Xintong Han
FlashPortrait: 6x Faster Infinite Portrait Animation with Adaptive Latent Prediction
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Current diffusion-based acceleration methods for long-portrait animation struggle to ensure identity (ID) consistency. This paper presents FlashPortrait, an end-to-end video diffusion transformer capable of synthesizing ID-preserving, infinite-length videos while achieving up to 6x acceleration in inference speed. In particular, FlashPortrait begins by computing the identity-agnostic facial expression features with an off-the-shelf extractor. It then introduces a Normalized Facial Expression Block to align facial features with diffusion latents by normalizing them with their respective means and variances, thereby improving identity stability in facial modeling. During inference, FlashPortrait adopts a dynamic sliding-window scheme with weighted blending in overlapping areas, ensuring smooth transitions and ID consistency in long animations. In each context window, based on the latent variation rate at particular timesteps and the derivative magnitude ratio among diffusion layers, FlashPortrait utilizes higher-order latent derivatives at the current timestep to directly predict latents at future timesteps, thereby skipping several denoising steps and achieving 6x speed acceleration. Experiments on benchmarks show the effectiveness of FlashPortrait both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Hunyuan3D Studio: End-to-End AI Pipeline for Game-Ready 3D Asset Generation
Sep 16, 2025



Abstract:The creation of high-quality 3D assets, a cornerstone of modern game development, has long been characterized by labor-intensive and specialized workflows. This paper presents Hunyuan3D Studio, an end-to-end AI-powered content creation platform designed to revolutionize the game production pipeline by automating and streamlining the generation of game-ready 3D assets. At its core, Hunyuan3D Studio integrates a suite of advanced neural modules (such as Part-level 3D Generation, Polygon Generation, Semantic UV, etc.) into a cohesive and user-friendly system. This unified framework allows for the rapid transformation of a single concept image or textual description into a fully-realized, production-quality 3D model complete with optimized geometry and high-fidelity PBR textures. We demonstrate that assets generated by Hunyuan3D Studio are not only visually compelling but also adhere to the stringent technical requirements of contemporary game engines, significantly reducing iteration time and lowering the barrier to entry for 3D content creation. By providing a seamless bridge from creative intent to technical asset, Hunyuan3D Studio represents a significant leap forward for AI-assisted workflows in game development and interactive media.
StableAvatar: Infinite-Length Audio-Driven Avatar Video Generation
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Current diffusion models for audio-driven avatar video generation struggle to synthesize long videos with natural audio synchronization and identity consistency. This paper presents StableAvatar, the first end-to-end video diffusion transformer that synthesizes infinite-length high-quality videos without post-processing. Conditioned on a reference image and audio, StableAvatar integrates tailored training and inference modules to enable infinite-length video generation. We observe that the main reason preventing existing models from generating long videos lies in their audio modeling. They typically rely on third-party off-the-shelf extractors to obtain audio embeddings, which are then directly injected into the diffusion model via cross-attention. Since current diffusion backbones lack any audio-related priors, this approach causes severe latent distribution error accumulation across video clips, leading the latent distribution of subsequent segments to drift away from the optimal distribution gradually. To address this, StableAvatar introduces a novel Time-step-aware Audio Adapter that prevents error accumulation via time-step-aware modulation. During inference, we propose a novel Audio Native Guidance Mechanism to further enhance the audio synchronization by leveraging the diffusion's own evolving joint audio-latent prediction as a dynamic guidance signal. To enhance the smoothness of the infinite-length videos, we introduce a Dynamic Weighted Sliding-window Strategy that fuses latent over time. Experiments on benchmarks show the effectiveness of StableAvatar both qualitatively and quantitatively.
StableAnimator: High-Quality Identity-Preserving Human Image Animation
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Current diffusion models for human image animation struggle to ensure identity (ID) consistency. This paper presents StableAnimator, the first end-to-end ID-preserving video diffusion framework, which synthesizes high-quality videos without any post-processing, conditioned on a reference image and a sequence of poses. Building upon a video diffusion model, StableAnimator contains carefully designed modules for both training and inference striving for identity consistency. In particular, StableAnimator begins by computing image and face embeddings with off-the-shelf extractors, respectively and face embeddings are further refined by interacting with image embeddings using a global content-aware Face Encoder. Then, StableAnimator introduces a novel distribution-aware ID Adapter that prevents interference caused by temporal layers while preserving ID via alignment. During inference, we propose a novel Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) equation-based optimization to further enhance the face quality. We demonstrate that solving the HJB equation can be integrated into the diffusion denoising process, and the resulting solution constrains the denoising path and thus benefits ID preservation. Experiments on multiple benchmarks show the effectiveness of StableAnimator both qualitatively and quantitatively.
MRStyle: A Unified Framework for Color Style Transfer with Multi-Modality Reference
Sep 09, 2024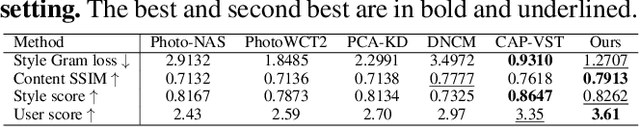
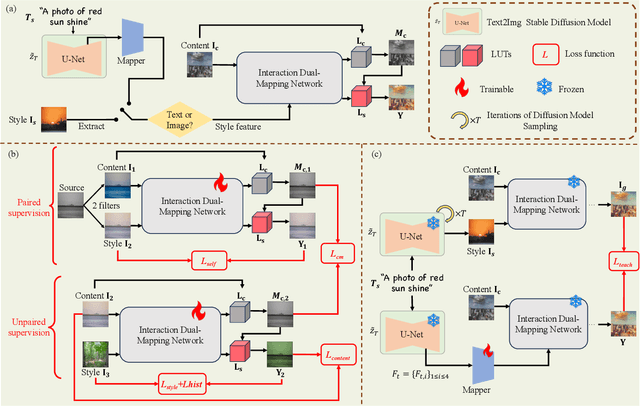
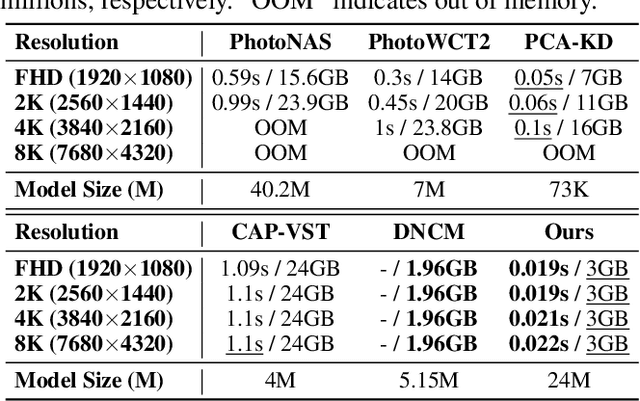
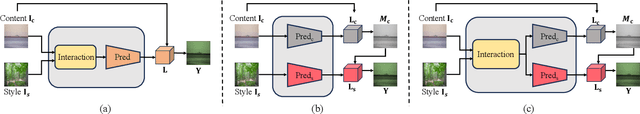
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce MRStyle, a comprehensive framework that enables color style transfer using multi-modality reference, including image and text. To achieve a unified style feature space for both modalities, we first develop a neural network called IRStyle, which generates stylized 3D lookup tables for image reference. This is accomplished by integrating an interaction dual-mapping network with a combined supervised learning pipeline, resulting in three key benefits: elimination of visual artifacts, efficient handling of high-resolution images with low memory usage, and maintenance of style consistency even in situations with significant color style variations. For text reference, we align the text feature of stable diffusion priors with the style feature of our IRStyle to perform text-guided color style transfer (TRStyle). Our TRStyle method is highly efficient in both training and inference, producing notable open-set text-guided transfer results. Extensive experiments in both image and text settings demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations.
MotionFollower: Editing Video Motion via Lightweight Score-Guided Diffusion
May 30, 2024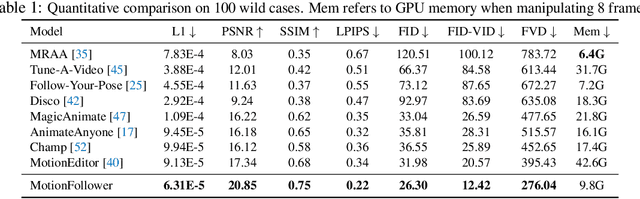
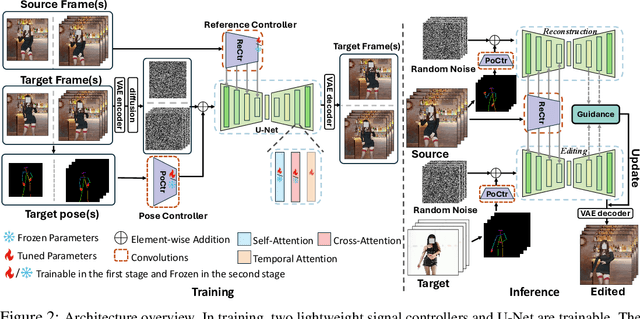
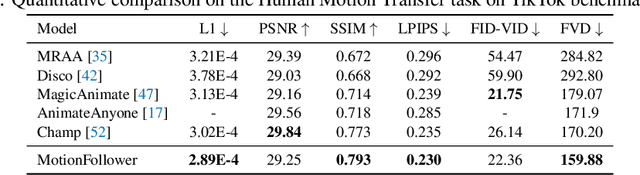
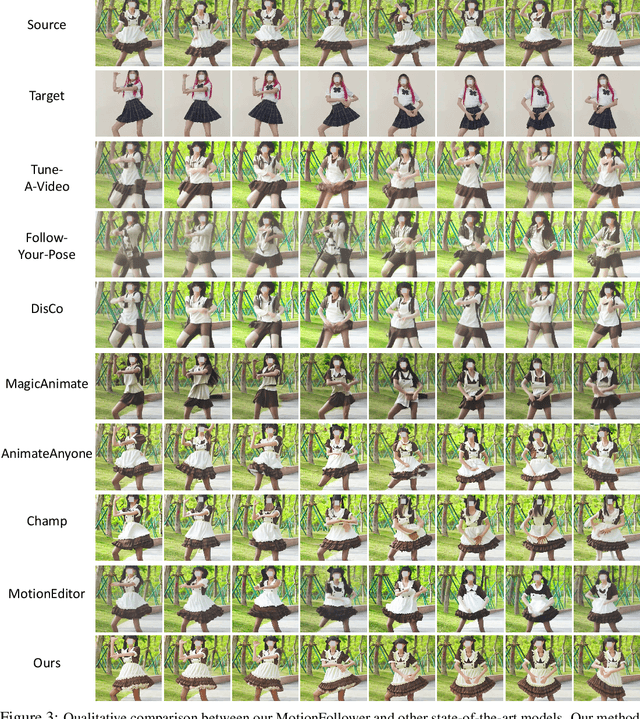
Abstract:Despite impressive advancements in diffusion-based video editing models in altering video attributes, there has been limited exploration into modifying motion information while preserving the original protagonist's appearance and background. In this paper, we propose MotionFollower, a lightweight score-guided diffusion model for video motion editing. To introduce conditional controls to the denoising process, MotionFollower leverages two of our proposed lightweight signal controllers, one for poses and the other for appearances, both of which consist of convolution blocks without involving heavy attention calculations. Further, we design a score guidance principle based on a two-branch architecture, including the reconstruction and editing branches, which significantly enhance the modeling capability of texture details and complicated backgrounds. Concretely, we enforce several consistency regularizers and losses during the score estimation. The resulting gradients thus inject appropriate guidance to the intermediate latents, forcing the model to preserve the original background details and protagonists' appearances without interfering with the motion modification. Experiments demonstrate the competitive motion editing ability of MotionFollower qualitatively and quantitatively. Compared with MotionEditor, the most advanced motion editing model, MotionFollower achieves an approximately 80% reduction in GPU memory while delivering superior motion editing performance and exclusively supporting large camera movements and actions.
MotionEditor: Editing Video Motion via Content-Aware Diffusion
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:Existing diffusion-based video editing models have made gorgeous advances for editing attributes of a source video over time but struggle to manipulate the motion information while preserving the original protagonist's appearance and background. To address this, we propose MotionEditor, a diffusion model for video motion editing. MotionEditor incorporates a novel content-aware motion adapter into ControlNet to capture temporal motion correspondence. While ControlNet enables direct generation based on skeleton poses, it encounters challenges when modifying the source motion in the inverted noise due to contradictory signals between the noise (source) and the condition (reference). Our adapter complements ControlNet by involving source content to transfer adapted control signals seamlessly. Further, we build up a two-branch architecture (a reconstruction branch and an editing branch) with a high-fidelity attention injection mechanism facilitating branch interaction. This mechanism enables the editing branch to query the key and value from the reconstruction branch in a decoupled manner, making the editing branch retain the original background and protagonist appearance. We also propose a skeleton alignment algorithm to address the discrepancies in pose size and position. Experiments demonstrate the promising motion editing ability of MotionEditor, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
CoverHunter: Cover Song Identification with Refined Attention and Alignments
Jun 15, 2023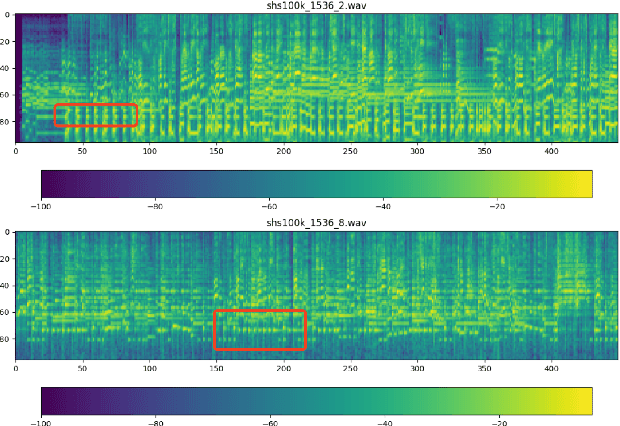
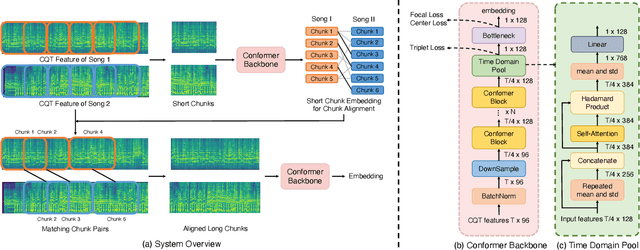
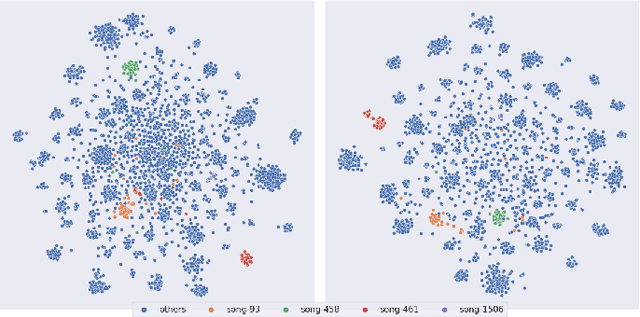
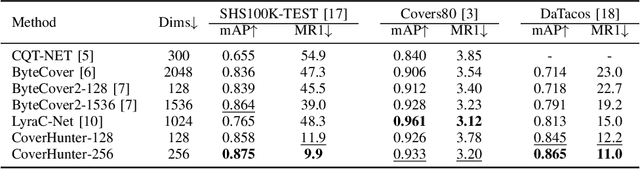
Abstract:Abstract: Cover song identification (CSI) focuses on finding the same music with different versions in reference anchors given a query track. In this paper, we propose a novel system named CoverHunter that overcomes the shortcomings of existing detection schemes by exploring richer features with refined attention and alignments. CoverHunter contains three key modules: 1) A convolution-augmented transformer (i.e., Conformer) structure that captures both local and global feature interactions in contrast to previous methods mainly relying on convolutional neural networks; 2) An attention-based time pooling module that further exploits the attention in the time dimension; 3) A novel coarse-to-fine training scheme that first trains a network to roughly align the song chunks and then refines the network by training on the aligned chunks. At the same time, we also summarize some important training tricks used in our system that help achieve better results. Experiments on several standard CSI datasets show that our method significantly improves over state-of-the-art methods with an embedding size of 128 (2.3% on SHS100K-TEST and 17.7% on DaTacos).
XFormer: Fast and Accurate Monocular 3D Body Capture
May 18, 2023Abstract:We present XFormer, a novel human mesh and motion capture method that achieves real-time performance on consumer CPUs given only monocular images as input. The proposed network architecture contains two branches: a keypoint branch that estimates 3D human mesh vertices given 2D keypoints, and an image branch that makes predictions directly from the RGB image features. At the core of our method is a cross-modal transformer block that allows information to flow across these two branches by modeling the attention between 2D keypoint coordinates and image spatial features. Our architecture is smartly designed, which enables us to train on various types of datasets including images with 2D/3D annotations, images with 3D pseudo labels, and motion capture datasets that do not have associated images. This effectively improves the accuracy and generalization ability of our system. Built on a lightweight backbone (MobileNetV3), our method runs blazing fast (over 30fps on a single CPU core) and still yields competitive accuracy. Furthermore, with an HRNet backbone, XFormer delivers state-of-the-art performance on Huamn3.6 and 3DPW datasets.
PromptFusion: Decoupling Stability and Plasticity for Continual Learning
Mar 13, 2023Abstract:Continual learning refers to the capability of continuously learning from a stream of data. Current research mainly focuses on relieving catastrophic forgetting, and most of their success is at the cost of limiting the performance of newly incoming tasks. Such a trade-off is referred to as the stabilityplasticity dilemma and is a more general and challenging problem for continual learning. However, the inherent conflict between these two concepts makes it seemingly impossible to devise a satisfactory solution to both of them simultaneously. Therefore, we ask, "is it possible to divide them into two problems to conquer independently?" To this end, we propose a prompt-tuning-based method termed PromptFusion to enable the decoupling of stability and plasticity. Specifically, PromptFusion consists of a carefully designed Stabilizer module that deals with catastrophic forgetting and a Booster module to learn new knowledge concurrently. During training, PromptFusion first passes an input image to the two modules separately. Then the resulting logits are further fused with a learnable weight parameter. Finally, a weight mask is applied to the derived logits to balance between old and new classes. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves promising results on popular continual learning datasets for both class-incremental and domain incremental settings. Especially on Split-Imagenet-R, one of the most challenging datasets for class-incremental learning, our method exceeds state-of-the-art prompt-based methods L2P and DualPrompt by more than 10%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge