Xu-Cheng Yin
Unsupervised Real-World Super-Resolution via Rectified Flow Degradation Modelling
Aug 10, 2025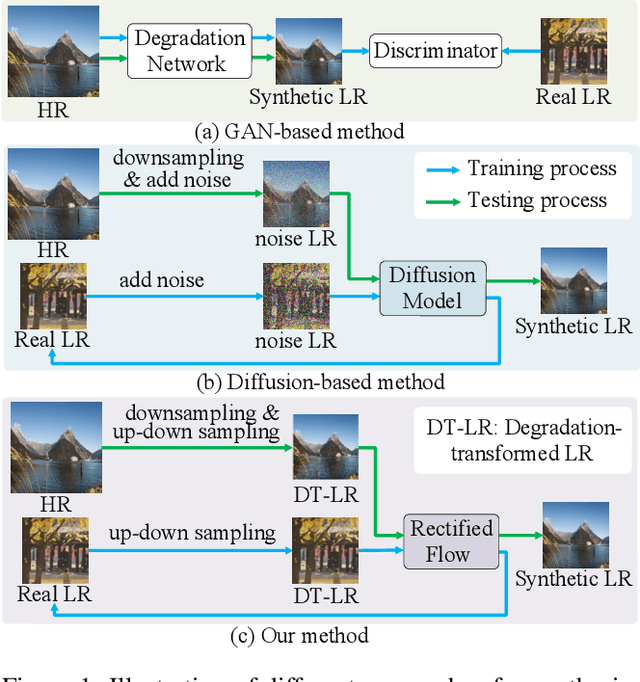
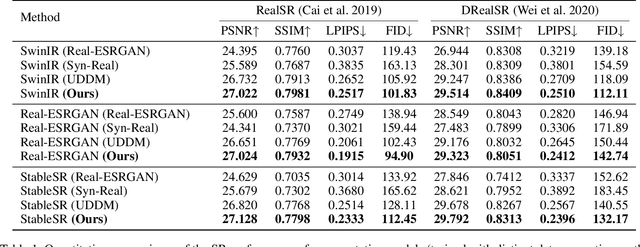
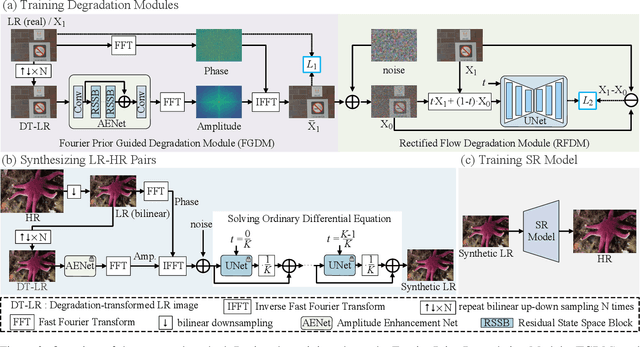
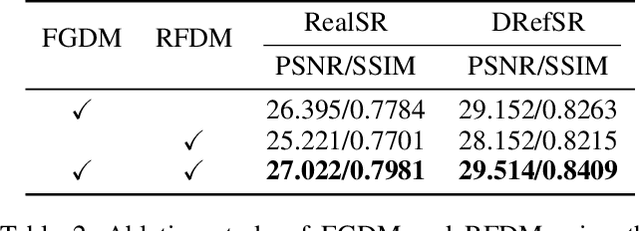
Abstract:Unsupervised real-world super-resolution (SR) faces critical challenges due to the complex, unknown degradation distributions in practical scenarios. Existing methods struggle to generalize from synthetic low-resolution (LR) and high-resolution (HR) image pairs to real-world data due to a significant domain gap. In this paper, we propose an unsupervised real-world SR method based on rectified flow to effectively capture and model real-world degradation, synthesizing LR-HR training pairs with realistic degradation. Specifically, given unpaired LR and HR images, we propose a novel Rectified Flow Degradation Module (RFDM) that introduces degradation-transformed LR (DT-LR) images as intermediaries. By modeling the degradation trajectory in a continuous and invertible manner, RFDM better captures real-world degradation and enhances the realism of generated LR images. Additionally, we propose a Fourier Prior Guided Degradation Module (FGDM) that leverages structural information embedded in Fourier phase components to ensure more precise modeling of real-world degradation. Finally, the LR images are processed by both FGDM and RFDM, producing final synthetic LR images with real-world degradation. The synthetic LR images are paired with the given HR images to train the off-the-shelf SR networks. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that our method significantly enhances the performance of existing SR approaches in real-world scenarios.
Similarity Matters: A Novel Depth-guided Network for Image Restoration and A New Dataset
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Image restoration has seen substantial progress in recent years. However, existing methods often neglect depth information, which hurts similarity matching, results in attention distractions in shallow depth-of-field (DoF) scenarios, and excessive enhancement of background content in deep DoF settings. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel Depth-Guided Network (DGN) for image restoration, together with a novel large-scale high-resolution dataset. Specifically, the network consists of two interactive branches: a depth estimation branch that provides structural guidance, and an image restoration branch that performs the core restoration task. In addition, the image restoration branch exploits intra-object similarity through progressive window-based self-attention and captures inter-object similarity via sparse non-local attention. Through joint training, depth features contribute to improved restoration quality, while the enhanced visual features from the restoration branch in turn help refine depth estimation. Notably, we also introduce a new dataset for training and evaluation, consisting of 9,205 high-resolution images from 403 plant species, with diverse depth and texture variations. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on several standard benchmarks and generalizes well to unseen plant images, demonstrating its effectiveness and robustness.
VCapsBench: A Large-scale Fine-grained Benchmark for Video Caption Quality Evaluation
May 29, 2025Abstract:Video captions play a crucial role in text-to-video generation tasks, as their quality directly influences the semantic coherence and visual fidelity of the generated videos. Although large vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in caption generation, existing benchmarks inadequately address fine-grained evaluation, particularly in capturing spatial-temporal details critical for video generation. To address this gap, we introduce the Fine-grained Video Caption Evaluation Benchmark (VCapsBench), the first large-scale fine-grained benchmark comprising 5,677 (5K+) videos and 109,796 (100K+) question-answer pairs. These QA-pairs are systematically annotated across 21 fine-grained dimensions (e.g., camera movement, and shot type) that are empirically proven critical for text-to-video generation. We further introduce three metrics (Accuracy (AR), Inconsistency Rate (IR), Coverage Rate (CR)), and an automated evaluation pipeline leveraging large language model (LLM) to verify caption quality via contrastive QA-pairs analysis. By providing actionable insights for caption optimization, our benchmark can advance the development of robust text-to-video models. The dataset and codes are available at website: https://github.com/GXYM/VCapsBench.
Visual Text Processing: A Comprehensive Review and Unified Evaluation
Apr 30, 2025



Abstract:Visual text is a crucial component in both document and scene images, conveying rich semantic information and attracting significant attention in the computer vision community. Beyond traditional tasks such as text detection and recognition, visual text processing has witnessed rapid advancements driven by the emergence of foundation models, including text image reconstruction and text image manipulation. Despite significant progress, challenges remain due to the unique properties that differentiate text from general objects. Effectively capturing and leveraging these distinct textual characteristics is essential for developing robust visual text processing models. In this survey, we present a comprehensive, multi-perspective analysis of recent advancements in visual text processing, focusing on two key questions: (1) What textual features are most suitable for different visual text processing tasks? (2) How can these distinctive text features be effectively incorporated into processing frameworks? Furthermore, we introduce VTPBench, a new benchmark that encompasses a broad range of visual text processing datasets. Leveraging the advanced visual quality assessment capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), we propose VTPScore, a novel evaluation metric designed to ensure fair and reliable evaluation. Our empirical study with more than 20 specific models reveals substantial room for improvement in the current techniques. Our aim is to establish this work as a fundamental resource that fosters future exploration and innovation in the dynamic field of visual text processing. The relevant repository is available at https://github.com/shuyansy/Visual-Text-Processing-survey.
DPFlow: Adaptive Optical Flow Estimation with a Dual-Pyramid Framework
Mar 19, 2025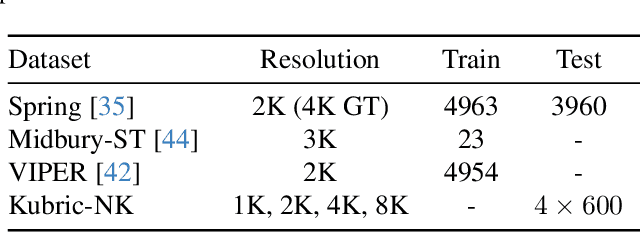
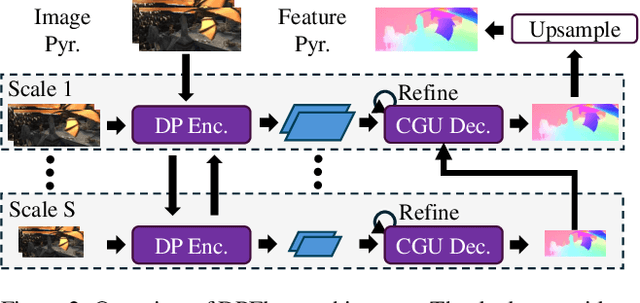
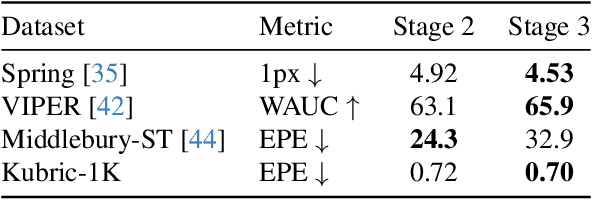
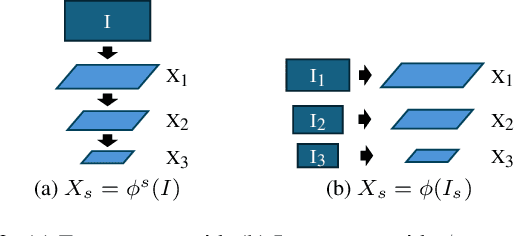
Abstract:Optical flow estimation is essential for video processing tasks, such as restoration and action recognition. The quality of videos is constantly increasing, with current standards reaching 8K resolution. However, optical flow methods are usually designed for low resolution and do not generalize to large inputs due to their rigid architectures. They adopt downscaling or input tiling to reduce the input size, causing a loss of details and global information. There is also a lack of optical flow benchmarks to judge the actual performance of existing methods on high-resolution samples. Previous works only conducted qualitative high-resolution evaluations on hand-picked samples. This paper fills this gap in optical flow estimation in two ways. We propose DPFlow, an adaptive optical flow architecture capable of generalizing up to 8K resolution inputs while trained with only low-resolution samples. We also introduce Kubric-NK, a new benchmark for evaluating optical flow methods with input resolutions ranging from 1K to 8K. Our high-resolution evaluation pushes the boundaries of existing methods and reveals new insights about their generalization capabilities. Extensive experimental results show that DPFlow achieves state-of-the-art results on the MPI-Sintel, KITTI 2015, Spring, and other high-resolution benchmarks.
FaceSpeak: Expressive and High-Quality Speech Synthesis from Human Portraits of Different Styles
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Humans can perceive speakers' characteristics (e.g., identity, gender, personality and emotion) by their appearance, which are generally aligned to their voice style. Recently, vision-driven Text-to-speech (TTS) scholars grounded their investigations on real-person faces, thereby restricting effective speech synthesis from applying to vast potential usage scenarios with diverse characters and image styles. To solve this issue, we introduce a novel FaceSpeak approach. It extracts salient identity characteristics and emotional representations from a wide variety of image styles. Meanwhile, it mitigates the extraneous information (e.g., background, clothing, and hair color, etc.), resulting in synthesized speech closely aligned with a character's persona. Furthermore, to overcome the scarcity of multi-modal TTS data, we have devised an innovative dataset, namely Expressive Multi-Modal TTS, which is diligently curated and annotated to facilitate research in this domain. The experimental results demonstrate our proposed FaceSpeak can generate portrait-aligned voice with satisfactory naturalness and quality.
Breaking Through the Spike: Spike Window Decoding for Accelerated and Precise Automatic Speech Recognition
Jan 01, 2025



Abstract:Recently, end-to-end automatic speech recognition has become the mainstream approach in both industry and academia. To optimize system performance in specific scenarios, the Weighted Finite-State Transducer (WFST) is extensively used to integrate acoustic and language models, leveraging its capacity to implicitly fuse language models within static graphs, thereby ensuring robust recognition while also facilitating rapid error correction. However, WFST necessitates a frame-by-frame search of CTC posterior probabilities through autoregression, which significantly hampers inference speed. In this work, we thoroughly investigate the spike property of CTC outputs and further propose the conjecture that adjacent frames to non-blank spikes carry semantic information beneficial to the model. Building on this, we propose the Spike Window Decoding algorithm, which greatly improves the inference speed by making the number of frames decoded in WFST linearly related to the number of spiking frames in the CTC output, while guaranteeing the recognition performance. Our method achieves SOTA recognition accuracy with significantly accelerates decoding speed, proven across both AISHELL-1 and large-scale In-House datasets, establishing a pioneering approach for integrating CTC output with WFST.
I2TTS: Image-indicated Immersive Text-to-speech Synthesis with Spatial Perception
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:Controlling the style and characteristics of speech synthesis is crucial for adapting the output to specific contexts and user requirements. Previous Text-to-speech (TTS) works have focused primarily on the technical aspects of producing natural-sounding speech, such as intonation, rhythm, and clarity. However, they overlook the fact that there is a growing emphasis on spatial perception of synthesized speech, which may provide immersive experience in gaming and virtual reality. To solve this issue, in this paper, we present a novel multi-modal TTS approach, namely Image-indicated Immersive Text-to-speech Synthesis (I2TTS). Specifically, we introduce a scene prompt encoder that integrates visual scene prompts directly into the synthesis pipeline to control the speech generation process. Additionally, we propose a reverberation classification and refinement technique that adjusts the synthesized mel-spectrogram to enhance the immersive experience, ensuring that the involved reverberation condition matches the scene accurately. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves high-quality scene and spatial matching without compromising speech naturalness, marking a significant advancement in the field of context-aware speech synthesis. Project demo page: https://spatialTTS.github.io/ Index Terms-Speech synthesis, scene prompt, spatial perception
HA-FGOVD: Highlighting Fine-grained Attributes via Explicit Linear Composition for Open-Vocabulary Object Detection
Sep 24, 2024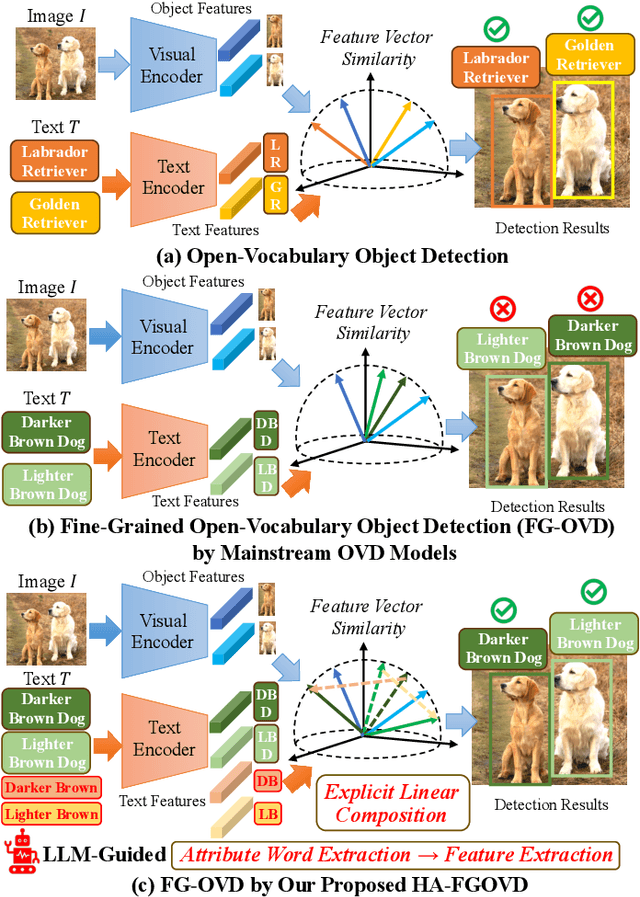
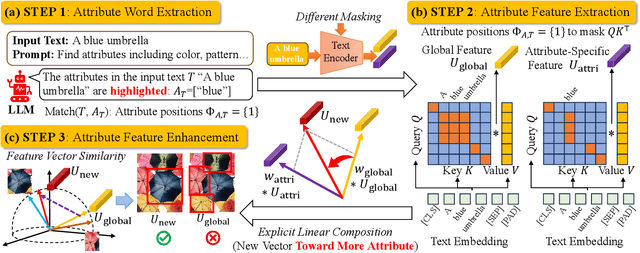

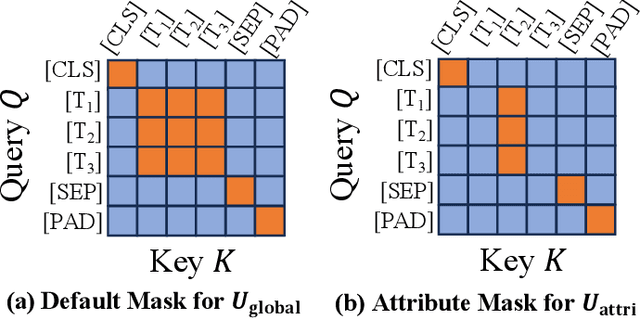
Abstract:Open-vocabulary object detection (OVD) models are considered to be Large Multi-modal Models (LMM), due to their extensive training data and a large number of parameters. Mainstream OVD models prioritize object coarse-grained category rather than focus on their fine-grained attributes, e.g., colors or materials, thus failed to identify objects specified with certain attributes. However, OVD models are pretrained on large-scale image-text pairs with rich attribute words, whose latent feature space can represent the global text feature as a linear composition of fine-grained attribute tokens without highlighting them. Therefore, we propose in this paper a universal and explicit approach for frozen mainstream OVD models that boosts their attribute-level detection capabilities by highlighting fine-grained attributes in explicit linear space. Firstly, a LLM is leveraged to highlight attribute words within the input text as a zero-shot prompted task. Secondly, by strategically adjusting the token masks, the text encoders of OVD models extract both global text and attribute-specific features, which are then explicitly composited as two vectors in linear space to form the new attribute-highlighted feature for detection tasks, where corresponding scalars are hand-crafted or learned to reweight both two vectors. Notably, these scalars can be seamlessly transferred among different OVD models, which proves that such an explicit linear composition is universal. Empirical evaluation on the FG-OVD dataset demonstrates that our proposed method uniformly improves fine-grained attribute-level OVD of various mainstream models and achieves new state-of-the-art performance.
HQOD: Harmonious Quantization for Object Detection
Aug 05, 2024

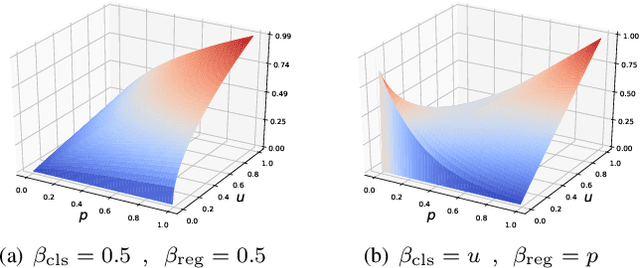
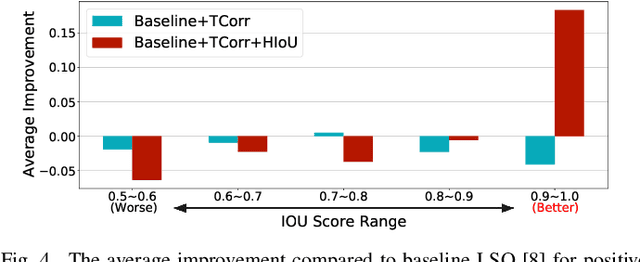
Abstract:Task inharmony problem commonly occurs in modern object detectors, leading to inconsistent qualities between classification and regression tasks. The predicted boxes with high classification scores but poor localization positions or low classification scores but accurate localization positions will worsen the performance of detectors after Non-Maximum Suppression. Furthermore, when object detectors collaborate with Quantization-Aware Training (QAT), we observe that the task inharmony problem will be further exacerbated, which is considered one of the main causes of the performance degradation of quantized detectors. To tackle this issue, we propose the Harmonious Quantization for Object Detection (HQOD) framework, which consists of two components. Firstly, we propose a task-correlated loss to encourage detectors to focus on improving samples with lower task harmony quality during QAT. Secondly, a harmonious Intersection over Union (IoU) loss is incorporated to balance the optimization of the regression branch across different IoU levels. The proposed HQOD can be easily integrated into different QAT algorithms and detectors. Remarkably, on the MS COCO dataset, our 4-bit ATSS with ResNet-50 backbone achieves a state-of-the-art mAP of 39.6%, even surpassing the full-precision one.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge