective exploration of chemical space. GenMol significantly outperforms the previous GPT-based model trained on SAFE representations in de novo generation and fragment-constrained generation, and achieves state-of-the-art performance in goal-directed hit generation and lead optimization. These experimental results demonstrate that GenMol can tackle a wide range of drug discovery tasks, providing a unified and versatile approach for molecular design.
BioNeMo Framework: a modular, high-performance library for AI model development in drug discovery
Nov 15, 2024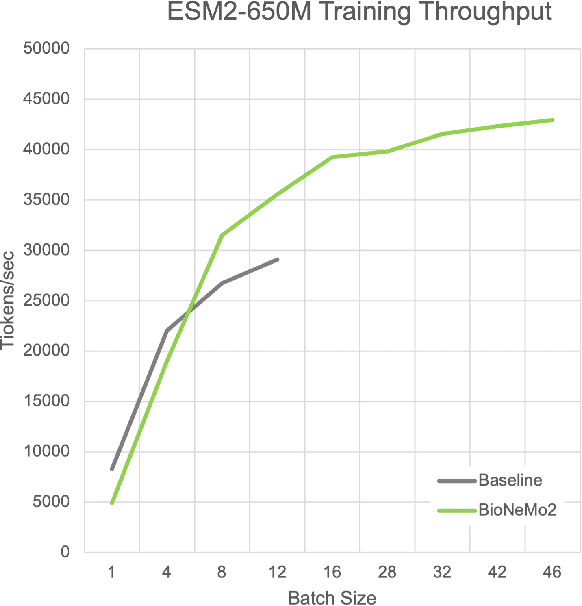
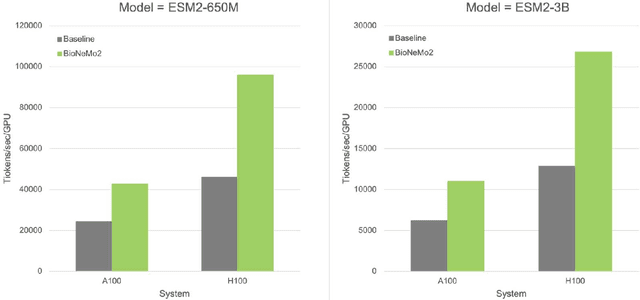
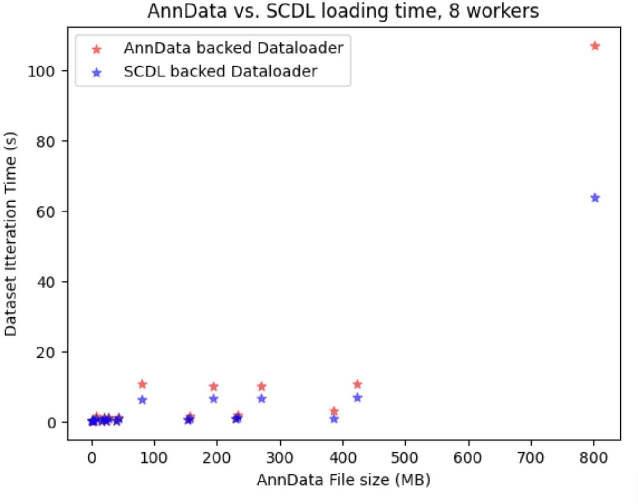
Abstract:Artificial Intelligence models encoding biology and chemistry are opening new routes to high-throughput and high-quality in-silico drug development. However, their training increasingly relies on computational scale, with recent protein language models (pLM) training on hundreds of graphical processing units (GPUs). We introduce the BioNeMo Framework to facilitate the training of computational biology and chemistry AI models across hundreds of GPUs. Its modular design allows the integration of individual components, such as data loaders, into existing workflows and is open to community contributions. We detail technical features of the BioNeMo Framework through use cases such as pLM pre-training and fine-tuning. On 256 NVIDIA A100s, BioNeMo Framework trains a three billion parameter BERT-based pLM on over one trillion tokens in 4.2 days. The BioNeMo Framework is open-source and free for everyone to use.
GeoTransformer: Fast and Robust Point Cloud Registration with Geometric Transformer
Jul 25, 2023



Abstract:We study the problem of extracting accurate correspondences for point cloud registration. Recent keypoint-free methods have shown great potential through bypassing the detection of repeatable keypoints which is difficult to do especially in low-overlap scenarios. They seek correspondences over downsampled superpoints, which are then propagated to dense points. Superpoints are matched based on whether their neighboring patches overlap. Such sparse and loose matching requires contextual features capturing the geometric structure of the point clouds. We propose Geometric Transformer, or GeoTransformer for short, to learn geometric feature for robust superpoint matching. It encodes pair-wise distances and triplet-wise angles, making it invariant to rigid transformation and robust in low-overlap cases. The simplistic design attains surprisingly high matching accuracy such that no RANSAC is required in the estimation of alignment transformation, leading to $100$ times acceleration. Extensive experiments on rich benchmarks encompassing indoor, outdoor, synthetic, multiway and non-rigid demonstrate the efficacy of GeoTransformer. Notably, our method improves the inlier ratio by $18{\sim}31$ percentage points and the registration recall by over $7$ points on the challenging 3DLoMatch benchmark. Our code and models are available at \url{https://github.com/qinzheng93/GeoTransformer}.
Deep Graph-based Spatial Consistency for Robust Non-rigid Point Cloud Registration
Mar 17, 2023



Abstract:We study the problem of outlier correspondence pruning for non-rigid point cloud registration. In rigid registration, spatial consistency has been a commonly used criterion to discriminate outliers from inliers. It measures the compatibility of two correspondences by the discrepancy between the respective distances in two point clouds. However, spatial consistency no longer holds in non-rigid cases and outlier rejection for non-rigid registration has not been well studied. In this work, we propose Graph-based Spatial Consistency Network (GraphSCNet) to filter outliers for non-rigid registration. Our method is based on the fact that non-rigid deformations are usually locally rigid, or local shape preserving. We first design a local spatial consistency measure over the deformation graph of the point cloud, which evaluates the spatial compatibility only between the correspondences in the vicinity of a graph node. An attention-based non-rigid correspondence embedding module is then devised to learn a robust representation of non-rigid correspondences from local spatial consistency. Despite its simplicity, GraphSCNet effectively improves the quality of the putative correspondences and attains state-of-the-art performance on three challenging benchmarks. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/qinzheng93/GraphSCNet.
Wound Segmentation with Dynamic Illumination Correction and Dual-view Semantic Fusion
Jul 12, 2022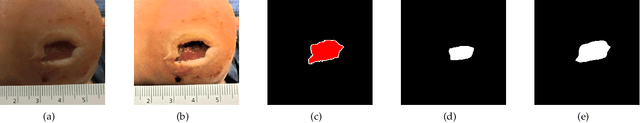
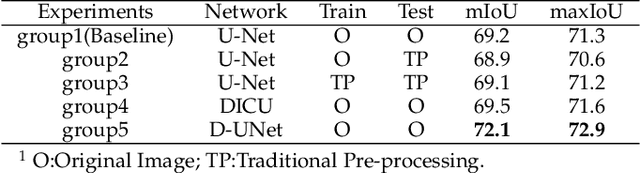
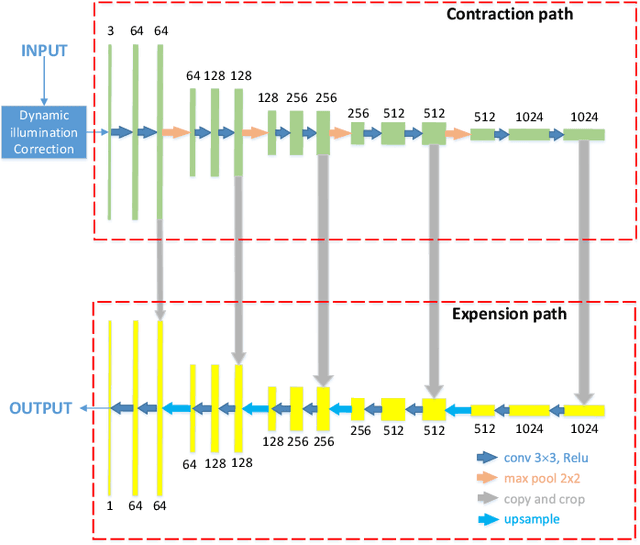
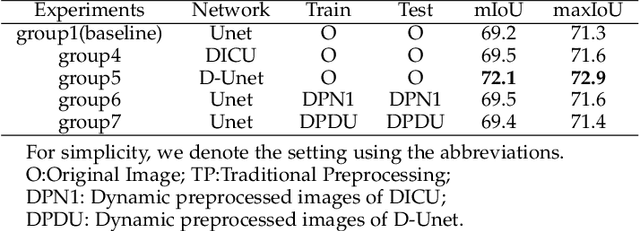
Abstract:Wound image segmentation is a critical component for the clinical diagnosis and in-time treatment of wounds. Recently, deep learning has become the mainstream methodology for wound image segmentation. However, the pre-processing of the wound image, such as the illumination correction, is required before the training phase as the performance can be greatly improved. The correction procedure and the training of deep models are independent of each other, which leads to sub-optimal segmentation performance as the fixed illumination correction may not be suitable for all images. To address aforementioned issues, an end-to-end dual-view segmentation approach was proposed in this paper, by incorporating a learn-able illumination correction module into the deep segmentation models. The parameters of the module can be learned and updated during the training stage automatically, while the dual-view fusion can fully employ the features from both the raw images and the enhanced ones. To demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed framework, the extensive experiments are conducted on the benchmark datasets. The encouraging results suggest that our framework can significantly improve the segmentation performance, compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
Unsupervised Voice-Face Representation Learning by Cross-Modal Prototype Contrast
May 02, 2022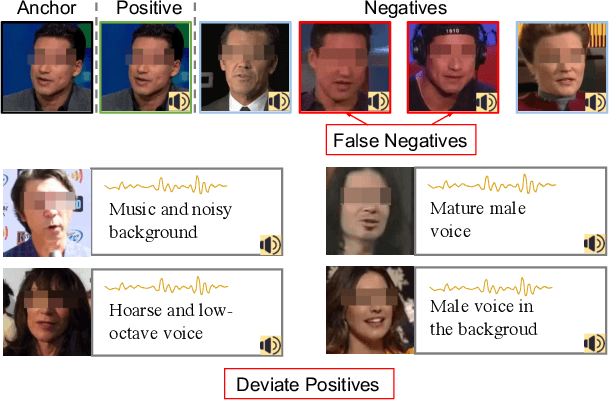
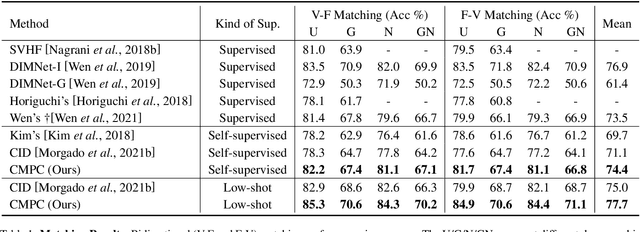
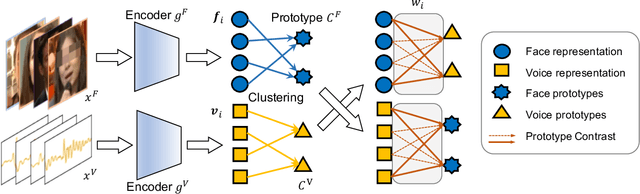
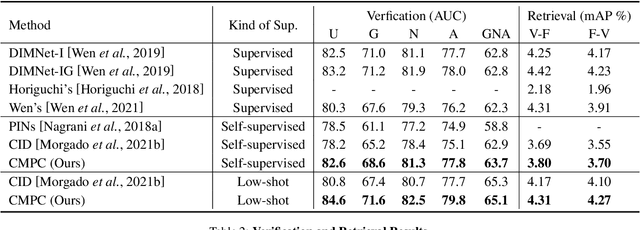
Abstract:We present an approach to learn voice-face representations from the talking face videos, without any identity labels. Previous works employ cross-modal instance discrimination tasks to establish the correlation of voice and face. These methods neglect the semantic content of different videos, introducing false-negative pairs as training noise. Furthermore, the positive pairs are constructed based on the natural correlation between audio clips and visual frames. However, this correlation might be weak or inaccurate in a large amount of real-world data, which leads to deviating positives into the contrastive paradigm. To address these issues, we propose the cross-modal prototype contrastive learning (CMPC), which takes advantage of contrastive methods and resists adverse effects of false negatives and deviate positives. On one hand, CMPC could learn the intra-class invariance by constructing semantic-wise positives via unsupervised clustering in different modalities. On the other hand, by comparing the similarities of cross-modal instances from that of cross-modal prototypes, we dynamically recalibrate the unlearnable instances' contribution to overall loss. Experiments show that the proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art unsupervised methods on various voice-face association evaluation protocols. Additionally, in the low-shot supervision setting, our method also has a significant improvement compared to previous instance-wise contrastive learning.
Geometric Transformer for Fast and Robust Point Cloud Registration
Mar 12, 2022



Abstract:We study the problem of extracting accurate correspondences for point cloud registration. Recent keypoint-free methods bypass the detection of repeatable keypoints which is difficult in low-overlap scenarios, showing great potential in registration. They seek correspondences over downsampled superpoints, which are then propagated to dense points. Superpoints are matched based on whether their neighboring patches overlap. Such sparse and loose matching requires contextual features capturing the geometric structure of the point clouds. We propose Geometric Transformer to learn geometric feature for robust superpoint matching. It encodes pair-wise distances and triplet-wise angles, making it robust in low-overlap cases and invariant to rigid transformation. The simplistic design attains surprisingly high matching accuracy such that no RANSAC is required in the estimation of alignment transformation, leading to $100$ times acceleration. Our method improves the inlier ratio by $17{\sim}30$ percentage points and the registration recall by over $7$ points on the challenging 3DLoMatch benchmark. Our code and models are available at \url{https://github.com/qinzheng93/GeoTransformer}.
Audio Tagging by Cross Filtering Noisy Labels
Jul 16, 2020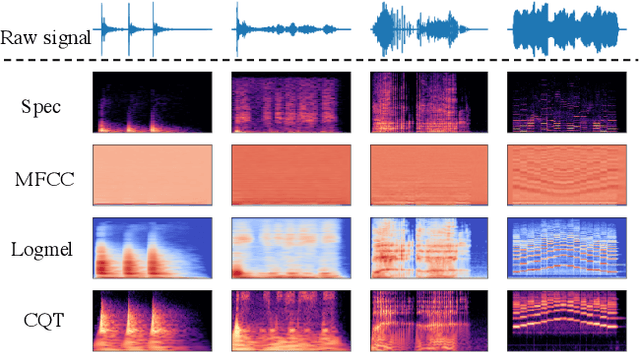
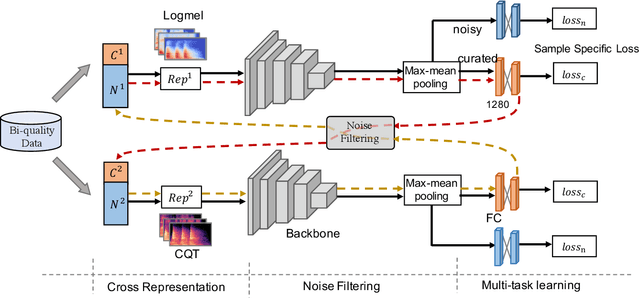
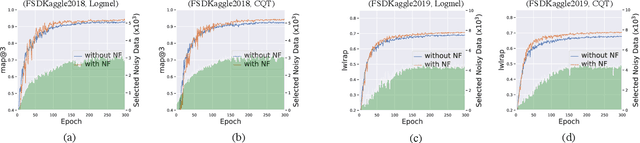
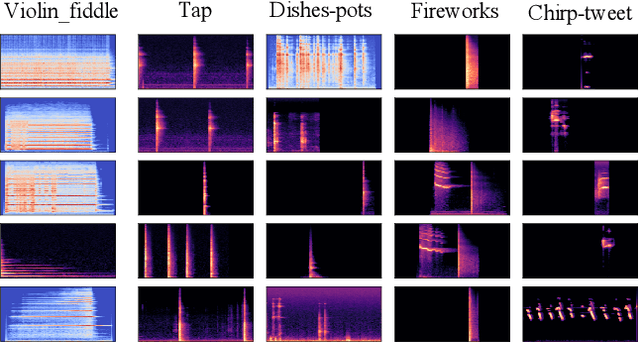
Abstract:High quality labeled datasets have allowed deep learning to achieve impressive results on many sound analysis tasks. Yet, it is labor-intensive to accurately annotate large amount of audio data, and the dataset may contain noisy labels in the practical settings. Meanwhile, the deep neural networks are susceptive to those incorrect labeled data because of their outstanding memorization ability. In this paper, we present a novel framework, named CrossFilter, to combat the noisy labels problem for audio tagging. Multiple representations (such as, Logmel and MFCC) are used as the input of our framework for providing more complementary information of the audio. Then, though the cooperation and interaction of two neural networks, we divide the dataset into curated and noisy subsets by incrementally pick out the possibly correctly labeled data from the noisy data. Moreover, our approach leverages the multi-task learning on curated and noisy subsets with different loss function to fully utilize the entire dataset. The noisy-robust loss function is employed to alleviate the adverse effects of incorrect labels. On both the audio tagging datasets FSDKaggle2018 and FSDKaggle2019, empirical results demonstrate the performance improvement compared with other competing approaches. On FSDKaggle2018 dataset, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance and even surpasses the ensemble models.
A Multi-Type Multi-Span Network for Reading Comprehension that Requires Discrete Reasoning
Aug 30, 2019



Abstract:Rapid progress has been made in the field of reading comprehension and question answering, where several systems have achieved human parity in some simplified settings. However, the performance of these models degrades significantly when they are applied to more realistic scenarios, such as answers involve various types, multiple text strings are correct answers, or discrete reasoning abilities are required. In this paper, we introduce the Multi-Type Multi-Span Network (MTMSN), a neural reading comprehension model that combines a multi-type answer predictor designed to support various answer types (e.g., span, count, negation, and arithmetic expression) with a multi-span extraction method for dynamically producing one or multiple text spans. In addition, an arithmetic expression reranking mechanism is proposed to rank expression candidates for further confirming the prediction. Experiments show that our model achieves 79.9 F1 on the DROP hidden test set, creating new state-of-the-art results. Source code\footnote{\url{https://github.com/huminghao16/MTMSN}} is released to facilitate future work.
Retrieve, Read, Rerank: Towards End-to-End Multi-Document Reading Comprehension
Jun 11, 2019



Abstract:This paper considers the reading comprehension task in which multiple documents are given as input. Prior work has shown that a pipeline of retriever, reader, and reranker can improve the overall performance. However, the pipeline system is inefficient since the input is re-encoded within each module, and is unable to leverage upstream components to help downstream training. In this work, we present RE$^3$QA, a unified question answering model that combines context retrieving, reading comprehension, and answer reranking to predict the final answer. Unlike previous pipelined approaches, RE$^3$QA shares contextualized text representation across different components, and is carefully designed to use high-quality upstream outputs (e.g., retrieved context or candidate answers) for directly supervising downstream modules (e.g., the reader or the reranker). As a result, the whole network can be trained end-to-end to avoid the context inconsistency problem. Experiments show that our model outperforms the pipelined baseline and achieves state-of-the-art results on two versions of TriviaQA and two variants of SQuAD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge