Xinping Zhao
On The Role of Pretrained Language Models in General-Purpose Text Embeddings: A Survey
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Text embeddings have attracted growing interest due to their effectiveness across a wide range of natural language processing (NLP) tasks, such as retrieval, classification, clustering, bitext mining, and summarization. With the emergence of pretrained language models (PLMs), general-purpose text embeddings (GPTE) have gained significant traction for their ability to produce rich, transferable representations. The general architecture of GPTE typically leverages PLMs to derive dense text representations, which are then optimized through contrastive learning on large-scale pairwise datasets. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive overview of GPTE in the era of PLMs, focusing on the roles PLMs play in driving its development. We first examine the fundamental architecture and describe the basic roles of PLMs in GPTE, i.e., embedding extraction, expressivity enhancement, training strategies, learning objectives, and data construction. Then, we describe advanced roles enabled by PLMs, such as multilingual support, multimodal integration, code understanding, and scenario-specific adaptation. Finally, we highlight potential future research directions that move beyond traditional improvement goals, including ranking integration, safety considerations, bias mitigation, structural information incorporation, and the cognitive extension of embeddings. This survey aims to serve as a valuable reference for both newcomers and established researchers seeking to understand the current state and future potential of GPTE.
KaLM-Embedding-V2: Superior Training Techniques and Data Inspire A Versatile Embedding Model
Jun 26, 2025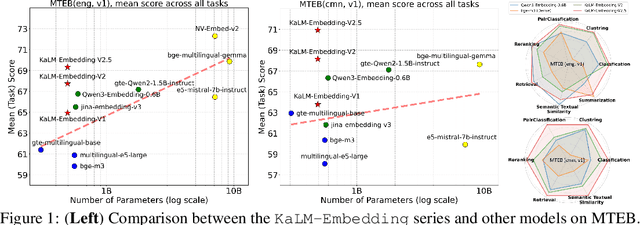
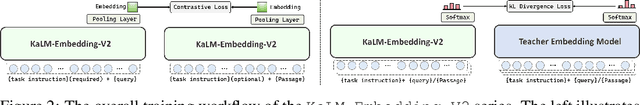

Abstract:In this paper, we propose KaLM-Embedding-V2, a versatile and compact embedding model, which achieves impressive performance in general-purpose text embedding tasks by leveraging superior training techniques and data. Our key innovations include: (1) To better align the architecture with representation learning, we remove the causal attention mask and adopt a fully bidirectional transformer with simple yet effective mean-pooling to produce fixed-length embeddings; (2) We employ a multi-stage training pipeline: (i) pre-training on large-scale weakly supervised open-source corpora; (ii) fine-tuning on high-quality retrieval and non-retrieval datasets; and (iii) model-soup parameter averaging for robust generalization. Besides, we introduce a focal-style reweighting mechanism that concentrates learning on difficult samples and an online hard-negative mixing strategy to continuously enrich hard negatives without expensive offline mining; (3) We collect over 20 categories of data for pre-training and 100 categories of data for fine-tuning, to boost both the performance and generalization of the embedding model. Extensive evaluations on the Massive Text Embedding Benchmark (MTEB) Chinese and English show that our model significantly outperforms others of comparable size, and competes with 3x, 14x, 18x, and 26x larger embedding models, setting a new standard for a versatile and compact embedding model with less than 1B parameters.
Semi-Supervised Multi-Label Feature Selection with Consistent Sparse Graph Learning
May 23, 2025Abstract:In practical domains, high-dimensional data are usually associated with diverse semantic labels, whereas traditional feature selection methods are designed for single-label data. Moreover, existing multi-label methods encounter two main challenges in semi-supervised scenarios: (1). Most semi-supervised methods fail to evaluate the label correlations without enough labeled samples, which are the critical information of multi-label feature selection, making label-specific features discarded. (2). The similarity graph structure directly derived from the original feature space is suboptimal for multi-label problems in existing graph-based methods, leading to unreliable soft labels and degraded feature selection performance. To overcome them, we propose a consistent sparse graph learning method for multi-label semi-supervised feature selection (SGMFS), which can enhance the feature selection performance by maintaining space consistency and learning label correlations in semi-supervised scenarios. Specifically, for Challenge (1), SGMFS learns a low-dimensional and independent label subspace from the projected features, which can compatibly cross multiple labels and effectively achieve the label correlations. For Challenge (2), instead of constructing a fixed similarity graph for semi-supervised learning, SGMFS thoroughly explores the intrinsic structure of the data by performing sparse reconstruction of samples in both the label space and the learned subspace simultaneously. In this way, the similarity graph can be adaptively learned to maintain the consistency between label space and the learned subspace, which can promote propagating proper soft labels for unlabeled samples, facilitating the ultimate feature selection. An effective solution with fast convergence is designed to optimize the objective function. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of SGMFS.
Perception, Reason, Think, and Plan: A Survey on Large Multimodal Reasoning Models
May 08, 2025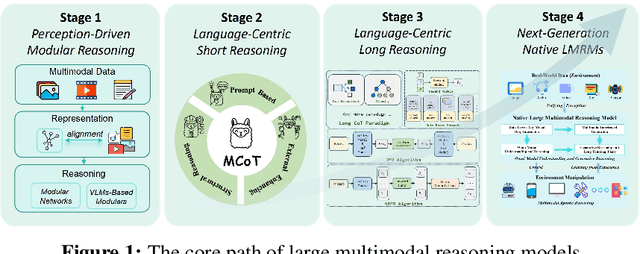
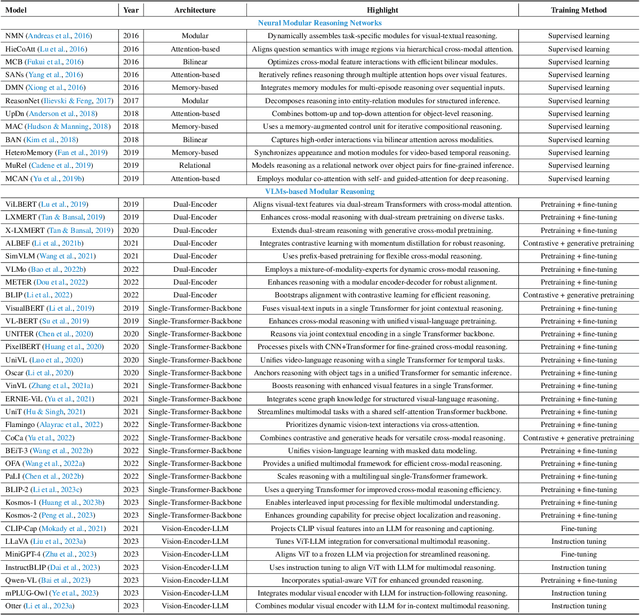
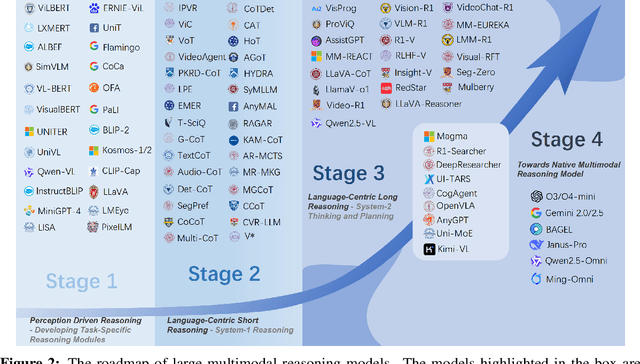
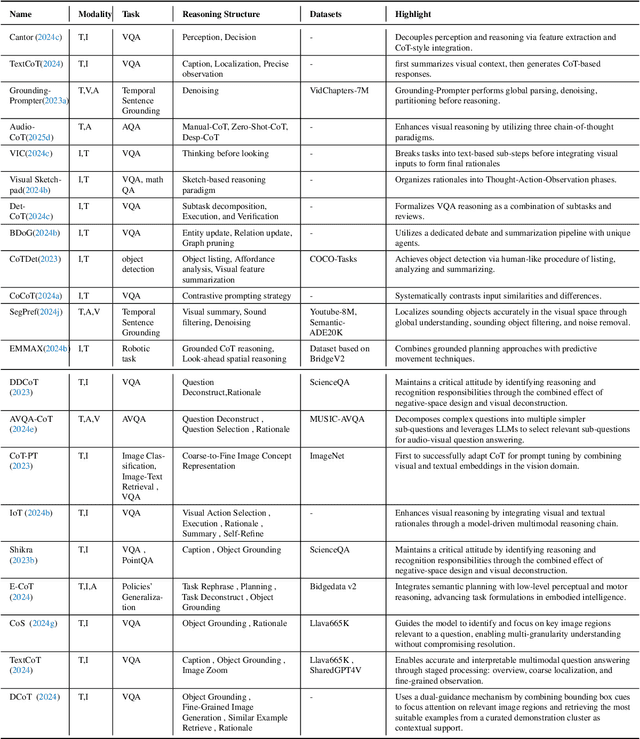
Abstract:Reasoning lies at the heart of intelligence, shaping the ability to make decisions, draw conclusions, and generalize across domains. In artificial intelligence, as systems increasingly operate in open, uncertain, and multimodal environments, reasoning becomes essential for enabling robust and adaptive behavior. Large Multimodal Reasoning Models (LMRMs) have emerged as a promising paradigm, integrating modalities such as text, images, audio, and video to support complex reasoning capabilities and aiming to achieve comprehensive perception, precise understanding, and deep reasoning. As research advances, multimodal reasoning has rapidly evolved from modular, perception-driven pipelines to unified, language-centric frameworks that offer more coherent cross-modal understanding. While instruction tuning and reinforcement learning have improved model reasoning, significant challenges remain in omni-modal generalization, reasoning depth, and agentic behavior. To address these issues, we present a comprehensive and structured survey of multimodal reasoning research, organized around a four-stage developmental roadmap that reflects the field's shifting design philosophies and emerging capabilities. First, we review early efforts based on task-specific modules, where reasoning was implicitly embedded across stages of representation, alignment, and fusion. Next, we examine recent approaches that unify reasoning into multimodal LLMs, with advances such as Multimodal Chain-of-Thought (MCoT) and multimodal reinforcement learning enabling richer and more structured reasoning chains. Finally, drawing on empirical insights from challenging benchmarks and experimental cases of OpenAI O3 and O4-mini, we discuss the conceptual direction of native large multimodal reasoning models (N-LMRMs), which aim to support scalable, agentic, and adaptive reasoning and planning in complex, real-world environments.
Take Off the Training Wheels Progressive In-Context Learning for Effective Alignment
Mar 13, 2025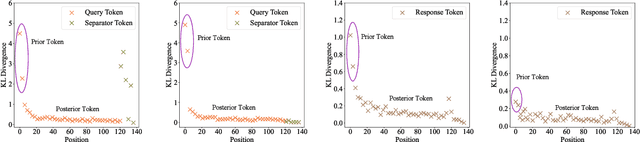
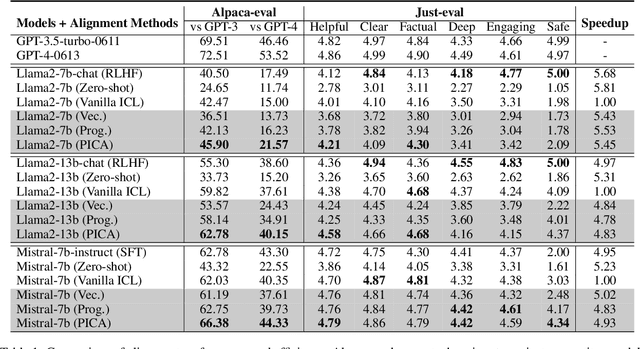
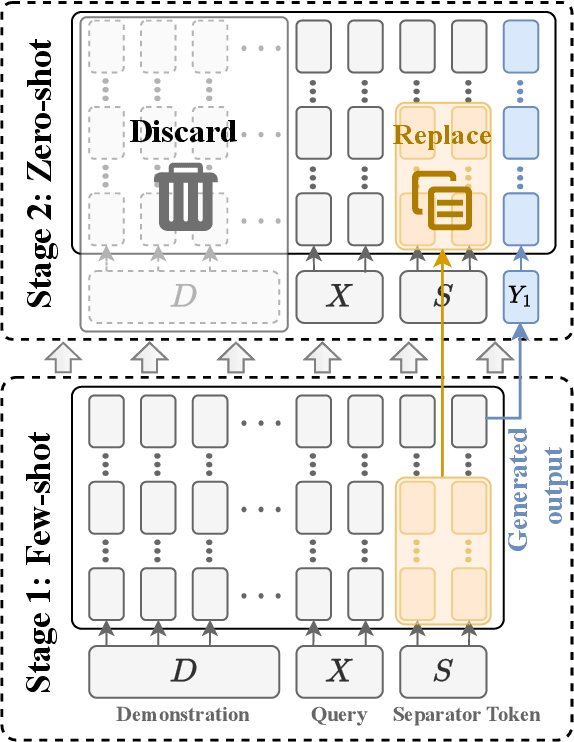
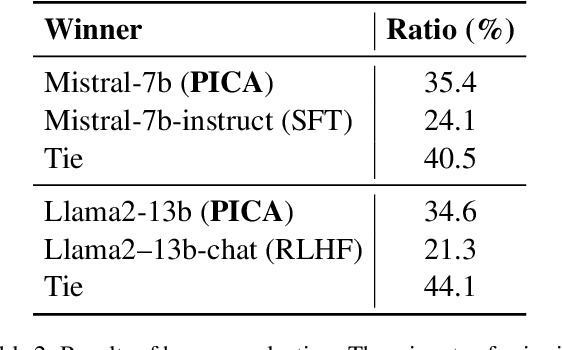
Abstract:Recent studies have explored the working mechanisms of In-Context Learning (ICL). However, they mainly focus on classification and simple generation tasks, limiting their broader application to more complex generation tasks in practice. To address this gap, we investigate the impact of demonstrations on token representations within the practical alignment tasks. We find that the transformer embeds the task function learned from demonstrations into the separator token representation, which plays an important role in the generation of prior response tokens. Once the prior response tokens are determined, the demonstrations become redundant.Motivated by this finding, we propose an efficient Progressive In-Context Alignment (PICA) method consisting of two stages. In the first few-shot stage, the model generates several prior response tokens via standard ICL while concurrently extracting the ICL vector that stores the task function from the separator token representation. In the following zero-shot stage, this ICL vector guides the model to generate responses without further demonstrations.Extensive experiments demonstrate that our PICA not only surpasses vanilla ICL but also achieves comparable performance to other alignment tuning methods. The proposed training-free method reduces the time cost (e.g., 5.45+) with improved alignment performance (e.g., 6.57+). Consequently, our work highlights the application of ICL for alignment and calls for a deeper understanding of ICL for complex generations. The code will be available at https://github.com/HITsz-TMG/PICA.
KaLM-Embedding: Superior Training Data Brings A Stronger Embedding Model
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:As retrieval-augmented generation prevails in large language models, embedding models are becoming increasingly crucial. Despite the growing number of general embedding models, prior work often overlooks the critical role of training data quality. In this work, we introduce KaLM-Embedding, a general multilingual embedding model that leverages a large quantity of cleaner, more diverse, and domain-specific training data. Our model has been trained with key techniques proven to enhance performance: (1) persona-based synthetic data to create diversified examples distilled from LLMs, (2) ranking consistency filtering to remove less informative samples, and (3) semi-homogeneous task batch sampling to improve training efficacy. Departing from traditional BERT-like architectures, we adopt Qwen2-0.5B as the pre-trained model, facilitating the adaptation of auto-regressive language models for general embedding tasks. Extensive evaluations of the MTEB benchmark across multiple languages show that our model outperforms others of comparable size, setting a new standard for multilingual embedding models with <1B parameters.
RaSeRec: Retrieval-Augmented Sequential Recommendation
Dec 24, 2024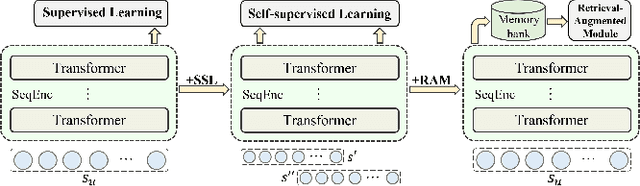
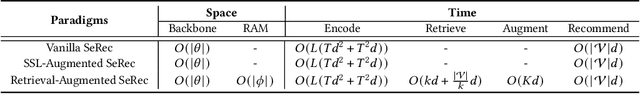
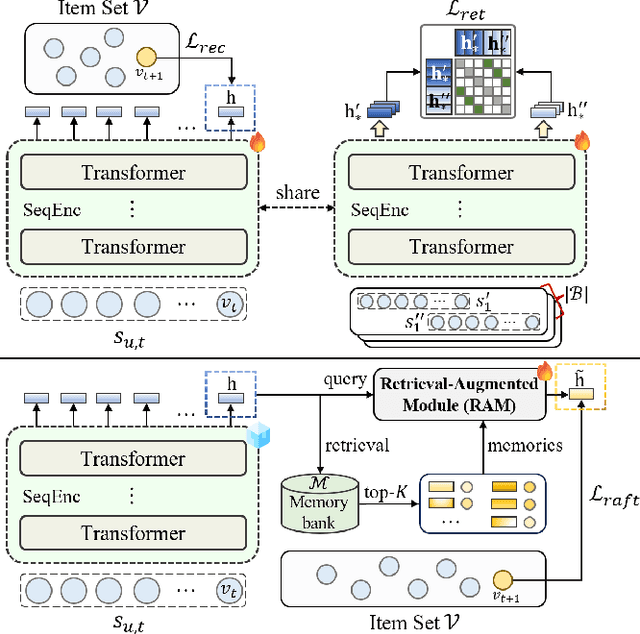
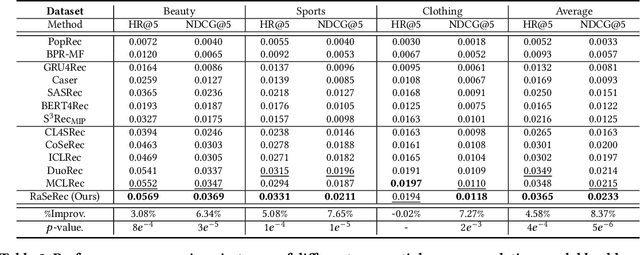
Abstract:Although prevailing supervised and self-supervised learning (SSL)-augmented sequential recommendation (SeRec) models have achieved improved performance with powerful neural network architectures, we argue that they still suffer from two limitations: (1) Preference Drift, where models trained on past data can hardly accommodate evolving user preference; and (2) Implicit Memory, where head patterns dominate parametric learning, making it harder to recall long tails. In this work, we explore retrieval augmentation in SeRec, to address these limitations. To this end, we propose a Retrieval-Augmented Sequential Recommendation framework, named RaSeRec, the main idea of which is to maintain a dynamic memory bank to accommodate preference drifts and retrieve relevant memories to augment user modeling explicitly. It consists of two stages: (i) collaborative-based pre-training, which learns to recommend and retrieve; (ii) retrieval-augmented fine-tuning, which learns to leverage retrieved memories. Extensive experiments on three datasets fully demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of RaSeRec.
SEER: Self-Aligned Evidence Extraction for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Oct 15, 2024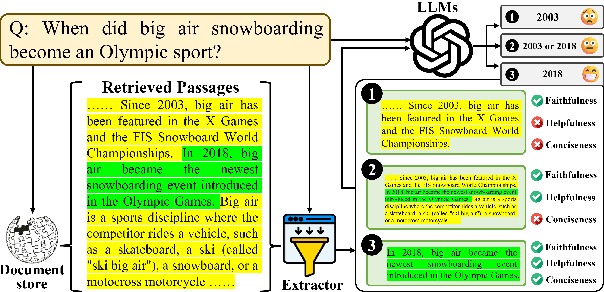
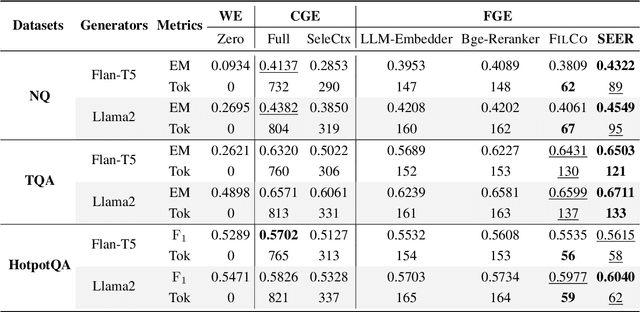
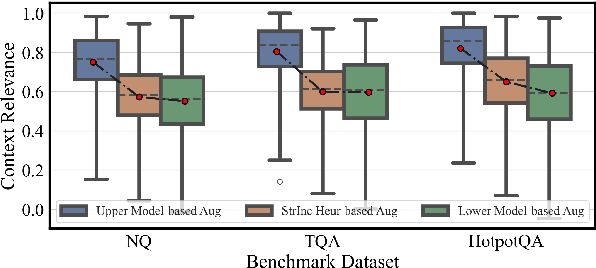
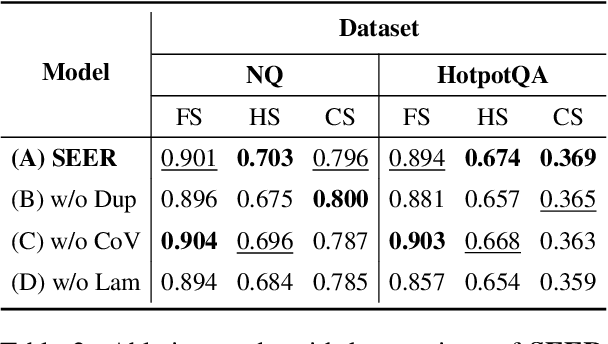
Abstract:Recent studies in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) have investigated extracting evidence from retrieved passages to reduce computational costs and enhance the final RAG performance, yet it remains challenging. Existing methods heavily rely on heuristic-based augmentation, encountering several issues: (1) Poor generalization due to hand-crafted context filtering; (2) Semantics deficiency due to rule-based context chunking; (3) Skewed length due to sentence-wise filter learning. To address these issues, we propose a model-based evidence extraction learning framework, SEER, optimizing a vanilla model as an evidence extractor with desired properties through self-aligned learning. Extensive experiments show that our method largely improves the final RAG performance, enhances the faithfulness, helpfulness, and conciseness of the extracted evidence, and reduces the evidence length by 9.25 times. The code will be available at https://github.com/HITsz-TMG/SEER.
Enhancing Attributed Graph Networks with Alignment and Uniformity Constraints for Session-based Recommendation
Oct 14, 2024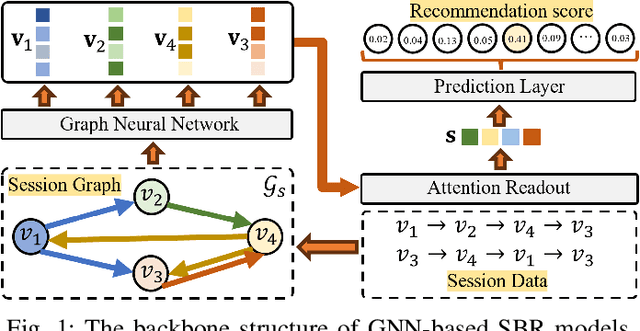
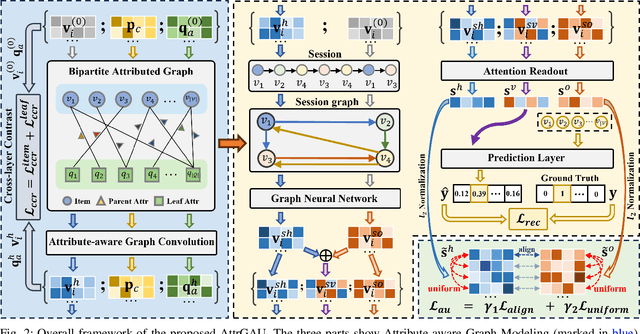
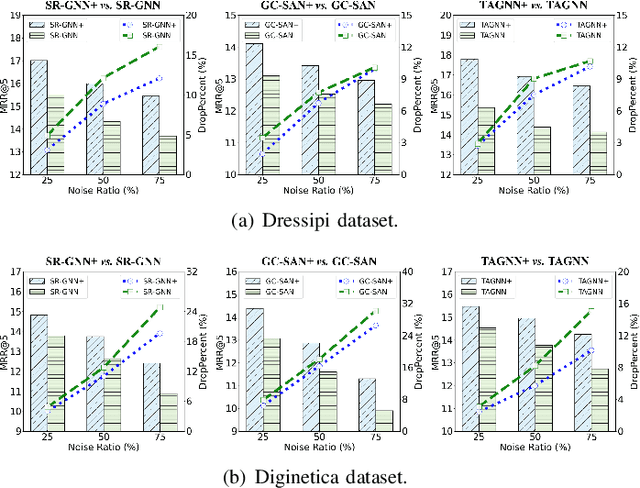
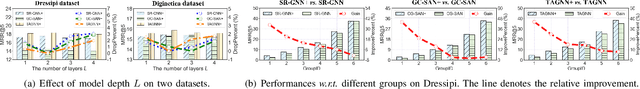
Abstract:Session-based Recommendation (SBR), seeking to predict a user's next action based on an anonymous session, has drawn increasing attention for its practicability. Most SBR models only rely on the contextual transitions within a short session to learn item representations while neglecting additional valuable knowledge. As such, their model capacity is largely limited by the data sparsity issue caused by short sessions. A few studies have exploited the Modeling of Item Attributes (MIA) to enrich item representations. However, they usually involve specific model designs that can hardly transfer to existing attribute-agnostic SBR models and thus lack universality. In this paper, we propose a model-agnostic framework, named AttrGAU (Attributed Graph Networks with Alignment and Uniformity Constraints), to bring the MIA's superiority into existing attribute-agnostic models, to improve their accuracy and robustness for recommendation. Specifically, we first build a bipartite attributed graph and design an attribute-aware graph convolution to exploit the rich attribute semantics hidden in the heterogeneous item-attribute relationship. We then decouple existing attribute-agnostic SBR models into the graph neural network and attention readout sub-modules to satisfy the non-intrusive requirement. Lastly, we design two representation constraints, i.e., alignment and uniformity, to optimize distribution discrepancy in representation between the attribute semantics and collaborative semantics. Extensive experiments on three public benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed AttrGAU framework can significantly enhance backbone models' recommendation performance and robustness against data sparsity and data noise issues. Our implementation codes will be available at https://github.com/ItsukiFujii/AttrGAU.
Medico: Towards Hallucination Detection and Correction with Multi-source Evidence Fusion
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:As we all know, hallucinations prevail in Large Language Models (LLMs), where the generated content is coherent but factually incorrect, which inflicts a heavy blow on the widespread application of LLMs. Previous studies have shown that LLMs could confidently state non-existent facts rather than answering ``I don't know''. Therefore, it is necessary to resort to external knowledge to detect and correct the hallucinated content. Since manual detection and correction of factual errors is labor-intensive, developing an automatic end-to-end hallucination-checking approach is indeed a needful thing. To this end, we present Medico, a Multi-source evidence fusion enhanced hallucination detection and correction framework. It fuses diverse evidence from multiple sources, detects whether the generated content contains factual errors, provides the rationale behind the judgment, and iteratively revises the hallucinated content. Experimental results on evidence retrieval (0.964 HR@5, 0.908 MRR@5), hallucination detection (0.927-0.951 F1), and hallucination correction (0.973-0.979 approval rate) manifest the great potential of Medico. A video demo of Medico can be found at https://youtu.be/RtsO6CSesBI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge